Hello again!
The technology for connecting metal and plastic in main pipes is only about 40 years old. On a planetary scale, this is not a period of time at all. But throughout this entire period, metal-plastic pipes have enjoyed enormous popularity, and today metal-polymers deservedly occupy a leading position in the field of arranging water supply and heating communications.
Let's get to know them better.
Structure and manufacturing technology
The secret of unquenchable consumer demand lies in a unique structure that combines the beneficial properties of metal and polymer - strength and flexibility.
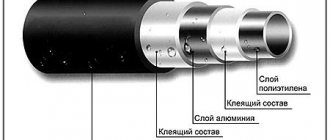
To understand the design of a metal-plastic pipe, just look at its cut. Even with the naked eye, 5 main layers are clearly visible:
- The middle aluminum or mesh frame layer, which is the “skeleton” and barrier element of the entire structure.
Among other things, the aluminum foil layer prevents the effect of oxygen diffusion and minimizes the effect of thermal expansion of the polymer due to exposure to high temperatures.
- Internal and external plastic.
In addition to additional strength, plastic serves to protect the metal layer from corrosion, which inevitably occurs during prolonged contact with water and when using fittings made of steel or brass. Also, the polymer coating prevents the formation of condensation and reduces the heat transfer index of the metal pipeline, making it safe and energy efficient when transporting hot coolant.
- Two adhesive layers that bind the polymer and aluminum together.
What are the disadvantages of metal-plastic pipes?
Metal-plastic pipes:
- Subject to mechanical damage;
- Less durable and have lower temperature resistance compared to copper and steel counterparts;
- Linear expansion coefficients are 2.5 times higher than those of steel pipes;
- When burning, metal-plastic pipes release large volumes of CO2 gas;
- In cases of long and active exposure to strong high-frequency and electric fields, gamma rays, and sunlight, the layers of metal-plastic pipes wear out prematurely;
- Not resistant to organic solvents and oils;
- Metal-plastic is not used for grounding;
- The structure may break if it is installed incorrectly, or if the permissible bending radius is exceeded;
- Brass fittings inside metal-plastic pipes may become unusable if the liquid in the pipeline freezes;
- Crimp connections are not capable of embedding, so they need to be serviced (tightened);
- To install press connectors, press pliers (manual or electric) for metal-plastic pipes are required;
- They have lower temperature resistance compared to analogues made of copper and steel;
- Over time, the layers of cross-linked polyethylene wear slightly;
- The local resistance coefficients of fittings are higher than those of connectors for steel, copper and polypropylene;
- Metal-plastic has less heat transfer compared to copper in underfloor heating structures (all other things being equal);
- Due to the apparent simplicity of installation, the work is often performed by installers with insufficient qualifications.
Production process
The production of metal-plastic (multilayer) pipes is carried out on special automated industrial-type flow complexes. Moreover, during the manufacturing process, not only the products are formed, but also they are computer checked for compliance with quality standards.
- First of all, a metal base (frame) is formed from aluminum foil.
- Then the aluminum billet is sent to the compartment, where its edges are joined using ultrasonic welding.
- By injecting air into the resulting pipe (under a pressure of 4-6 atmospheres), the strength of the weld is controlled.
- After checking, the workpiece enters the extruder, where an adhesive and polymer layer is gradually applied. First, the inner surface of the aluminum billet is processed, then the outer surface. At the same stage, a marking strip - blue or red - is applied to the product.
- At the final stage, the product is cooled: first with air, then in a water bath.
- At the exit, the pipe goes to the so-called quality control department, where the “scanning” and measurement of the geometry of the layers takes place.
- Finally, the product is labeled and wound into coils.
What does MP pipe consist of?
A metal-plastic pipe is a product in the form of a complex five-layer structure. Each of the existing layers performs certain functions.
MP pipe structure
Outer polymer layer
The outer layer is presented in the form of a pipe made of particularly durable plastic (polymer material). It protects the product from mechanical damage, exposure to chemically aggressive substances and reduces its thermal conductivity, thereby reducing the intensity of condensation formation on the surface of the pipe.
