Chemical composition
Grade St3 is classified as carbon structural steel of ordinary quality. The composition includes the following chemical elements:
- carbon up to 0.22%;
- silicon up to 0.17%;
- manganese up to 0.65% and many others, including chromium and nickel.
GOST
Metallurgical plants produce the following range of products from the St3 grade:
- Forgings GOST 8479-70;
- Rental GOST 2591-2006;
- Strip and tape products GOST 14918-80;
- Rails GOST 5812-82;
- Pipes and fittings for them GOST 10705-80;
Decoding steel St3
The steel supplied to the customer must be marked in accordance with GOST 380-2005. The full name of St3 should be as follows St3Gsp GOST 380-2005. Its decoding is as follows:
- St – this is the designation for carbon steel of ordinary quality;
- 3 – serial number of the alloy grade according to GOST 380-2005;
- G is the designation for manganese. If the alloy contains more than 0.8%, then it must be indicated.
- Sp – level of deoxidation.
Steel C245 can be used as a substitute; this is defined in GOST 27772-88 and C285
Carbon steel grade st3sp - ordinary quality
Substitutes
Steel StZps, Steel S245
Foreign analogues
| Europe EN 10027-1 (EN 10027-2) | S235JR (1.0038) |
| Germany DIN | RSt37-2, USt37-2 |
| USA (AISI, ASTM) | A238/C |
| France (AFNOR) | E 24-2 |
| UK BS | 40B |
| Czech Republic (CSN) | 11375 |
| Poland PN/H | St3SV, St3SJ, St3S4U |
Decoding steel St3sp
- The letters “B” indicate that this steel, supplied according to mechanical properties and with separate requirements for chemical composition,
- The letters "St" stand for "Steel"
- number 3 indicates the conventional brand number depending on the chemical composition,
- the letters "sp" - calm (degree of steel deoxidation),
- If the letter “sp” is followed by a number, then it indicates the category. If there is no number, then steel category 1. Depending on the category, steel has different standardized indicators (see below).
Type of delivery
- Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88, GOST 535-88, GOST 2879-88, GOST 19771-93, GOST 19772-93, GOST 8278-83, GOST 8281-80, GOST 8282 -83, GOST 8283-93, GOST 380-94, GOST 8509-93, GOST 8510-86, GOST 8239-89.
- Thick sheet GOST 19903-74.
- Thin sheet GOST 19903-74.
- Tape GOST 503-81, GOST 6009-74.
- Strip GOST 103-76, GOST 82-70, GOST 535-88.
- Forgings and forged blanks GOST 8479-70.
- Pipes GOST 8734-75, GOST 10706-76, GOST 10705-80.
Characteristics, application and purpose
St3sp steel belongs to structural carbon steels of ordinary quality for general purpose and is used for the manufacture of the following parts and structures:
- Load-bearing elements of welded and non-welded structures and parts operating at positive temperatures.
- Shaped and sheet products (5th category) - for load-bearing elements of welded structures operating under variable loads: with a thickness of rolled products up to 25 mm in the temperature range from -40 to +425 °C;
- for rolled products with thickness over 25 mm in the range from -20 to +425 °C, subject to delivery with guaranteed weldability.
According to the international standard ISO 630:1995, St3sp steel is designated E 235-C (Fe 360-C)
Steel 3 is a widely used steel in the petroleum, petrochemical and oil and gas industries. Welded and stamped products can be made from steel of this grade:
- frames,
- frames
- heavy oilfield equipment skids
- bases (blocks)
- parts of drilling and production derricks and masts
- brake bands
- pulleys
- Cam couplings for drilling rigs
- keys
- stubs
- mud pump covers
- racks
- brackets
- gear housings
- drilling rig frames, etc.
