Why do we need a storm drain?
This drainage system is used for three purposes:
- To remove melt and rain water from the territory in the off-season;
- To reduce damage caused by floods;
- For recycling of technical water on an industrial scale.
- If rainwater is necessary for nature, then it is better to divert it from buildings and road surfaces, so as not to have to constantly restore the foundation, blind areas, etc. Rainwater, entering the external part of the drainage system, reaches the ground or storm water inlet. Next, the water passes through an inspection well and a system of drainage pipes and is discharged either into a natural reservoir, outside the site, or into a collector well.
Why is a drainage ditch along the road to the site so important?
In one of the previous articles, I already wrote about the importance of roads, which it is advisable to do before construction begins. Today I will try to explain the need for proper drainage from the road from personal experience.
Storm drainage is an integral part of the overall improvement system - one of the most important sewer systems that serves the purpose of draining rain and melt water from a site.
For me, the topic of roads is a sore point, because... the plot is almost in the middle of the street and there is no neighbor or road behind my plot, i.e. I'm stuck.
Standard equipment of the storm system
A modern stormwater system contains interconnected elements:
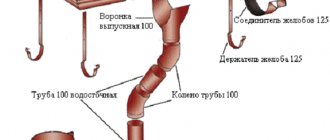
- Storm water inlets . There are usually several of them. They are points for collecting water from vertical external drains and from the surfaces of blind areas. They have a basket in which garbage is collected. Stormwater inlets are installed in lowlands, near intersections, and under gutters near buildings. To prevent the spread of unpleasant odors from the sewer, a siphon is often built into them.
- Door pallets . They work the same way as rainwater inlets - they collect water directly from the building in front of the entrance.
- Gutters, channels, trays , which are equipped with lattice covers. Used in surface drainage. The base is made of concrete or plastic, and the grate is chosen from plastic, stainless steel or cast iron. These elements are used to reduce the length of the pipeline.
- Sand catchers . It is through sand traps that water enters the general sewerage pipeline. Consists of a base and a basket. The latter is designed to capture suspended particles. It is periodically removed for cleaning (cleaning is carried out twice a year). It is suggested to use two or more sand traps to prevent the system from becoming clogged with debris.
- Inspection well with sump . Installation of this container is carried out at branching points, at the corners of the underground part of the stormwater system. Through such tanks, drainage lines are cleaned and dirt is removed. Used in closed or mixed sewer systems.
- Pipes . Non-pressure plastic products are installed. For this, orange (red) pipes are usually chosen.
- The laying of an external storm sewer system is carried out from the drainage points related to the external drainage system to the beginning of the underground part of the system.
When the length of the storm drain is more than 100 meters, the installation of one or more inspection wells is required at the point of integration and at the corners of the underground pipeline, which depends on the volume of water and the scale of the entire system.
PLC software
Regulates the design standards of storm sewerage in the city - SNiP. This document was created a long time ago, but has been successfully tested by time. It spells out all the nuances related to planning, placement of structures, and correct calculation of communications. Innovative information products are also adjusted to the norms of current legislation and the engineering requirements of a particular facility.
ZWSOFT company offers specialists in various fields tools to make their work easier. To draw up diagrams in the field of construction and communications, applications have been developed:
- Program "INZHKAD". With its help, they design utility networks, using BIM technology for ZWCAD 2021 PRO, AutoCAD, BricsCAD, not only to design storm drains into the sewer system. It is used for planning water and heat supply and laying gas pipelines. Its specialty is multitasking. The software generates an engineering plan for communication networks, details wells and geowells and enters data into a table.
- The development for cadastral engineers "ProGeo" is included in the EP of Russian computer programs and information base of Russia.
- ZWCAD 2021, 2021, released in several versions - Professional and Standard. The set of functions of each of them is different, which allows you to choose the best option for the client. The main advantage is the ability to 2D and 3D image editing and modeling, VBA / .Net support; / ZRX, display of CAD elements and many other useful features. The simple interface of the intuitive editor makes the work process convenient. The cost of the programs is significantly lower than its analogue - AutoCAD.
- Adapted software for ZWCAD 2021 Pro is Geoniun 2021. It has a permanent license, which makes it a profitable purchase. The peculiarity of this program is that it produces ready-made drawings with stamps and explications filled in.
