Definition and Applications
A biological wastewater treatment plant is an autonomous sewage system designed for the treatment and collection of household and industrial wastewater.
Such a sewerage system is installed in cases where it is not possible to connect to a central wastewater disposal system or it is not rational.
A biological treatment station is not one unit, but a whole chain consisting of various equipment. The final modification of any system depends on the needs of the customer.
Typically, highly efficient biological treatment plants consist of:
- distributor;
- sand traps;
- rotary well;
- sludge storage tank;
- compressors;
- UV disinfectant;
- mechanical grid;
- pumps;
- biological filters.
SBOs are mainly used in everyday life . In industry, biological treatment stations can serve as the final link that cleans wastewater to the level of discharge into fishery reservoirs.
Application areas of biological treatment stations:
- private residential buildings, cottages;
- roadside cafes;
- hotels;
- baths, saunas;
- small settlements;
- airports;
- small businesses;
- warehouses;
- recreation centers.
Waste and sewage water treatment: what is it for?
An urgent problem today remains ensuring the proper quality of treated waste water. For many years, various scientific institutes in Russia have been working on this problem. They talk about the existence of a series of basic provisions that need optimization:
- Inconsistencies with material and moral standards. A lot of equipment needs to be completely reconstructed, since it was built before the 90s of the last century. New technologies will help improve the safety of structures.
- Financial component. The entire water treatment park in the Moscow region requires comprehensive modernization. Today there is no shortage of specialists and desire to carry out work, but material resources are limited.
- Profiles of industrial enterprises in the Moscow region and Russia as a whole. In the 90s, many of these either closed or underwent reorientation without paying adequate attention to improving technical characteristics, including cleaning equipment.
Consequently, at many enterprises, the wastewater separation process is carried out, but it is not established, does not provide appropriate treatment, and cannot cope with the incoming volumes of waste and the types of their contaminants.
Also, due to the increasing need for industrial, agricultural and domestic sectors to use water resources, there is a shortage of fresh water. To guarantee its optimal consumption, a number of directions have been developed, the main ones being aimed at:
- The use of new methods for purifying used water to renew and preserve clean and fresh water supplies.
- Minimizing the consumption of water resources and promoting their moderate consumption.
Everyone knows that wastewater should not be discharged into a pond or ground. Most do not do this successfully, plus they use modern technologies, thanks to which wastewater can be reused for industrial and domestic needs, as well as for watering green areas.
Taking into account all of the above, we can draw a conclusion about the current state of water treatment structures and the need to use the latest techniques. Our company, having many years of experience and the availability of all resources and specialists, is developing installations for improved wastewater treatment.
Types of treatment facilities
The treatment plant is a reservoir, which, depending on the needs, can be of different volumes.
Biological treatment stations differ in:
- degree of purification;
- case material;
- location;
- by type of body orientation;
- energy dependence, etc.
There are types of treatment facilities that are only an alternative to settling pits - storage systems.
They have 1 filter or no filter at all; they perform the function of collecting liquid and preserving unpleasant odors.
The operating principle is based on sedimentation of suspended substances and ineffective filtration.
At the outlet of such devices, the liquid is purified by no more than 40%. The water is not suitable for reuse and disposal into the ground. Additional facilities are needed for more thorough cleaning. Such water is removed from the site using a sewer truck.
Another type of treatment facilities is chamber systems. They can have from 1 to 5 filters. The operating principle is based on biological wastewater treatment due to the vital activity of microorganisms.
The most effective of them can purify wastewater up to 98-99% (HBO). The water passed through such a system is suitable for household use (watering plants, washing vehicles, etc.).
The body is made of various materials:
- plastic;
- become;
- fiberglass;
- concrete, etc.
Most often, there are autonomous sewers with a tank made of fiberglass.
The wide distribution of this material is due to the fact that it is lightweight, durable and airtight.
By location, cleaning systems can be:
- underground (goes underground);
- aboveground (the tank remains on the ground).
