Quite often it happens that the site has high-lying groundwater or there is no space to organize filtering devices in the garden, then a drainage ditch or a low-lying section of the relief can be used.
It is on such an area that wastewater can be discharged onto the terrain; however, one must not forget that there are special standards for this process, which are, in principle, the same as the standards for the discharge of wastewater into a reservoir.
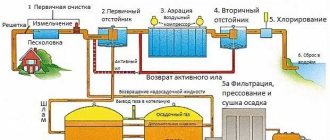
Wastewater drainage diagram
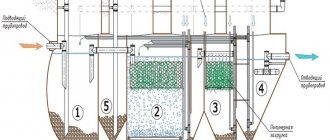
Scheme of wastewater treatment on water-resistant soils: 1 - irrigation pipe; 2 - filter layers of crushed stone and sand; 3 - soil; 4 - drainage pipe; 5 — ventilation risers; 6 - disinfection well; 7 — chlorine cartridge; 8 — discharge pipe; 9 - stone embankment.
You should also take into account the distance at which residential buildings are located on neighboring plots, since your drains will emit an unpleasant odor, causing you a lot of problems that will end in a meeting in court. That is why it is necessary to have the highest quality and highest degree of wastewater treatment.
Most often, in such cases, it is recommended to use aerobic reactors with different configurations, however, they also cannot always provide the required quality of treatment of economic and domestic wastewater.
SNiP (building codes and regulations) allocates fifty meters for the sanitary protection zone, of course, if the productivity of aeration structures is no more than 700 cubic meters.
Of course, drainage may not always be able to be drained by gravity and may need to be pumped using the sump pump of choice. The truth is that if the electricity is turned off, the sewerage system will be unusable.
Advice! If you still decide to discharge wastewater onto the terrain, then you should line the pipe with insulation and tilt it in the direction in which the treatment facility is located. The end of the pipe must be made higher than the ditch so that water does not freeze at the outlet.
Integrated solution for domestic and industrial wastewater treatment schemes
1 - populated area; 2 - industrial enterprise; 3 - group treatment facilities; 4 - joint cleaning at aeration stations; 5 – post-treatment facilities; 6 — return of treated wastewater to the recycling water supply system
Before discharging wastewater onto the terrain, you should know what conditions exist for receiving wastewater.
- All sewerage systems in populated areas are designed to receive and transport industrial and domestic wastewater. The sewerage system is not allowed to receive and transport drainage water and surface runoff from industrial sites and urban areas.
- The list of concentrations of pollutants that are maximum permissible is established based on the following:
- standards for maximum permissible discharges of harmful substances at the outlets of sewerage systems into water bodies, depending on the Main Directorate of Natural Resources and Environmental Protection of the Ministry of Natural Resources of the Russian Federation, treatment carried out at wastewater treatment plants is also taken into account;
- permissible concentrations of pollutants for biological treatment and sewerage.
- Conditions are also affected by:
- requirements and properties of discharged water received by the sewerage system;
- standards for pollutants that are accepted into the sewer system;
- list of substances prohibited for discharge into the sewer system.
- It is necessary to provide information on pollutants discharged into the sewer system every quarter no later than the tenth day of the month following the reporting quarter.
- The properties of wastewater are general and are established uniformly for all waters, regardless of where the wastewater is discharged.
- Standards for hazardous substances are calculated differentially, taking into account the category of subscribers, the number of services for discharging wastewater into sewers, as well as the receivers into which they are discharged.
- The standard on which the volume of wastewater received from subscribers depends is calculated depending on the water disposal limit.
- All subscribers are divided into two categories:
- those who own or manage the housing stock;
- those who have sewerage treatment facilities and those who do not have such facilities.
Treatment of wastewater from cottages
Also, in order to be able to discharge water onto the terrain, treatment of natural and waste water is required . This can be done using adsorption, which can reach most types of contaminants, regardless of their concentration, even if it is small.
Adsorption is very often used for water and wastewater treatment. Thanks to adsorption, substances that impair the odor and taste of water, insecticides, herbicides, viruses and bacteria are removed.
Using adsorption, industrial wastewater that contains organic impurities such as benzene, phenols, aliphatic amines and other compounds is effectively treated.
