Structural steel is an alloy or carbon steel intended for the manufacture of various parts, mechanisms and structures in mechanical engineering and construction and having certain mechanical, physical and chemical properties. For example, ShKh15 is a specialized material for bearings.
In terms of shape, size and maximum deviations, metal products meet the requirements:
- round rolled products (steel circle 40x) - GOST 2590-88, GOST 7417;
- square rolled products - GOST 2591-88, GOST 8559;
- hexagonal rolled products - GOST 2879-88, GOST 8560;
- forged square and round rods - GOST 1113-88;
- stripes - GOST 103-76, GOST 4405;
- profiles for oblique washers: GOST 5157;
- with special surface finishing - GOST 14955.
Classification of material and application of grade 18ХГТ
Brand: 18ХГТ Classification of material: Structural alloy steel Application: Improved or cemented parts for critical purposes, which require increased strength and toughness of the core, as well as high surface hardness, operating under impact loads.
Chemical composition of 18ХГТ material in percentage terms
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Ti | Cu |
| 0.17 — 0.23 | 0.17 — 0.37 | 0.8 — 1.1 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.035 | up to 0.035 | 1 — 1.3 | 0.03 — 0.09 | up to 0.3 |
Mechanical properties of 18ХГТ at a temperature of 20oC
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Rod, GOST 4543-71 | 980 | 885 | 780 | Quenching and tempering | ||||
| Steel | 1520 | 1320 | 720 | Quenching 850oC, oil, Tempering 200oC, air, | ||||
| Steel | 980 | 730 | 1130 | Quenching 850oC, oil, Tempering 200oC, air, |
Technological properties of 18ХГТ
| Weldability: | no limits. |
| Flock Sensitivity: | not sensitive. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness: | less inclined. |
Explanation of symbols, abbreviations, parameters
| Mechanical properties : | |
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, |
| sT | — Limit of proportionality (yield strength for permanent deformation), |
| d5 | — Elongation at break, |
| y | — Relative narrowing, |
| KCU | — Impact strength, |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, |
| Physical properties: | |
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o-T), |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), |
| r | — Density of the material, |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o-T), |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, |
| Weldability: | |
| no limits | — welding is performed without heating and without subsequent heat treatment |
| limited weldability | — welding is possible when heated to 100-120 degrees. and subsequent heat treatment |
| difficult to weld | — to obtain high-quality welded joints, additional operations are required: heating to 200-300 degrees. during welding, heat treatment after welding - annealing |
Chemical composition and heat treatment modes of 18KhGT steel.
Analysis of the selected steel grade for the manufacture of the “axle” part.
For the part, we select 3 grades of steel from the group of structural steels.
Our part experiences high dynamic loads, therefore, we need to choose maintenance operations such as hardening (after which maximum hardness is achieved) and high tempering (it removes internal stresses and gives a combination of strength and ductility). Therefore, we choose 3 steel grades after this maintenance:
1. 45Х (low alloy);
2. 40ХС (alloyed);
3. 18ХГТ (alloyed).
The choice of these grades was based on the specified parameters: core yield strength σ0.2, core hardness NV, impact strength KCU, hardenability.
1. Steel 45X has a yield strength after heat treatment of 830 MPa with a part diameter of up to 25 mm, the hardness of the HB core is not specified, the impact strength KCU is 49 J/cm2. Hardenability in oil is 20-38 mm.
2. Steel 40ХС has a yield strength after heat treatment of 640 MPa with a part diameter of 25 mm, core hardness НВ – 270, impact strength KCU – 88 J/cm2. Hardenability is not specified (for steel 33ХС - 30mm).
3. Steel 18KhGT has a yield strength after heat treatment of 950 MPa with a part diameter of up to 20 mm, the hardness of the HB core is 302, the impact strength KCU is 144 J/cm2. Hardenability in oil is 20-52 mm.
Based on the above parameters, we conclude that the most suitable steel for the manufacture of the axle part (Ø 17mm) is steel grade 18ХГТ.
Chemical composition and heat treatment modes of 18KhGT steel.
The chemical composition is presented in Table 2. The mechanical properties, depending on the cross-section of the rod, are presented in Table 3. For the manufacture of the axle part, a rolled product was chosen - a 20 mm rod, since the specifications indicated that the type of production was small-scale.