Depending on the orientation of the body, autonomous sewerage equipment can be:
- vertical;
- horizontal.
Belonging to one species or another can be determined visually.
Among the local treatment facilities (WTP) there are:
- energy dependent;
- non-volatile.
For the operation of volatile systems, additional energy sources are required - connection to electrical networks. In the case of non-volatile ones, here the wastewater moves by gravity, their work does not determine the availability of any resources.
On sale you can find septic tanks designed for premises inhabited by 1 to 350 people.
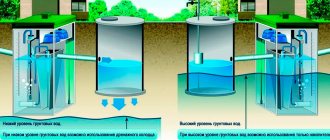
Some devices can only be used in certain conditions:
- if there is no reservoir or well nearby;
- specific groundwater level;
- specified soil type and distance from a residential building.
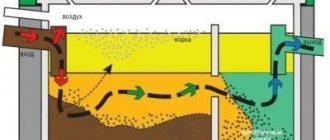
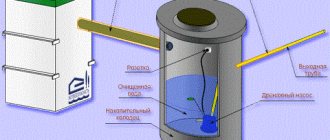
Aerotank
Aerotanks are reservoirs with a depth of 3 to 6 meters, equipped with devices for aeration. In these tanks, microorganisms live on activated sludge flakes that break down organic matter. After cleaning in the aeration tank, the water enters the settling tank. Here the activated sludge settles (part of the settled sludge is then returned to the aeration tank). When constructing aeration tanks, special tanks are often provided in which activated sludge is regenerated. The most effective cleaning system based on aeration tanks is SBR technology (sequencing batch reactor - an aerobic reactor with cyclically interrupted activity). A feature of the operation of such a system is the periodic transfer of aeration tanks to anoxic mode (the oxygen level in the system is low, which activates new biochemical reactions in the tank). This variable operating mode allows you to improve the quality of water purification, which in turn makes it possible to use this water in recycling water supply systems. One example of SBR technology is the Russian developments “YUBAS”, “TOPAS” and “UNILOS”.
Principle of operation
The operating principle of wastewater treatment plants is based on the decomposition of pollutants with the help of microorganisms that are active in the presence of oxygen in the liquid.
The most advanced systems are deep biological treatment stations. Effluents passed through the gas treatment facility are suitable for reuse, discharge into the ground or reservoir . They do not require additional devices for post-treatment.
The system itself consists of modules (chambers) in which phased neutralization of pollutants occurs. There are also pumps that perform the function of moving wastewater from one chamber to another and a compressor that enriches the liquid with oxygen.
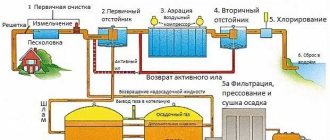
The main stages of HBOT occur as follows:
- Through sewer networks, wastewater enters the first chamber. It works on the principle of a settling tank—substances with a higher density precipitate, while substances with a lower density form a film on the surface of the water.
- Using pumps, the liquid moves to the next compartment. There are bacteria here, the vital activity of which is supported by the compressor. Microorganisms (activated sludge) decompose pollutants.
- In the next chamber, the sludge is separated from the liquid, and then enters the collection compartment - the sludge accumulator. Clean water is pumped into a drainage well.
These are just the basic stages of wastewater treatment. Depending on the model, stations may contain such links as:
- sand trap - in addition to settling, here suspended substances are removed due to centrifugal forces;
- dehydrator - reduces the amount of water in accumulated contaminants;
- mechanical grid - collects large debris at the initial stage of cleaning;
- UV disinfectant - destroys microorganisms using ultraviolet radiation;
- sorption filters - post-treatment: eliminates excess chlorine and specific pollutants.
Operation of SBO using the example of a BIO-B-P series system
This system is designed for wastewater treatment with a permanent residence of no more than 345 people. In 1 s, 100 m3 of wastewater passes through the system. The cleaning efficiency, depending on the type of pollutants, is 97–99.3%.