Intermediate aluminum layer
The aluminum pipe serves to increase the rigidity of the product, partially compensate for its thermal expansion during operation, and also prevents the penetration of oxygen from the environment.
Inner polymer layer
Increase
The inner tube is made of food-grade plastic and has a particularly smooth surface. This reduces the internal resistance of the pipe when liquids flow through it and prevents the formation of deposits in the form of scale and rust.
Adhesive layer
Layers of adhesive composition between the aluminum pipe and the outer and inner polymer layers ensure reliable connection of all layers, forming a single, durable structure.
The following are used as external and internal polymer layers:
- most often - high-density cross-linked polyethylene (PEX);
- less often - polymers made of heat-resistant polyethylene (PE-RT), polyethylene (PE-R) or polypropylene (PP-R).
Specifications table
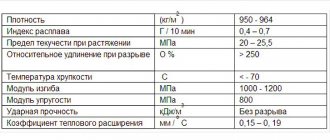
Today, metal-plastic pipes are presented on the market in a very wide range, and each modification is characterized by its own technical parameters, and therefore its scope of application. However, there are indicators that are common to all types of composite reinforcement. They are established by GOST R 53630-2009, and deviation from these standards indicates the low quality of the pipe material:
| Standard parameters of metal-plastic (multilayer) pipes | |
| Transverse tensile strength | 2880 N |
| Weld strength | 57 N/mm² |
| Bond strength | 70 N/10 mm |
| Linear expansion coefficient per 1°C | 0,26×10-4 |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.43-0.45 W/m K |
| Material surface roughness index | 0,007 |
| Oxygen diffusion | — |
| Resistance to delamination of the inner layer of polymer and metal | not less than 50 N/cm |
| Resistance to delamination of the outer layer of polymer and metal | not less than 15 N/cm |
| Flammability class | G4 |
| Flammability class | AT 3 |
| Smoke emission class | D3 |
| Toxicity class of combustion products | T3 |
The appearance of the product also characterizes its quality:
- Both inside and outside the surface should be flat and smooth. Cracks, gouges, bubbles and scratches indicate a significant disruption of technological processes, which will ultimately reduce the strength of the main pipeline.
- Inclusions in the polymer mass that are visible to the eye and uneven coloring indicate a poor quality polymer composition.
Dimensions
Based on standard size, there are 2 groups of composite pipes:
- Small, the outer diameter of which is in the range from 10 to 63 mm.
- Medium with an outer diameter in the range of 75 – 110 mm.
Products are supplied in coils, the footage of which varies depending on the diameter. Minimum length – 50 m, maximum – 200 m.
The most popular are pipes with a cross section of 16-32 mm. Below we compare their technical and operational properties:
| Dimensions | Outside diameter | |||
| 16 mm | 20 mm | 26 mm | 32 mm | |
| Metal layer thickness, mm | 0,2 | 0,25 | 0,3 | |
| Weight 1 l.m., g | 115 | 170 | 300 | 370 |
| Capacity (water volume) 1 m.p., l | 0,11 | 0,2 | 0,315 | 0,53 |
| Coil length, m | 200/100 | 100 | 50 | |
Inner diameter
When choosing a suitable pipe, you should focus on its internal diameter, which determines the hydraulic performance of the system. The internal cross-section of any pipe depends on the thickness of its wall.
| Pipe dimensions | Pipe outer diameter, mm | |||
| 16 | 20 | 26 | 32 | |
| Wall thickness, mm | 2 | 3 | ||
| Inner diameter, mm | 12 | 16 | 20 | 26 |
Permissible temperature and pressure
Operating parameters such as operating pressure and temperature are interrelated. The hydraulic performance of the pipeline depends on the temperature the composite pipe can withstand:
| Media temperature | Maximum circuit pressure |
| 25-95 °C | 10 bar (1 MPa) |
| 0-25 °C | 25 bar (2.5 MPa) |
A short-term increase in the temperature of the working environment up to 110⁰C is allowed. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures destroys the integrity of the multilayer structure, causing delamination.
Marking
During the production process, each product is marked with an indelible marking, which, for the convenience of the consumer, is repeated along the entire length of the pipe. Depending on the country of origin, it may differ slightly.
