Some owners know nothing at all about this element of the home’s sewer system. That is, neither about its existence, nor about its purpose, nor about the importance of the installation, where it is necessary. I think it makes sense to clarify this issue, to “paint over the white spot.”
Vacuum valve for sewerage
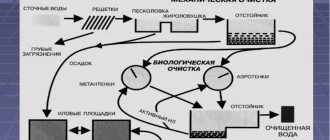
So, the sewer system must be created according to certain rules. These standards are not taken out of thin air - they are, one might say, “hard-won”, representing a kind of generalized experience of several generations, supplemented by scientific research and confirmation. And neglecting these requirements often leads to increased sewerage breakdown rates, and, perhaps, always to a sharp decrease in the comfort of living in a house where it is not equipped according to the rules.
But it also happens that some recommendations are difficult to implement in practice due to the specifics of the system. Then certain deviations are allowed, true, but with mandatory compensation of one kind or another. Such cases include the installation of a vacuum valve for sewerage.
Necessary information about the sewer drain pipe
The importance of using a vacuum valve will be difficult for an ignorant person to immediately understand if he does not have an idea of the general structure of the sewerage system. And in particular - about the need for ventilation and pressure equalization in pipes. Generally speaking, about the role of the vent pipe.
Let's take it step by step.
The sewage system must be ventilated...
In the sewerage system, all the main parameters are closely interconnected. This refers to the diameters of laid pipes in various areas, from plumbing fixtures to a collector or septic tank (cesspool), the angle of inclination to the horizontal at which they are installed, the speed of movement of wastewater and the degree of filling of pipe channels. There are special methods for calculating these characteristics, and with proper selection and installation, the system should operate without failures.
The optimal slope is designed to ensure that the speed of movement of the wastewater at which the water almost completely transfers all contaminants. And at the same time, the pipe is not filled completely, but only to 0.5÷0.7 of the height of its cavity. In the upper part of the channel, air and gases that always accompany any sewer move freely, of course, a very unpleasant “aroma”.
Sewer pipes are laid with a certain slope i (depending on their diameter Dn), so that the optimal speed V of fluid movement and the required filling level of the pipe cavity are maintained inside.
We will not dwell on these aspects in more detail - they are already covered on the pages of our portal.
Why is the correct slope of sewer pipes so important?
Just so that the sewage system fully copes with its direct tasks. By the way, an excessive slope of sewer pipes is no less harmful to the system than an insufficient one. More details about this, with justifications and calculations, can be found in a separate publication on our portal.
So, if the sewer system is designed and installed correctly, the air channel in it always remains free. It plays the role of ventilation - through it air and gases must be discharged into the atmosphere. Moreover, in sewer pipes and chambers, due to the saturation of wastewater with organic waste, the processes of fermentation and decay do not stop. And this is always accompanied by the release of a considerable amount of gases, many of which, by the way, are very unsafe both from the point of view of toxicity and from the point of view of fire safety. That is, their timely withdrawal must be provided for.
This is precisely why ventilation outlets of pipes are provided to the outside. It is these ventilation risers that are called fan pipes.
Various options for the location of the drain pipe
For example, very often they are equipped with septic tank chambers or cesspools (position 4 in the figure). But if these local treatment facilities are located near the house, then sewer odors can greatly spoil the cozy atmosphere in the yard. Therefore, they usually try to place the head of such a pipe higher so that the “aromas” are immediately picked up and carried away by the wind. This could simply be some kind of vertical ventilation outlet, raised to a certain height, if the specifics of the site allow (item 3)
The most common option, especially when building several levels (floors), is to create a vertical riser (item 1), to which drainage sections from plumbing fixtures are connected. Above the highest high point of connection of the branch section, this riser itself turns into a drain pipe, passes through the roof covering and ends at the cap on the roof. This option can be considered the most reliable, since it fully copes with all absolutely the tasks of a fan pipe (one such important function will be discussed below).
Some owners, not wanting to organize the passage of a vent riser through the attic floor and roof, act as shown in the diagram - pos. 2. That is, the ventilation pipe is inserted into the area where it is laid horizontally outside the house, and then it rises vertically along the wall and ends above the eaves of the roof.
Of course, when bringing the vent pipe outside, certain rules must be observed based on its location relative to other objects:
- Wherever the pipe is located, its head should not be closer than four meters from opening windows or balconies.
- The cut of the vent pipe cannot be closer than 200 mm to the roof surface on pitched roofs or on flat unused ones.