Temperature of critical points, °C
| Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar3 | Ar1 |
| 735 | 850 | 835 | 680 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 380-94)
| C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu | As |
| no more | ||||||||
| 0,14-0,22 | 0,40-0,65 | 0,12-0,30 | 0,04 | 0,05 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,08 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 380-2005)
| steel grade | Mass fraction of chemical elements | ||
| carbon | manganese | silicon | |
| St3sp | 0,14-0,22 | 0,40-0,65 | 0,15-0,30 |
NOTE.
- The mass fraction of chromium, nickel and copper in St3sp steel should be no more than 0.30% each.
- The mass fraction of sulfur in St3sp steel should be no more than 0.050%, phosphorus - no more than 0.040%.
- The mass fraction of nitrogen in steel should be no more than:
- smelted in electric furnaces - 0.012%;
- open hearth and converter - 0.010%.
- The mass fraction of arsenic should be no more than 0.080%.
Standardized indicators of St3sp steel by rolled category (GOST 535-2005)
| Category | Chemical composition | Temporary resistance σв | Yield strength σt | Relative elongation δ5 | Cold bending | Impact strength | ||||
| KCU | KCV | |||||||||
| At temperature, °C | After mechanical aging | At temperature, °C | ||||||||
| + 20 | -20 | + 20 | -20 | |||||||
| 1 | — | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — | — |
| 2 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — | — |
| 3 | + | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — |
| 4 | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | — | — | — |
| 5 | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | — | — |
| 6 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | — |
| 7 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — | + |
NOTE
- The “+” sign means that the indicator is normalized, the “-” sign means that the indicator is not normalized.
- The chemical composition of steel according to heat analysis or in finished rolled products is in accordance with the order.
Parameters for the use of electric-welded straight-seam pipes made of St3sp steel (GOST 32569-2013)
| Steel grade, strength class, standard or specifications | StZsp5 GOST 380 | StZsp4-5 GOST 380 | StZsp4 GOST 380 | ||||
| Technical requirements for pipes (standard or specifications) | GOST 10705 group B | GOST 10706 group B | TU 14-3-377-87 | TU 14-3-1399-95 | GOST 10706 group B | ||
| Nominal diameter, mm | 10-500 | 450-1400 | 200-400 | 200, 350, 400, 500 | 400-1400 | ||
| Types of tests and requirements (standard or specifications) | GOST 10705 | GOST 10706 | TU 14-3-377-87 | TU 14-3-1399-95 | GOST 10706 | ||
| Transported medium (see designations in table 5.1) | Group B, C environments | Group B media Group B media, except LPG | Group B media, except steam and hot water | All media except group A(a) and LPG | Group B media, except LPG | ||
| Pipeline design parameters | Maximum pressure, MPa | ≤1,6 | ≤2,5 | ≤1,6 | |||
| Maximum temperature, °C | 300 | 200 | 300 | 200 | |||
| Pipe wall thickness, mm | — | ≤12 | — | ≤10 | — | ||
| Minimum temperature depending on the pipe wall thickness with stress in the wall from internal pressure [σ], °C | more than 0.35[σ] | minus 20 | |||||
| no more than 0.35[σ] | minus 40 | ||||||
NOTE. Groups of media, see table 5.1 GOST 32569-2013
Parameters for the use of electric-welded spiral-welded pipes made of St3sp steel (GOST 32569-2013)
| Steel grade, strength class, standard or specifications | StZspZ, StZsp2 GOST 380 | StZsp5 GOST 380 | ||
| Technical requirements for pipes (standard or specifications) | TU 14-3-943-80 | TU 14-3-954-80 | ||
| Nominal diameter, mm | 200-500 | 500-1400 | ||
| Types of tests and requirements (standard or specifications) | TU 14-3-943-80 | TU 14-3-954-80 taking into account the requirements of clause 2.2.10 GOST 32569-2013 | ||
