In nature, metals actively enter into chemical reactions with acids, alkalis and atmospheric oxygen. In most cases, this does not require additional processing (chemical, thermal). When heated strongly, metals begin to actively react with carbon, which leads to the formation of complex compounds called carbides. These compounds are distinguished by a number of unusual properties - high strength, refractoriness, chemical inertness. What types of metal carbides are there? How are these compounds used in industry? Which substances are most widely used?
Composition and types of carbides
Carbides are not a separate substance. It is a compound of carbon with metals and non-metals. Moreover, it should be taken into account that carbon must have greater electronegativity in the resulting substance compared to other elements used. This makes it possible to avoid the production of halogens, oxides and other carbon compounds.
Today, there are three types of carbide , the composition of which is different from each other:
- Covalent compounds. This type includes two elements - silicon and bromine. These are compounds with strong interatomic bonds, which ensures a high melting point and chemical inertness. Oxidation of substances in this group is possible only when they are heated above 1000 degrees Celsius. The hardness of the substance containing bromine is so high that it can even compete with diamonds. The substance with silicon is less durable, but has 8 points on the Mohs scale. However, this substance can only be dissolved in aqua regia or using concentrated nitric or hydrofluoric acid.
- Ionic or salt-like compounds . Substances of this group are formed with the help of metals of groups 1 and 2 of the periodic table, as well as aluminum. These compounds are characterized by a high melting point. Ionic carbides decompose under the influence of water and acids. When the reaction occurs, hydrocarbon is released and metal hydroxide remains.
- Ionic covalent metal or metal-like compounds. They are formed with the help of metals from group 4 to 8, as well as cobalt, nickel and iron. A distinctive feature of metal-like substances is their high strength and melting point. This type of connection is divided into two types:
- Acetylenides - upon hydrolysis they form ethylene or acetylene. Calcium carbide belongs to this type of compound.
- Methanides - when reacting with water or dilute acids, they form methane. Most often colorless. These include aluminum, magnesium, and beryllium carbide.
Read also: Svaris 200 schematic diagram pdf
What is carbide. Properties of carbide. Application of carbide
Childhood fun. This is how many people remember carbide, especially former boys, and now, of course, adult men.
They took stones from construction markets. They didn’t buy it, but instead dragged it from dump stations and from the backs of trucks.
The prey was placed in bottles, filled with water, closed, and shaken. All that was left was to throw the container and admire the explosion.
We also admired the whitish bubbles that carbide gave when falling into puddles. However, to whom they owe such fun, the tomboys of yesteryear often did not know.
What is carbide ? Let's try to answer a question that seemed unimportant in childhood.
What is carbide
Carbite is not a specific substance, but a group of compounds of elements with carbon. The latter must be more electronegative than its “neighbor”.
This is a mandatory condition that excludes carbon halides and oxides from the range of carbides.
Electronegativity refers to the ability of an atom to shift electrons of other substances towards itself.
The electronegativity of carbon is 2.6. This is the Pauling scale data. It is built taking into account that ionicity in a covalent bond makes this bond stronger.
It turns out that the electronegativity of the second elements in carbides should be less than 2.6.
Most suitable elements are metals. But about 15% of carbides do not contain them.
Externally, carbides are crystalline, usually colorless, transparent substances. They have a diamond shine.
The compounds owe them to carbon, which is the basis of not only carbides, but also diamonds.
In fact, the heroes of the article are diamonds in which some of the atoms are replaced by other elements.
There are also colored duets with carbon, for example, iron carbide . This is the familiar cement. The color of the connection is gray.
It turns out that the properties of carbides may vary. We will consider discrepancies in the chapter “Types”. For now, let's study the general characteristics of the class of compounds.
Carbide properties
The general properties of carbides include hardness. It may be more or less, but always above average.
Some representatives of the group have an indicator close to corundum and diamond. These are the hardest minerals on earth.
Transition metal carbides were especially distinguished. These are elements of side subgroups of the periodic table. All transition metals have electrons in d and f orbitals.