Table 2. Chemical composition
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | P | S | Ni | Cu |
| 0,17-0,23 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,8-1,1 | 1,00-1,30 | ≤0,035 | ≤0,035 | ≤0,30 | ≤0,30 |
Table 3. Mechanical properties of 18KhGT steel depending on tempering temperature
| Temperature °C | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв(MPa) | δ5 (%) | ψ % | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB |
| Bar. | ||||||
| 200 300 400 500 | 1150 1150 1150 950 | 1370 1330 1210 940 | 11 10 9 15 | 57 57 57 66 | 98 78 78 144 | 387 387 375 302 |
Critical point temperature: Ac1 = 740°C, Ac3 = 825°C, Mn = 360°C,
Ar3(Arcm) = 730°С, Ar1 = 650°С
Stages of heat treatment of steel 18ХГТ.
Quenching at temperature Ac3 + 30…50°С (825 + 30..50°С) through oil.
Hardening is heating the steel 30–50°C above the temperature of phase transformations, holding it at this temperature and then very quickly cooling it in water or oil. Hypoeutectoid steels are heated to a temperature 30–50°C above the upper critical point Ac3. In this case, steel with the initial pearlite-ferrite structure, when heated, acquires an austenitic structure, which, upon subsequent cooling at a rate equal to or higher than the critical one, turns into martensite. Full hardening for hypereutectoid steels is carried out at a temperature of 30-50 °C above Ac3, followed by rapid cooling in water (oil). As a result of such hardening, we obtain a martensite structure. 18KhGT is a hypoeutectoid steel, so we choose the temperature Ac3 +30...50°C for hardening. Hardened steel is characterized by a nonequilibrium structure and therefore this type of heat treatment is used: tempering.
High tempering at 500 °C, air cooling.
The choice of temperature is based on Table 3. If you select Tmp below 500°C, the part will not be suitable for impact strength (KCU will be less than 100 kJ / m2). If you choose a higher Tomp, the part will not be suitable in terms of strength and hardness (HB will be less than 290, the yield strength of the core will be less than 800 MPa).
Tempering is a heat treatment process consisting of heating hardened steel to a temperature below the critical point Ac1, holding at this temperature and subsequent cooling (usually in air). The purpose of tempering is to obtain a more stable structural state, eliminate or reduce stress, increase toughness and ductility, as well as reduce hardness and reduce brittleness of hardened steel.
High tempering is performed at temperatures of 500-650°C (in our case 500°C). During the high tempering process, martensite decomposes to form a tempered sorbitol structure. This structure provides the best combination of strength and ductility of steel. In tempered sorbitol, cementite takes on a granular form, in contrast to sorbitol obtained after normalization, in which cementite has a lamellar structure. Thanks to this, the impact strength is significantly increased at the same or even higher hardness compared to normalized steel. This type of tempering is used for parts made of structural steels operating under shock loads. Hardening of steel followed by high tempering is called improvement.
The Temperature-Time diagram of the hardening treatment is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 – Temperature-time diagram
When heated above the point Ac1 = 740°C, austenite grains are formed from pearlite, then austenite grains grow with increasing temperature. When heated above the point Ac3 = 825°C, the transformation of the mixture of ferrite and austenite into austenite is completed, the chemical composition of which, upon exposure, becomes homogeneous and corresponds to the content of elements in the steel. When tempered at a temperature of 500°C, martensite decomposes to form a tempered sorbitol structure. This structure provides the best combination of strength and ductility of steel. High tempering completely relieves quenching stresses.
Conclusion.
After strengthening heat treatment of 18KhGT steel, we obtained the following mechanical properties: yield strength 950 MPa, core hardness NV – 302, impact strength KCU – 144 J/cm2, which corresponds to the stated task conditions. From this we conclude that the selected steel 18ХГТ is suitable for the manufacture of the “axle” part.
Answers on questions:
3)
Hypoeutectoid steels are heated approximately 30...50° above the critical point Ac3 (GS line): tzak = Ac3+ 30...50°C. Hypereutectoid steels should be heated for hardening above Ac1 (line SK) by 30...50°.
4)
Hardened steel is under stress and therefore has significant brittleness. To improve the properties of steel and increase the durability of its service, it is necessary to remove internal stresses or at least reduce them. For this purpose, steel products are almost always tempered after hardening. After hardening, tempering is also needed in order to obtain a more stable structural state.