Adsorption is also very beneficial in technical and economic terms in order to extract substances from multicomponent mixtures. Adsorption is also used for complex purification schemes for domestic water from the organic compounds it contains, and is suitable for the final stage of purification, when the water contains only small concentrations of such substances.
This is achieved using activated carbon, which concentrates organic substances remaining in the water on its surface, which makes water of high quality.
Conducted research has proven that as a result of dynamic adsorption, which takes place on active carbon and is used for wastewater treatment, thanks to which it is possible to discharge wastewater onto the terrain, biological processes also occur, and not purely physical and chemical ones.
Organic substances that are adsorbed on active carbon in the presence of oxygen, dissolved in water, serve as a nutrient medium for the development of aerobic microorganisms, while organic substances are oxidized.
Since microorganisms develop on the surface of active carbon grains, a biological film also forms, which gradually clogs the pores of the carbon, thereby preventing subsequent adsorption of substances. Sometimes it is necessary to regenerate coal.
It was also noted that when filtering water during deep purification in real conditions, active carbon regenerates itself . At the same time, the adsorption filter can operate for a very long time without regeneration. The film that grows on top gradually prevents the flow of oxygen into the film, and oxygen is necessary for the respiration of aerobic microorganisms.
This creates conditions for the development and activity of anaerobic microorganisms. Thanks to them, incomplete oxidation of organic substances to low molecular weight substances occurs.
Due to their low adsorbing energy, low molecular weight substances are effortlessly desorbed into the daily liquid from the surface of the coal, where they are then destroyed by aerobic microorganisms due to the presence of oxygen. As a result, the coal is biologically regenerated.
As for the report
As mentioned earlier, after wastewater has been discharged onto the terrain, a report must be provided.
Advice! In order to make such a quarterly report, all chapters of the declaration must be completed. It was also previously noted that it must be submitted no later than the tenth day of the month following the end of the quarter.
There are several ways to submit a report. The first is to simply send it by mail. Just enclose the prepared report in the envelope, as well as a list of the documents you provide. Don’t forget to indicate the value of the letter in the upper right corner and make a note “with inventory.”
When you send a letter by mail, you will receive a receipt and inventory. This will confirm that the report has been submitted.
You can also submit a report yourself. True, as a rule, employees are not very keen to accept it, since they will need to write everything down manually, which, you see, will not bring pleasure. This is why they require reports to be submitted via email.
By the way, this is another option. This option is very reliable and can save you effort and nerves.
Law regulating wastewater discharge
On May 22, 2020, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 728 was adopted, which changed the procedure for controlling the composition of wastewater and introduced changes to the rules for cold water supply and wastewater disposal.
According to the new rules, there is no need to develop and approve a program for monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater.
Mandatory wastewater compliance criteria are now:
- Actual indicators of the composition and properties of wastewater, which are included in the Declaration on the composition and properties of wastewater
and/or
- Standards for the composition of wastewater, requirements for the composition and properties of wastewater discharged to the central wastewater treatment plant, established by the Rules for cold water supply and wastewater disposal, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 29, 2013 No. 644.
Thus, for CSV subscribers, the requirements for parallel sampling have been transformed, and requirements for “visual inspection” have been established. The old Rule No. 525 has been permanently repealed. In addition, the Rules for charging fees for the discharge of wastewater and pollutants into the sewerage systems of populated areas have been abolished. Significant changes have also affected the Rules for cold water supply and sanitation.
For the legal disposal of wastewater, there are a number of provisions developed on the basis of the Water Code, Order of the Ministry of Natural Resources No. 2:
- The distance of residential buildings to the discharge zone complies with the standards.
- The power of the cleaning filter must allow the discharge of wastewater with an acceptable level of contamination.
- In wastewater from residential buildings, after passing through an aerobic reactor, there is a low concentration of polluting components.
- Multi-stage cleaning structures in factories consist of mechanical and biological cleaning systems.
- To install treatment facilities with increased capacity, the design of a sanitary zone with an area of 50 m2 is required.
- According to the standards, the outlet pipe is insulated with a slope of the head above the location of the drainage ditch.
- Draining by gravity is common; a drainage pump is used if there is no natural drainage.
The fine for violating the rules for the protection of water bodies is specified in Articles 8.13 and 8.14 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses - “Violation of the rules for the protection of water bodies.”
Fine under these articles
- for individuals – from 500 to 1000 rubles;
- for officials from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles;
- for legal entities from 80,000 to 100,000 rubles.