Summarizes carbides and high melting point. As a rule, it is higher than that of the metal included in the connection.
If it is transitional, softening can begin only at 3000 degrees Celsius.
It is interesting that the melting point rises along with the number of the group to which the “neighbor” of carbon belongs.
The most refractory are carbides with elements from groups 5-7 of the periodic table.
Where carbide can be understood by the structure of the compounds. Their grilles are often defective.
This means that there are deviations from the theoretical scheme, breaks and displacements. This is why the properties of carbides can differ 100 or even 1000 times from those calculated using formulas.
Thus, many compounds of the class are resistant to corrosion and are insoluble in most acids.
Types of carbides
There are three main types of carbides. The first is covalent compounds. Valence is a predisposition to a certain number of chemical bonds.
A covalent bond is the overlap of valence clouds of different elements. That is, they form common electron pairs. These are the ones that form the basis of covalent carbides.
Covalent carbides include carbides of only two elements: bromine and silicon. Both compounds are chemically inert. Their interatomic bonds are strong.
As a result, the carbides of the group are difficult to melt - the lattice does not want to collapse. The strength of the bond makes both connections solid.
Bromine carbide even rivals diamond. Some carbon samples scratch diamonds, meaning they are harder than diamonds.
Silicon carbide does not “win” diamond, but it has its own decent 8 points on the Mohs scale.
Only hydrofluoric acid, concentrated nitric and aqua regia dissolve covalent carbides. Oxidation of carbides of the group occurs only when heated to 1000 degrees.
The second type of carbides is ionic. It is also called salt-like. All are formed by metals of the 1st and 2nd groups of the periodic table.
The class also includes aluminum carbide . Compounds of the group are decomposed not only by acids, but also by water.
Pebbles that make puddles “boil,” for example, are calcium carbide . By the way, it is quite toxic and can corrode mucous membranes. Why it is brought to construction markets, we will understand in the next chapter.
When ionic carbides react with water, hydrogen is released. Metal hydroxide forms and precipitates in the liquid.
The reaction proceeds rapidly. A sudden release of hydrogen onto the surface of the water produces that same bubbling.
The third type of carbides is ionic-covalent-metallic, simply metal-like.
Such compounds are formed by elements of the 4th, 5th, 6th, 7th groups of the periodic table. Exceptions: - nickel, cobalt and iron carbides.
If covalent carbides have low chemical activity, and ionic carbides have high chemical activity, then the third type of compound has average activity.
The molecular structure is remarkable. Their basis is metal atoms. Carbon atoms are located in the voids between them.
Therefore, for example, tungsten carbide is called embedded. This means that carbon has penetrated into the crystal lattice of the metal.
This structure provides record strength and a high melting point. Another well-known compound of the group is titanium carbide .
Application of carbide
Titanium carbide has become the basis for tungsten-free but equally hard alloys.
In addition, the compound serves as a coating for tools, mainly industrial and construction.
This spraying minimizes the wear of parts and allows them to process even the hardest materials.
Silicon carbide is also used as an abrasive. In its natural form, which is the mineral moissanite, the compound is valued by jewelers, moreover, higher than cubic zirconia, which is similar in appearance and properties.
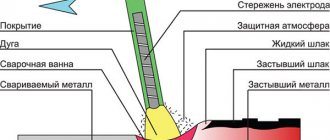
Calcium carbide is needed for welding work. is obtained from the compound . Carbide serves as its source, and at the same time, as fuel for oxygen welding machines.
Acetylene is a gas. One is enough to operate the devices. But there is also water. Calcium carbide reacts violently with it.
The result is not only bubbles that children like, but also an abundance of heat - another source of energy.
Boron carbide is used as a refractory. The melting point of the compound is almost 2500 degrees.
The strength of carbide allows it to be added to body armor. The material can protect not only from bullets, but also from radiation.
Therefore, one of the answers to the question of where to get boron carbide is in protective screens that block radiation.
