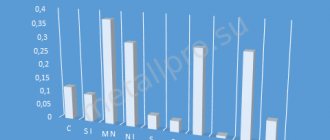
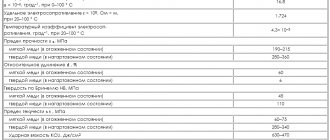
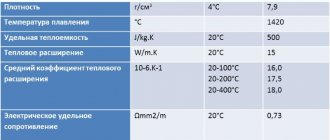
Types of rubber sheets
The fundamental document for sheet rubber manufacturers is GOST 7338-90. This document applies to rubber plates, which are intended for the production of parts used to seal fixed joints, preventing friction between the surfaces of parts made of metal. In addition, parts made of this type of rubber must withstand shock loads that can occur in machines and mechanisms operating in various industries and construction. The same documents define the types of rubber and the operating conditions for which they are intended. Thus, oil-resistant rubber has three degrees of hardness, and can operate at temperatures from -40 to +90 degrees Celsius. It must remain operational in environments containing fats, oils, emulsions, inert gases and steam.
GOST determines that, depending on the scope of application and operating conditions, three main types of technical sheet rubber are produced.
Oil and petrol resistant sheet rubber
Sheet rubber oil-resistant
Heat-frost-acid-shallow-resistant sheet rubber
- heat-frost-acid-shallow-resistant (TMKShch);
- oil resistant MS;
- oil and petrol resistant MBS.
The TMKShch rubber plate remains operational in environments such as aqueous, acidic, alkaline and gas. It can be used, depending on the degree of hardness, from -45 to +90 degrees Celsius.
Oil-gasoline-resistant (MBR) sheet rubber can operate in oily or in environments in which hydrocarbon fuels are present. The operating temperature range is from -30 to +80 degrees Celsius.
Several other types of rubber are produced in sheet form:
- vacuum;
- silicone;
- spongy.
Sponge sheet technical plate
Silicone rubber sheets Vacuum sheet technical plate
White vacuum rubber brand 7889 is distinguished by the following parameters - it is insensitive to high pressure and temperature, has high elasticity and at the same time it successfully resists compression. Vacuum rubber, in addition to the sheet version, can be supplied to the consumer in the form of sleeves, cords, etc. Vacuum rubber also includes colored vulcanized sheet rubber. By the way, different colors do not carry any meaning. Such rubber is produced solely for aesthetic reasons. Silicone sheet rubber is a material that is produced using high molecular weight substances, which include silicon and some organic substances. In appearance it is indistinguishable from that produced from ordinary rubber. But its chemical formula allows it to work in a temperature range from -50 to +480 degrees Celsius. If the ambient temperature is no more than +100 degrees, then we can say that parts made of this type of rubber will work forever. By the way, working in such extreme conditions for a long time does not affect its operational workshops.
Spongy (porous) rubber is essentially foamed rubber that can be molded into sheets, etc. The industry produces several brands of these products, which differ from each other in density and areas of application. By the way, porous rubber is often used for creativity.
Food grade sheet rubber is produced in accordance with the requirements of GOST 17133-83. Products made from this material are used to make seals that come into contact with food substances. The technical plate can be supplied to the customer in the form of plates of a certain size or in the form of rolls.
GOST 7338-90
Rubber (technical plates) according to GOST 7338-90 (weather-oil-resistant rubber AMS, oil- and gasoline-resistant MBS and heat-freeze-acid-alkali-resistant TMKShch)
Designed for the manufacture of molded rubber products used to seal fixed joints operating under pressure up to 0.1 MPa, to prevent friction between metal surfaces, to absorb single impact loads, and also as gaskets, decking and other non-sealing joints, etc. Depending on the purpose, design and manufacturing method, the following plates are produced:
- brands:
- TMKShch - heat-frost-acid-alkali-resistant ;
- AMS - weather-oil-resistant (limitedly ozone-resistant );
- MBS - oil and petrol resistant ;
- 1 - plate with a thickness of 1.0 to 20.0 mm intended for the manufacture of rubber products used to seal units operating under pressure above 0.1 MPa (1.0 kg/cm2);
- 2 - a plate with a thickness of 1.0 to 60.0 mm intended for the manufacture of rubber products used to seal units operating under pressure up to 0.1 MPa (1.0 kg/cm2), to prevent friction between metal surfaces, and also for the perception of single shock loads or as linings, floorings;
- F - molded plates , produced by vulcanization in molds on vulcanization presses, thickness from 2.0 to 70.0 mm, size 500x500 mm, 700x700 mm, 1000x1000 mm;
- N - non-shaped ( rolled plates ), manufactured by extruding the rubber mixture through dies followed by vulcanization without molds in boilers, as well as on continuous vulcanizers, thickness from 1.0 to 20.0 mm, size width 800 - 1200 mm, length from 1200 mm;
- I — rubber technical plate (brands TMKShch, AMS, MBS);
- II - rubber-fabric plate, with one or several fabric layers (for every 2 mm of the plate there should be no more than one fabric layer);
- M - soft ,
- C - average ,
- T - increased .