- It cannot be closer than 100 from the edge of the prefabricated ventilation shaft.
- If the flat roof is in use, then the height of the drain pipe above it must be at least three meters. And this necessarily presupposes the presence of stretch marks.
- Deflectors or wind vanes are never put on the fan pipe.
Possible effect of water seal failure
Sometimes it can be very difficult to comply with all these requirements, which makes owners think about the question: is it possible to do without a vent pipe, that is, without ventilation. Limiting yourself, for example, to the growth of a small “fungus” in the area of the septic tank, and in the house - leaving the riser or wiring unventilated.
In principle, it is possible, although not advisable. But now is the time to remember the second important function of the fan pipe. We are talking about equalizing the pressure in the system.
It was already mentioned above that gases with a very unpleasant aroma are always “walking” in the sewer pipe. Why don’t we feel them with a properly assembled system?
Yes, simply because any plumbing fixtures connected directly to sewer pipes are equipped with a water seal. Or, as it is more often called, a siphon.
Siphons in plumbing fixtures connected to sewer pipes: 1 - toilet with rear connection; 2 - toilet with bottom connection; 3 - bath or shower tray; 4 and 5 - sinks of washbasins or kitchen sinks; 6 - ladder on the floor.
The diagram above clearly shows the principle of siphon design for various plumbing fixtures. Pay attention to the water level in the curved lower part of this valve - in a “quiet” state it corresponds to the level of overflow into the sewer pipe extending from the device. The design is thought out in such a way that the air from the sewer cannot overcome this water barrier - the smell does not enter the room.
The throughput of siphons is always made slightly lower than that of the pipes to which they are connected:
- For example, both the cross-section of the outlet pipe of the flush tank and the cross-section of the siphon in the toilet usually correspond to a maximum diameter of 70 mm. Whereas the toilet is always connected to a pipe with a diameter of 110 m.
— The cross-section of the sink or bathtub siphon tubes is usually similar to a pipe with a diameter of 30÷40 mm, and the connection is made to a 50 mm one.
Why was it designed this way in the first place? For reasons that even with the maximum output of water through the siphon (flushing a full toilet tank or opening the drain plug in a fully filled bathroom), the flow of escaping water in no case overflows the sewer pipe. That is, in any case, the air space that we have already discussed above should remain in the pipe.
Siphon for kitchen sink. Please note that the diameter of the tube coming from the sink drain is 32 mm, coming from the siphon is 40 mm, and it will connect to a 50 mm pipe. That is, overflowing a sewer pipe under normal conditions is impossible.
Why is it dangerous, overflow? It would seem like a few minutes - and still the water will disappear completely. Just think, there will be no ventilation for a short time...
That's not the point - the danger here is of a completely different kind.
If water (wastewater) upon exiting fills the entire cavity of the pipe, without an air gap, then it begins to act like a piston during movement. That is, leaving behind an area of low pressure - rarefaction. And this vacuum can become so great that it “takes with it” the water that should remain in the siphon. Or it will “suck” water from the water seal of another plumbing fixture connected to the same sewer pipe. There is not so much water in the siphons, and excessive efforts are not required to move it from its place and draw it into the pipe.
This effect is commonly referred to as siphon stalling. But no matter what it is called, the consequences of such a phenomenon are always the same. Namely, the water seal does not work. There is not the required amount of water to block the passage of gases, and an unpleasant odor from the sewer begins to penetrate into the room.
But how can a siphon break if, as we have seen, strong vacuums should not occur in the pipe - its diameter is always larger than the diameter of the plumbing fixture drain? Yes, this is true if we are talking about one device. But several devices are most often connected to one outlet pipe, and even more so to one riser. Moreover, in the case of a common riser, the number of connection points can be quite significant.
Thus, there is always the possibility that at some point several drains will be involved simultaneously. In this case, the total flow of wastewater collected from various points may temporarily exceed the throughput capacity of the pipe, and it will be filled to capacity. That is, the same “piston” will work, breaking the water seals.
Let's look at the diagram. It just shows a toilet as an example, but the “mechanism” for breaking the shutter is the same for all other plumbing fixtures.
Too large a volume of wastewater passing through the pipe (riser) at a time can create a zone of strong rarefaction of air behind it. And this vacuum can empty the siphons of connected plumbing fixtures - literally suck the water out of them.
But nothing like this will happen if such an overflow occurs below the connection point of the waste pipe - due to the openness to the atmosphere, rarefaction simply will not arise - it is compensated by the influx of air from the outside.
Let's look at the same diagram, but with a slight change.
