Gutters are an integral part of all buildings, performing a very important function - draining melt and rain water from the roof surface .
If this is neglected, water can flow directly down the walls themselves and into the basement, which can lead to the destruction of the entire construction site.
In addition, the drain also plays a certain decorative role in the exterior of the entire building, so this fact must be taken into account during construction.
Organized drainage for a pitched roof - what is it and why is it needed?
Today there are several types of drainage:
- Disorganized.
- Organized internal.
- Organized outdoor.
External organized drainage is considered the most popular , so let's start the story with it. It is a whole system consisting of various gutters, drainage pipes, fasteners and other parts that secure the structure to the roof and walls of the building.
IMPORTANT!
The principle of operation of such a structure is quite simple, consisting in collecting water from the surface of the roof , after which it circulates through gutters, ending up in drainpipes. The water then moves through the pipes and then flows directly into the sewer.
This type of drainage has undoubted advantages over other types of drainage:
- The organized drainage system is completely thought out, so all the water ends up outside the premises, i.e. outside the building itself . This suggests that moisture cannot have a negative impact on the structure itself, which can significantly extend its service life.
- The system is designed in such a way that all fasteners are fully accessible , which greatly simplifies various repair work in the event of breakdowns.
- Organized drainage can be done on your own, without the involvement of third-party labor.
- An organized drain not only performs its direct function - it drains water from the roof, but also decorates the facade of the building . There are modern materials on sale from which the drain is made, so it is quite possible to choose the option you are interested in.
Elements of the drainage system
An organized external drainage system is very suitable for a pitched roof.
The following materials are most often used to construct this system:
- Galvanized metal. This material was most popular several decades ago, but is now gradually losing its position to more modern materials . The average service life of a gutter made of galvanized steel is 12 years.
- PVC or plastic. This material is now the most popular in the construction of gutters , which is explained by its low weight, as well as the relative ease of installation. The average service life can reach 30-35 years.
- Copper drain. This material outperforms all those named according to a variety of criteria, but there is one significant drawback - the high cost of copper itself .
- Metal-plastic. This material is considered relatively young, so it is not as widespread as the previous ones. However, it combines the advantages of PVC material and galvanized metal , and its service life can reach 50 years.
Drainage system
Drainage systems for a private home
Among the functions entrusted to roofing systems are drainage activities. The runoff of precipitation and melt water is facilitated by the slope, which is characteristic not only of pitched roofs, but also of flat roofs. However, the inclined configuration is not able to perform the work of protecting facades and blind areas with foundations. Guttering is required to protect structures below the roof.
Classification by degree of organization
In order for the result of the invested efforts to become a reason for well-founded pride, you need to understand the design subtleties and technological nuances of the drainage system.
According to the degree of organization, drainage systems are divided into two types:
- Unorganized. According to the unorganized scheme, the flow of precipitation and the results of snow melting occurs freely. Along all areas of slopes, water simply flows onto the blind area, ground or paved path, persistently causing damage to the property that is initially imperceptible.
- Organized. According to the organized scheme, all types of atmospheric water rushing down the slopes are captured by water receiving gutters or funnels. They are then transported through pipelines to points designated for the collection and disposal of stormwater.
Note that the SNiP regulation 06/31/2009 allows the use of an unorganized option in private construction. The regulations allow not to use a drainage system when arranging the roofs of one- and two-story cottages. True, eaves overhangs narrower than the full 60 cm are not allowed to be built, and entrance lobbies and balconies must be equipped with canopies without any dispute.
An organized option is required for buildings with a height of three meters or more, but zealous owners do not refuse it when equipping one-story houses and domestic buildings. It’s a worthwhile task if you put your own hands into it and it’s not too costly, and the benefits from it are quite real and economically tangible.
Organized drainage systems are, in turn, divided into internal and external options. Internal gutters are typical for flat roofs. External ones are universal, they are successfully involved in the arrangement of almost all types of roofing structures. We will carefully study their design and installation technology.
Design specifics of gutters
All external water drainage systems from roofs of any type and steepness include two main components, these are:
- Water intake devices. These include gutters, trays and funnels designed to directly collect water flowing from slopes.