However, there are a number of basic operational characteristics that must be reflected in the marking code:
- Manufacturer's name.
- The standards to which the product is manufactured.
- Type of material from which it is made:
- PP-R – polypropylene.
- PE or PE-R - polyethylene.
- PE-X – cross-linked polyethylene (additional letters “a, b, c or d” indicate the method of “cross-linking” polyethylene).
- PE-RT – heat-resistant polyethylene.
- PB - polybutene.
- AL – aluminum.
- Size: outer diameter and wall thickness (in millimeters or inches).
- Nominal working pressure.
Additionally, the following may be indicated:
- Area of use: heating, water supply (technical or drinking).
- Temperature regime.
On a note! In some cases, the temperature marking is a colored line soldered into the outer polymer casing. Blue color means that the product is intended for transporting cold media (temperature no higher than 25⁰C). Red color indicates the possibility of using the product for heating or hot water supply.
Production date and batch number.
Life time
With proper operation, the guaranteed service life of a metal-plastic pipeline is:
- 25 years in heating and hot water supply systems.
- 50 years – in cold water systems.
How to choose metal-plastic pipes for water supply
The choice of metal-plastic products should be approached taking into account the following characteristics:
Reinforcing layer thickness
If we need to understand the concept of the quality of metal-plastic pipes and make a choice accordingly, then it will be useful to first study their structure. Metal-plastic pipes have five layers in their structure, three are main and two are binders. Main layers:
- Internal (polymer materials);
- Load-bearing or reinforcing (aluminum);
- External (plastic).
Layers of metal-plastic pipe
The reinforcing layer serves for:
- Protection against linear expansion caused by heating of the plastic;
- Oxygen-proof thanks to the aluminum layer;
- Protection against damage caused by external careless actions (bending pipes during installation, mechanical loads) or due to changes inside pipes, such as pressure surges. The aluminum layer in manufactured products can have different thicknesses: from 0.15 mm to 0.6 mm.
If for metal-plastic pipes the thickness of the reinforcing layer is in the range from 0.3 to 0.55 mm, then such products will be the best option. They have very high strength, although it has been noted that during installation they exhibit relative “softness” and flexibility.
Pipes with a thicker supporting layer are more expensive and their installation is quite labor-intensive. Products with an aluminum layer thickness of less than 0.3 mm are dangerous because they can be damaged even when slightly bent.
Read the material on the topic: Supplier of engineered plumbing: criteria for the right choice
Aluminum joining method
When making pipes, metal is joined by welding. It can be laser or ultrasonic. There are two ways to join metal: butt and overlap. When laser welding, metal is joined end-to-end, and then the pipes are called seamless. In the process of ultrasonic welding, the metal is joined with an overlap, after which a seam remains, which is why such pipes are called seamed.
Seamless metal-plastic pipes can have an aluminum layer of any thickness. When joining aluminum with an overlap, the thickness of the reinforcing layer must be reduced to compensate for the thickening.
These manufacturing features have a negative impact on the durability of the products, reduce the service life of the pipeline, and complicate the installation process due to the fact that the pipes are not equally ideal along their entire length.
Material of outer and inner layers
The material from which the inner and outer layers of metal-plastic pipes are made is also of great importance. In most cases, cross-linked polyethylene PEX or linear polymer PE-RT is used in production. This material has improved properties, thanks to which the products become more durable and reliable, and become more resistant to environmental influences, as well as to significant temperature loads. Products made from PEX or PE-RT materials are guaranteed to maintain their high quality for a long time.
PEX or PE-RT pipes will last a long time.
In the manufacture of metal-plastic pipes, low-density polyethylene (PE, PEHD, HDPE, PE-RS) is also used. It should be noted that it is not particularly durable or heat-resistant.
This material also does not have resistance to direct sunlight, as a result of which it wears out quickly. Products made from PE-RS polyethylene have operating temperature restrictions: the temperature should not exceed 75 C, otherwise the polyethylene will begin to melt, which can lead to deformation and subsequently rupture.
There are many offers on the market from European manufacturers with low prices for their products. The reduction in cost occurs due to the use of low-density polyethylene in the manufacturing process of pipes.