A small change in the circuit - and you no longer have to worry about the water seal breaking.
Almost the same, but the changes are that a vertical drain pipe with access to the street is connected to the sewer pipe above our conventional “toilet bowl”. Now you don’t have to be afraid of the water seal breaking – the “deficit” of pressure in the vacuum zone will be immediately covered by the flow of air through it. That is, the pressure will equalize.
It would seem like a ready-made solution to the problem. But it was not there. Is it possible to install a drain pipe for every “problem” plumbing fixture? No, of course, it will be extremely difficult, and very inconvenient, costly, etc.
Further, even if the vertical common riser has a drain outlet, is there a guarantee that an overflow will not occur in the outlet area to which, for example, a bathtub, washbasin and washing machine drain hose are connected? And here, too, the possibility of such an unpleasant incident remains. Moreover, over time, sewer pipes can gradually become overgrown with sediment, that is, slightly decrease in diameter. In addition, the hydraulic strain of the pipes gradually increases due to interference adhering to the walls. That is, the wastewater does not flow out as quickly, and the risk of the formation of vacuum zones may increase.
This means that some compact device could help, which, on the one hand, would prevent unpleasant odors from entering the premises from the sewerage system. On the other hand, it would prevent the creation of vacuum zones during the massive release of wastewater, that is, it would ensure equalization of pressure.
Such a device exists. This is exactly the vacuum valve that is the topic of our consideration.
Installing a vacuum valve on the sewer allows, in some cases, to do without a drain pipe.
In fact, we have already quietly figured out the main purpose of this valve. It is difficult to add anything on this issue. Therefore, you can go straight to the consideration of the design of the aerator (the second name for such a device) and the basic principles of its installation.
Operating principle of sewer ventilation
Water valves in the siphons of plumbing fixtures are barriers to odor from the sewer system. But when a large amount of water is suddenly drained, the pressure in the pipes decreases and water is sucked out of the siphons. At this moment there are no longer any obstacles to the penetration of the smell and it can freely penetrate into the room. The causes of odor can also be the small size of siphons or prolonged downtime of plumbing, leading to evaporation of water in the siphons.
Sewage ventilation in the form of a drain pipe or air valve helps protect the room from unpleasant odors. The air entering through them equalizes the internal pressure in the pipeline with atmospheric pressure. Under such conditions, gases are not forced out through siphons, but move further through pipes into a collector system or septic tank.
How does a vacuum valve work?
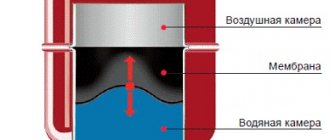
It is already clear from the purpose of this device that it must remain closed when there is excess pressure in the sewer pipe or when it is equal to atmospheric pressure. But if a vacuum occurs in the pipe, the valve mechanism must ensure the opening of the passage for air to enter from the outside.
The principle is easily implemented with the “involvement” of ordinary gravitational forces. The diagram below shows the structure of one of the aerator models. Despite possible differences in the design of valves from different manufacturers, the principle remains virtually unchanged.
An example of a device and a demonstration of the principle of operation of a vacuum valve for sewage.
The entire valve mechanism is assembled in a polymer housing (item 1). The device itself implies only a horizontal arrangement, so in its lower part one or another device must be provided for a sealed connection with the sewer pipe. In the example shown, this is an elastic cuff (item 2) for inserting the aerator into a socket or even just into a cut pipe. There may be a connecting unit in the form of a standard sewer pipe socket or other options. But this installation is always simple, reliable and understandable.
Air can enter the aerator through the intake grille or slot-like openings (item 3). They are located at the bottom or on the side of the valve "head", but outside air will almost always be applied to the valve diaphragm from below.
This is very easy to explain. The valve flap (pos. 5) is located in the seat assigned to it (pos. 4) and fits tightly to its edges with an elastic cuff (membrane), preventing air from passing from the pipe into the room. And the fit is ensured by the banal force of gravity of this damper. That is, even if the atmospheric and established pressures in the pipe (riser) are equal, the valve will be closed. This can also be facilitated by some excess pressure in the pipe, since gas formation in the sewer almost never stops. That is, the valve will thereby be pressed even more against the seat (in the diagram it is the left fragment).
But if, for one reason or another, even a slight vacuum is created in the pipe, atmospheric pressure will overcome gravity and lift the valve above the seat. As they say, “nature abhors a vacuum,” and the outside air will rush into the pipe, equalizing the pressure and preventing the siphons from breaking.