- Drainpipes. Vertical sections of drainage designed to drain collected water with its subsequent transfer to a storm sewer or with the discharge of wastewater to the ground outside the blind area.
In the external drainage family there is also a division into systems with wall-mounted, mounted and remote gutters, but the only difference is in the layout of the water intake device. The wall-mounted option we are studying is most in demand as it is the simplest and most practical.
Hook-shaped brackets are used to attach drainage systems to the rafters, sheathing or front board of the roof being constructed. Clamps are used to secure horizontal sections of the drain. Together, a set of basic and fastening parts makes it possible to quickly and easily, like a designer, assemble and install a drain.
The choice of fasteners for fixing gutters depends on the type of construction work (repairs are being carried out or new construction):
- Long metal brackets are used when installing a drainage system before laying the covering. They are attached to the laths or rafter legs.
- Short metal brackets are used during repair work. They are fixed on the front board.
- Plastic hooks are used when carrying out repairs or during new construction, if a plastic drainage system is being laid. The plastic parts are attached to the front board.
The brackets are fixed with anti-corrosion fasteners with wide caps with a diameter of no more than 8 mm. Fastening is done with galvanized screws, self-tapping screws with press washers, and ordinary roofing screws. The diameter of the working part of the fastener is at least 4.2 mm.
The installation step of the hooks determines the material from which the drain is made. For metal systems it varies from 60 cm to 90 cm, for copper circuits that are sensitive to deformation from 30 to 60 cm. Under plastic gutters, hook holders are installed every 50 - 60 cm.
The drainage system kit can be purchased fully assembled and ready for installation. Its modular elements are produced so that from individual components you can easily build a drain for a roof of any size and configuration with your own hands. Using industrial prototypes as a template, you can make elements from available and available materials, for example, from plastic bottles, roofing sheet or polymer sewer pipes.
Drainpipes and water intake devices come with round, rectangular and combined cross-sections. Rectangular and combined types have greater “throughput”. This characteristic is not very interesting for private owners, because for the arrangement of cottages, the option with an oval gutter is most often sufficient.
The size of the drainage system depends on the area of the roof being treated:
- If the roof area does not exceed 70 m², then the gutter should be Ø 100 mm, and the Ø of the downpipes 75 mm.
- If the roof area is in the range from 70 m² to 120 m², then a gutter is needed Ø 125 mm, drainpipes Ø 90 mm.
However, when choosing the shape and cross-section of the system, it is not necessary to focus only on technical characteristics, because Gutters play a significant role in exterior design.
Materials used in production
The specific operation of external drains limits the choice of materials suitable for the manufacture of systems. It is clear that they will have to endure all the hardships of direct contact with atmospheric phenomena. This means that the elements of drains must be frost-resistant, “indifferent” to heavy rains, snow deposits and the scorching sun.
The following materials are used in the manufacture of drainpipes, water inlets and gutters:
- Roofing steel. The priority is galvanized options, sheet thickness 0.63 mm or 0.7 mm.
- Corrosion resistant roofing steel . Similar to the previous position, but with a protective and decorative polymer shell. In production, rolled sheet metal with a thickness of 0.6 mm to 0.7 mm is used.
- PVC . Light plastic gutters with a wall thickness of 2.2 mm to 3.3 mm are produced from polyvinyl chloride.
- Aluminum . The systems are made of lightweight durable metal 0.8 mm thick. The decorative and protective functions of aluminum gutters are performed by a polymer shell.
- Copper. An elite material that pleases with a service life of 150 - 200 years, but cools the dust at a respectable price. Wall thickness 0.6 mm.
- Zinc-titanium . A new word in the production of gutters with excellent performance characteristics. The price tag is also unmerciful, but the promised 100 years of trouble-free service make us take a closer look at the specified sales position with interest. The thickness of the material used in the manufacture is 0.7 - 0.8 mm.
The choice of a drainage system based on the type of material is focused not only on the personal preferences and financial capabilities of the future owner. To a greater extent, it depends on the type of roofing and architectural features of a private house.
Expensive copper and zinc-titanium options are appropriate on roofs with ceramic tiles, copper sheet roofing, and slate tiles. Budget PVC is in perfect harmony with soft roofing, steel gutters fit perfectly with metal tiles and corrugated sheets.
