Benefits of use
There are many advantages to using turning inserts.
- First, as stated above, the main function of the insert is to increase the durability of the cutter. Cutters are quite expensive and wear out very quickly. The plates significantly extend their “life”.
- Secondly, cutters are much less versatile than inserts. Having a sufficient set of plates, you can process metals and alloys of different compositions and structures.
- Thirdly, changing plates is much more convenient and faster than changing cutters. And this is an essential component of productivity per piece of equipment.
- Fourthly, there is a huge assortment of attachments, which means that choosing a plate for any technological operation is much easier than a cutter.
- And finally, fifthly, savings. Buying a new insert to replace the one that broke will cost much less than purchasing a new cutter. This is perhaps one of the main advantages of turning plates.
Advantages of using carbide inserts for cutters
Inserts for boring or cutting cutters can be made of various grades of hard alloys, which is very convenient, as this allows you to have a whole set of cutting elements for processing workpieces made of different materials.
The use of replaceable inserts for a cutting tool is also a cost-effective solution, since in case of breakage or wear there is no need to replace the entire cutter with a new tool: only its cutting part needs to be replaced. It is advisable to use a tool with replaceable carbide inserts even if the task is to automate technological processes, which is especially important in small- and medium-scale production, where the range of manufactured products can change quite often.
Cutters with replaceable inserts
Among the advantages of carbide inserts mounted on turning tools, the following should be highlighted.
- Compared to solid cutters, inserts are low in cost.
- Replacing a carbide cutting element does not take much time.
- We can talk about the high reliability of inserts made of hard alloys even under conditions of intensive use.
- If necessary, such replaceable cutting elements can be readjusted.
- All modern models of replaceable cutting elements for turning tools are unified, which makes it possible to easily select the best option for a certain type of processing and grade of workpiece metal.
Thanks to the use of replaceable carbide inserts with mechanical fastening, the service life of the turning tool holder is significantly increased, and there is no need for such auxiliary operations as sharpening the cutting part and soldering it. What is important is that when using such a cutting tool, the reduction in temperature and cutting force can be 40%. Due to the characteristics of the carbide alloys that are used to make the inserts, the latter can be used to process metal by changing cutting conditions.
Some types of carbide insert shapes for cutters
Modern industry produces various types of replaceable inserts made of carbide materials. Requirements for the parameters of each of these types are specified in the relevant state standards.
- GOST 19086-80 defines the characteristics of cutting, support type inserts and chipbreakers.
- GOST 19042-80 specifies the requirements for the classification, form and designation system of replaceable inserts made of carbide materials.
- GOST 25395-90 applies to carbide inserts of types 01, 02, 61, 62, which are fixed on the turning tool holder using soldering. The requirements of this regulatory document apply to elements that are connected by soldering to boring, pass-through and turret cutters.
You can familiarize yourself with GOST 19086-80 “Replaceable multifaceted carbide inserts” below:
Classification of carbide inserts for metal
The plates differ:
- Shape: rhombic, square, triangular, round, etc.
- According to the processed material - steel, cast iron, non-ferrous metals, hard metals, etc.
- By radius (from 0.1 to 2.4) and size (from 6 to 33).
- By type of processing - from heavy roughing to finishing finishing.
- By purpose - plates for turning, for threading, for grooving, cutting off.
Sandvik inserts
Sandvik carbide inserts are available in a variety of grades. For example, the AC25 is a product that can be considered one of the latest advancements. Such inserts are widely used in machining in a wide range of cutting conditions. They are especially suitable for working with cast iron, stainless alloys, and structural steels. Using these elements, you can achieve high processing accuracy, as well as wear resistance at cutting speeds from 100 to 200 m per minute. AC40 are replaceable carbide inserts that are also used for processing different materials. They proved to be ideal for working with alloys based on chromium and nickel; the insert is able to perform its job without flaws, and during semi-finishing it shows high efficiency even at a cutting speed of 200 m per minute.
How are they labeled and who produces them?
The marking of the plate provides information about the composition of the manufacturing material, as well as the shape, angles, length of the cutting edge, various tolerances, etc.
Important!
Letters and numbers in plate markings must always be deciphered from left to right.
Each symbol represents a specific indicator. The first letter characterizes the shape of the plate, the second - the clearance angle, the third - the tolerances for height, thickness and size of the inscribed circle, and the fourth indicates the presence of a chip breaker or hole.
After the letters there are numbers. The first two determine the length of the plate, the next two determine the thickness, and the last two determine the corner radius. The two letters after this indicate the type of chip grinder, or lack thereof.
In the latter case, “None” is written instead of two letters. Finally, the very last designation (two letters and four numbers in a row) characterizes the alloy of the plate.
The most popular manufacturers include manufacturers from Ukraine - Novomoskovsky Pipe; from Germany - Proxxon Company and BDS-Machinen Company; from Luxembourg – Ceratizit Company
Plate alloys
AL20 is an element that has a titanium coating and an additional lubricating layer; during operation, the elements provide a low friction coefficient, which allows for less heating in the cutting zone. It is especially preferable to use such inserts for machining alloy steels.
AL40 is a carbide insert that also has a titanium coating, but is used for milling operations that involve vibration. It is preferable to operate these elements at low cutting speeds, only then will the plate cope with the processing of heat-resistant alloys.