Disposal of wastewater to the terrain if the groundwater level is average
The wastewater is first subjected to biological treatment, and then goes for further treatment into a filter trench or sand and gravel filter . The filter is made in the form of a three-layer cake. The first layer is a network of irrigation pipes, below it is a system of drainage pipes that exactly follows the contours of the previous network. Between them there is a sand and gravel filter filling, one meter thick.
Structurally, such filters are arranged either as a network, which looks like a collector with transverse pipes, or like a trench. Its type depends on the configuration of the unoccupied area on the site. The length of the trench directly depends on the volume of wastewater. The load is approximately one hundred liters per day per meter of pipe.
Rules for receiving wastewater into the city network
Requirements for the acceptance of wastewater into the city sewerage network are determined by a regulatory document that defines the rules for the acceptance of used industrial waters into the sewerage network of settlements.
Basic principles of reception:
- joint collection of industrial and domestic waters is advisable if the former requires treatment and they can be jointly purified by biological or mechanical treatment at city treatment facilities;
- the discharge of wastewater should not lead to disruption of the network operation, the formation of blockages or toxic gases;
- wastewater disposal should not allow pathogenic bacteria to enter the city sewer system, and not disrupt the operation of cleaning devices.
The list of facilities that have the ability to discharge wastewater into the city network is determined by water supply and sewerage organizations.
They are responsible for calculating the permissible concentration of wastewater pollution.
To date, a procedure has been defined for monitoring compliance with the requirements for the reception of wastewater.
It includes the following activities:
- carrying out laboratory control of wastewater;
- identification of unorganized discharges exceeding the content of pollutants;
- imposition of penalties upon detection of violations.
Discharge into water bodies
Acceptable provided all hygiene requirements are met. It is necessary to obtain a permit, carry out control intakes for water quality, as well as the volumes discharged. The requirements presented will directly depend on the reservoir and its use. Any discharge on the territory of domestic water supply farms, as well as fisheries protection zones, protected areas, etc. is prohibited.
There are prohibitions on the discharge of water that:
- Can be reused, after appropriate cleaning, or for other urban needs.
- Contain bacteria of viral and bacterial, parasitic diseases.
- Contain substances that do not have permissible concentration standards.
- Contains unacceptable, excessively hazardous substances.
Types of release
In order to release already purified water into reservoirs, several outlets are used: coastal and channel. Coastal ones can also be divided into two groups: flooded and non-flooded. For flooded outlets, special wells are made that have access to the reservoir. Accordingly, unflooded outlets are structures that connect flows at a certain angle.
Channel outlets are usually located at some distance from the coastal zone. They can also be subdivided: concentrated and scattering, as well as ejector. The choice of method is influenced by:
- Requirements of sanitary services.
- The need to dilute wastewater.
- From the water level in the well.
- From the water level of the reservoir itself.
Concentrated releases are necessary mainly to dilute the main water flow (supplying water from the reservoir with pumps), or following the main flow, water will be supplied to a certain point where the level of pollutants will correspond to the standards.
If it is necessary to discharge into a river, a dispersive release must be used. When the water density in the drain is greater than in the reservoir, it is necessary to use high-pressure distributors.
The deep-sea type of release can provide a large volume of discharge. It will allow the release point to be located far from the shore.
The video below shows an example of water being released into the Doibitsa River:
What kind of water can be discharged into reservoirs?
Discharge of untreated wastewater is strictly prohibited. Enterprises must have local treatment facilities. All wastewater must be treated, this can be done using various methods.
Biological consists of physical and biological purification of water bodies. There are several cleaning systems: aeration tanks, biological filters, special ponds. The main task is to completely remove organic matter, all phosphorus-nitrogen compounds.
Mechanical cleaning includes the removal of all mechanical impurities through filtration and sedimentation. In order to catch coarse particles, special sieves and settling tanks are installed at treatment facilities, all of which makes it possible to remove more than 60% of insoluble substances and impurities.
If the physicochemical method is chosen, then the wastewater is purified with reagents, which, after reacting with impurities, cause a sediment that does not dissolve.
The chemical method allows cleaning by 90%, and it also allows you to isolate all fine microparticles.
After cleaning activities, wastewater must comply with established permissible standards.
The wastewater treatment technology is described here with comments from experts.