The list of carbides and their role in society could take many pages. There are several dozen compounds and each of them has a use, and more than one. There is no single scheme for producing carbides.
We will have to limit ourselves to general phrases. However, they also contain a lot of useful information.
Preparation of carbides
Most carbides are produced rather than mined. The first synthesis was carried out at the beginning of the 19th century.
An Englishman named Davy obtained potassium carbide . In 1863, copper carbide was created.
It turned out to be unstable, unlike the third synthesized carbon-iron compound.
Looking at the prototypes, scientists could not figure out where to find carbide outside the laboratories.
Minerals in which metals are combined with carbon were discovered only at the beginning of the 20th century.
In addition to moissanite, geologists found cohenite - a mixture of cobalt carbide with nickel and iron.
Judging by the date of discovery of carbide minerals, they are not common.
Therefore, on an industrial scale, the heroes of the article are still being synthesized. The mass of carbide can be obtained, for example, from charcoal and metal oxides.
They are converted into carbides using a voltaic arc and an electric furnace.
Carbide price
to buy calcium carbide for about 40-90 rubles per kilogram. The combination of carbon and boron costs from 100 rubles per kilo.
to buy silicon carbide for about 160 rubles per 1000 grams.
But for a kilo of hafnium carbide you will have to pay about 21,000 rubles, moreover, for wholesale purchases.
That is, the cost of the material largely depends on the metal or non-metal present in it. There is even gold carbide .
By the way, it is capable of exploding simply by pouring powder. So, even at a high price, delivering raw materials to the consumer is not an easy task.
Properties
Due to their properties, these compounds are widely used in mechanical engineering , as well as in construction.
- High hardness of the material. It varies for different compounds, but always remains above average. They are the hardest minerals.
- Melting temperature . Almost always it is higher than the melting point of the metal included in the connection and can exceed 2000 degrees.
- Corrosion resistance. Many compounds do not react with various acids and are quite resistant to external aggressive factors.
- Interaction with water. Almost all carbide compounds react with water; for example, when interacting with calcium carbide, it can explode. The terms of interaction may vary and depend on the nature of the connection in the connection.
Qualitative reaction
With little knowledge of where to find carbide, it is necessary to verify the authenticity of the substance. For a high-quality reaction, you only need a little water (on the street you can even use your own saliva). When CaC2 interacts, methane and calcium hydroxide are released. You can observe a characteristic hissing, and if you bring a match at this moment, it will ignite.
Due to a violent reaction with water, carbide decomposes from atmospheric moisture. Therefore, the question of where to find calcium carbide on the street is very controversial. It is known that it does not exist in its pure form; this compound is mostly artificial rather than natural.
Carbide production
Covalent and salt-like compounds are obtained by a simple method. A mixture of crushed coke and metal oxide is placed in an electric furnace and heated. At high temperatures, the element's oxide reacts with coke. With this method, part of the coke, which consists of carbon, combines with the atoms of the element included in the oxide. As a result, the required carbide and carbon monoxide are formed. The finished molten mixture is poured into special molds, and after solidification, it is crushed and sorted by granule size. Despite the simplicity of this method, producing carbide using it is quite energy-intensive, since it requires maintaining high temperatures (1600-2500 degrees) throughout the reaction.
There are alternative ways to obtain some types of substances. As a rule, this is the decomposition of a compound as a result of which the required element is obtained. The breakdown formula will differ depending on the specific compound.
What does carbide look like?
To determine where to find carbide on the street, you need to know its physical properties. Physically, the substance is solid, its color can be dark, having a grayish or brown tint. The color depends on the amount of carbon. There is also a specific odor that characterizes this substance.
It is solid in consistency, but crumbles easily, turning into powder. If you bring a match, combustion will begin, releasing carbon and decomposing calcium. True, this can be achieved at high temperatures, for example with a hunting match.
Industrial Applications
Calcium carbide is an important compound for the production of acetylene, a gas used in oxy-fuel welding and metal working . When burning with oxygen, acetylene can reach 3150 degrees Celsius. This allows you to work with refractory metals that require a temperature twice as high as the melting point of the metal itself.
