Acid battery desulfation
When a battery releases energy, it discharges due to a chemical reaction:
Pb +2H2SO4 +2PbO2 -> 2PbSO4 +2H2O
Pb is lead plate
PbO2 – active putty on carbon grate
PbSO4 - small crystals that grow and cover the plate
But when the battery is charged from a generator or network, the reaction goes in the opposite direction, that is, lead sulfate breaks down into lead ions and an acid residue. And everything would be fine, but some of the crystals, with chronic undercharging and deep discharge of the battery, grow and do not participate in the reaction. The substance covers the plate with an insoluble gray-yellow film, clogs the pores, and prevents the passage of charged ions to the conductive plates. This explains the rapid recharging of the battery and instantaneous discharge - there is no capacity.
You can return the capacity to the battery if the putty has not crumbled and the plates have not collapsed - that is, the electrolyte in the jars is light, without suspension. The purpose of battery desulfation is to clean the plates mechanically, chemically or electrically, to restore or replace the electrolyte. Sludge removal schemes have been developed for years. There are methods for desulfating batteries, used in service centers and available at home.
How to desulfate a car battery
The natural process of battery aging due to loss of capacity as a result of precipitation of poorly soluble salts can be delayed by timely desulfation of the starting or traction battery.
All methods can be classified by type:
- Exposure to electric charge - low-level direct current, pulsed current, polarity reversal.
- Chemical methods using sediment destroyers followed by replacement of the electrolyte. Or dissolving the precipitate in distilled water with a low charging current
- Mechanical - when plates removed from cans are restored by mechanical processing.
For preventive purposes, additives are periodically added to the electrolyte to prevent the formation of sulfate stone, but they destroy the plates, shortening the battery life.
Circuit for car battery desulfation
Of the chemical methods for desulfating batteries, the most commonly used is a complex composition of Trilon B and ammonia. These substances are available, but they should be used in accordance with the instructions and on strong batteries. Trilon B, sodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, soluble in water, sodium replaces the lead ion in the salt and the precipitate dissolves. But the active putty also dissolves.
The procedure for desulfating a battery chemically:
- Prepare a solution - take 60 g of Trilon B, 622 ml of NH4OH 25%, 2340 ml of distilled water for 3 liters. You can take 10% ammonia solution 1560 ml, water 1140 ml and 60 g Trilon B.
- Drain the electrolyte from the battery into a suitable container.
- Immediately fill the wet jars with the prepared mixture and leave them in the battery for no more than 60 minutes.
- Drain the contents and rinse the jars 3-4 times with distilled water.
- Fill in fresh electrolyte of the required density and perform a full charge cycle.
The method must be used with caution. If desulfation of a car battery is carried out to remove a small amount of sediment, the exposure time is reduced to 30-40 minutes. Trilon B doesn’t care whether it dissolves a harmful sediment or an active mass. At the moment of the reaction, the liquid heats up and boils. You need to work outdoors and use protective equipment.
Desulfation Charger for Car Battery
In industrial conditions, at car depots, where batteries are charged by trained workers, battery desulfation is carried out using a special desulfation charger. To remove sediment from a heavily clogged battery, reverse pulse currents are used.
Reversible current is alternating, with different amplitude and polarity, repeated cyclically. Pulsed desulfation by charging and discharging acts gently on the battery, the temperature of the electrolyte does not rise, and gas evolution does not occur.
To create reverse currents, a special device is used, a reverse current generator, the cost of which is approximately equal to two batteries. How to desulfate a battery using a reverse current generator?
The generator is used for medium sulfation of plates with a current supply of 0.5 - 2.0 A for 20-50 hours. The process is completed when the voltage and density of the electrolyte remain unchanged for 2 hours.
A heavily clogged battery is cleaned using a desulfation device with distilled water in several stages. To do this, the voltage on the battery must be reduced to 10.8 V, the electrolyte removed, and filled with distilled water into the jars.
Carry out desulfation of the battery with a low current so that the voltage is up to 2.3 V. Gradually the sediment dissolves in water, the electrolyte acquires a density of about 1.11 g/cm3. Replace the solution with fresh distilled water, and continue the process until the density is 1.12 g/cm3. Now set the current strength to 1 A and watch the voltage increase until the indicator stabilizes.
After the first stage of battery desulfation, the current is increased to 20% of the discharge value, the battery is charged for 2 hours, discharged, and so on until a constant density and voltage is achieved 3-5 times.
Bring the acid to a density of 1.21-1.22 g/cm3, charge the battery completely and after 3 hours adjust the density using the table. The method is labor-intensive, but the desulfation of the plates is complete. The battery returns to its second youth.
Battery desulfation by charger
You can get by with a cheaper desulfation method using a conventional charger. But an indispensable condition is the ability to regulate current and voltage. If the sediment still occupies less than half of the plates, the following battery desulfation scheme is used:
- Bring the electrolyte level to the normal level with distilled water.