To prevent the damper from warping, it may have special guides (item 6). However, many models can do without them - centering is done due to the cylindrical shape of the valve assembly.
Aerator for 110 mm pipe - model with two valve heads. One of them has been disassembled to demonstrate its simple device.
Out of pure curiosity, you can “disassemble” several more vacuum valves of various models. But we still won’t find any fundamental differences there.
The differences in the design of different valve models are not fundamental.
By the way, since the device is being considered, you can immediately draw the readers’ attention to the “Achilles heel” of any valve. This, of course, is the membrane itself, or more precisely, the area of it that is pressed by gravity against the valve seat.
And here we are not talking about wear (if it exists, it is very unnoticeable), but about other obstacles that can prevent the sash from sealing:
- Over time, dust can accumulate on the valve seat or on the membrane itself, which can turn into hard lumps of dirt that prevent the valve from sealing tightly. Often the owners are notified of this by the “aroma” of sewerage entering the premises. The first thing to do when such a “bell” comes up is to check the cleanliness of the membrane and its fit, and carefully clean the assembly from contaminants.
- The second conclusion is that the vacuum valve must be installed only in a heated room of the house. Otherwise, with the onset of cold weather, drops of condensate may freeze on the seat or on the membrane, and the valve mechanism will not fit properly. And in general, too large temperature changes do not benefit the rubber membrane - it begins to “tan” in the cold, losing the necessary elasticity.
Otherwise, the mechanism is extremely simple, and it is difficult to come up with any circumstances that would lead to a breakdown of the vacuum valve.
Valve installation recommendations
When installing, it is important to follow the rules that will help maximize the efficiency of the sewer valve:
- Installation is only permissible in a heated room. This will help avoid valve failure due to low temperatures.
Installed device under the bathroom Source homemasters.ru
Which valve should I buy?
The question is difficult in the sense that there are no obvious “favorites” or “promoted” models. But at the same time, there is a very serious range of prices. And on top of that, there are no clear selection criteria, except, perhaps, the diameter of the pipe on which the valve is mounted, the dimensions if the space for its installation is limited, and the most convenient method of connecting to the pipe.
The drain pipes from the shower stall and washbasin converge at one point. To protect this unit from the siphon breaking, it was decided to install an aerator on a 50 mm pipe. In this case, of course, the dimensions of the device are important.
Moreover, if you “browse” through online stores of plumbing equipment, you will see that often no parameters other than diameter and dimensions are indicated at all. Sometimes you can see air throughput (liters per second), but that's probably all.
Of course, you should assume that more well-known manufacturers of plumbing products and valves will offer the most durable and reliable valve. But you can find a lot of examples where the most uncomplicated and inexpensive domestically produced aerators serve for decades and continue to serve.
Therefore, this is just a brief overview of the models offered for sale and their prices, but without any recommendations in favor of this or that product.
| Illustration | Short description | Approximate cost, rub. |
| "MkAlpine HC 50-50" - products of a company from the British Isles." Polypropylene. Model for pipe ø50 mm. Fits in a standard bell. Capacity – 3 l/s. | 850 rub. | |
| Model “MkAlpine” for DN110 mm pipe. Polypropylene. | 2500 rub. | |
| "HL900NECO" Austrian. Available in three versions - for pipes DN50, DN70 and DN110 mm. Polypropylene. Mesh on the side surface of the case. The flow capacity of the DN110 valve is 37 l/s. Thermally insulated housing walls. | For model DN110 – 2800 rub. | |
| Air valve “Wavin Optima Mini vent” from the famous Dutch company. Compact models for installation on sewer pipes with a diameter of 30, 40 and 50 mm. Polyvinyl chloride. Capacity – 7.5 l/s. Installation - in a standard socket. | 3600 rub. | |
| The Finnish product is the HTL vacuum valve. Manufactured for 110 mm, equipped with adapters for 50 and 70 mm. Polypropylene. | 4700 rub. | |
| Valve of the German brand "Ostendorf" made in Russia. Diameter – 110 mm. Polypropylene. | 1900 rub. | |
| Vacuum valve made in Russia. Diameter – 110 mm. | 190 rub. | |
| Valve made in Russia. Polypropylene. Diameter – 110 mm. | 240 rub. |
Probably, this is already enough to understand how “dancing” the prices for such products are. Moreover, with approximately equal characteristics, materials of manufacture, etc. So the author of this article does not take responsibility for recommending certain models - everything is too unobvious.
True, they can, but why do some DN110 aerators have one common head, while others have two small ones?