For purely economic reasons, gutters made of galvanized steel and PVC are most in demand. The first will last 10 years, the second 25 - 35 years, depending on the manufacturer’s assurances. It is difficult to select the optimal option for resistance to atmospheric attacks, because... their performance characteristics are very similar. However, metal is preferred in the northern regions, and plastic in the temperate climate zone.
There are no particular differences in the design and installation sequence between steel and polymer gutters. Almost identical gutters, pipes, and funnels are supplemented with specially produced bends, couplings, tees, and plugs.
You only need to take into account the fact of linear expansion that occurs when the systems heat up. Polymer ones can elongate 5 times more than metal ones, the linear movements of which can be completely neglected.
DIY options
The elementary design of a gutter is unlikely to puzzle the home craftsman. Everything is extremely simple: after meticulously executed markings, rolled sheet metal must be cut into strips and bent according to the preferred cross-section configuration. Cutting and bending can be done by hand, but it is wiser to do it on a bending machine.
You'll have to tinker with the pipes. They can consist of several links depending on the height of the pipeline section and the size of the sheet. The algorithm for making your own drainpipes looks like this:
- Open it up. It is carried out with special care and taking into account allowances for roller joints.
- Formation of longitudinal edges. Bends are made along the allowance lines for roller seams.
- Rolling out blanks. It is produced on roller machines or manually using a mandrel: a straight long pipe or bar.
- Roller seam connection. The rolled out blanks are connected according to the markings and pressed onto the previously used mandrel.
- Narrowing of one side of the link. They are narrowed by 5 - 6 mm so that the upper link fits freely into the lower element.
- Formation of stiffening rollers. They are formed along the upper and lower edges of the links by rolling wire. Produced manually or using a zigging machine.
- Assembling a drain riser.
Rolling out metal blanks will require the most effort if done manually. Each of the cut blanks is placed under a mandrel and, grasping the edges, is carefully bent in one place.
Having ensured that a sufficiently curved plane has been formed, the workpiece is moved 20º - 30º relative to the mandrel used. Then they bend it again until it takes the required configuration.
Making a drain from polymer sewer pipes is much simpler. They are produced with a fairly wide range of shaped parts suitable for the construction of full-fledged systems. In fact, the home craftsman will only need to make a gutter by dissolving a solid pipe into two symmetrical parts.
Organized flat roof drainage – why is it needed and how is it designed?
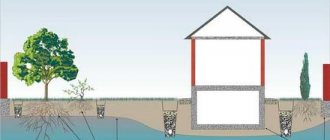
An organized drain for a flat roof is also necessary to collect water from the roof surface for its further transmission through drainage pipes. Water flows from the pipes into the sewer, into a water collection tank, or directly onto the ground itself.
The service life of a flat roof directly depends on the quality of the drainage system. That is why it is very important to follow the basic recommendations when installing drainage systems.
Installation of drainage on a flat roof is carried out in two ways:
- On overhangs located just below the surface of the roof itself.
- On specially equipped ledges.
The essence of the first method is to locate the funnels in close proximity to the roof overhang. In this case, the water flows through drainpipes, which are installed in channels under the funnels.
NOTE!
External drainage on flat roofs can only be installed in regions with warm climates . If the climate is moderate or cold, then it is more advisable to design an internal roof drain, because with an external system the water will freeze, thereby creating ice jams.
Organized internal drainage
Design and types of drainage systems
Structurally, any drainage system consists of a pipe, gutters and drainage funnels. Once in these elements, water from the roof surface is sent to the storm drain, where its impact will no longer harm the building.
There are three basic diagrams of the drainage system:
- Unorganized drainage of rainwater from the roof . This design, which is also called spontaneous, in accordance with its name, ensures independent drainage of water from the roof. A distinctive feature of spontaneous drainage is its simplicity - nothing needs to be installed to ensure drainage. The problem is that the flowing water washes away the building, damages the wall finishing and negatively affects the waterproofing layer.
- Organized external drainage of water from the roof . This is a classic design consisting of a drain pipe, a gutter and several funnels that are connected to a storm drain. As a result of installing an organized external drain, water is collected from all slopes and removed from the roof surface. External drainage is quite simple to install and maintain.