| Transported medium (see designations in table 5.1) | All media except group A and LPG | All media except group A and LPG | ||
| Pipeline design parameters | Maximum pressure, MPa | ≤1,6 | ≤2,5 | |
| Maximum temperature, °C | 200 | 300 | ||
| Pipe wall thickness, mm | ≤6 | ≤12 | ||
| Minimum temperature depending on the pipe wall thickness with stress in the wall from internal pressure [σ], °C | more than 0.35[σ] | minus 30 | minus 20 | |
| no more than 0.35[σ] | — | minus 20 | ||
NOTE. Groups of media, see table 5.1 GOST 32569-2013
Application of St3sp steel for fasteners (GOST 32569-2013)
| steel grade | Technical requirements | Acceptable operating parameters | Purpose | |
| Wall temperature, °C | Medium pressure, MPa (kgf/cm2), no more | |||
| StZsp4 GOST 380 | STP 26.260.2043 | -20 to +300 | 2,5 (25) | Studs, bolts, nuts |
| 10 (100) | Washers | |||
Conditions for using St3sp steel for bodies, covers, flanges, membranes and valve assembly made from rolled products, forgings (stampings) (GOST 33260-2015)
| Material | ND for supply | Temperature of the working medium (wall), °C | Additional instructions for use |
| St3sp GOST 380 | Forgings GOST 8479 Long products GOST 535, categories 3-5 | -30 to 300 | For welded fittings for pressure PN≤2.5 MPa (25 kgf/cm2) |
| Sheet GOST 14637, categories 3-6 | -20 to 300 | For welded fittings for pressure PN 5 MPa (50 kgf/cm2). For categories 4, 5, sheet thickness for St3sp is no more than 25 mm; for category 3 sheet thickness no more than 40 mm |
Resistance of structural materials against crevice erosion (GOST 33260-2015)
| Durability group | Point | Erosion resistance against steel 12X18H10T | Material |
| Unstable | 6 | 0,005-0,05 | Steel VSt3sp3 and its welded joints. |
NOTE. The coefficient of erosion resistance of a material is the ratio of the rate of erosive wear of the material to the rate of erosive wear of steel 12Х18Н10Т (taken as 1).
Mechanical properties of rolled products under tension, as well as cold bending test conditions (GOST 535-2005)
| steel grade | St3sp | |
| Tensile strength σв, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), for rolled thickness, mm | up to 10 incl. | 380-490 (39-50) |
| St.10 | 370-480 (38-49) | |
| Yield strength σт, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), for rolled thickness, mm (not less) | up to 10 incl. | 255(26) |
| St. 10 to 20 incl. | 245(25) | |
| St. 20 to 40 incl. | 235(24) | |
| over 40 to 100 incl. | 225(23) | |
| St. 100 | 205(21) | |
| Relative elongation δ5, %, for rolled thicknesses, mm (not less) | up to 20 incl. | 26 |
| over 20 to 40 incl. | 25 | |
| St.40 | 23 | |
| Bending until the sides are parallel (a - sample thickness, d - mandrel diameter), for rolling thicknesses, mm | up to 20 incl. | d = a |
| St.20 | d = 2a | |
NOTE
- By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the following is allowed:
- reduction in yield strength by 10 N/mm2 (1 kgf/mm2) for shaped steel with a thickness of over 20 mm;
- reduction in relative elongation by 1% (abs.) for shaped rolled products of all thicknesses.
- It is allowed to exceed the upper limit of tensile strength by 49.0 N/mm2 (5 kgf/mm2), and by agreement with the consumer - without limiting the upper limit of tensile strength, provided that other standards are met. At the request of the consumer, exceeding the upper limit of temporary resistance is not allowed.
Impact strength of rolled products (GOST 535-2005)
| steel grade | St3sp | ||
| Rolled thickness, mm | St. 5.0 to 10.0 incl. | ||
| KCU, J/cm2 (kgf*m/cm2), not less | Sample type according to GOST 9454 | 2,3 | |
| At temperature, °C | +20 | 108(11) | |
| -20 | 49(5) | ||
| After mechanical aging | 49(5) | ||
| KCV, J/cm2 (kgf*m/cm2), not less | Sample type according to GOST 9454 | 12,13 | |
| At temperature, °C | +20 | 34(3,5) | |
| -20 | — | ||
NOTE
- The “-” sign means that the indicator is not standardized.