5)
The process of hardening steel consists of heating it to a certain temperature (30...50° above the GSK line according to the Fe - Fe3C diagram), holding it and then rapidly cooling it in water, oil, molten salts or other media. Tempering is heating the hardened steel to a temperature below the critical temperature Ac1, holding at this temperature and subsequent cooling (usually in air).
7)
The purpose of tempering is to obtain a more stable structural state, eliminate or reduce stress, increase toughness and ductility, as well as reduce hardness and reduce brittleness of hardened steel. Tempering is based on the transformation of martensite during heating, which results in a change in the structure and properties of steel.
The purpose of low tempering (100-250°C): relieving internal stress while maintaining hardness. Structure of tempered martensite.
The purpose of medium tempering (350-450°C): high elastic limit. The structure is troostite leave.
The purpose of high tempering (500-650°C): achieving the best combination of strength and ductility of steel. Structure of sorbitol release.
Other brands from this
Please note that this information about the 18ХГТ brand is provided for informational purposes. The parameters, properties and composition of the actual 18ХГТ brand material may differ from the values given on this page. More detailed information about the 18ХГТ grade can be found on the information resource Brand of steel and alloys. You can check with our managers for information about the availability, delivery times and cost of materials. If you find inaccuracies in the description of materials or errors found, please inform the site administrators using the feedback form. Thanks in advance for your cooperation!
Low-alloy steel, high-quality structural
Regulatory document: high-quality structural low-alloy steel is manufactured in accordance with GOST 19281-89.
Low-alloy steel - alloy steel with a total mass of alloying elements less than 2.5% of the total mass of steel.
Low alloy steel grades
Steel grades: 09G2, 09G2S, 0KHSND, 17G1S, 16G2AF, 10KHNDP, 15KHNDP, 0KHSND, 15KHSND, etc.
Low-alloy steel grades 10KhNDP, 15KhNDP, 0KhSND, 15KhSND are atmospherically corrosion-resistant (AKS).
Substitutes for some grades of steel:
- 09G2S - 09G2, 09G2DT, 09G2T, 10G2S;
- 10HSND - 16GAF.
Application of low alloy steel
Low-alloy steel is used for the manufacture of railway, metro and tram car bodies, load-bearing structures of locomotives, agricultural and other field machines and engineering structures operating under conditions of variable dynamic loads and seasonal and daily heat changes.
Weldability: low-alloy steel can be welded without restrictions.
Structural alloy steel 18ХГТ
Substitutes
- 30ХГТ,
- 25ХГТ,
- 12ХН3А,
- 12X2NAA,
- 20ХН2М,
- 14ХГСН2МА,
- 20HGR.
Analogs
Decoding
According to GOST 4543-2016, the number 18 before the letter designation indicates the average mass fraction of carbon (C) in steel in hundredths of a percent, i.e. The average carbon content in 18KhGT steel is 0.18%. The letter X means that the steel is alloyed with chromium; the absence of a number behind the letter means that the chromium content is up to 1.5%. The letter G means that the steel is alloyed with manganese, the absence of a number behind the letter means that the manganese content is up to 1.5%. The letter T means that the steel is alloyed with titanium, the absence of a number behind the letter means that the titanium content is up to 1.5%.
Type of delivery
- long products, including shaped steel: GOST 4543-71, GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88, GOST 2879-88.
- Calibrated rod GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78, GOST 1051-73.
- Polished rod and silver steel GOST 4543-71, GOST 14955-77.
- Strip GOST 103-76.
- Forgings and forged blanks GOST 1133-71.
Characteristics and application [1]
— Steel 18ХГТ is a chromium-manganese structural alloy steel and is used for the manufacture of improved or cemented parts for critical purposes, which require increased core strength and toughness, as well as high surface hardness, operating under impact loads, for example:
- gears of axle shafts and gearboxes,
- satellites,
- front drive axle hinge cams,
- bushings,
- worm shafts,
- claw couplings,
- fingers,
- tapered bearing rings with a diameter of 60-250 mm,
- rollers with a diameter of up to 25 mm.
Steel grade 18ХГТ in some cases is used in industry instead of steel grade 12ХН2. This steel can be used for both cemented and improved parts. This steel is hardened at a temperature of 850-880°C in oil, followed by tempering at a temperature of 500-650°C.