There is no special secret here. It’s just that the manufacturer produces models for both 50 mm and 110 mm pipes. And it is technologically easier for him to combine two smaller valve heads in one body to obtain an aerator for a larger diameter. But this does not particularly affect the operation of the device itself. Except that you have to take care of two membranes. But if one fails, it will cost less to replace than one large one.
Instructions for installing a check valve for sewage with your own hands
A sewer check valve is a device that prevents flooding of housing in emergency situations (due to blockages in the sewer, etc.)
Before you buy a 50 or 100 mm sewer valve, you need to understand the specifics of the operation of shut-off devices and the principle of their operation. It would be a good idea to collect all the information about the sewerage system.
To install a check valve for sewage with your own hands, as a rule, no additional equipment is required.
General information
Important! Buy the device from a reputable place of sale and be sure to ensure that there is a warranty.
A sewer check valve is a shut-off mechanism that prevents the reverse movement of water due to blockage and prevents leaks. Even a package accidentally falling into the pipeline can lead to clogged sewers and flooding of housing.
A sewer check valve is installed in private houses, offices, apartments, as well as in water supply and heating systems (for a pump).
The mechanism itself is a cylinder with a small spring inside and a round overlapping plate. The check valve is initially closed using a spring.
The spring becomes weaker with water pressure, and the valve opens, allowing water to pass through. If a leak occurs, the pump or something else stops, and the power of the water flow decreases, the shut-off plate closes. A check valve prevents unpressurized water from flowing back.
There is a need to install a check valve for sewerage when
- Garbage and large objects regularly enter the sewer system and other operating rules are violated;
- The pipeline has been in use for a long period of time, during which a layer of grease has accumulated on the inner walls. In this case, the likelihood of clogging increases;
- the slope of the pipeline is too small or large, which prevents the free gravity flow of wastewater;
- the outlets are located at a perpendicular angle to the sewer pipe. This can cause a water blockage as the water speed will change dramatically.
In country houses, it is recommended to install water check valves on the street, where all sewer pipes are collected together.
Types of check valves
Sewer shut-off mechanisms at the installation site can be:
- for the street;
- for the premises.
Advice! Choose models that are resistant to negative temperatures and have good throughput if the device is installed in a sewer pipe outside.
According to the installation method they are divided into:
- flanged;
- wafer;
- coupling
Wafer check valves are installed in metal pipes; welding will be required for their installation. However, it will not take much time to install it.
The flange method is used to install check valves on pipes with a large diameter. Usually on the street. On pipes of small diameter, it is more convenient to install locking mechanisms using the coupling method. For indoor installation, this method is most often used.
Advice! When installing the check valve, choose a location so that when you need to clean it from blockages, you can easily remove the cover.
Depending on the type of shut-off device, check valves are divided into:
- Check valves. The locking element is a “slam.” With normal water flow, it is in the open position, but if the pressure begins to drop, the lid slams shut and blocks the flow of liquid.
- Lift valves. The shutter mechanism is a lifting spool. With normal fluid flow, the spool is raised. If there is a need to repair such a valve, it is not necessary to completely dismantle it. Its disadvantage: it is too sensitive to environmental pollution.
- IMPORTANT! The axis of the lift-spool valve must be located vertically, so they can only be installed on sections of pipelines that are in a horizontal position.
- Ball valves. The spring presses the ball against the seat during normal water flow. If the pressure drops, the ball will block the walls of the hole, pressing against its walls. They are most often used in plumbing.
When choosing the appropriate option, pay attention to the following characteristics:
- diameter of sockets;
- material;
- device size;
- complexity of installation;
- quality and guarantee;
- price.
The diameter of the sockets is the most important parameter and must be the same as the pipe in the sewer into which the check valve will be installed. The wrong decision would be to buy a device with a larger or smaller cross-section; this will not allow creating a tight connection with the sewer pipe.
Check valves are made of the same material as the pipes:
- plastic;
- bronze;
- steel, including stainless steel;
- cast iron;
- other materials that are less common.
Choose a material that matches the material of the sewer pipes installed in a country house or apartment. It would be impractical to embed a plastic valve into a cast iron pipeline, and vice versa. The most affordable price for plastic check valves.
Select the size of the locking mechanism based on how much free space there is for its installation. You also need to remember that some valves must be installed vertically, others horizontally (used more often).
Valve installation
Installation instructions for a 110 mm sewer check valve:
- Considering the cross-sectional diameter of the sewer pipe, select a valve of 40, 50, 100 or 110 mm and a location for its installation.