- Connect the charger and set the voltage to 14 V, current to 1 A. Charge for 8 hours. Measurements should show that the density of the electrolyte has increased, the voltage has risen to 10 V. If the readings are lower, the battery cannot be restored.
- The battery rests for a day, disconnected from the charger.
- Connect with a voltage of 14 V and a current of 2-2.5 A for 8 hours. The voltage should be 12.7-12.8 V. Electrolyte in jars with a density of 11013 g/cm3.
- Discharge the battery to 9 V using a high beam lamp in 6-8 hours.
- Repeat the discharge-charge several times until the electrolyte density becomes 1.27 -1.28 g/cm3. During the cycles, the process of desulfation occurs, the stone dissolves, and the acidic residue SO4 strengthens the electrolyte.
Read also: Plasma welding principle of operation
As a result, the capacity of the lead acid battery will be restored by 80-90%. But this is not the way to desulfate a calcium or gel battery.
Most often, the Vympel installation is used for desulfation with a charger. It is affordable and has the necessary adjustment. You can connect to it an attachment in the form of a blinker or other electronic device for removing lead stone.
In maintenance-free batteries, desulfation is effective only at the initial stage of stone deposition. It is carried out using a pulse charger. But you need to know that the stone in the calcium battery contains gypsum, which is not destroyed under the influence of pulsed currents. Therefore, maintenance-free batteries cannot be restored after 3 deep discharges.
Preventive measures
To reduce the effect of sulfation, it is necessary to check the density and level of the electrolyte (distilled water is used to top up). The recommendation applies only to power sources equipped with screw caps in the lids of the cans.
Long-term storage of a battery connected to the vehicle's on-board network negatively affects the condition of the plates. The sulfation process intensifies at low air temperatures. An additional preventive measure is to comply with the charging current parameters, which should not exceed 10% of the battery capacity.
Device for desulfation of car batteries
Desulfation on car battery plates under the influence of alternating currents with a change in polarity at high frequencies is carried out well. The industry offers devices and charging attachments for battery desulfation.
The battery charger Kedr Auto-10, with desulfation mode, is an automatic charger. It provides charging with a current in % A of the battery capacity, fast mode with a current of 5 A and cyclic mode - desulfation. The compact charger is affordable.
Charger desulfating devices are selected for a specific type of battery. The following products are considered the best for servicing one battery:
- single-channel device intended for car batteries;
- It is better to take a device with manual adjustment of the charging current;
- study the possibilities of protection, blocking and permissible temperatures;
- know the parameters of your battery and select the appropriate device.
According to technical indicators, a device with an adjustable voltage of 0-36 V, with different methods of desulfation, is suitable for a motorist:
- gentle – low current, constant voltage;
- intense – cyclic pulse, supplying asymmetric current;
- cyclic charge with a decrease in charging voltage.
Compatibility with your battery capacity is a must.
If you purchased a desulfating attachment, then it should be connected between the charger and the battery, and its wires should not be thinner than others in the connection diagram. The charger must support pulse mode.
Other methods or how else you can clean it
I don’t encourage you to do this, and sometimes the methods are really expensive and complicated:
- Disassemble and clean physically. To be honest, it’s very difficult for me to imagine this, but I read on the Internet that in principle this is possible, and most importantly, there are “craftsmen”. The principle is simple - we need to physically cut the top of the battery and pull out the bags with plates, then they are disassembled and cleaned of plaque, then they are installed back into the plastic case! It’s very difficult and I can’t imagine what’s possible! However, there is such a thing.
- Pour a special chemical solution into the battery that will dissolve the sulfate. This seems more like the truth, but it doesn’t always work. They usually wash it with TRILON B , do it at your own peril and risk, I won’t advise you anything here! Many write that it helps, others that you completely kill the battery, in general the “50/50” method
All souls are pure, we talked about other methods, let’s move on to our more correct one. But first I would like to say a few words about chargers
Battery desulfation at home
Often desulfation of passenger car batteries is carried out with your own hands, guided by the diagrams provided on various resources. Many of them rely on using a regular charger, but require a lot of attention. On average, manual sulfation using low currents and several cycles takes more than 2 weeks.
Connecting the set-top box to the charger will speed up the battery desulfation mode. An example of a set-top box is a pulse converter called a blinker, since LEDs signal the passage of alternating current. You can assemble the device yourself.
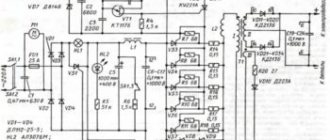
Here is a diagram of a charger for sulfation of a car battery, called a “blinker”.
The “blinker” principle is the passage of 10% of the current from the battery capacity, voltage 13.1 - 13.4 V. The circuit represents discharge with 12 V light bulbs and a relay that turns on charging at the end of discharge. The result is a blinking with a pulsation of 4.3 seconds per discharge with a current of 1 A and 3 seconds per charge with a current of 5 A. Current pulses first loosen the monolithic film on the plate, then dissolve small crystals.