Since 18KhGT steel is characterized by temper brittleness, accelerated cooling of parts is necessary after high tempering.
Cementation of 18KhGT steel is carried out at 940-950°C, followed by quenching from a temperature of 780-800°C in oil and tempering at 180-200°C.
Comparative characteristics of the mechanical properties of steel grades 18ХГТ and 12ХН2
As a result of carburization and subsequent heat treatment, 18KhGT steel acquires slightly greater strength compared to 12KhN2 steel with almost equal values of impact toughness and ductility.
| steel grade | Heat treatment modes in °C | σа, kg/mm 2 | σt, kg/mm 2 | δ% | ψ % | an in kg*m/cm 2 | |
| Oil hardening | Vacation | ||||||
| 18ХГТ | 800 | 200 | 120 | 90 | 13 | 55 | 7 |
| 12ХН2 | 780 | 200 | 80 | 60 | 12 | 50 | 8 |
However, it should be taken into account that 18KhGT steel is calcined worse than 12KhN2 steel.
In petroleum engineering, 18KhGT steel is used for the manufacture of critical, highly loaded parts, for example:
- shafts,
- gearbox gears,
- axes,
- worms,
- jaw couplings, etc.
Temperature of critical points, °C
| Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar3 | Ar1 | Mn |
| 740 | 825 | 730 | 650 | 360 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 4543-71)
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ti | R | S | Cu | Ni |
| no more | ||||||||
| 0,17-0,23 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,80-1,10 | 1,00-1,30 | 0,03-0,09 | 0,035 | 0,035 | 0,30 | 0,30 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 4543-2016)
| steel grade | Mass fraction of elements, % | |||||||||
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Al | Ti | V | B | |
| 0,17-0,23 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,80-1,10 | 1,00-1,30 | 2,75-3,15 | — | — | — | 0,030-0,090 | — | — |
- The sign “-” means that the mass fraction of this element is not standardized or controlled, unless otherwise specified in 7.1.2.3 GOST 4543-2016.
General characteristics of steel grade 18ХГТ
High-quality chromium-manganese grade 18ХГТ belongs to the group of structural alloy steels.
It contains chromium, manganese and titanium . Chromium increases hardenability and hardness , and also improves corrosion resistance . Manganese provides strength, wear resistance, and high hardenability of steel ; in addition, the presence of this element in the composition gives the metal great strength during plastic deformation and resistance to impact wear.
Titanium is introduced into the composition to obtain high hardness . Silicon has a positive effect on the elastic characteristics of steel.
SPECIAL OFFER! Call 380-22-16!
Name
| steel grade | Size | Quantity | Price >0.1t | ||
| Circle | 18ХГТ | 56 | 0,239 | 52700 | get an invoice |
| Circle | 18ХГТ | 75 | 0,714 | 52700 | get an invoice |
| Circle | 18ХГТ | 85 | 0,41 | 52700 | get an invoice |
| Circle | 18ХГТ | 90 | 0,19 | 52700 | get an invoice |
| Circle | 18ХГТ | 95 | 5,424 | 52700 | get an invoice |
| Circle | 18ХГТ | 110 | 0,928 | 52700 | get an invoice |
| Circle | 18ХГТ | 130 | 0,714 | 55000 | get an invoice |
| Brand: | 18ХГТ |
| Classification: | Alloy structural steel |
| Substitute: | 30ХГТ, 25ХГТ, 12ХН3А, 12Х2Н4А, 20ХН2М, 14ХГСН2МА, 20ХГР |
| GOST standards: | GOST 1133-71, GOST 8319.0-75, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006, GOST 2879-2006, GOST 103-2006, GOST 1051-73, GOST 4543-71, GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78, GOST 14955-77 |
| Application: | improved or cemented parts for critical purposes, which require increased core strength and toughness, as well as high surface hardness, operating under impact loads. |
Read more about the use of 18HGT >>
Structural alloy steel 18ХГТ
Steel 18ХГТ is a structural alloy. Adding letters to its name means the presence of the indicated elements in the alloy. For example, the letters ХГТ in the decoding of 18ХГТ steel make it clear that it contains chromium, manganese and titanium. Additional components are introduced specifically so that the alloy can achieve the mechanical or physical properties required of it. Such additives increase the strength, anti-corrosion and other properties of the metal.
Chemical composition
According to the chemical composition, 18KhGT steel contains the following elements in percentage:
- Chromium – 1.3%.