- Check manually whether the valve structure is tight. Contact the retail outlet and change the device if you have the slightest suspicion that there are defects;
- Carefully cut the pipeline and install the check valve. Look carefully at the direction of flow of the drains and the direction of the arrow on the valve body. They must match;
- Place silicone or rubber sealants on the edges of the cut pipe;
- Check the functionality of the check valve. If there are violations in the installation, the drains will rise up.
Recommendations for installing a check valve for sewage 50/110 mm:
- Make sure that the direction of the drains and the arrows on the device body match;
- Installation of the plastic model is quite simple: the edges of the pipeline are connected to the valve socket. The connection is already sealed, but it is still better to apply silicone sealant to it for plumbing work;
- When installing a valve made of cast iron, a sealing rubber band is used, as well as tightening mounting plates and bolts. Installation of models with bells is no different from installation of plastic valves;
- When choosing a location to install the valve, consider the possibility of free access to the cover in case it is necessary to clean the locking mechanism.
Where and how to install the vacuum valve
We should start, of course, with the installation sites. But they should already be generally understandable – based on the valve’s tasks.
Nevertheless, let’s list:
- The classic installation location is the “crowning” of the riser, which for some reason cannot be made ventilated, that is, through the roof. Installation is carried out at the highest point.
Mandatory installation - at the top point of the riser, which will not be discharged to the street. Not a plug, but a vacuum valve!
- On a horizontal outlet section, if several plumbing fixtures are connected to it, then there is a possibility of the water seal breaking during a massive discharge of water.
In this case, it is advisable to place the valve at the farthest point of the horizontal section, so that it is located above the highest siphon on this branch.
- At the point of convergence of drain pipes from several plumbing fixtures, if their one-time total discharge at some point may exceed the capacity of the common pipe. Such an example was shown above in more than one of the illustrations.
There is no riser in this house at all, which means you need to install a vacuum valve at the highest point of the largest pipe. And, perhaps, you cannot do without valves on long horizontal sections.
- A one-story house may not have a riser at all. That is, horizontal outlet sections of 50 mm converge to the toilet, glued to a 110 mm pipe, and from there the pipe immediately descends and releases outwards, towards the septic tank or collector. This means that a vacuum valve would also come in handy in the area where small pipes are inserted into large pipes, in case of a massive discharge of water.
- Sometimes the circumstances themselves begin to “dictate” to the home owner where it is advisable to install a vacuum valve. For example, sewer pipes are probably overgrown, their internal diameter has decreased, and it would seem that the normal discharge of water still leads to the failure of the siphon. If it is not yet possible to completely change the entire pipe section, installing an aerator will save you.
Apparently, the owners were fed up with the frequent breakdown of the siphon due to poor permeability of the old cast iron pipe.
And they solved the problem by installing an aerator. Wherever the vacuum valve is installed, it is mandatory to ensure a free flow of air to the place of its installation. This means that it should not be a locked cabinet or a tightly closed, unventilated room. The volume of air entrained by water is very considerable - approximately 25 times greater.
In addition, it is necessary to consider easy access to the valve for checking, cleaning or other maintenance.
The position of the vacuum valve, as already mentioned, is exclusively vertical, without options.
It is advisable to protect the valve from splashing. This is achieved by placing it at a height of approximately 250÷350 from the horizontal pipe.
Options for inserting valves into different sections of pipes
Well, the installation of the valve itself probably doesn’t make sense to describe in detail. Anyone who has at least once seriously engaged in assembling sewer lines on their own can cope with the task without difficulty. The main thing is to understand the type of connection, do not forget to put the cuffs in the sockets. Switching to old cast iron pipes always causes a little more fuss - but here everything can be solved.
That is, the installation itself does not hide any serious features or differences from the assembly of other sewer units.
Do-it-yourself check valve for sewerage - Metals, equipment, instructions
In all systems where water is used, it is assumed to flow in a certain direction.
Backflow can be caused by various reasons, which we will look at later, and is considered an emergency situation.
A check valve will help prevent system failures. You can also make this mechanism with your own hands. Let's look at how to make a check valve for a pump and sewer with your own hands, where the device is used and how it works.
DIY sewer check valve
The traditional scheme of operation of the sewer system provides for the removal of wastewater outside the premises.
Sometimes there are cases when water from sewer pipes flows back into the plumbing fixture due to a blockage. This can happen not only on the first floors of an apartment building, but also in country houses.