TMKShch – heat-freeze, acid-alkali-resistant rubber .
Working environment: Air of premises, containers, vessels; nitrogen , inert gases at a pressure of 0.05 to 0.4 MPa or fresh, sea water without organic solvents and lubricants; solutions of salts with a concentration up to the saturated limit: acids , alkalis with a concentration of no more than 20% at a pressure from 0.05 to 10.0 MPa.
Operating temperature range:
| Class | View | Type | Hardness degree | Temperature range, °C |
| 1, 2 | N, F | I, II | WITH | from -30 to +80 |
| I | T | from -30 to +80 | ||
| M, S1, T1 | from -45 to +80 | |||
| C2, T2 | from -60 to +80 |
Specifications:
| Hardness degree | Hardness units ShorA | Conditional tensile strength, MPa | Elongation at break, % |
| M | 35 — 50 | 4,0 | 300 |
| WITH | 50 — 65 | 5,0 | 250 |
| T | 65 — 85 | 6,5 | 200 |
Example of a symbol:
| Plate 2 N – I – TMKShch – S –3 GOST 7338-90 | |||||
| 2 | N | I | TMKSH | C | 3 |
| Class 2 | Type, N-unmolded | Type, I-rubber | Brand, TMKShch | Hardness degree, C-medium | Thickness, 3mm |
| Plate 2N-II- TMKShch – S-2x6 GOST 7338-90 | |||||
| 2 | N | II | TMKSH | C | 2x6 |
| Class 2 | Type, N-unmolded | Type, II-rubber-fabric | Brand, TMKShch | Hardness degree, C-medium | with 2 fabric pads, 6mm thick |
AMC – weather-oil-resistant (limitedly ozone-resistant) rubber.
Working environment: atmospheric air, rooms, containers, vessels; nitrogen, inert gases at a pressure of 0.05 to 0.4 MPa or petroleum-based oils at a pressure of 0.05 to 10.0 MPa.
Operating temperature range:
| Class | View | Type | Hardness degree | Temperature range, °C |
| 1, 2 | N, F | I | S, M, T | from -30 to +80 |
| S1, M1, T1 | from -40 to +80 |
Specifications:
| Hardness degree | Hardness units ShorA | Conditional tensile strength, MPa | Elongation at break, % |
| M | 35 — 50 | 4,5 | 300 |
| WITH | 50 — 65 | 5,0 | 250 |
| T | 65 — 85 | 7,0 | 200 |
Example of a symbol:
| Plate 2 N – I – AMS – S –5 GOST 7338-90 | |||||
| 2 | N | I | AMS | C | 5 |
| Class 2 | Type, N-unmolded | Type, I-rubber | Brand, AMC | Hardness degree, C-medium | Thickness, 3mm |
MBS – oil and petrol resistant rubber .
Working environment: indoor air, containers, vessels; inert gases, at a pressure from 0.05 to 0.4 MPa or oils and petroleum-based fuels gasoline at a pressure from 0.05 to 10.0 MPa, nitrogen.
Unshaped: thickness 0.5 - 6.0 mm, length, from 500 to 5000 mm (in rolls), width from 300 to 1200 mm. Molded: thickness 8.0 - 60.0 mm, size 500x500 or 700x700 mm.