- Carbon – 0.23%.
- Manganese – 1.1%.
- Titanium – 0.09%.
- Silicon – 0.37%.
Sulfur, phosphorus, nickel, copper and nitrogen are contained in very small quantities. The percentage of specified elements is given as a maximum value. It may be a little less, but it must be within the values allowed by GOST.
Chemical composition of steel 18ХГТ
Basic properties
The main characteristics of 18ХГТ steel are the presence of elements such as chromium. It is a cheap alloying element. In combination with carbon, the chemical element gives the grade of this alloy the strength and stability of the material. In this case, a slight decrease in viscosity is observed. Chromium also has a positive effect on the critical heat treatment rate of 18KhGT steel.
The presence of manganese has a positive effect on ductility and gives good weldability to the metal. This component does not form carbide. It dissolves and turns into alloyed cementite. The presence of a large amount of manganese makes it brittle when hardened.
The presence of silicon in this type of alloy gives it strength. Thanks to this element, plasticity is also not lost. Another element is titanium. When combined with carbon, the component forms highly hard products. Parts containing titanium are able to resist crushing.
The weldability of 18ХГТ has no restrictions. The metal combines well with any alloys.
- Contact spot welding.
- Manual arc welding.
Parts are welded without heating or heat treatment subsequently. Only with parts treated chemically and thermally are problems possible during welding.
Structural alloy steel is not susceptible to various internal defects. When testing for fracture or rupture, the alloy of this brand shows excellent results. Products made from it are also not prone to brittleness during tempering of the part and testing for fracture.
Physical properties include excellent wear resistance and toughness. This grade is used to produce parts that can operate under prolonged and high vibration and dynamic loads.
The temperature of the environment in which the operation of parts made of structural alloy is permissible can range from minus seventy degrees Celsius to four hundred and fifty plus.
Circle made of steel 18ХГТ
The mechanical properties of 18ХГТ are such that a five-millimeter product can withstand pressures of up to 1520 MPa if the material has undergone heat treatment at 850 degrees Celsius with a tempering of two hundred degrees. Twenty-millimeter parts made from it can withstand pressures of up to 950 MPa with the same hardening and tempering. Oil is used instead of water for cooling. It slows down the process, since the effectiveness of hardening depends on the cooling rate.
The hardness of a product made of this metal after annealing is 217 HB. When the temperature rises to 500 degrees, the hardness of 18KhGT steel increases. GOST for this material 4543-71.
18ХГТ
- Products made of steel 18ХГТ in stock:
Circle - Band
- Square
to make a request
Structural alloy steel 18ХГТ
Substitutes: Steel 20ХГР, Steel 30ХГТ, Steel 25ХГТ, Steel 12ХН3А, Steel 12Х2Н4А, Steel 14ХГСН2МА
18ХГТ steel is used: for the production of improved or cemented parts for critical purposes, which require increased strength and toughness of the core, as well as high surface hardness, operating under impact loads.
Specifications
| Chemical composition in% |
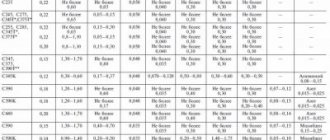
| NTD | C | S | P | Mn | Cr | W | V | Ti | Si | Ni | Mo | Cu |
| TU 14-1-3238-81 | 0,17-0,23 | ≤0,030 | ≤0,030 | 0,80-1,10 | 1,00-1,30 | ≤0,20 | ≤0,050 | 0,03-0,099 | 0,17-0,37 | ≤0,30 | ≤0,15 | ≤0,30 |
| GOST 4543-71 | 0,17-0,23 | ≤0,035 | ≤0,035 | 0,80-1,10 | 1,00-1,30 | ≤0,20 | ≤0,050 | 0,03-0,09 | 0,17-0,37 | ≤0,30 | ≤0,15 | ≤0,30 |
According to GOST 4543-71, the content in high-quality steel is regulated: P≤0.025%; S≤0.025%; Сu≤0.30%; in especially high-quality steel: P≤0.025%; S≤0.015%; Сu≤0.25%. According to TU 14-1-3238-81, the chemical composition is given for steel grade 18KhGTA.