- Determination of the impact strength of round rolled products is carried out starting from a diameter of 12 mm, square - starting from the square side of 11 mm.
- It is allowed to reduce the value of impact strength on one sample by 30%, while the average value must not be lower than the standards specified in this table.
- Impact strength KCV is determined for rolled products with a thickness of up to 20 mm inclusive.
Mechanical properties of rolled products
| GOST | Delivery status | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5(δ4),% |
| no less | |||||
| GOST 380-94 | Hot rolled products | Up to 20 | 245 | 370-480 | 26 |
| St. 20 to 40 | 235 | 25 | |||
| St. 40 to 100 | 225 | 23 | |||
| St. 100 | 205 | 23 | |||
| GOST 16523-89 (transverse samples) | Hot rolled sheet | Up to 2.0 incl. | — | 370-480 | (20) |
| St. 2.0 to 3.9 incl. | (22) | ||||
| Cold rolled sheet | Up to 2.0 incl. | — | 370-480 | (22) | |
| St. 2.0 to 3.9 incl. | (24) | ||||
Mechanical properties of forgings
| GOST | Heat treatment | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5,% | ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness HB |
| no less | ||||||||
| GOST 8479-70 | Normalization | Up to 100 | 175 | 353 | 28 | 55 | 64 | 101-143 |
| 100-300 | 175 | 353 | 24 | 50 | 59 | |||
| Up to 100 | 195 | 392 | 26 | 55 | 59 | 111-156 | ||
| 100-300 | 195 | 392 | 23 | 50 | 54 | |||
Impact strength KCU (GOST 380-94)
| Type of rental | Pattern cutting direction | Section, mm | KCU, J/cm2 | ||
| +20 °C | -20 °C | after mechanical aging | |||
| no less | |||||
| Sheet | Transverse | 5-9 | 78 | 39 | 39 |
| 10-25 | 68 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 49 | — | — | ||
| Wide band | Longitudinal | 5-9 | 98 | 49 | 49 |
| 10-25 | 78 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 68 | — | — | ||
| Varietal and shaped | Same | 5-9 | 108 | 49 | 49 |
| 10-25 | 98 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 88 | — | — | ||
Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures
| tsp, °C | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5,% | ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 |
| Hot rolled billet dimensions 140×120 mm | |||||
| 20 | 220 | 445 | 33 | 59 | 154 |
| 300 | 205 | — | — | — | 199 |
| 500 | 180 | 285 | 34 | 80 | 119 |
| Hot-rolled sheets and shapes up to 30 mm thick | |||||
| 20 | 205-340 | 420-520 | 28-37 | 56-68 | — |
| 200 | 215-285 | — | — | — | — |
| 300 | 05-265 | — | — | — | — |
| 400 | 155-255 | 275-490 | 34-43 | 60-73 | — |
| 500 | 125-175 | 215-390 | 36-43 | 60-73 | — |
| A sample with a diameter of 6 mm and a length of 30 mm is forged and normalized. Deformation speed 16 mm/min, strain rate 0.009 1/s | |||||
| 700 | 73 | 100 | 57 | 96 | — |
| 800 | 51 | 63 | 95 | 95 | — |
| 900 | 38 | 65 | 84 | 100 | — |
| 1000 | 25 | 43 | 79 | 100 | — |
| 1100 | 19 | 31 | 80 | 100 | — |
| 1200 | 14 | 25 | 84 | 100 | — |
Endurance limit
| Sample | σ-1, MPa | n |
| Smooth | 191 | 107 |
| Notched | 93 | 107 |
NOTE. Sheet 40 mm thick in hot-rolled condition.
