Concrete is a durable building material that can easily withstand heavy loads. But during operation, concrete foundations are additionally affected by tensile forces. To strengthen the foundations, they are additionally reinforced with metal frames that resist stretching of the concrete structure. Therefore, when independently building a country house, you need to know the consumption of reinforcement per 1 m3 of concrete.
Consumption directly depends on the type of foundation and the weight of the structure being built, as well as the type of soil on which it is planned to build them.
What does the consumption rate depend on?
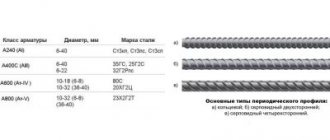
Depending on the type of construction project, concrete reinforcement is carried out using reinforcement of different classes. The weight of 1 m of reinforcement depends on its cross-sectional area.
To calculate the amount of reinforcement, you need to know the following information:
- type of foundation;
- total weight of the building.
- class and cross-sectional area of steel rods;
- soil type;
Main options for reinforced concrete foundation:
- columnar;
- slab;
- tape
The cross-section of the reinforcement can also affect the material consumption.
General recommendations for reinforcement:
- when constructing a private country house, the foundation is reinforced with iron rods with a cross-section of up to 1 cm;
- for concrete foundations for brick buildings, steel rods with a cross-section of 1.4 cm are used;
- reinforcing bars are laid in the foundation in increments of 20 cm;
- the concrete reinforcement bond is made in 2 belts, i.e. one reinforcement mesh is installed, a second one is installed above it, and they are connected with metal rods;
- The main tensile force occurs on the upper part of the concrete base, so it is not recommended to deepen the reinforcement cage too much.
The footage and weight of the rods are calculated after calculating the depth and length of the reinforced concrete base. The minimum consumption of reinforcement according to construction requirements is 8 kg/m³.
GESN and GOST regulate the consumption of reinforcement, but it is better to start from the design of the foundation or other structure that needs to be reinforced.
Minimum percentage of reinforcement in reinforced concrete structures
Depending on the characteristics of the load application, the minimum indicator varies within the following limits:
- with a coefficient of 0.05, the structure is capable of withstanding tension and compression when exposed to a load outside the working section;
- the minimum degree of reinforcement increases to 0.06% when loads are applied to the concrete layer located between the elements of the reinforcement frame;
- for building structures subject to eccentric compression, the minimum concentration of steel reinforcement reaches 0.25%.
When performing reinforcement in the longitudinal plane along the contour of the working section, the reinforcement coefficient is twice the specified values.
How much reinforcement is needed per cubic meter of concrete (building codes)
By saving building materials, the service life of the constructed structure is reduced. It is especially not recommended to save on the reinforcement of the foundation. Correct calculation of the reinforcement of the reinforced concrete base is the key to the strength and durability of the building.
The number of metal rods depends on the type of concrete structure, the weight of the reinforcing bars depends on the class and section, and the required length of the reinforcement depends on the area and height of the concrete base.
The consumption for a monolithic slab is calculated based on its area and the distance between the reinforcing slabs.
To correctly calculate the consumption of iron rods, you need to know the dimensions of the ceiling and information about support:
- The dimensions are affected by the length and width of the span. For buildings of standard sizes, these parameters are established by SNiP.
- When calculating the support, the type of brick or building blocks, the type of floor, and building materials of external and internal width are taken into account.
Metal consumption also depends on the purpose of the base and the fillers used in the cement mixture. The calculation of metal rods for reinforcing 1 m³ of base is performed individually for each construction project.
Consumption is regulated by building codes:
- state standards - GOST;
- federal unit prices - FER;
- elemental estimate standards - GESN.
FERs are provided for different categories of building structures. For example, when laying reinforced concrete foundation slabs with pillars, grooves and cups (slab dimensions: thickness - up to 100 cm, height - up to 200 cm), the metal consumption is 187 kilograms per cubic meter of cement. For flat slabs - 81 kg per cubic meter of concrete.
For the construction of general-purpose reinforced concrete foundations in accordance with GESN 81-02-06-2001, the consumption of steel rods is 1000 kg/5 m³.
What is the size of the protective layer of concrete
To prevent corrosion destruction of the load-bearing frame, a fixed distance from the steel grating to the surface of the concrete mass should be maintained. This interval is called the protective layer.
Its value for load-bearing walls and reinforced concrete panels is:
- 1.5 cm – for slabs thicker than 10 cm;
- 1 cm – for concrete walls less than 10 cm thick.
Kawabanga!
Weight of expanded clay concrete block 400x200x200 - table The size of the protective layer for reinforcement ribs and crossbars is slightly higher:
- 2 cm – with a concrete mass thickness of more than 25 cm;
- 1.5 cm – when the concrete thickness is less than the specified value.
It is important to maintain a protective layer for support columns at a level of 2 cm or higher, and also to maintain a fixed interval from the reinforcement to the concrete surface for foundation beams at a level of 3 cm or more.
The size of the protective layer varies for different types of foundations and is:
- 3 cm – for prefabricated foundation structures made of precast reinforced concrete;
- 3.5 cm – for monolithic bases made without a cement pad;
- 7 cm – for solid foundations that do not have a damping cushion.
Building codes and regulations regulate the size of the protective layer for various types of building structures.