| Mechanical properties |
| Mechanical properties at 20°C |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Normalization at 930-960 °C + carburization at 930-950 °C + quenching in oil from 825-840 °C + tempering at 180-200 °C | ||||||||||||||||
| Long products | ≤50 | 800 | 1000 | 9 | ≥285 | 57-63 | ||||||||||
| Carburization at 920-950 °C, air cooling + oil quenching from 820-860 °C + tempering at 180-200 °C, air cooling | ||||||||||||||||
| Long products | ≤20 | 930 | 1180 | 10 | 50 | 765 | 300-341 | 53-63 | ||||||||
| Long products | 20-60 | 780 | 980 | 9 | 50 | 765 | 240-300 | 57-63 | ||||||||
| Mechanical properties depending on the section |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Quenching in oil from 850 °C + tempering at 200 °C, air cooling | ||||||||||||||||
| Long products | ≤5 | 1320 | 1520 | 12 | 50 | 706 | ||||||||||
| Long products | 15-20 | 730 | 980 | 15 | 55 | 1108 | 30 | |||||||||
| Long products | 20-25 | 690 | 980 | 19 | 50 | 912 | 28 | |||||||||
| Long products | 5-15 | 930 | 1180 | 13 | 50 | 765 | 38 | |||||||||
| Mechanical properties depending on tempering temperature |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Quenching in oil from 880 °C + tempering | ||||||||||||||||
| 200 | 1150 | 1370 | 11 | 57 | 41 | |||||||||||
| 300 | 1150 | 1330 | 10 | 57 | 41 | |||||||||||
| 400 | 1150 | 1210 | 9 | 57 | 40 | |||||||||||
| 500 | 950 | 940 | 15 | 66 | 32 | |||||||||||
| 600 | 720 | 780 | 20 | 73 | 22 | |||||||||||
| Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Normalization [82] | ||||||||||||||||
| 20 | 420 | 520 | 26 | 77 | 156 | |||||||||||
| 200 | 360 | 460 | 24 | 78 | ||||||||||||
| 300 | 310 | 465 | 24 | 68 | ||||||||||||
| 400 | 300 | 470 | 29 | 75 | ||||||||||||
| 500 | 300 | 410 | 27 | 76 | ||||||||||||
| 600 | 240 | 325 | 45 | 86 | ||||||||||||
| Sample 6 mm in diameter, 30 mm in length, forged and normalized. Deformation speed 50 mm/min. Strain rate 0.03 1/s [81] | ||||||||||||||||
| 700 | 205 | 235 | 46 | 88 | ||||||||||||
| 800 | 76 | 135 | 51 | 94 | ||||||||||||
| 900 | 54 | 95 | 55 | 96 | ||||||||||||
| 1000 | 50 | 78 | 58 | 100 | ||||||||||||
| 1100 | 25 | 43 | 61 | 100 | ||||||||||||
| 1200 | 13 | 25 | 56 | 100 | ||||||||||||
| Technological properties |
| Machinability | After normalization at HB 156-159 and sB=530 MPa Kn tv.all.=1.1 Kn b.st.=1.0 |
| Weldability | welded without restrictions (except for chemically and thermally treated parts). Welding methods: RDS, KTS. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness | less inclined |
| Forging temperature | Start - 1200 °C, end - 800 °C. Sections up to 250 mm are cooled in air, 251-350 mm - in a pit. |
| Flock sensitivity | not sensitive |
| Critical point temperature |
| Critical point | Temperature °C |
| AC1 | 740 |
| AC3 | 825 |
| AR3 | 730 |
| AR1 | 650 |
| MN | 360 |
| Impact strength |
| Delivery condition temperature | +20 | -20 | -40 | -60 |
| 1118 | 991 | 912 | 834 |
| Hardness |
| Delivery condition, heat treatment mode | HRC surface | HRCE cores | HRB | HB | H.V. | HSD |
| after annealing | 217 |
| Endurance limit |
| Heat treatment, steel condition | s-1 (MPa) | t-1 (MPa) | n | sB (MPa) | s0.2 (MPa) |
| Sample with a cross section of 50 mm, HB 240-300 | 490 | 294 | 980 | 780 | |
| Cementation at 960 °C, oil quenching at 840 °C + tempering at 180-200 °C. HB 240-300. | 637 | 1E+6 | |||
| Normalization at 1100 °C, cooling to 870 °C, quenching in oil, tempering at 200 °C. HB 415. | 480 | 5E+6 |
| Hardenability |
Hardening 900 °C.