Technological properties
Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1300, end 750. Cooling in air.
Cutting machinability - Kv tv.spl = 1.8 and Kv b.st = 1.6 in the hot-rolled state at HB 124 and σw = 400 MPa.
Flock sensitivity - not sensitive.
Tendency to temper brittleness - not prone.
Welding
Weldability - weldable without restrictions; welding methods: RDS, ADS with flux and gas protection, ESW and KTS. For thicknesses above 36 mm, heating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended.
It is allowed to use steel st3sp for welded connections of pipeline fittings at a temperature of the working medium (wall) from -20 to 300 °C.
Welding materials for electric arc welding
| Base material grade | Electrode type according to GOST, TU (recommended brands of electrodes) | Application temperature, °C | Additional instructions |
| St3sp | E42, E46 GOST 9467 (ANO-4, ANO-5,OZS-6) | Not lower than -15 | — |
| E42A, E46A GOST 9467 (UONI-13/45, UONI-13/45A, 0ZS-2, SM-11) | Not lower than -30 | — | |
| E50A GOST 9467 (UONI-13/55) | below -30 to -40 | After welding, heat treatment - normalization plus tempering (630–660) °C, 2 hours |
Welding materials for gas shielded welding
| Base material grade | Welding wire grade according to GOST 2246, TU, recommended shielding gas or mixture of gases | Application temperature, °C |
| St3sp | Sv-08G2S Carbon dioxide GOST 8050, argon GOST 10157 | -20 to 300 |
Welding materials for submerged arc welding
| Base material grade | Welding wire grade according to GOST 2246, TU, Recommended flux grade according to GOST 9087 | Additional instructions | ||
| Electrodes, type according to GOST 10052 (recommended brands) | Welding wire, GOST 2246 or TU | |||
| Group A | Group B | |||
| 10Х18Н9Л, 12Х18Н9ТЛ GOST 977 08Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н9Т, 12Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н9 GOST 5632 08Х18Н10Т-VD TU 14-1-3581 10Х18Н9, 10Х18Н9-VD, 10Х1 8N9-Sh TU 108.11.937 15Х18Н12СЧТУ (EI 654) GOST 5632 10Х17Н13М3Т (EI 432) 10Х17Н13М2Т ( EI 448) GOST 5632 | St3sp GOST 380 | E-10Kh15N25M6AG2 (EA-395/9) E-10Kh25N13G2 (OZL-6, ZIO-8), E-11Kh15N25M6AG2 (NIAT-5, TsT-10) | Sv-07Х23Н13 | The welded joint is of unequal strength |
| E-10Х15Н25М6AG2 (EA-395/9) 582/23, 855/51 | Sv-10X16N25AM6 Sv-06X15N35G7M6B Sv-03X15N35G7M6B | The welded joint is of unequal strength. Welding materials are used for products under the jurisdiction of Rostechnadzor | ||
Welding materials for welding steel st3sp with other steels
| Grades of welded steels | Welding materials | Application temperature, °C |
| St3sp | Sv-08, Sv-08A AN-348A, OSTS-45 ANTS-1 | Not lower than -20 |
Temperature of preliminary and accompanying heating and tempering when welding structures made of steel st3sp
| Grades of welded steels | Thickness of welded edges, mm | Temperature of preliminary and accompanying heating, °C | Interval between the end of welding and the start of tempering, hour | Temperature, °C | |
| welding | surfacing with austenitic class materials | ||||
| St3sp | Up to 36 | Not required | Not required | Not limited | Not required |
| Over 36 to 100 | 630-660 | ||||
| Over 100 | 100 | ||||
Recommended welding modes for correcting weld defects
| Welding materials | Main material | Diameter of electrode, wire, mm | Welding current strength, A | Arc voltage, V |
| USENI 13/45A* USENI 13/55 | St3sp | 3,0 4,0 5,0 | From 100 to 130 From 160 to 210 From 220 to 280 | From 22 to 26 |
| Sv-08G2S | 1,6 | From 100 to 120 | From 12 to 14 | |
| 2,0 | From 140 to 160 |
NOTE. * - along with the electrode brand UONI 13/..., it is possible to use the brand UONII 13/..., depending on the designation of the brand in the specifications of the electrode manufacturer.