AP25 is a replacement part that is used on the cutting tool. The insert acts as a general purpose product, has no coating and is advantageously used when processing stainless, alloy and carbon steels. The carbide alloy allows for high stability and strength of the insert during roughing.
AP40 is commonly used for roughing and roughing structured and tool steels, as well as for working with steel castings. It copes well with heavy loads, so the plate can be used under particularly difficult conditions.
Price
Plates are always sold in sets, and their price varies quite a bit depending on a number of indicators. In particular, on the configuration, shapes and sizes. On average, the price of one set is about 5,300 rubles.
Often the set includes a cutter body, then its price increases significantly. In this case, it is about 8,000 rubles. In general, the use of turning inserts on one cutter creates a monthly savings of approximately 450 rubles.
Turning inserts have a lot of advantages - from high productivity and durability to significant savings. This means that their use will significantly improve the quality of work performed, as well as the pleasure from it.
Types of plates by mounting method
Carbide inserts, which are on sale today in a large assortment, can be classified according to different criteria, among them it is necessary to highlight the method of fastening in the tool. Based on this parameter, elements can be divided into two groups. First group: brazed plates. The second category includes replaceable carbide plates. The latter are fixed mechanically, which speeds up the process of replacing failed plates. Among other things, they can be used repeatedly.
The first method is provided by turning the plate over, while it is possible to operate multi-faceted disposable elements. Replacement in this case is not provided due to the difficulty of ensuring the required edge geometry. Brazed plates are attached and held in the tool, and as they become dull they are sharpened again.
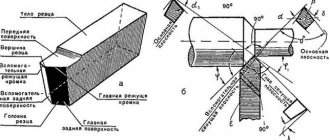
Designation of inserts / ISO insert designation chart
Interpretation of the designation of replaceable cutting inserts according to the ISO standard Part 1 Turning tools Insert shape Hexagonal Octagonal Pentagonal
Decoding of the designation of replaceable cutting inserts according to the ISO standard Part 1 Turning tools Insert shape Hexagonal Octagonal Pentagonal _ Square Triangular c Rhombic 80 o D Rhombic 55 Z7 E Rhombic 75 o F Rhombic 50 7 M Rhombic 86 V Rhombic 35 Z7 W Three-tone L Rectangular o A Rhombic 85 o B Rhombic 82 o K Rhombic 55 R Round O X Special design Insert shape designation AG 0D1 S1 Triangular chamfered insert (Auxiliary cutting Tolerance class designation Features of tolerance of class M inserts Tolerance for cutting edge height m (mm) (Kime Height tolerance cutting edge m (mm) Inscribed circle diameter tolerance 0D1 (mm) Insert thickness tolerance S1 (mm) Triangular Square Rhombic 80 Rhombic 55 Rhombic 35 Round A 0.005 0.025 +0.025 F 0.005 0.013 +0.025 6.35 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.11 0.16 C 0.013 0.025 +0.025 9.525 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.11 0.16 N 0.013 0.013 +0.025 12.70 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.15 E 0.025 0.025 +0.025 15.875 0.1 5 0.15 0.15 0.18 G 0.025 0.025 +0.13 19.05 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.18 J 0.005 0.05 0.15 +0.025 25.40 0.18 K 0.013 0.05 0.15 +0.025 31.75 0.20 1 +0.025 +0.05 +0.15 +0.025 Tolerance for piston circle diameter (ft w) M 0.08 0.18 0.05 0.15 0.13 Circular Triangular Square Rhombic 80 Rhombic 55 Rhomb ical 35 Round N 0.08 0.18 0.05 0.15 0.025 The sign indicates the surfaces of the sintered plates. 12.70 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.08 - 0.08 15.875 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10 - 0.10 19.05 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10 - 0.10 25.40 - 0.13 - 0.13 31.75 - 0 .15 - 0.15 Designation of tolerance class C N M G Designation of rear angle INN Standard angle A 3 B 5 C 7 15 E 20 F 25 -JV G 30 N 0 P 11 O Other angle values Main angles used Chipbreaker fixation designation Metric system Presence of hole Hole shape Chipbreaker Fig. Both Presence of hole Hole shape Chipshopper Fig. W With a cylindrical hole + one countersink (40-60) No I 1 I A With a cylindrical hole No 1111 1 With a hole One-sided GI1 VH7 With a cylindrical hole One-sided VI 17 Q With a cylindrical hole + two countersinks (40-60) No G With a hole cylindrical double-sided and with hole double-sided N Carried hole. — No B With a cylindrical hole + one countersink (70-90) No P7 R Without holes. — Single-sided GIG 7 With Hole Single-sided F Without hole. — double-sided rm VM7 LJ With a cylindrical hole + two countersinks (70-90) No X — Special design J With a double-sided hole A002 DESIGNATION OF PLATE FOR TURNING
Selecting a cutting insert when machining various metals
The feasibility of using one type or another of carbide inserts is determined by the following factors:
- Brand of processed material;
- Workpiece condition;
- Type of technological operation;
- Type of equipment use;
- Cutting mode.
In general, when cutting cast iron, non-ferrous alloys and plastics, it is recommended to use tungsten-cobalt based inserts. These alloys have a higher resistance to pulsating loads, which is typical for this type of work.
If there is a cutting speed of over 200 m/s and a cutting load on the cutter of more than 800 kgf, carbide inserts are used, additionally alloyed with tantalum and titanium.
Rate this article:
Rating: 0/5 — 0 votes