It may seem that manufacturers are thus reducing their production costs by deliberately lowering the quality of the products they offer. But the fact is that PEHD pipes are not suitable for all types of pipelines. For such products, it is necessary to comply with special conditions, which narrows the scope of their application, which is why the price also drops.
Quality of binder layers
The quality of the bonding layers is determined by the amount of effort expended in order to separate one layer from the other.
When choosing metal-plastic pipes, you need to pay attention to the connecting layers. They are one of the important components of the quality of metal-plastic products.
The main task of the connecting layers is to give the pipe integrity by connecting its main layers: internal, reinforcing and external. The quality of the product directly depends on the condition of the binder layer and how flawlessly this element is made.
How to choose the best metal-plastic pipes, taking into account the condition of the connecting layers? The answer is simple: do not choose in favor of those products, upon inspection of which you saw signs of delamination. Peeling is the first reason for the fragility of the future pipeline.
Manufacturer's choice
In many countries you can find manufacturers of metal-plastic pipes. Such countries include Russia, Germany, Italy, China, Turkey and others.
Most manufacturers have the necessary experience and knowledge to withstand competition in their niche. Manufacturers, of course, assign a huge role to the quality level of their products.
An important factor in choosing one manufacturer or another will be the price. The difference in price plays a significant role when purchasing material for long-distance pipelines.
Information on prices for metal-plastic pipes is available directly on the websites of manufacturers or their official dealers.
You need to understand that the price per meter for metal-plastic pipes is determined not in accordance with quality, but mostly in connection with the degree of brand recognition and the duration of its presence on the market.
Therefore, we often find exorbitant prices on the market for metal-plastic pipes, sometimes exceeding 600 rubles per meter.
Naturally, this price is much too high, and therefore in reality you can find products of the same quality for 50 rubles per meter.
Turkish and Chinese manufacturing companies, such as AQUAPIPE® and LTM, are known for their affordable prices with a decent level of product quality and compliance with all necessary standards.
On our website you can find a catalog containing a detailed description of each product separately and a presentation of the entire range of products as a whole, as well as prices for each product, which will help you make the right choice in accordance with your requirements and wishes.
Read material on the topic: How to choose heating pipes: types, criteria, manufacturers
Application area
The scope of application of composite pipes is not limited to the organization of heating and plumbing distribution. Today these products are actively used:
- In the industrial sector for transporting compressed air, gas mixtures or chemical liquids.
- For arranging protective lines when laying cables for various purposes.
- When installing ventilation and air conditioning systems.
- In irrigation systems.
Need for standardization of pipe measurements
The main goal of establishing standard product dimensions, including wall thickness, length, external and internal diameters of pipes, is to simplify the work with these products at all stages: from design to circuit arrangement, scheduled or unscheduled repairs and dismantling of the system.
In order not to set impossible tasks and not to overly complicate the production of products, GOSTs and TUs regulate only the basic, most necessary dimensions of pipes, in accordance with which designers carry out all further calculations.
Restrictions on use
However, it should be taken into account that the limited technical characteristics of metal-plastic pipelines also impose some restrictions on their use. This is how they cannot be used:
- In heating circuits or DHW systems with a working environment temperature above 110⁰С.
- In close proximity to sources of thermal radiation when they are heated above 150⁰C.
- In heating systems equipped with an elevator unit.
- For the installation of safety, signal, expansion or overflow lines;
- As chimneys.
- For the installation of fire protection circuits, as well as in buildings of low fire safety category (class G).
The outer and inner diameter of the pipe and the purpose of the product.
1. A pipe with a diameter of 16 - 12 has an internal cross-section of 12 millimeters and an external cross-section of 16 mm. The thickness is two millimeters, the aluminum layer is 0.2 millimeters. Used for laying hot and cold water supply in a private house.
The products are used for meters and to supply water to mixing structures. In the apartment, these pipes are used to make wiring for the kitchen or bath.
Important! The pipes do not deposit layers of dirt and silt inside and have high strength, which allows them to withstand heavy loads. The products have a low price compared to larger pipes, but they have the same throughput. The pipes are in the form of coils, a minimum of fifty meters long and a maximum of two hundred meters.
