Carbide inserts used for turning tools can increase the productivity of work performed on metalworking equipment. Such plates make the use of the cutter more convenient, since they are removable and allow you to quickly replace them in case of wear or breakage. Naturally, cutters of a solid design, in which the cutting part is made integral with the holder, are not suitable for using replaceable elements.
Carbide inserts for turning tools
Advantages of using carbide inserts for cutters
Inserts for boring or cutting cutters can be made of various grades of hard alloys, which is very convenient, as this allows you to have a whole set of cutting elements for processing workpieces made of different materials.
The use of replaceable inserts for a cutting tool is also a cost-effective solution, since in case of breakage or wear there is no need to replace the entire cutter with a new tool: only its cutting part needs to be replaced. It is advisable to use a tool with replaceable carbide inserts even if the task is to automate technological processes, which is especially important in small- and medium-scale production, where the range of manufactured products can change quite often.
Cutters with replaceable inserts
Among the advantages of carbide inserts mounted on turning tools, the following should be highlighted.
- Compared to solid cutters, inserts are low in cost.
- Replacing a carbide cutting element does not take much time.
- We can talk about the high reliability of inserts made of hard alloys even under conditions of intensive use.
- If necessary, such replaceable cutting elements can be readjusted.
- All modern models of replaceable cutting elements for turning tools are unified, which makes it possible to easily select the best option for a certain type of processing and grade of workpiece metal.
Thanks to the use of replaceable carbide inserts with mechanical fastening, the service life of the turning tool holder is significantly increased, and there is no need for such auxiliary operations as sharpening the cutting part and soldering it. What is important is that when using such a cutting tool, the reduction in temperature and cutting force can be 40%. Due to the characteristics of the carbide alloys that are used to make the inserts, the latter can be used to process metal by changing cutting conditions.
Some types of carbide insert shapes for cutters
Modern industry produces various types of replaceable inserts made of carbide materials. Requirements for the parameters of each of these types are specified in the relevant state standards.
- GOST 19086-80 defines the characteristics of cutting, support type inserts and chipbreakers.
- GOST 19042-80 specifies the requirements for the classification, form and designation system of replaceable inserts made of carbide materials.
- GOST 25395-90 applies to carbide inserts of types 01, 02, 61, 62, which are fixed on the turning tool holder using soldering. The requirements of this regulatory document apply to elements that are connected by soldering to boring, pass-through and turret cutters.
You can familiarize yourself with GOST 19086-80 “Replaceable multifaceted carbide inserts” below:
Types of plates
Removable retainers are divided into several subtypes , differing in purpose and structure:
- Single jawed. They are used to restore the dentition when it is shortened and narrowed and to eliminate deformation of individual teeth. They consist of a plate base and orthopedic screws that are tightened at the right time. Suitable for children and adults.
- With retraction arch. Suitable for both jaws, in which the protrussin position of the dentition is corrected. The result of restoration is based on the spring properties of the arc.
- With a hand-shaped process located on an arch. Placed on the upper or lower jaw, correcting the position of individual teeth. The hand-shaped process presses on the deformed tooth, placing it in the desired position.
- With active pusher. It is used to restore the frontal teeth of the upper jaw, the alignment of which occurs due to one or two spring mechanisms.
- Andrez-Goipl activator. The plate consists of two interconnected parts, which are simultaneously put on the upper and lower jaw. With its help, you can correct several dental anomalies at once.
- Bruckle's apparatus. Corrects bite defects in the anterior dentition of the lower jaw.
- Frenkel apparatus. Consists of lip pads, cheek shields and additional elements. All of them are connected into one device using a metal frame to correct open, distal and mesial bites.
Types for adults
In most cases, adult patients are prescribed single-jaw plates. Occasionally, arm-shaped structures may also be used.
Single jawed
The plate base of the structure is supplemented with special orthodontic screws. When tightened, they allow the device to exert directed and adjusted pressure. mainly used for narrowed or shortened dentition , as well as in case of deformation of some teeth.
photo: colored single-jaw plates
The cost depends on the number of screws with which the structure is equipped. A plate with one screw costs about 7–9 thousand rubles, and each screw costs from 1000 to 1300 rubles.