Modes of electric arc welding of samples and products
| Electrode brand | Main material | Electrode diameter, mm | Welding current strength, A | Arc voltage, V |
| USENI 13/45A*, USENI 13/55 | St3sp | 3 4 5 | From 110 to 130 From 160 to 210 From 220 to 280 | From 22 to 26 |
NOTE. * - along with the electrode brand UONI 13/..., it is possible to use the brand UONII 13/..., depending on the designation of the brand in the specifications of the electrode manufacturer.
Modes of argon arc welding of samples for incoming inspection of welding materials
| Electrode brand | Main material | Electrode diameter, mm | Welding current strength, A | Arc voltage, V |
| Sv-08G2S | St3sp | 1,6 2,0 3,0 | From 100 to 120 From 150 to 170 From 200 to 240 | From 12 to 14 |
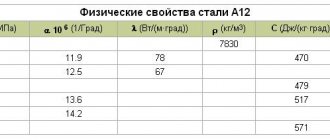
Linear expansion coefficient α*106, K-1
| steel grade | Temperature, K (°C) | |||||||||||
| 323 (50) | 373 (100) | 423 (150) | 473 (200) | 523 (250) | 573 (300) | 623 (350) | 673 (400) | 723 (450) | 773 (500) | 823 (550) | 873 (600) | |
| St3sp5 | 11,5 | 11,9 | 12,2 | 12,5 | 12,8 | 13,1 | 13,4 | 13,6 | 13,8 | 14,0 | 14,2 | 14,4 |
Young's modulus (normal elasticity) E, GPa
| steel grade | Temperature, K (°C) | ||||||||||
| 293 (20) | 323 (50) | 373 (100) | 423 (150) | 473 (200) | 523 (250) | 573 (300) | 623 (350) | 673 (400) | 723 (450) | 773 (500) | |
| St3sp5, | 200 (2,04) | 197 (2,01) | 195 (1,99) | 192 (1,96) | 190 (1,94) | 185 (1,88) | 180 (1,84) | 175 (1,79) | 170 (1,73) | 165 (1,68) | 160 (1,63) |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ W/(m*K)
| Steel grade | λ W/(m*K), at test temperature, °C | |||||||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | |
| St3sp | — | 55 | 54 | 50 | 45 | 39 | 34 | 30 |
Find out more
Structural alloy steel 40ХН2МА...
Steel 50(50A) - structural carbon...
Steel 6ХС tool stamping…
Structural alloy steel 18ХГТ…
Application of steel St3
The technical parameters of St3 allow it to be used for the production of loaded elements of welded structures and parts of machines and mechanisms operating at positive temperatures.
Some types of rolled products, in particular those of the fifth category, are used in the production of metal structures that can operate at temperatures from -40 to 425 degrees Celsius under alternating loads.
After constructing complex structures, it makes sense to carry out heat treatment, in particular annealing. This operation is necessary to relieve stress arising after welding work.
In addition, this material is used in the production of At400s construction reinforcement.
Sheets made from this steel are used for the production of parts produced using cold stamping technology. It is used to produce troughs for collecting coolants and waste oils installed on machines, containers of various sizes and purposes, covers for machine equipment, casings, etc.
Application
The following are made from St3sp metal:
- shaped metal products, which include a channel, an I-beam and other types of products;
- varietal;
- rolled sheets of various thicknesses.
In addition, the material is widely used in the production of pipes for various purposes and sections, steel strips, hardware and stampings.