The basic package of BIO-B-P consists of:
- Sewage pumping system (sewage pumping system);
- sand traps;
- UV disinfectant;
- sludge storage tank;
- biological treatment systems;
- compressor;
- dehydrator.
The process is as follows:
- Through the incoming pipes, the liquid enters the compartment where large debris is retained.
- The water is collected in a container, where it is subsequently supplied for purification in portions (SPS works).
- The wastewater enters the sand trap, and then into the biological treatment unit.
- Excess sludge with pollutants goes into a collection block - a sludge accumulator, and then into a dewaterer.
- After biological treatment, water passes into the UV disinfection compartment.
- Through the outlet pipe, purified wastewater is removed from the system to its destination (well, reservoir, etc.).
Deep biological treatment station
Let's look at the advantages of a biological treatment station and how wastewater is purified.
UNILOS, a manufacturer of autonomous local sewerage systems, Maxim Beskishchenko .
– The operating principle of a deep biological treatment station is based on the method of continuous cultivation of microorganisms, which occurs under the influence of oxygen, or as it is also called the aeration method. And wastewater purification occurs due to activated sludge resulting from bacteria and microscopic animals.
Activated sludge is an active biomass suspended in water that carries out the process of wastewater treatment in an aeration tank. The large community of microorganisms formed during biological treatment intensively oxidizes organic substances.
Thanks to the organic substances in the wastewater and the excess oxygen entering the installation, these bacteria begin to develop rapidly and then stick together into flakes, after which they secrete enzymes that mineralize organic contaminants. When sludge and flakes enter the outlet settling tank, it quickly settles, separating from the purified water.
A biological treatment station allows you to use purified water for irrigation. And the activated sludge formed in the aeration tank is very similar in structure to river sludge and is a valuable fertilizer. So you don’t have to call a sewer truck.
Unlike cesspools, a biological treatment station does not accumulate sewage, but ensures its biochemical decomposition into simple, safe compounds - process water and stabilized activated sludge, therefore, there is no bad odor. Therefore, a biological treatment station can be installed near the house, at a distance of 2 meters, and the purified water can be immediately discharged to the terrain without the use of soil treatment systems.
Let's look at the operating features of such a system.
Beskischenko Maxim:
– Despite the reliability of the system, there are a number of rules that must be followed for the effective operation of the deep treatment station, namely: it is prohibited to discharge construction waste, chemicals, polymeric materials, petroleum products and other biologically non-degradable compounds into the sewer system. And when there is a power outage, it is necessary to reduce water consumption, since it is possible that the receiving chamber of the biological treatment station may overflow and untreated wastewater may enter the environment. It is also necessary to carry out timely pumping of activated sludge.
To summarize, it can be noted that the biological treatment station has the following main advantages:
- The degree of purification in modern aeration plants exceeds 95%, and purified water can be sent to water bodies without installing additional filtration fields;
- The biological treatment station is easy to transport. Also, when installing the station, there is no need to carry out large-scale excavation work or install it on a concrete base and anchor it;
- The mechanical properties of the body made of foamed polypropylene allow the station to be installed in any, even the “heaviest” soil, even with a very high groundwater level;
- The durability of the biological treatment station, its absolute tightness, environmental safety, resistance to corrosion, as well as to aggressive acids and alkalis, allows the deep biological treatment station to be operated for at least 50 years.
Installation
Installation work is carried out in the following order:
- A pit is dug according to the size of the station. If necessary, with a reserve for insulating the structure.
- A concrete slab is laid on the bottom. A biological treatment station is placed on top of the slab. The body is secured with straps.
- The pipes are connected to sewerage and wastewater drainage networks. Electrical installation is in progress.
- The installation is filled with water. Covered with soil.
System installation may depend on the type of installation or model, natural factors, location, etc.
Important! If the inlet pipe supplying wastewater to the system is installed above the freezing point of the soil, the station may fail.
Help from microorganisms and bacteria
Aerobic bacteria trigger the processes of oxidation and nitrification . For this they need oxygen. Microorganisms live in the temperature range - from +9 to +28 degrees, pH - 5.0-7.0.