Boron carbide is used as a refractory material, since the melting point of such a compound is above 2400 degrees. At the same time, it is also found in body armor, as it can protect not only from bullets and shrapnel, but also from radiation. Titanium carbide is used to coat industrial and construction tools. Its strength allows you to increase the wear resistance of parts and process even the most durable materials.
Read also: Drawing of a spur gear
Application
Carbides are used in the production of cast irons and steels, ceramics, various alloys, as abrasive and grinding materials, as reducing agents, deoxidizers, catalysts, etc. WC and TiC are part of the hard alloys from which cutting tools are prepared; calcium carbide CaC2 is used to produce acetylene; Grinding wheels and other abrasives are prepared from silicon carbide SiC (carborundum); Iron carbide Fe3C (cementite) is a component of cast iron and steel; tungsten carbide and chromium carbide are used to produce powders used in thermal spraying.
Storage and transportation
Since carbide, when reacting with moisture, leads to the release of large amounts of heat and explosive acetylene gas, this substance is stored in sealed tanks or drums. Working with such tanks requires special care. Acetylene gas is lighter than air and is capable of self-ignition, while it has a narcotic effect . When opening drums with carbide, a special tool is used to prevent the occurrence of sparks, and if the substance gets on the skin, you must immediately rinse the affected area with water and lubricate it with a rich cream.
Storage areas must be well ventilated, and keeping other substances in the vicinity is prohibited. This may lead to dangerous reactions. Improper storage can either explode the carbide or render it unusable.
The shelf life is only up to six months.
Transportation is carried out only by covered transport. Air delivery is prohibited.
Safety precautions
Carbide for welding belongs to the class of explosive substances. Safe use of carbide is ensured by taking into account a number of conditions:
- Acetylene is a flammable gas, and dry carbide itself is also explosive, so there should be no open flames near the work site, even small ones such as lighters and lit cigarettes.
- It is prohibited to use carbide in granules up to 2 mm or carbide dust, as it dissolves very quickly, which leads to the release of large amounts of gas. Because of this, ultra-high pressure forms in the generator and an explosion may occur.
- It is prohibited to work with an angle grinder or an electric welding machine near gas welding operations and places where carbide drums are installed.
- The substance must be stored in a dry and sealed place, in which there are no water pipes, sewer pipes and, especially, gas equipment.
- Carbide dust upon contact causes irritation to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Work with this substance must be carried out using personal protective equipment - goggles, gloves and a respirator.
- If carbide gets on your skin or eyes, rinse it with plenty of warm water and then carefully remove any remaining carbide with tweezers or a damp swab.
- When working with carbide in a workshop, all welding equipment must be placed in separate parts of the room, the ventilation system of the room must ensure the removal of flammable gases, and the room must be cleared of flammable materials.
- Acetylene generators are prohibited from being installed in basements and residential buildings.
- Before starting, the generator should be inspected for visible cracks or dents in the housing.
- During work, the generator must remain in a vertical position, the pressure gauge must be in working order and clearly visible to the welder or his assistant.
- At the end of the work, the carbide solution remaining in the generator must be completely exhausted, and the resulting lime must be disposed of.
- Reuse of wet carbide pieces is not permitted;
- Do not open the generator under pressure (during an ongoing reaction).
- Acetylene cylinders are stored and transported with special safety caps on the valves.
Compliance with these simple rules will ensure your own safety and the safety of people near the work site.
Carbide should be purchased from reputable welding equipment stores, since purchasing low-quality carbide can complicate welding work.
You can also order it in online stores. The price of carbide varies from 75 to 190 rubles per kilogram, depending on the manufacturer. If there is a need to regularly use equipment for gas welding and cutting, it is better to buy professional equipment manufactured at an industrial enterprise. The use of homemade generators can result in serious injuries and a threat to life.