Hardness for hardenability strips HRCе. Distance from the end, mm/HRCе
| 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 | 6 | 7.5 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 |
| 41.5-50.5 | 39.5-49.5 | 36.5-47.5 | 33-46 | 30-44.5 | 27.5-42.5 | 24.5-42.5 | 23-37.5 | 35.5 | 34 |
| Heat treatment | Amount of martensite, % | Crete. dia. in water | Crete. dia. In oil | Crete. hardness, HRCе | Dist. from the cooled end, mm |
| 50 | 33-82 | 12-52 | 32-36 | ||
| 90 | 23-48 | 6-24 | 38-43 |
| Physical properties |
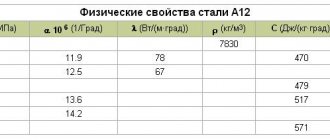
| Test temperature, °C | 0 | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 1000 |
| Modulus of normal elasticity (E, GPa) | 211 | 211 | 205 | 197 | 191 | 176 | 168 | 155 | 136 | 129 | |
| Modulus of elasticity under torsional shear (G, GPa) | 84 | 80 | 77 | 75 | 68 | 66 | 59 | 52 | 49 | ||
| Density (r, kg/m3) | 7800 | 7800 | |||||||||
| Thermal conductivity coefficient (l, W/(m °C)) | 37 | 37 | 38 | 38 | 37 | 35 | 34 | 31 | 30 | 29 | |
| Ud. electrical resistance (R, NΩ m) | |||||||||||
| Linear expansion coefficient (a, 10-6 1/°С) | 10 | 11,5 | 12,3 | 12,8 | 13,3 | 13,3 | 13,6 | ||||
| Specific heat capacity (C, J/(kg °C)) | 495 | 508 | 525 | 537 | 567 | 588 | 626 | 626 | 705 |
| Designations |
Mechanical properties:
|
Application of material
18ХГТ steel has found application in the manufacture of parts such as piston pins and axle gears. Great demands are placed on the latter, since they operate at medium pressure and high speeds. The material from which they are made must have high strength, toughness and hardness. The characteristics of 18HGT meet all of the above criteria.
This metal compound is also used to make reverse driven shafts, reverse-mode gearbox gears, and hydraulic transmission wheels for rear axle tractor gears. Split rings, collets, friction discs are also popular products made from this steel grade.
It also has foreign analogues. For example, in Germany 20MnCr5G is used, in Bulgaria - 18ChGT. The closest neighbor, China, uses an analogue - 20CrMnTi.
Purpose and application
According to its intended purpose, grade 18ХГТ belongs to structural alloy steels. It is widely used in the machine tool industry, the automotive and tractor industries.
The most popular parts made from it are shafts, gears, claw couplings, bushings, spindles, and worms.
Why is steel so good? What's original about it?
To better understand the importance of 18KhGT steel for industry, it is necessary to consider at least one example:
Gears. Everyone knows these gears. They work in difficult conditions. 18ХГТ steel is ideal for their manufacture for the following reasons:
- Manufacturability, mechanical processing without problems. To make gears, the initial steel should not be too hard or brittle. The required properties are achieved by special heat treatment.
- Provides wear resistance. This, on the contrary, requires high surface hardness. It is obtained due to the good cementability of steel. A mandatory requirement for cementation is the presence of free carbon that penetrates the surface layers. After carburization, hardening occurs, the structure changes, and the hardness of a 2 mm layer increases to 60 HRC. The core hardness is less than 40 units.
- High strength. Often the gears work with overload, and sometimes the teeth jam. The higher the tensile strength of the steel, the greater the contact load the gears can withstand. The tensile strength of 18KhGT steel is quite high, about 1000 MPa.
- Increased endurance. Endurance, or fatigue strength, determines the ability of parts to work under cyclic loads. For gears this parameter is very relevant. The endurance value is about 700 MPa, like 18ХГТ, which allows it to withstand millions of cycles.
The given example shows the variety of positive characteristics of 18KhGT steel. But this list is not exhaustive.
In addition to carburization, steel can be nitrided. Due to this, the scope of application of the material is expanded. Nitrogen-saturated surface layers up to 0.6 mm thick acquire increased hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. After nitriding, no heat treatment is required, parts do not warp.
The service life of such critical parts as ship propeller shafts is significantly increased.