2. A pipe with a diameter of 20 - 16 has an outer diameter of twenty millimeters and an inner diameter of 16 mm. The thickness of the foil layer is 0.25 millimeters. They are used for water supply in an apartment or country house, so it is cheaper to use a 16 mm analogue outside. Pipes are also used in heated floors if the water pressure is weak or the pipeline network is long. The disadvantages include the high price of fittings to hold the parts together during installation.
3. Pipes with a diameter of 26 - 20 have a forming layer of three millimeters.
Used for installation of risers in heated floors. In private homes, there are pressure differences in the network, so pipes with a cross-section of twenty-six millimeters are the most suitable.
4. Pipes with a diameter of 32 - 26 are installed in systems that transport large volumes of water, because the products have a high throughput. Water flows through the system at a uniform speed, flowing uninterruptedly to consumers. Used for risers, for installation of the main water main, for heating devices.
5. Pipes with a diameter of 40 - 32 are installed in central heating networks, water supply systems, ventilation systems, to insulate power lines in places with difficult access. They can serve for many years without inspections or repairs.
Pipes can transport aggressive liquid compositions, so they are used for laying a sewer system.
6. Pipes with a diameter of 50-40 have an outside size of 48 millimeters according to the standard, but in practice they take a size of 50 millimeters. The internal cross-section is 48, with a pipe thickness of 4 millimeters. Capable of handling large volumes of liquid, they are used for laying communications in industries.
They can transport harmful liquids and various gases, having high pressure in the system. They are often used in industrial applications, although they have limitations for use.
Advantages and disadvantages
Metal-polymer pipes have many advantages:
- Anti-corrosion. The polymer coating is not prone to corrosion even in aggressive environments.
- Inertness of polymers to the transported medium.
- Plasticity and, as a consequence, the ability to make do with a minimum number of connecting elements when laying a pipeline.
- The strength of both the pipe itself and the main circuit, because the fewer fittings there are in the main, the more reliable it is.
- The ideal smoothness of the surface prevents the deposition of various types of sediment inside the pipes, and this, in turn, does not lead to a narrowing of the passage opening and does not reduce the throughput and hydraulic pressure of the circuit.
- Low thermal conductivity.
- No effect of stray currents.
- Silence.
- Light weight, which means minimal load-bearing load on the building.
- Aesthetic appearance that does not require painting throughout its entire service life.
- Long service life.
- Safety for humans.
- Easy installation and maintainability. Minimum percentage of waste.
Of the minuses it should be noted:
- Sensitivity to temperature changes. Frequent surges, especially those accompanied by exceeding the temperature standard, cause delamination of composite pipes.
- Susceptibility to ultraviolet radiation.
- Intolerance to sub-zero temperatures requires thermal insulation of pipelines laid outdoors.
- The need to comply with standards when bending pipes.
- Insufficient strength of threaded connections limits the use of metal-plastic lines inside walls. For these purposes, special press fittings should be used.
Kinds
Depending on the type of material used to reinforce thermoplastics, composite pipes are:
- Reinforced with aluminum foil.
- Reinforced with metal mesh.
A foil-based product is more flexible and therefore most convenient for use in private construction. A rigid mesh frame increases strength but reduces flexibility, so it is more profitable to use such pipes when laying straight sections of highways.
Tips for choosing
When choosing a metal-polymer pipe, you need to be guided by the operating conditions in which it will be used.
- If we are talking about the arrangement of low-temperature networks, then there is no point in splurging on expensive types of polymers. PPR polypropylene or PER polyethylene are quite suitable.
- For hot water supply and heating, the best option would be products made from PEX or PERT polyethylene.
- If you plan to take the pipeline outside, it is better to take polybutene (PB) pipes.
When determining the required diameter, you can use the following recommendations:
- For small pipeline networks used in apartments and private houses, diameters of 16, 20, 26 mm are used. In this case, for the main main circuit and installation of risers, a pipe with a cross-section of 26 mm is taken, and with smaller diameters, network household and other appliances (radiators, plumbing fixtures, mixers, etc.) are connected.
- When connecting network equipment to pipes, the diameter of the latter is taken into account, and only then is the transition to a new standard size made.