Price
Calcium carbide can be purchased on the market at a price of 80 rubles per kilogram. This mixture is sold in barrels or special bags. The substance with silicon is not much more expensive. Its cost is 82 rubles per kilogram. But tungsten carbide will cost 1,400 rubles per kilo. Moreover, a minimum purchase weight can be set, for example, from 10 kg. Boron carbide will cost even more - from 2000 rubles, and packaging starts from 35 kilograms. The cost of connections with hafnium or molybdenum is negotiated with the supplier separately.
| Calcium carbide | |
| Are common | |
| Systematic name | Calcium carbide |
| Chem. formula | CaC2 |
| Physical properties | |
| State | hard |
| Molar mass | 64.0994 (±0.004) g/mol |
| Density | 2.22 g/cm³ |
| Thermal properties | |
| T. float. | 2160 °C |
| T. kip. | 2300 °C |
| Structure | |
| Coordination geometry | 6 |
| Crystal structure | Tetragonal |
| Classification | |
| Reg. CAS number | 75-20-7 |
| PubChem | 6352 |
| Reg. EINECS number | 200-848-3 |
| SMILES | |
| RTECS | EV9400000 |
| ChemSpider | 6112 |
| Data given is based on standard conditions (25 °C, 100 kPa) unless otherwise stated. | |
Calcium carbide
(calcium carbonate, calcium acetylenide) - CaC2 - in its pure form, a white crystalline substance. A compound of calcium with carbon.
Application of the substance
Calcium carbide is actively used in industry. It is a catalyst in the synthesis of organic compounds. With its help, it became possible to synthesize rubber at a lower price. However, to do this, you first need to carry out the necessary chemical reactions to synthesize your own carbide, and only then rubber. More and more chemists are wondering where to find carbide in nature to make their work easier.
Carbide has found its application in gardening. Based on it, farmers obtain a fertilizer called calcium cyanide. Used to improve the growth of the root system of seedlings and adult plants.
Receiving [edit | edit code ]
Currently, a mixture of calcium oxide and coke is produced by calcination in electric furnaces (temperature 1900-1950 °C).
C a O + 3 C → C a C 2 + CO >> 2>
The technical product obtained in this way has a dirty gray color due to contamination with coal and other coloring impurities. It also contains impurities of calcium phosphide and sulfide, as a result of which such calcium carbide and the acetylene obtained from it have an unpleasant odor.
Read also: Compare washing machines by characteristics
Physical properties [edit | edit code ]
- Colorless tetragonal crystals.
- Density: 2.2 (+20 °C, g/cm3).
- Specific heat capacity at constant pressure (in J/g·K): 0.92 (+20–325 °C).
- Standard enthalpy of formation ΔfH (298 K, kJ/mol): −62.8 (t).
- Standard Gibbs energy of formation ΔfG (298 K, kJ/mol): −67.8 (t).
- Standard entropy of formation S (298 K, J/mol·K): 70.3 (t).
- Standard molar heat capacity Cp (298 K, J/mol·K): 62.34 (t).
- Melting enthalpy ΔHmelt (kJ/mol): 32.2 [1].
Appearance and characteristics of technical calcium carbide [edit | edit code ]
Calcium carbide is produced by fusing coke and quicklime in electric furnaces. Molten calcium carbide is released from the furnace into special forms - molds, in which it hardens. The solidified calcium carbide is crushed and sorted into pieces of certain sizes.
Technical calcium carbide is a solid crystalline substance. In appearance, calcium carbide is a dark gray or brown solid. It produces a gray crystalline fracture with varying shades depending on purity. Calcium carbide greedily absorbs water. When interacting with water, even in the cold, calcium carbide decomposes with the rapid release of acetylene and a large amount of heat. The decomposition of calcium carbide also occurs under the influence of atmospheric moisture.
According to GOST 1460-56, the following dimensions (granulation) of calcium carbide pieces are established: 2×8; 8x15; 15×25; 25x80. Technical calcium carbide contains up to 80% of chemically pure calcium carbide, the rest is made up of impurities - quicklime, carbon, silicic acid and others [3].