With retraction type arc
It consists of the retraction arch itself (vestibular, that is, external) and the obligatory plastic base. The operating principle of this device is based on the fact that the wire included in the structure can spring. Due to this, the position of the teeth during a protrusive bite is corrected.
photo: plate with retraction type arc
Estimated cost – 7000 rubles.
With a hand-shaped process
The basis of the design - the plate base - is complemented by a hand-shaped process, which is used to exert pressure on the required tooth in the area of its neck for greatest efficiency . The action is based on the elasticity of the wire from which the appendage is made.
photo: plate with a hand-shaped process
The approximate price is about 7 thousand. At the same time, the cost of manufacturing one appendage is about 400 rubles.
Bruckle apparatus
The base is the same plate base for the lower jaw. It is complemented by an inclined plane in the area of the anterior teeth and the retraction arch. Makes it possible to move the front teeth using the masticatory muscles and a springy retraction arch.
photo: trouser apparatus
Price – about 10 thousand rubles.
Types for children
For children's teeth, all types and types of structures that are listed above are used.
Removable retainers
Removable structures are popular in pediatric dentistry.
Such plates are installed if the child requires minor bite correction. The staples consist of a plastic base and hooks. Removable retainers do not pose a danger to the child, do not create discomfort while wearing, they can be easily tightened, distributing the necessary load on the jaw.
Advantages:
- adequate cost;
- ease of use.
Flaws:
- effective only for minor malocclusions;
- are intended to correct only one unit.
Removable retainers are classified according to other criteria, distinguishing the following subtypes:
- Single jawed. Recommended for wearing in case of pathological deformation of separately located units in children, as well as adult patients. They allow you to restore the optimal size of the dentition if it is narrow or insufficiently long. Pressure is applied to the jawbone by tightening special screws.
- With a branch on a metal arc. Used when the angle of only one tooth is disturbed. Under the influence of the screed, the process affects only the pathologically changed unit and gradually levels it out.
- With a retraction type arc. Installed when the incisors of the lower or upper jaw are protussive. The result is achieved by regularly tightening the screw elements.
- With a pushing fragment. The block consists of one or two parts on springs. Ideal for eliminating deformities along the upper jaw line.
- Bruckle's apparatus. Effective for eliminating minor defects in the frontal dentition on a mobile jaw.
- Andresen-Goipl activator. Suitable for correcting pathologically altered teeth on the upper and lower jaw bones simultaneously. Consists of several parts.
- The Frenkel apparatus is designed to correct irregularities in the dentition, as well as to restore the correct bite. Refers to complex structures in structure. In addition to hooks and clasps, cheek shields and lip pads are installed on a metal base.
This is interesting: How to use Nurofen for toothache
The main advantage of removable appliances is the ability to remove or provide some rest to the mouth. These braces are worn for about 18 months, but the period of wearing may vary as directed by your doctor.
Fixed structures
Fixed plates look like a metal arc (wire) with locks. With the help of locks, the arc is firmly fixed, while maintaining the ability to change position.
Fixed structures are used by both adults and children. The appointment for the installation of such retainers assumes a severe curvature of the dentition.
The duration of wearing depends entirely on the severity of the dental situation. Permanent plates are installed for up to two years, but if necessary, the doctor can extend the wearing period.
The non-removable design allows you to eliminate severe pathological bites and straighten your teeth.
The staples have high fastening strength and guarantee almost 99% success in correction. Such installation systems are more expensive due to the high quality of the material used and the complexity of the product parts.
Frenkel apparatus
Consists of plastic lip pads and cheek shields (2 of each element). They are connected using a durable metal frame, which can take the form of a palatal clasp, lingual or vestibular arch. Moves the anterior teeth using a springy retraction arch and masticatory muscles.
photo: Frenkel apparatus
Price – from 11.5 to 22 thousand rubles.
Andresen-Goipl activator
Consists of two base plates connected into a single block. May have screws, retraction arch, and other components. Helps activate jaw growth if necessary, uncouples the bite, and also returns individual teeth to their correct position.
photo: andresen-goipl activator
Price – from 12 thousand rubles.