Products made from this type of steel are used in a wide variety of areas: from the construction and laying of above-ground and underground communications to the manufacture of industrial machines and units operated even in difficult conditions.
The technical characteristics of the material allow it to be used in the construction of frames and supporting structures, which are subject to increased requirements.
Analogs
As already noted, the St3 grade is in demand in the production of various structures, and in fact, is the most popular structural steel. This is the reason why it is produced by metallurgical plants located in all parts of the world, for example:
- USA - A284Gr.D, A57036;
- Germany - 1.0038;
- Japan - SS330;
- European Union - Fe37-3FN;
- China - Q235.
Suppliers of steel produced outside our country must submit documents confirming the compliance of imported materials with domestic GOST and TU.
Technological properties
Steel of this grade has no restrictions on welding by any available method, incl. gas, electric.
The key indicators are the following:
- resistance to corrosion;
- mechanical characteristics;
- weldability.
These indicators make it possible to divide steel alloys into groups such as: regular, increased and high strength. For parts with a thickness or diameter greater than 36 mm, after welding it makes sense to perform heat treatment, which will relieve the stresses that arise in the weld area under the influence of high welding temperatures.
Full description of the brand
If you rely on GOST, then you must use the St3sp steel grade in its entirety. Designation in the form St3 is not permitted. According to the international standard, there is a clear division into the markings St3sp, St3ps, St3kp. Depending on the modification and increase in manganese content during deoxidation, the St3gps and St3gsp grades may also appear. It is also worth paying attention to the fact that if no index was added by the manufacturer during the installation of the marking, then the degree of deoxidation can be set by the buyer. If you place an order for this raw material, then in the form you need to write something like this - “steel St3sp GOST 380-2005”.
These indices are deciphered as follows:
- St - designation of ordinary quality carbon steel.
- 3 is a conditional number that is assigned to any steel grade. There are seven such rooms in total. A change in number means a change in the chemical composition of the raw material.
- Sometimes you can find an additional letter G. It is placed only if the percentage of the chemical substance - manganese - exceeds 0.8% of the total mass fraction of substances.
- Sp is the degree of deoxidation of the composition.
The full decoding of St3sp steel looks exactly like this.
Mechanical restoration
The choice of cutting modes and selection of tools is an important part necessary for creating the correct technological process for processing parts made from St3.
For its turning or milling, a cutting tool made of hard alloys VK8, T5K10 is used. To obtain threads, both internal and external, taps and dies made of steels R18, R6M5 are used. When processing on turning-milling machines, it is advisable to use water-based coolants, for example, Emulsol. By the way, when cutting threads by hand, it is advisable to use castor oil, which makes the work much easier.
The choice of processing speed is made based on the properties of the steel, the technical parameters of the machine equipment and the type of processing. For example, with a workpiece diameter of 60 to 100 mm, it is permissible to use a turning tool with a holder size of 16x25 mm. With a cutting depth of 3 mm, the feed rate of the caliper should be from 0.7 to 1.2 mm per spindle revolution. When processing on a lathe, the spindle rotation speed is allowed within 700 rpm.
Production Features
The properties of the finished material are determined by the substances that make up its composition and largely depend on what technologies were used in the production of a particular alloy.
The basis of the steel alloy is ferrite. It is a component of iron-carbon alloys. It is, in fact, a solid solution of carbon and alloying components. To increase its strength, the melt is saturated with carbon.
Impurities from which nothing but harm can be expected include phosphorus and sulfur, as well as their derivatives. Phosphorus, reacting with ferrite, reduces the ductility of the alloy when exposed to high temperatures and increases brittleness when exposed to cold. During the melting process, iron sulfide may be formed, which can lead to red brittleness. St3 steel contains no more than 0.05% sulfur and 0.04% phosphorus.
For the production of structural steels, two steelmaking technologies are used:
- open hearth;
- converter
The parameters of the St3 grade, obtained by one or another method, differ little from each other, but the converter technology is simpler and cheaper.