At what depth should trays or pipes be laid?
If the question arises about what depth to lay pipes when installing stormwater communications for wastewater disposal, then just look at SNiP issue 2.04.03-85. Here, the rules for forming the depth of a trench on the ground are prescribed specifically for each type of pipe in accordance with their diameter.
So, if the diameter of the tray (pipe) for treated or untreated wastewater is up to 500 mm, then the minimum trench depth can be from 30 cm.
Types and arrangement of storm sewer wells
If the diameter of the gutters (pipes) is more than 500 mm, then their depth should be at least 70 cm. More can be done.
As for the slope of gutters or pipes for discharging/discharging waste liquids, here too it is necessary to make accurate calculations, since the slope angle depends entirely on the diameter of the gutter or pipe.
Thus, according to generally accepted technical rules, for pipes with a diameter of 20 cm, the slope level for each meter of the collector should be 0.7 cm. If the pipes have a smaller diameter, then the slope must be increased from 0.8 to 1 cm for each linear meter of the network.
Important: this slope level allows you to save about 2 mm per meter of pipeline in the presence of complex terrain. But at the same time, we should not forget that SNiP prescribes not only the minimum slope indicators for sewage trays, but also indicates the maximum slope indicator, which should not exceed 1.5 cm for each meter of the collector.
How to calculate the volume of wastewater discharged?
In order to avoid unorganized drainage and discharge of waste liquid from rain or snow clouds, it is necessary to first calculate the average volume of liquid that will pass through the entire collector. To do this, you need to take into account the following terrain and relief parameters:
- Average amount of precipitation falling in the area per month;
- The total area of the territory from which liquid will be drained;
- Features of soil and terrain.
And for calculations use the following formula:
Q = q20 x F x Ψ,
Where:
- Q is the average volume of water discharged;
- q20 is the intensity of precipitation in a specific area. Here the data can be obtained in SNiP tables for a specific area;
- F is the total area of all surfaces from which storm water will need to be removed;
- Ψ is the correction factor, which completely depends on the coating material from which water will be removed.
Important: the coefficient is specific for each type of material. So, for a roof - 1. For asphalt areas and paths, the number is 0.95. For concrete sites - 0.85. For crushed stone treated with bitumen - 0.6. And for simple crushed stone - 0.4.
Reset control
Control by the organization that carries out wastewater disposal is required. First of all, the composition is checked for contaminants, as well as various microorganisms. There is a reconciliation with the declaration data provided by each enterprise regarding the presence of harmful substances.
Control work includes several points:
- Selection of wastewater at the enterprise.
- Conducting analysis.
All planned work on control (selection) of wastewater is carried out no more than once every three months, but at least once a year. But in some cases, an unscheduled inspection may be carried out if:
- Inconsistencies with the data included in the declaration of composition and content, and prohibited substances were identified.
- The occurrence of an accident, disruption of the entire drainage system.
- If violations are detected during the discharge, including without the use of cleaning systems.
- If during the inspections violations were discovered that were ordered to be corrected.
If wastewater from enterprises has specific contaminants, then their discharge is limited by the following requirements: they should not adversely affect the operation of networks, as well as the material of pipes (not deposited on the walls) and all treatment facilities.
The composition should contain no more than 500 mg/l of suspended and floating substances. The temperature should not be higher than 40 degrees, and the pH should be neutral 6.5 and not exceed 9.
Under no circumstances should water be discharged that contains substances that can form explosive mixtures, toxic gases, or harmful impurities that interfere with the biological treatment of wastewater. If wastewater contains harmful substances, it must first be cleaned.
Permissible standards (substances not listed in the table are prohibited from being discharged).
| Substance name | Permissible concentration (mg/l) |
| Suspended solids | 134,17 |
| Chlorides | 5302,85 |
| Sulfates | 3303,5 |
| Petroleum products | 0,47 |
| Phenols | 0,0047 |
| Alkyl sulfates | 6,107 |
| Alkynesulfonates | 6,48 |
| Chrome 3 shaft. | 9,28 |
| Chrome 6 shaft. | 0,704 |
| Nickel | 1,03 |
| Zinc | 18,75 |
| Iron | 3,10 |
| Nitrates | 36,94 |
| Caprolactam | 5,67 |
| Biochemical consumption oxygen | 1007,34 |
| Dissolved oxygen | 46,07 |