Reinforcement calculation methods
The building transfers its load to the foundation, which then distributes it evenly to the ground surface. A significant load falls on the concrete reinforcing structure. Therefore, when concreting the base, you need to choose the right type and size of reinforcing bars.
Rules for calculating reinforcement:
- manually - the type and composition of concrete, the magnitude of the load that will affect the foundation after the building is erected, and the dimensions of the steel frame are taken into account;
- using a computer program - the working data is entered, the program automatically calculates the required number of steel rods.
Correctly calculated parameters of the reinforcing bars and a developed scheme for laying the metal grating will ensure the necessary margin of strength of the base and increase the service life of the structure.
What is the consumption of reinforcement for the foundation?
When purchasing building materials for monolithic foundations, it is recommended to make a preliminary calculation, otherwise one structural element may not be enough, another component will be in excess. And metal is an expensive building material, so you need to know exactly its consumption per 1 cubic meter of concrete.
Initial data
Information needed for calculations:
- type of concrete floor (foundation structure);
- soil type in the region where construction work is being carried out;
- width, height of reinforced concrete base;
- weight of the structure;
- class, section of metal rods.
For foundations for light wooden buildings or slab foundations built on dense soils, steel rods with a diameter of 1 cm are used. Concrete foundations for houses made of bricks (building blocks) are reinforced with steel rods with a diameter of 1.4-1.6 cm. The average pitch of the rods is - 20 cm.
Methodology for calculating the need for reinforcement
An example of performing metal calculations for reinforcing concrete structures:
- the soil on the site is dense and characterized by high load-bearing characteristics;
- the foundation is being converted into a wooden country house.
It is recommended to trust the calculation of concrete foundations with reinforcement for heaving and floating soils to experienced engineers.
To calculate reinforcement, you can use special online calculators, which can be found through a search engine.
Slab foundation
According to the technology for constructing a slab foundation, the reinforcing frame is made of steel rods Ø 1 cm in increments of 0.2 m.
Calculation of rods for armored belts:
- parameters of the concrete slab - 6 x 6 m;
- for such an area you will need 31 rods for transverse placement and 31 rods for longitudinal placement;
- in total, 62 metal rods 6 m long are needed to construct one armored belt;
- the frame provides 2 reinforcement belts, so to equip them you need 124 metal rods;
- the required metal in linear meters is 124 pcs. x 6 m = 744.
The reinforcing belts must be connected to each other with the same metal rods, the length of which depends on the thickness of the metal structure. A bunch of armored belts is made at all intersections of horizontal rods. Accordingly, the number of vertical rods is 31 x 31 = 961 pcs.
The height of the steel structure depends on the thickness of the concrete slab. In this case, the frame is additionally covered with a concrete layer 5 cm thick.
Calculation of connecting steel rods for a monolithic slab 0.2 m thick:
- number of connecting elements - 961;
- length of rods = 0.2 - 0.1 = 0.1 m;
- translation into linear m - 0.1 x 961 = 96.1.
The total footage of reinforcement for the construction of the reinforcing frame will be:
744 + 96,1 = 840,1
Volume of concrete (m³) for a monolith = 6 x 6 x 0.2 = 7.2.
Linear meters (840 linear meters) of metal rods required for the manufacture of the structure are divided by the volumetric indicator of the concrete slab (7.2 m³), resulting in a reinforcement consumption of 116.7 m/m³.
Strip foundation
The difference between a strip base and a slab base is in the geometry of the steel frame.
The amount of reinforcement for a strip base greatly depends on the pitch between the reinforcement belt strips.
When reinforcing concrete tape, armored belts are most often made of two horizontal metal rods each. The bundle of armored belts is performed in increments of 0.5 m.
When calculating linear meters of reinforcement, the perimeter of the foundation is taken into account, including under the internal load-bearing walls of the building being constructed.
Converting linear meters to tons
Steel bars are often sold by weight rather than by meter. Therefore, after calculation, the resulting metal footage is converted into kilograms.
To translate the values, you need to know the specific coefficient of metal rods, which is:
- for metal products Ø 10 mm - 0.617;
- for Ø 14 mm - 1.21.
When the specific gravity is multiplied by the value in meters, the mass of steel products is obtained in kg. To convert the value to tons, you need to divide kilograms by 1000.
What is the size of the protective layer of concrete
To prevent corrosion destruction of the load-bearing frame, a fixed distance from the steel grating to the surface of the concrete mass should be maintained. This interval is called the protective layer.
Its value for load-bearing walls and reinforced concrete panels is:
- 1.5 cm – for slabs thicker than 10 cm;
- 1 cm – for concrete walls less than 10 cm thick.
Kawabanga! What determines the adhesion of concrete to mortar and how to improve it
The size of the protective layer for reinforcement ribs and crossbars is slightly higher:
- 2 cm – with a concrete mass thickness of more than 25 cm;
- 1.5 cm – when the concrete thickness is less than the specified value.
It is important to maintain a protective layer for support columns at a level of 2 cm or higher, and also to maintain a fixed interval from the reinforcement to the concrete surface for foundation beams at a level of 3 cm or more.
The size of the protective layer varies for different types of foundations and is:
- 3 cm – for prefabricated foundation structures made of precast reinforced concrete;
- 3.5 cm – for monolithic bases made without a cement pad;
- 7 cm – for solid foundations that do not have a damping cushion.
Building codes and regulations regulate the size of the protective layer for various types of building structures.