The cost of each type in this case may be even higher than for plates for adults. This occurs due to the child’s choice of the pattern configuration and the variety of colors that will be present on the plate base of the device.
Modern technologies make it possible not only to make the plate itself multi-colored, you can also add glitter, all kinds of decorations and designs to the plastic.
The average cost of a plate for one jaw will be about 8 thousand rubles. But a simple plate for one jaw without additional functional elements, such as screws, costs about 3-4 thousand.
Classification options
In order to classify replaceable carbide inserts that are installed on a turning tool, a number of parameters are used.
Tool type
Turning cutters include boring, cutting, scoring, grooving, shaped, etc. Each of these types of tools requires its own profile shape, which is formed at the stage of manufacturing the carbide insert for the cutter.
Material of manufacture
The properties of materials that fall into the category of carbide alloys vary depending on the ratio of tungsten, titanium and a number of other metals they contain. It should be noted that replaceable inserts can also be ceramic; they are used mainly when processing heat-resistant alloys. In addition, ceramic products are optimally used in cases where it is necessary to perform continuous semi-finishing and finishing processing of metal workpieces.
Dimensions
Depending on the size of the workpiece that needs to be processed on a lathe, carbide inserts with the appropriate geometric parameters are also selected. For any type of turning cutter, products can be selected that differ in their geometric dimensions.
Relief angle size
The cleanliness of processing the metal workpiece depends on this parameter, which can be determined by the grade of the plate. The larger the relief angle, the higher the surface finish. Carbide inserts with large clearance angles are used primarily for turning soft metals.
Accuracy class
Modern manufacturers produce plates of five accuracy classes. These products can be used to process different tolerances to match the geometric parameters of the workpiece.
Indications for installation
There are no specific guidelines for the use of plates at a certain age. Their installation is possible both in early childhood and in adult patients. Most often, corrective braces are installed on children who have molars.
Many orthodontists recommend starting to correct the primary bite; just like the molars, there may be pathologies in location or angle of inclination. Plates are prescribed in the following situations:
- acceleration or deceleration of the processes of formation of jaw bones;
- correction of jaw shape;
- eliminating possible bias;
- changing the angle of one unit;
- correction of sky parameters;
- formation of a normal bite;
- preparing teeth and jaw bones for installation of braces;
- maintaining results after removing braces.
Dentists are of the opinion that it is advisable to correct the bite with corrective plates in children during the period of replacing baby teeth with permanent ones.
This is interesting: The best teethers for teeth according to customer reviews
The video shows in which cases leveling plates are used.
Labeling and manufacturers
The marking of carbide inserts for equipping turning tools indicates the composition of the material of manufacture. For example, the marking T15K6 means that in front of you is a plate made of a titanium-tungsten-cobalt group alloy. It should be noted that tungsten is required in such alloys. In addition to this metal, the alloy may additionally contain titanium, cobalt, tantalum, etc. The composition of the alloy we are considering as an example, in accordance with its marking, contains 15% titanium carbide and 6% cobalt.
The most popular manufacturers of carbide inserts used for mechanical fastening on turning tools include:
- LLC "Instrument-Service" (Ukraine);
- Novomoskovsk Pipe Plant (Ukraine);
- BDS-Machinen Company (Germany);
- Proxxon Company (Germany);
- Ceratizit company (Luxembourg).
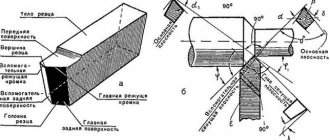
Types of carbide inserts for cutters
Carbide cutters
Carbide cutters
In the 20s of the last century, a new tool material appeared - hard alloys, which have high temperature resistance - up to 900 - 1000 ° C.
Carbide alloys do not contain iron
They are based on so-called carbides (chemical compounds with carbon of refractory metals) of tungsten and titanium. In its structure, the metal-ceramic hard alloy resembles a grinding wheel. The alloy consists of many tiny carbides connected to each other by cobalt, which not only acts as a kind of cementing agent, but also gives the carbide its toughness.