Operating temperature range:
| Class | View | Type | Hardness degree | Temperature range, °C |
| 1, 2 | N, F | I | S, M, T | from -30 to +80 |
| S1, M1, T1 | from -40 to +80 |
Specifications:
| Hardness degree | Hardness units ShorA | Conditional tensile strength, MPa | Elongation at break, % | ||
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 1 | Type 2 | ||
| M | 40 — 55 | 6,0 | 5,0 | 250 | |
| WITH | 55 — 70 | 8,0 | 7,0 | 200 | |
| T | 70 — 90 | 8,5 | 7,5 | 200 | 150 |
Example of a symbol:
| Plate 2 N – I – MBS – S –5 GOST 7338-90 | |||||
| 2 | N | I | MBS | C | 5 |
| Class 2 | Type, N-unmolded | Type, I-rubber | Brand, MBS | Hardness degree, C-medium | Thickness, 3mm |
Technical characteristics of sheet rubber
As already noted, the main technical parameters of sheet rubber are regulated in GOST 7338-90. By the way, in some documents you can find references to GOST 7339-65, which is no longer valid.
Technical characteristics of sheet rubber
In particular, it determines that the finished product has the following dimensions:
- Sheets width from 250 to 1350, length from 250 to 1000 mm.
- Rolls width range from 250 to 1750, length can reach 10,000 mm.
- The thickness of the technical plate ranges from 1 to 60 mm.
- The specific gravity of the technical plate varies within 1000 g per 1 cubic meter. dm.
The technical characteristics of the vacuum plate are supplemented with the following parameters:
- The dimensions of the technical plates, mostly square in shape, are 500x500, 600x600, 700x700, etc.
- It must remain operational at temperatures from -8 to +70 degrees Celsius.
The vacuum plate is produced in accordance with the requirements of TU 38105116-81. Special transformer materials are also produced in the form of sheets or rolls. It is used in the production of transformers and other devices used in electrical engineering. Technical requirements for it are defined in GOST 12855.
Technical characteristics of individual brands
| Options | 7889 | 51-2062 | 9024 |
| Operating temperature (short term) | -50…+80 °C (-50…+90 °C) | +8…+70 °C (-30…+90 °C) | -20…+90 °C (-30…+90 °C) |
| Elongation at break | 550 % | 550 % | 300 % |
| Conditional tensile strength | 16.7 MPa (170 kgf/cm2) | 14.7 MPa (150 kgf/cm2) | 9.81 MPa (100 kgf/cm2) |
| Residual deformation after compression | 20 % | 40 % | 60 % |
| Shore A hardness | 45–60 units | 40–55 units | 58–72 units |
| Temperature limit of brittleness | — | — | -32 °C |
Designation of sheet rubber
Sheet rubber designations
In order for consumers of products of this class to be able to easily navigate the nomenclature of rubber goods, a procedure for designating finished products has been determined. For example, the entry plate 2N-1-TMKShch-S-5 means that in front of the customer there is an unmolded (N) sheet of rubber (1) plate of the second class, medium hardness (C). TMKShch – plate grade. The last number indicates the thickness of the sheet.
Technical characteristics of vacuum rubber plates of different brands
| Options | 7889 | 51-2062 | 9024 |
| Tensile strength | 1670 N/cm sq. | 1470 N/cm2 | 981 N/cm sq. |
| Elongation at break | 550 % | 550 % | 350 % |
| Residual relative elongation after rupture, no more | 20 % | — | 17 % |
| Residual deformation after compression to 45% of the original height for 100 hours at 70 °C, no more than 96 hours 40% | 10 % | 20-40 % | 15 % |
| Swelling in Vaseline oil for 24 hours at 70° C, no more | 90 % | — | 5 % |
| Frost resistance, not less | 8 °C | 8 °C | -40 °C |
| Heat resistance | 70 °C | 70 °C | 100 °C |
| Gas permeability constant at 20 °C | 1.3×10-7 cm2/atm×s | — | 4.2×10-8 cm2/atm×s |
| Gas permeability constant at 50 °C | 4.5 x10-7 cm sq./atm×s | — | 1.7 x10-7 cm sq./atm×s |
| Operating environment | water, dust, air | water, dust, air | oils, dust, air, water |
Scope of application of sheet rubber
Technical plates produced in accordance with the requirements of GOS 7338-90 have found their application in various industries - mechanical engineering, aviation, machine tools, food, nuclear, etc. Products made from this material are used in the production of products used in healthcare, sports, etc.
Most often, sheet rubber is used for the production of insulating and sealing gaskets. In addition, it is used in shock-absorbing devices, etc.