Groups of bacteria:
- Pseudomonas - occupy 80% of activated sludge. They process alcohols, fatty acids, aromatic hydrocarbons, paraffins and other organic substances.
- Nitrifying agents - oxidize nitrogen compounds.
- Sulfur bacteria and thionic bacteria - process reduced sulfur compounds.
- Filamentous - oxidize carbon compounds.
- Cellulose decomposing – process cellulose fiber.
Activated sludge also contains:
- yeast,
- molds,
- protozoa,
- rotifers,
- oligochaete annelids.
Anaerobic bacteria do not require oxygen. They trigger the processes of fermentation, anoxygenic oxidation and methane formation.
Reference. Microorganisms can withstand a temperature range from +9 to +37 degrees, the pH value ranges from 6.0 to 8.0.
Groups of anaerobic bacteria:
- Hydrolytics are responsible for the first stage of methanogenesis. Bacteria break down proteins, fats, cellulose compounds, starch, and have ammonifying activity. As a result, glycerol, fatty acids, amino acids, peptides, mono- and disaccharides are formed.
- Acidogenic – responsible for the second stage of methanogenesis. With the help of bacteria, butyric acid, acetone-butyl, propionic, and alcoholic fermentation occurs. Intermediate hydrolysis products are processed.
- Heteroacetogenic - responsible for the third stage of methanogenesis. Bacteria convert organic acids (butyric, propionic) into acetic acid.
- Methanogenic - complete anaerobic treatment. Microorganisms form biogas by processing hydrogen, carbon dioxide and fumes, acetate, methylamine, and methanol.
The composition of the dominant microflora depends on the characteristics of the wastewater.
Service
Maintenance of biological treatment stations does not involve transporting wastewater using a sewage truck, since the liquid, after passing through the system, is suitable for reuse.
Care comes down to the following activities:
- removal of excess silt and sediment;
- renewal of compressor membranes;
- checking electrical equipment;
- cleaning pumps and filters;
- flushing the inside of the tank.
The following should not enter the biological treatment station:
- chlorine-containing substances,
- acids,
- medicines,
- large garbage.
What is important to know:
Strength characteristics
- the material must withstand constant exposure to flows of water and air; if the material is pliable, this will lead to a sudden breakdown of the biofilm, which will cause an accident at the treatment plant.
The specific surface area of the material
- a parameter measured in m²/m³ - actually tells how many colonies of bacteria are placed on the bioload.
For reference: in domestic wastewater treatment plants, materials with characteristics close to 200 m²/m³ are used. Free volume
is a parameter characterizing the ability of a liquid to pass through a material, indicating how easily purified water will pass through the material.
This parameter also affects air permeability - the higher the value, the easier it is to “blow out” the volume of the biofilter with fresh air, and as a result reduce energy costs for compressor equipment. For polymer loads the parameter is always greater than 90%. For comparison, for expanded clay and gravel, this number is 30%. Service life
- coincides with the service life of the structure, unless planned replacement is provided due to the destruction of the product.
Local treatment facilities EvoStok Bio are equipped with trickling biofilters; in these installations, waste liquid is sprayed over the surface of the filter material, simultaneously delivering food to bacterial colonies and saturating the effluent with air oxygen. Excess bacterial populations are washed into the primary settling tank where all stages of activated sludge mineralization take place. The drainage from the third chamber of the septic tank is processed in a biofilter; for this reason, only water with dissolved nutrients reaches the Matala loading unit located in the structure.
Top 3 manufacturers
Today it is possible to select treatment facilities to suit every taste and budget from domestic and foreign manufacturers. Here are some of the most famous biological sedum stations.
Biotank
Biotank is a deep biological treatment station produced by the Russian company. This company is today considered one of the leading local treatment facilities in Russia.
Advantages of Biotank:
- Compact. There are varieties in horizontal and vertical versions.