To prevent this phenomenon, experts recommend installing a check valve.
installing a check valve on a sewer pipe
As a rule, the higher the apartment is, the lower the likelihood of it being flooded by sewer water. The cause of a clogged riser can be various types of debris that does not dissolve.
As a result, all the contents begin to flow upward, flooding the neighbors above. By installing a check valve, you can save the situation. The principle of its operation is quite simple: wastewater passes through it, but does not come back out.
Such a plumbing element can be installed not only in an apartment building, but also in a country cottage.
Does installing a vacuum valve solve all problems?
Alas, no, of course not.
Let's return again to the fan pipe, made according to all the rules. It not only performs the function of equalizing pressure inside the system, but also provides effective ventilation. Its installation is highly recommended in the following cases?
- If the house has more than two levels (floors) with installed plumbing and sewerage running through all these levels.
- If for some reason you had to install a riser from a 50 mm pipe.
- If the house has a large tank, something like a sauna pool, which has to be emptied periodically.
- If the septic tank is located close to the house, and an unpleasant odor emanates from it into the living area.
That is, in such situations, the need for a vent pipe, in theory, should not even be discussed.
Sometimes homeowners are tempted to not bother with running pipes through the roof. That is, limit yourself to installing a vacuum valve at the top point. I must say right away - this is not the best option.
The aerator should be considered as a necessary measure when removing the drain pipe is impossible in principle. Or - to simplify and reduce the cost of a general scheme with several risers. There is no need to bring them all out through the roof to the street - one drain pipe will be enough, and on the remaining risers, high-quality valves at the highest point in the premises are quite sufficient. That is, ventilation will be provided - and the issue will also be resolved with vacuum.
Here is one acceptable solution to the problem: several risers, of which one goes into a waste pipe, and the rest are equipped with vacuum valves at their highest point.
Is sewer pipe ventilation really that important?
- Firstly, when organic matter decomposes, gases that are extremely dangerous to human health are released. And poisoning with such products, including fatal ones, is not at all such a rarity. It is better that they do not concentrate, but release into the atmosphere in a timely manner.
- Secondly, there is another pitfall. If there is no ventilation air circulation in the pipes, then the accumulation of fetid gases has nowhere to go, and sooner or later it will leak into the premises. A simple example: a family, having been out of town for the weekend, went to “winter quarters” for a week. During this time, water simply dried up (evaporated) from some very small siphon (say, a drain in a shower room or a siphon under a bathtub). And the beloved dacha greets its owners with a wild stench in the rooms, as gases accumulated in high concentrations from the sewer rush out.
And with a drain pipe, such large-scale troubles can be avoided.
* * * * * * *
Conclusion: a vacuum valve is a very useful element of the sewerage system, which in some cases allows you to significantly simplify the circuit and avoid breakdowns of water valves on long horizontal and other problem areas. But considering it as a full-fledged replacement for a waste pipe is unacceptable!
The reason is that it does not provide the necessary ventilation of the sewer line. Without this, talking about the usefulness of the system being created will still be an exaggeration.
Design and principle of operation of the fan valve
The air valve device includes:
- plastic case with a side hole;
- a cover that can be removed to clean the device or carry out repair work;
- rubber membrane or rod;
- a sealing gasket designed to seal the structure and limit the stroke of the rod.
The operating principle of the device is as follows:
- if the pressure in the riser is equal to atmospheric or slightly exceeds it, the valve is closed and does not allow gases from the sewer to pass into the room;
- when draining water from plumbing fixtures, a vacuum occurs inside the pipeline, resulting in the displacement of the rod (membrane) and the opening of the fixture;
- air enters through the valve, which equalizes the pressure. The rod begins to move in the opposite direction and closes the valve.
Based on their operating principle, air valves are divided into three types:
- automatic - used mainly for installation in small private houses, as they are not able to withstand strong water pressure and a significant volume of air. Works only to relieve accumulated air;
- kinetic (anti-vacuum) - designed for the release or intake of air in systems with low pressure levels;
- combined - combine all the best technological capabilities of the two previous devices.