Hard slav groups
Our industry produces two groups of hard alloys: tungsten-cobalt and titanium-tungsten-cobalt. Alloys of the first group consist of tungsten and cobalt carbides and are designated by the letters B K and a number indicating the percentage of cobalt. For example, alloy B Kb contains about 6% cobalt and about 94% tungsten carbides.
Alloys of the second group, in addition to tungsten carbides, also contain titanium carbides. These alloys are designated by letters and numbers. The number after the letter T indicates the percentage of titanium carbides, and the number after the letter K indicates cobalt. For example, the T15K6 alloy contains about 15% titanium carbides and about 6% cobalt, the rest (about 79%) is tungsten carbides.
In our country, the production of tri-carbide group alloys has also begun, containing in addition to tungsten and titanium carbides also tantalum carbides. Alloys of the three-carbide group, such as TT7K12 and TT7K15, are distinguished by very high strength and allow planing of the most difficult materials, and in particular planing of surfaces obtained after welding (along the weld seam).
Hard alloys have high cutting properties; they do not require heat treatment, but acquire these properties during the manufacturing process.
Hardness
One of the main properties of hard alloys is their high hardness. It ranges from 88-90 HRA, while the hardness of hardened high-speed steel is 80-83 HRA. This high hardness makes it possible to process bleached cast iron, hardened steel, glass, marble and other very hard materials with hard alloys.
The hardness of the alloy depends on the cobalt content in it. The more cobalt, the lower the hardness of the alloy. Thus, alloy 6 is less hard than alloy VKZ.
Titanium carbides have a higher hardness than tungsten carbides, therefore the alloys of the group are harder than the alloys of the B K group at the same quantitative cobalt content. For example, the T14K8 alloy has greater hardness than the VK8 alloy.
Hard alloys also differ from other tool materials in their high wear resistance, i.e., the resistance provided to the abrasive action of chips and the cutting surface, while alloys of the TK group are more wear-resistant than alloys of the VK group.
Hard alloys also have high heat resistance - they retain cutting properties when heated to a temperature of '900-1000 ° C. And in this case, the alloys of the group turn out to be more heat-resistant than the groups.
As the titanium carbide content in the alloy decreases, the heat resistance of the hard alloy decreases. Thus, the T5KYu alloy is less heat-resistant than T15K6.
Disadvantages of carbide
The main disadvantage of hard alloys is their high fragility, which decreases with increasing cobalt content. For example, T15K6 alloy is more brittle than T5K10. In this regard, alloys with a high cobalt content are used for roughing. Low cobalt alloys are used in finishing; they have greater heat resistance and therefore allow higher cutting speeds.
With equal cobalt content, the alloys of the group are more viscous than the . Thus, the VKb alloy is more viscous than TI5K6. That is why VK alloys are used in the processing of cast iron and other brittle materials, during cutting of which fracture chips are separated, characterized by the fact that the center of its pressure on the front surface of the cutter is in close proximity to the cutting edge, and this often leads to chipping. If in this case you use an alloy of the TK group, then the tool life will be even less. It is more advisable to use TK alloys, which have greater wear resistance, when processing steels and other viscous materials, during cutting of which drain chips are separated, which actively abrade the front surface of the cutter.
Planing is usually carried out with a tool equipped with a hard alloy of the most durable grades - 8 and T5K10, which resist chipping under the influence of impact load better than others.
For finishing planing, alloys with a lower cobalt content are also used - VK6 and T15K6.
Solderable carbide inserts
Hard alloys are produced in the form of plates of various shapes and sizes. These plates are soldered to rods - cutter holders made of structural steel or attached to them mechanically.
As the practice of using hard alloys has shown, when planing, chipping of the cutting edges of cutters is observed, even with the correct choice of their sharpening geometry and cutting modes, while chipping does not appear during the working stroke as a result of the impact action during the cutting process, but during the reverse, when the back surface of the cutter slides along the machined surface of the part.
In order to eliminate this drawback, special devices are used that automatically raise the cutter during the reverse stroke.