- An embedded application for ZWCAD+ versions with a local SPDS license GraphiCS 10.x offers automatic documentation creation. Used in construction, adhering to SPDS standards. Useful in designing a drainage system, based on SNiP for storm drainage.
Design easily with the right program!
Do you need a well or a collector?
Using a collector or well is relevant if:
- 2 or more streams of rainwater converge;
- It is necessary to radically change the height, as well as the direction and inclination of the pipeline;
- It is necessary to switch to large volumes of pipes;
- If it is necessary to treat wastewater before discharging it into a reservoir.
The diameter of the collector is determined by the designer based on data relating to a specific site. The larger the cross-section of the well, the greater the interval when placing the tanks. For example, with tanks with a diameter of up to 150 mm, the distance between objects is 30-35 m, up to 200 mm - 40-50 m, and so on.
Road drainage systems: types, purpose, features of use
News
News
November 26, 2021 at 12:50 pm
Drainage trays solve the problem of waterlogging of roads with surface water. They are also needed to prevent their erosion. Trays are only part of the ditch drainage system. It also includes ditches, absorption wells and other elements. Drainage of wastewater is also necessary for heating mains and railway tracks. We will tell you in what cases certain drainage trays are used.
Types of trays and drainage systems
Inter-track and inter-sleeper channels have become widespread. They are needed for drainage in the following places:
— railway tracks;
— passenger platforms;
— near crossings;
- in the presence of a large number of drains in places where the stationary canvas is lowered.
The trays in this case are made of reinforced concrete. They extend the life of railway routes and crossings, and protect them from precipitation and melt water.
Concrete and plastic trays are no less in demand. This type of drainage is needed on highways. Installed along the road surface or in conventional linear drainage. Fiber-reinforced concrete products have the following sections: 200 mm, 300 mm, 400 mm and 500 mm. Solve the following tasks:
— collection and disposal of wastewater from roads and surrounding areas;
— prevention of erosion of the subgrade, serve as the base of the road surface;
— ensuring the safety of vehicles in bad weather.
Products made from plastic are no less practical than those made from concrete. They are light in weight, which simplifies the installation of drainage systems. Cross-section of these products: 200 mm, 300 mm and 500 mm.
Problems that can be solved using plastic trays:
— drainage of storm water from roads and their protection, while embankments adjacent to roads are also protected;
— trays are suitable for use in places with difficult engineering and geological conditions.
The material has frost resistance and the necessary strength.
Fiberglass high-flow tubes and plastic cuvette trays are currently a popular solution. Such products are needed if there are ditches in a certain place, and there is a possibility of soil erosion near the road.
Products made from reinforced plastic are used in the following temperature range: -60°C - +60°C. It is easy to install and use and has many unique properties.
What are the quality standards for drainage systems?
There are several such standards. For example, for polypropylene trays the following standard is provided: GOST 26996-86. Concrete structures for water drainage are manufactured in accordance with GOST 21509-85. There are no separate standards for drainage systems. However, all concrete trays for collecting water are manufactured in accordance with GOST 13015 - 2003 “Reinforced concrete and concrete products for construction”.
The concrete used in the manufacture of drainage elements must meet the GOST 26633 standard. The tempering strength of the concrete must be 50% of the grade strength for concrete of class B15 and higher, and at least 70% for concrete of class B12.5 and lower.
Where can I find drainage trays?
This product is manufactured by. Always available here:
— inter-track and inter-sleeper trays made of reinforced concrete;
— open drainage trays made of fiber-reinforced concrete;
— cuvette plastic products;
— fiberglass options;
— suspended drainage systems (ISO 9001:2008).
Features and advantages of Standardpark drainage systems
Let's name the main ones. This:
— effective drainage of wastewater from roads and adjacent areas near railway tracks;
— the ability to extend the service life without special costs;
— prevention of erosion of soil and embankments.
The result is clean and practically dry highways. High-quality drainage on roads is an effective protection of the surface of the roadway, the area near highways, as well as guaranteed safety of transport in any weather.
You can find out more about highway speeding by following this link.
Photo courtesy of the advertiser
As an advertisement
What to consider when designing a storm drain
The following factors should be considered during installation:
- If the system receives dirty wastewater, then the project also provides for the installation of treatment facilities;
- It is important to calculate the approximate amount and intensity of rainfall for the region before designing;
- Calculate the duration of passage of liquid through all sewer channels to the collector;
- Drain area;
- The surrounding area, its relief and other nuances.