- Prices vary from 30 to 90 thousand.
- Maintenance every 1-3 years.
- They can work for days without power.
- The degree of wastewater treatment is 95-98%.
- Can be installed at any groundwater level and soil type.
The manufacturer has one big drawback - the Biotank series is represented only by models that are designed for 1-10 people.
The lineup:
- BIOTANK-8 Ave.
- BIOTANK 3 ave.
- BIOTANK-3 itself.
- BIOTANK-5 itself.
- BIOTANK 10 itself, etc.
Count Picobell
The brand belongs to a German company. The products of this company are the best in the world on the treatment plant market.
Pros of Graf Picobell:
- maintenance 1-2 times a year;
- 15 year warranty;
- the minimum volume of the tank is designed for 4-5 people;
- degree of purification 95-98%;
- water inside the system moves by gravity;
- simplicity of design;
- can operate in normal mode even with a one-time discharge of wastewater up to 800 liters.
Minuses:
- aggressive detergents should not enter the sewer system;
- price – 150-300 thousand;
- works only from the network.
AquaBiome
One of the largest Russian companies engaged in the production of autonomous sewers.
Advantages of AquaBiom:
- models are designed for 300-345 people;
- lightweight body;
- treated wastewater can be discharged into fishery reservoirs;
- productivity from 40 to 500 m3 per day;
- operates down to -350C;
- low price – from 70 thousand.
Flaws:
- it is impossible to carry out a volley discharge of wastewater;
- Chlorine-containing substances and medications should not enter the system.
Model names:
- BIO-B-P-100.
- BIO-B-P-50.
- BIO-B-P-450.
- BIO-S-P-40, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages
A biological sewage treatment station has several important advantages:
- Easy assembly and installation. This allows you to install stations at home without the help of specialists.
- Compactness. A station for biological dissolution of contaminants occupies a small area and is therefore often installed in private areas.
- High degree of sewage treatment.
- Thanks to timely recycling of liquid from the sewer, there are no unpleasant odors.
- Possibility of installing modules on any type of soil.
- Same operating efficiency at any time of the year, regardless of air temperature.
However, such effective equipment has its drawbacks:
- Electrical power is required; if there is no connection to electricity, the station cannot operate.
- The need for regular inspection of the main working units.
- Mandatory cleaning of equipment using detergents.
- During seasonal use, equipment conservation and subsequent restarting is required.
Septic tanks and their varieties
A septic tank is a sewerage element that serves for partial filtration (clarification) of wastewater. Based on their operating principle, they are divided into:
- flow type;
- local wastewater treatment plants (WTP);
- aeration units (AU).
The main differences between septic tanks are the filtration method. This can be settling, or processing by microorganisms (bioseptics).
Bacteria are loaded artificially into pumping treatment stations, and in aeration plants they are bred thanks to specially created conditions.
Flow septic tanks have the simplest design. They consist of several cameras (usually 2 or 3), and according to the production method they can be either factory-made or home-made.
Biological products
Biological products are used to perform the following tasks :
- Decomposition of organic matter: fats, carbohydrates, proteins;
- Stimulation of activated sludge operation;
- Reducing the volume of by-products in the form of sediment;
- Acceleration of the processing process;
- Decrease in biochemical oxygen consumption (BOD, COD);
- Build-up and restoration of activated sludge.
Manufacturers produce drugs that contain a certain number of strains of natural bacteria.
Each biological product contains different strains of microorganisms , which are selected depending on the composition of the wastewater.
Attention. The manufacturer in the description of its products indicates what kind of pollution it copes with.
Popular biological products:
| Name | Purpose of use | Price |
| Biofos | Domestic wastewater treatment | 43 RUR/25 mg |
| bioExpert BIO STARTER | Stimulation of the development of activated sludge in a septic tank or cesspool | 565 RUR/400 g |
| Unibac (compost, start, winter, effect) | Treatment of domestic and industrial wastewater, build-up of activated sludge | 470-750 rub./0.5 l. |