- For long highways, pipes with a diameter of 32 and 40 mm are used.
- For heated floors, pipes with a cross section of 20 mm are used.
In any case, it is better to give priority to proven brands.
Characteristics of metal-plastic pipes
The main characteristics of polymer and aluminum pipes include:
- Inner diameter. Necessary for connection with fittings and other components. Characterizes the throughput of the pipe.
- Outer radius. They pay attention to it when taking measurements and purchasing a product. Indicators vary between 16-63 mm.
- Layer thickness. It is selected taking into account the cross-section and can be 2-3.5 mm.
Additional characteristics:
- Bend radius. It has different sizes: from 80 mm with an outer section of 16 mm to 550 mm with a diameter of 40 mm. Data is given for manual pipe bending. When using a pipe bender, the radius may be larger.
- The amount of liquid per 1 running meter is determined in liters and depends on the characteristics of the product.
The best manufacturers
| № | Manufacturer | Brand | Manufacturer country |
| 1 | Rehau | Rehau | Germany |
| 2 | Kermi | Kermi | Germany |
| 3 | Oventrop | Oventrop | Germany |
| 4 | Uponor | Uponor | Finland |
| 5 | HENCO | HENCO | Belgium |
| 6 | VALTEC | VALTEC | Italy |
| 7 | Unidelta | Deltall-ISO | Italy |
| 8 | Valsir | Pexal | Italy |
| 9 | Valtec | Valtec | Italy/Russia |
| 10 | MPT-Plastik R | Liral | Russia |
| 11 | Nefteprom | Altais | Russia |
| 12 | HydroSta | HydroSta | South Korea |
Installation features
Let's look at the key aspects of installing composite pipes:
- The installation of the contour should begin from the entry point.
- Due to the difference in the expansion indices of metal and plastic, metal-polymer pipes cannot be laid stretched.
- It is better to use press fittings for joining pipes; they provide a stronger and tighter connection than conventional crimp fittings.
- The installed pipeline is fixed to the wall using fasteners in 1 m increments.
The process of bending composite pipes requires special attention.
- Bending of metal-polymer pipes is carried out manually or using special tools - a pipe bender and a spring:
- The first method is used when a large radius bend is needed.
- The pipe bender is used for small bending radii.
- The spring is used in both cases, but provided that the end of the pipe is close to the bend point, so that the spring can then be easily removed.
- The following actions are prohibited:
- Multiple bending.
- Twisting of pipes along the central axis.
- For each pipe diameter and bending method, standard bending radius values are established, violation of which increases the likelihood of damage to the pipe structure.
| Pipe outer diameter, mm | Allowable bend radius, mm | Minimum bend pitch, mm | ||
| Manual method | With a spring | Using a pipe bender | ||
| 16 | 80 | 50 | 45 | 50 |
| 20 | 100 | 65 | 60 | |
| 26 | 130 | 105 | 95 | |
| 32 | 160 | 135 | 125 | |
| 40 | 550 | 220 | 180 | |
- Compensation loops must be installed at bends.
How to install metal-plastic pipes
Press fittings for metal-plastic pipes contribute to their better connection during installation. This is especially important when laying heated floors and between walls, that is, for hidden installation of pipelines. Fittings are installed using special press jaws. Below we will tell you more about this tool.
All types of press pliers have a similar principle of operation: they mechanically compress a metal sleeve, which is installed on the pipe in the connecting part with the fitting.
The connecting fitting is installed in a pre-prepared pipe, and a crimp sleeve is placed on top.
The crimping head of the press pliers is placed on the sleeve; under the influence of the drive, it compresses the metal sleeve with equal force along its entire circumference.
As a result, the shell of the metal-plastic pipe is tightly clamped between the fitting on the inside and the sleeve on the outside, resulting in a continuous and tight connection.
Reviews
| Review of reviews on composite pipes | |
| Positive | Negative |
| Convenient, quick installation | Deformation due to excessively high temperatures |
| Practical and inexpensive | Connections weaken over time |
| Allows you to hide wiring in the wall | Undesirability of hidden installation of pipes for water supply and heating in walls |
| No rust | |
| Aesthetics, easy care | |