We know that maintenance-free batteries are difficult to desulfate. But if the battery is new, has served no more than 2 years, and the electrolyte level in the banks is low, you can try to restore the capacity. First you need to add distilled water to the jars and seal the holes with epoxy glue. Then try charging with pulsed current. In the battery desulfation mode, the active putty will be destroyed simultaneously with the crust of sulfated lead. The capacity will not be restored much and not for long.
Possible difficulties
Possible problems when desulfating power supplies:
- Maintenance-free batteries and devices with thickened electrolyte cannot be restored, since they do not allow replacement of the substance. But the design of power supplies ensures reduced formation of lead sulfates, which extends the life of the products.
- A calcium-type battery is assembled on the basis of plates made of an alloy of lead and calcium. The use of additional alloying material made it possible to reduce the evaporation of water from the electrolyte and reduced the self-discharge of the power source. When the device operates, simultaneously with the formation of lead sulfate, calcium sulfate settles on the surface of the plates, which is not decomposed by applying reverse current or introducing chemical reagents.
Video
You may find it helpful to watch the video provided on battery desulfation.
Any car enthusiast has encountered the phenomenon when a battery, after lying idle for some time, stops delivering its rated capacity, turns the starter for half a second, then dies, but the voltage on it is normal - 12 volts.
Anyone can face this, but why does it happen. A car battery consists of lead plates in an electrolyte solution - in this case, the electrolyte is sulfuric acid.
The process of charging and discharging a battery is nothing more than a redox process; a chemical reaction occurs during which the lead plate reacts with oxides on the adjacent plate. During this reaction, sulfates are formed, which over time accumulate on the plates. Sulfates prevent the flow of current because they are a poor conductor and over time the battery loses capacity and is not able to deliver large current to operate the starter.
If your battery charges and discharges faster than before, without any mechanical damage, it most likely failed due to sulfation of the plates.
The proposed device (desulfator) creates short pulses of high amplitude and frequency. The desulfation pulse lasts for a certain time, then a simple one, then another pulse. Such impact processes can destroy the sulfate layer, and in theory this is possible; in practice, not all batteries can be restored due to the design features of the latter, but judging by statistics, about 85% of old batteries can be restored, of course, if the cause of inoperability is sulfation and not a break lead plates or other mechanical damage.
How to use the device?
This option is a charger-desulfation device, a conventional desulfator is powered by a battery, which it desulfates and gradually discharges, while in this case the device charges the battery with short bursts of high-frequency high voltage.
This circuit can also be used to charge low-voltage lead-acid batteries with a nominal voltage of 4-6 volts; these are used in Chinese lanterns, children's electric cars, and so on.
The circuit was originally created for charging low-capacity batteries, but it can also be used to desulfate car batteries. Before starting the desulfation charging process, the battery must be slightly recharged.
Read also: Lathe 1m63 deep 300 technical specifications
First you need to find any power source with a voltage from 8 to 12 Volts and connect it to the desulfator input, but not directly, but through a 12 Volt incandescent lamp with a power of 21 watts, so as not to exceed the charge current, we’ll talk about this in more detail at the end . A battery that needs to be restored is connected to the output of the device. Since the device operates in the audio range, you will most likely hear a faint whistle; the power components of the circuit should heat up slightly.
How does the scheme work?
The voltage from the charger is supplied to the desulfator circuit through a fuse and diode. For the low-power portion of the circuit, power is supplied through a current-limiting resistor, then smoothed by a small electrolytic capacitor.
The NE555 chip contains a rectangular pulse generator, the frequency of these pulses is about 1 kHz. Fill factor is about 90%. The CD4049 chip inverts and amplifies this signal, turning it into pulses with a fill rate of about 10%. From the output of the inverters, pulses are sent to the gate of the field-effect transistor VT1. When it opens, it closes the inductor to the power ground, energy accumulates in the inductor, when the transistor closes, the circuit breaks, due to the phenomenon of self-induction, which is characteristic of inductive loads, the inductor releases the accumulated energy. This is a short-term voltage surge with a high amplitude, and the self-induction voltage is several times higher than the supply voltage. This voltage surge is rectified and applied to the battery. The process occurs more than a thousand times per second, that is, short-term high-voltage pulses with high frequency are applied to the battery, which is what destroys the sulfate film.
The circuit involves a fuse and another rectifier diode. The fuse will protect the desulfator in case of accidental short circuits at the output, and the diode performs several functions - firstly, it protects the circuit if you accidentally connect it to the charger incorrectly and, secondly, it protects the charger from possible impulse noise and voltage surges that form on the desulfator board.
Battery recovery process
Before restoring, it is advisable to fully charge the battery. If you are going to restore the battery in your car, be sure to disconnect one power terminal of the car so as not to damage the electronics of your car.
Next, connect the desulfator and wait. The waiting time is always individual. All you need to do is periodically monitor the battery - measure the voltage to prevent complete discharge. Voltage measurements must be made with the desulfator turned off, this is mandatory.
The maximum result can be obtained only after 4 weeks of continuous operation of the desulfator.
Although the device is autonomous, I do not recommend leaving it unattended.