The optimal option for installing a storm sewer is considered to be a project that takes into account all regulatory sanitary and hygienic requirements, and also actively uses the natural slopes of the landscape. Thus, the system becomes more economical during installation and further operation.
The use of modern materials and technologies makes it possible to simplify the use of storm drainage and extend its service life. Therefore, in creating such a system, concrete and plastic products are used, which are highly durable.
Storm gutters for drainage: price of products and types
After the winter period, when the snow begins to melt, as well as in rainy weather, any private house needs a storm drain. Precipitation from the roof usually ends up in special storm gutters attached to the roof. Moisture collects there, which then goes down into the gutters. If the house does not have such a unified system for draining water flows, then this will soon lead to the destruction of the building’s facade, its foundation and base, and damage to the thermal insulation. Water will accumulate in the basement and under the foundation , and moisture will collect and puddle around the structure itself. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to create a drain; it will solve all the problems of water drainage.
Types of stormwater system
Water enters the storm drain directly in a closed way or openly through a grate and drain elbow. Each type of stormwater system has its own characteristics, which must be taken into account at the design stage and then used during installation.
Open surface drainage
An open drain means a system of gutters, channels through which water will flow into a specially designated place or simply into the ground (for example, a vegetable garden). This drainage system is efficient and economical. It is important to consider that surface stormwater will freeze. Therefore, it is most often used in summer cottages and private houses.
With an open type of drain, you need to carefully calculate the height at which the drain elbow is located so that you can periodically remove the grate and clean the storm drain basket. The tiles or asphalt should be 3-4 mm higher than the level of the grid with trays. The general slope is directed towards the drainage trays. From there, the liquid reaches the general storm sewer. The required slope of the gutters is organized taking into account the design of the gutters and the features of the landscape.
Closed underground drainage system
This system is located below the zero point and involves working with the soil. Unlike an open system, which can be installed by an amateur, this type of drainage system must be carefully designed and installed by a specialist. This storm drain is relevant for industrial enterprises where a large amount of wastewater is expected, especially if it is contaminated and requires pre-treatment before being discharged into a reservoir or ground.
A closed or underground version of a storm drain is installed with a slope of 3 cm per linear meter in relation to the storage well. To facilitate the planning of the slope, a sand cushion is used. A pipe system is being laid underground through which water will flow into the collector.
Mixed type
This is the most common type of storm drain, which takes into account all sanitary and hygienic standards. It contains elements of both an open system and a closed one. Mixed storm sewerage is used when it is necessary to save on the arrangement of the system. It also helps to cover a much larger area.
Features of the design of storm drains on the highway
The main destructive factor is considered to be ground moisture, which accumulates in the upper layers of the soil. When the temperature drops, it hardens and begins to expand, tearing the road surface. Small cracks appear in it, through which additional volumes of water seep into the ground. This accelerates and makes destructive processes more intense.
The presence of free water on the coating contributes to the aquaplaning effect. This makes driving uncontrollable and increases the number of accidents. This effect often manifests itself on intercity highways, and in urban conditions it is doubly dangerous. There is a serious threat to the life and health of pedestrians and vehicles. All elements of storm drainage on highways are located in the embankment (under the roadbed), or along the sides of the road (edge trays, gutters).
To maximize water flow, the road surface is made with a one- or two-sided slope towards the side of the road. One-way slope is used on relatively narrow roads with one-way traffic. Highways with multi-lane traffic in both directions are equipped with a two-way slope. Rainwater flows into edge trays, from where it is directed to discharge points.
For the widest canvases, an additional slope is made towards the center, where a receiving tray with a grid is installed. It is connected by transverse underground pipes with edge gutters.
Also read: Ventilation from sewer pipes: pros and cons, review of how to do it yourself
How wastewater is collected
The principle of collecting water from the roadway is the same for all drainage schemes. The structural elements of the network differ:
- type of drainage (trays or underground pipelines);
- base for storm drainage (compacted soil, concrete base, piece parts);
- number of receiving strips (on one or both sides, with an additional strip in the center).
The choice of the optimal type occurs at the road design stage. Criteria determining the type of receiving parts:
- climatic conditions in the region. The average annual precipitation, frequency and intensity are taken into account;
- maximum (peak) amount of waste. Data from long-term observations are monitored and included in the calculation as the maximum volume. A reserve is made for it in case the calculated amount of waste is exceeded;
- duration of the warm season, amount of snow, volumes of melt water;
- possibility of floods or flooding.