Since the sewer line has vertical and horizontal sections, a ventilation valve with a different design of the operating mechanism is selected for each of them:
- ball aerator. The valve part has the shape of a ball, which is pressed against the bleed hole using a spring. Used for installation on horizontally located sections of small-diameter pipes at the connection point of plumbing fixtures;
- receiving model. The design of the device includes a filter designed to capture solid particles from wastewater and prevent them from passing further into the sewer system. Available with a diameter of 20 cm and used for installation in front of the pump of a horizontal pipeline line;
- Wafer aerator. This is a compact and lightweight device that can be placed both on a vertical riser and on a horizontal pipeline line. Depending on the design of the body, it can be through (the flow of water passes through it without changing its direction) and angular (when passing through the valve, the flow of the transported medium changes direction by 90º). Modifications with a plate-shaped locking organ have a diameter from 1.5 to 20 cm. The diameter of bivalve models ranges from 5 to 70 cm;
- check valve equipped with a rotary or petal mechanism. It has a shut-off element in the form of a spool, which, when the pressure in the system drops, is pressed tightly against the seat. Large diameter aerators can quickly break due to strong impacts of the spool on the surface of the seat. Continued operation of such a damaged device may result in water hammer in the system. To reduce the impact of impact, valves of large diameters are equipped with a damper.
The valves differ in the method of fastening:
- for welding. It is used in systems transporting particularly aggressive media of industrial enterprises;
- coupling - threaded couplings are used for fastening;
- flanged - the vacuum valve is clamped between flanges installed at the ends of the pipes;
- flanged with sealing gaskets.
Device
The operating principle of a vacuum valve for sewerage is quite simple. When a vacuum occurs, the valve is activated, opening the membrane. As a result, air enters the system and the pressure equalizes. When the situation normalizes, the membrane falls into place.
The standard aerator has a polypropylene body. The main element is the rod, the movement of which opens and closes the valve. The rubber gasket limits the movement of the rod, preventing it from rising higher than permissible. The second design option is a valve with a spring-loaded diaphragm, but this option is considered less durable.
Advice! The vacuum valve membrane wears out relatively quickly, so this part must be replaced periodically.
Two versions of aerators are available:
- for sinks, showers and other plumbing fixtures, a valve with a diameter of 50 mm is used;
- For installation on a riser, a model with a diameter of 110 mm is used.
Installation
The device can be placed in any suitable place at the top of the sewer near the riser. Please note that the distance between the vacuum valve and the riser should be less than that between the nearest plumbing fixture with a water seal and the riser. The valve can also be placed on a horizontal branch of the system near the last plumbing fixture. Most often, the vacuum valve is installed directly on the riser.
The only thing that is important to ensure is to create a tight connection between the socket and the valve and other connections with plumbing fixtures.
You can make this advice more specific:
- In the socket of a plastic sewer pipe (polypropylene or PVC), the tightness of the connection is ensured using a standard seal. It will be easier to assemble the pipe if you coat it with soap;
- For a cast iron pipe you need to buy a special rubber cuff. Cast iron pipes are a little more difficult to assemble;
- Connections between corrugated siphons and elbows are made by installing rubber cuffs.
Sometimes apartment residents want to install a vacuum valve instead of a drain pipe.
This can lead to a picture like this:
- It is convenient to solve difficulties with ventilation of the sewer system using a vacuum valve in 1 and 2 storey buildings. In multi-storey buildings the load is greater;
- In a multi-storey building, it is impossible to remove the vent riser and install a vacuum valve in its place without permission. As a result, it may turn out that residents of the first floors will constantly hear the smell of sewage. As a result, the relevant authorities will conduct an inspection of the system and demand that everything be restored.
Advantages and disadvantages
Vacuum valves have several pros and cons. The most important advantage is that it is designed to reduce costs when creating a sewer system. It is much more expensive to make and install a vent pipe, you need to buy a lot of materials and seriously change the layout.
Positive properties include:
- There is no need to punch a special hole in the roof, which makes it possible to keep it intact and simplifies the work on installing the sewer system;
- The riser outside the house will not be noticeable, which will improve the appearance of the building;
- The vacuum valve requires no maintenance or repair;
- A valve whose design uses a membrane will significantly improve the efficiency of the sewage system;
- You will reduce heat loss;
- Installation of the device is quick, operation is clear and easy.
This device has few disadvantages, but they need to be taken into account:
- The device cannot operate under heavy loads;
- The high cost of the vacuum valve.
It is foolish to think that by installing a vacuum valve you can get rid of all problems with the sewer system. It will certainly help if a drain pipe is not installed in a multi-story building. It will significantly reduce the cost estimate when building a country house (in this situation it is not advisable to install a fan riser, because the load on the sewerage system will be small).
It is advisable to use the valve when connecting a small number of plumbing fixtures to the sewer pipe. Ideally, install 2-3 devices. Otherwise, it may not always retain the unpleasant odor, and some of the “aromas” of the sewage system will penetrate into the premises.