- Organized internal rain drainage from the roof . The main difference between an internal drain and an external drain is the installation of structural elements in the building itself in such a way that they are not noticeable. As a rule, such a drain is installed in the case of flat roofs. Installing an internal drain is complicated, and maintaining it will be very difficult, especially if mistakes were made during the installation.
Installation rules and standards (SNiP)
Organized internal drainage is a fairly popular method of drainage from roofs, because it can be organized regardless of the climatic conditions of the region.
Such a system includes several parts:
- a funnel into which flowing water flows;
- riser;
- outlet pipe;
- release.
Here are some recommendations that will be useful when installing this drainage system:
- It is necessary to divide the entire roof surface into sections.
- One drain pipe should go for every 200 square meters of roof space.
- It is necessary to maintain the slope of the roof to the water intakes - it should be about 2%.
- A collector must be constructed under the building to collect water, which must also be connected to the main sewer system.
- When installing the system, you can use pipes of a certain diameter and length. The allowed diameters are 10, 14 and 18 cm, and the length must be 70 or 138 cm.
- In order for the system to operate reliably all year round, all risers must be located in a heated area.
- The funnel must be built into the roof hermetically so that water does not seep through the cracks.
Don't forget about regular drain cleaning.
Gutter installation
Internal drain
This is a mandatory element of flat roofs.
In this case, the drainpipes are located inside the building. In houses made of reinforced concrete panels, they are located on the stairwells outside, and in brick houses they are hidden in grooves, which are included in the project and made during the construction of the walls. After installing the drainage system, they are laid with bricks or covered with plasterboard.
The drain of such a system is most often connected directly to the drainage well, but there are cases when it goes out onto the street from the base of the building.
Special requirements apply to drainage funnels. The role of the gutter on flat roofs is played by the ramp, although in houses with a technical floor there is also a large central gutter in which the funnels are located. They must have a sealed connection with the drainpipe, and a pressure flange with the roof waterproofing. On inversion roofs, two-level funnels are used to collect water from both the waterproofing layer and the ballast layer.
Drainpipes were previously made of cast iron, but now plastic has become widespread. These are ordinary sewer pipes, but they do not corrode and can last almost forever.
Sometimes a siphon is built into the internal drainage system, creating a water plug, similar to the siphon of a domestic sewer. It creates a vacuum effect, due to which water does not accumulate at the funnel, but is sucked inside.
Unorganized drainage - what is it, advantages and disadvantages
Unorganized roof drainage involves the random flow of water from the roof directly onto the ground . This is achieved by a certain slope of the roof, while there are no structures or pipes for collecting water.
This method of drainage involves minimal costs, but there are a number of undeniable disadvantages:
- Such drainage can lead to destruction of the foundation , because water will freely penetrate into its structure.
- It is necessary to periodically change the waterproofing layer of the basement of the building, because water will get there too.
- It is also necessary to provide an additional layer of waterproofing of the walls so that moisture does not destroy their structure.
It would seem, why arrange such a drainage system at all if there are so many shortcomings in it? However, such drains are found everywhere, but there are a number of factors that influence the feasibility of installing such a system:
- The building should not have more than five floors .
- The region should not be very rainy - no more than 300 mm of precipitation per year .
- Such a drain can be installed on a pitched roof . In addition, there should be no paths or balconies under the slope.
- The roof canopy must be of sufficient length - at least 600 mm . This will provide at least minimal protection of the walls from moisture.
Unorganized drainage system
How does the drainage system work?
We have already said that you can easily build an external organized drain with your own hands. To do this you will need the following elements:
- Pipes for draining water. In this case, it would be more advisable to use plastic pipes, because they are much easier to install.
- Sealant for lubricating cracks and joints.
- Gutters.
- Clamps and brackets holding pipes.
- Adhesive composition.
- Funnels.
- Anti-icing system.
Along the entire perimeter of the slope, it is necessary to install special brackets that will hold trays for drainage of water. They are installed at a distance of 50 cm from each other, and attached to the board or to the last element of the roof sheathing.
The tray must be installed at a certain angle to the funnel with the riser so that the water flows down it on its own. The riser can be installed at an angle or straight, there are no special recommendations for this.
Drainage system design