The last point poses the greatest danger to storm sewers. If spring water spills are considered normal for a given area, underground pipelines cannot be built. They will be completely clogged by the first flood; labor-intensive cleaning or complete reconstruction of the drainage system will be required.
Arrangement of outlet trays
One of the most critical areas are ditches and drainage ditches located on the sides of the road surface. They accept the flow of wastewater along with small debris, dust and other particles. These are important elements of storm drainage, drawings of which are made during design work. Depending on the weather conditions of the region, the method of strengthening slopes and trays is chosen:
- use of prefabricated concrete segments;
- precast concrete slabs;
- filling with crushed stone and sowing perennial grasses.
During the manufacturing process of the project, a drawing of the system is made, which shows the profile of the canvas and the type of receiving tray. In most cases, proven and proven schemes are used. Standard drawings of storm drainage on a road are used for the construction of highways in a variable climate, with alternating warm and cold seasons. However, for areas with specific conditions, special storm drainage on roads is required, the design of which will ensure stable operation.
A good material for strengthening trays is sandy asphalt concrete. It differs from prefabricated asphalt blocks in its resistance to water. Ditches reinforced in this way retain their performance even in conditions of severe flooding. After the water drains away, the material remains intact and does not develop cracks or other defects. Such a base is considered strong and reliable, but its cost limits its use on a wide scale. The high price of the material makes it possible to strengthen only the most critical sections of highways, expressways or sections of city roads.
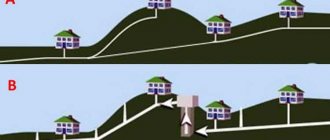
How to install a pipe in a ditch with your own hands
To quickly and efficiently carry out work on arranging the entrance to the site, it is worth hiring an experienced team of craftsmen. But, if you are confident that you can handle it on your own, then prepare the necessary tools and materials in advance, and also organize timely delivery of special equipment.
Required tools and materials
In addition to the pipe itself, the following materials are needed:
- Crushed stone.
- Sand.
- Geotextiles.
- Concrete.
- Reinforcement and binding wire.
- Boards for formwork.
- Nails.
- Paving slabs or asphalt concrete mixture.
- Curbs.
- Two decorative grilles to protect the pipe cavity from blockages.
- Moisture-loving plants for beautifying the entrance: irises, asters, vines, peonies, etc.
To dig a trench you need an excavator with a bucket capacity of 0.4–05 m3, and to lay heavy pipes made of metal or reinforced concrete - a truck crane. In addition to special equipment, you will need the following hand tools and accessories:
- Shovels - bayonet and shovel.
- Manual tamping.
- 2 buckets.
- Container for preparing concrete mixture.
- Vibrator for uniform concrete placement.
- Hammer.
Necessary equipment for beautifying the entrance
The beautification of the driveway is also not complete without the use of special construction equipment: an excavator and a bulldozer. If asphalt concrete is chosen as the road surface, then a special roller will be required to compact it.
Laying technology
The step-by-step installation technology is as follows:
- Marking the area for the ditch and trough of the driveway embankment.
- Digging a trench with sloped walls and cutting the soil around it to a depth of 35–40 cm.
- Cutting pits along the bottom of the trench and on the side walls.
- Compaction of soil at the bottom of pits.
- Filling the lower pit with crushed stone with layer-by-layer compaction.
- Construction of a crushed stone cushion 15–20 cm thick.
- Laying a layer of geotextile to prevent sand from going into the ground.
- Installation of a sand cushion 15–20 cm thick across the entire width of the ditch.
- Pipe installation.
- Installation of formwork and knitting of reinforcement cage for concrete caps.
- Pouring concrete into formwork with compaction using vibrators.
- Filling the ditch with a layer of sand 10–15 cm thick.
- Wrapping the edges of the geotextile fabric.
- Filling side pits with crushed stone.
- Backfilling of the trench with sand and soil with layer-by-layer compaction.
- Installation of a sand cushion under the embankment along the ditch.
- Laying geotextiles on a sand layer.
- Construction of a crushed stone base for the road.
- Road surface devices for crossing a ditch.
- Installation of curbs.
- Dismantling formwork from the ends.
- Layout of the site and layout of the flower bed.
- Planting and watering plants.
Installation video
Watch the video for a budget option for arranging the entrance to a dacha from craftsmen.