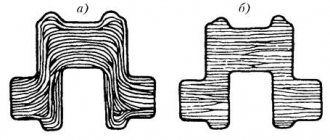
When heat treating copper and its alloys, two features of the material are taken into account: increased thermal conductivity and interaction with gases when heated. It is these factors that cause rapid and uniform heating of the metal along the perimeter of the section. Annealing copper is heating the metal followed by cooling, allowing you to change the properties of the material. Heat treatment makes the metal softer and more ductile. Copper is used in various fields where ductility is important.
Annealing of copper
Advantages and disadvantages of processing
An undeniable property of copper is its high electrical conductivity. It is used in construction and the manufacture of electrical equipment. The mechanical parameters of the metal are quite low, so it is not often used as a pure structural material.
Benefits of annealing:
- the treatment removes harmful substances from the metal and removes bacteria;
- the workpiece becomes soft and elastic, withstands pressure over 200 atmospheres;
- the material becomes resistant to corrosion;
- increase in hardness - the part can be bent several times without fear of cracks;
- reduction of residual stress during incomplete annealing.
There are significantly fewer disadvantages, but they still exist:
- the material requires slow cooling;
- copper is an expensive material;
- If handled incorrectly, soft metal can be damaged.
How to anneal copper at home - Metalworker's Guide
- Date: 10-08-2015
- 449
- : 10
At home, there is often a need to weld copper during the installation of plumbing and heating systems. In most cases, water pipes are made of copper. The material has a smooth base, does not corrode, is able to provide good water flow and does not contain any harmful substances.
Color characteristics of copper alloys.
Welding is the process of forming permanent connections between different elements. This can be achieved by heating the metals being welded or deforming them. Various energy sources are used for welding:
- gas flame;
- electric arc;
- ultrasound;
- laser radiation, etc.
The process of welding copper is significantly different from welding steel, since non-ferrous metals have a high level of thermal conductivity, and in the molten state they will react with gases. To avoid negative consequences, you will need to choose the right materials for welding, prepare the elements to be joined and follow the welding instructions.
Today, welding can be done not only at enterprises, but also at home. You should know that the copper welding process has a large number of nuances. Welding will largely depend on the physical and chemical properties of the material.
Difficulties in welding copper are associated with the tendency of the material to oxidize in the molten state, a high level of thermal conductivity, a high level of linear expansion of the metal during heating, and high fluidity.
The weldability of metal may deteriorate if it contains sulfur, lead and other elements. Lead will make such a metal brittle.
Do-it-yourself resistance welding.
During the copper welding process, oxygen will be absorbed from the atmosphere, so this should be taken into account.
Today, there are several different methods of welding this non-ferrous metal.
Elements that will be necessary in order to independently produce high-quality copper welding:
- Acetylene cylinders.
- Burners.
- Asbestos sheets.
- Wire.
- Water.
- Profiled spacer.
- Solders.
- Fluxes.
What you need to know about electrodes for copper welding?
Design of transformers for spot welding.
To obtain a high-quality and even welding seam, you should use an electrode that is coated with a special composition. The coating is used to produce slag, which appears with metal oxides. The composition will prevent the weld seam from coming into contact with air.
The coating will fill the loss that is formed during the welding process due to burnout of elements and introduces new elements into the seam. Thanks to the coating, the stability of the electric arc will be increased.
The slag coating produced by such a coating will slow down the cooling of the molten copper, resulting in more gases being released from the weld.
Electrodes that are used in the process of joining metals can be divided into 2 types:
- Consumable, which are made from copper, aluminum, steel or cast iron wires.
- Non-consumable, which are made from electrical coal, synthetic graphite and other elements.
To select suitable electrodes, you will need to pay attention to their color:
- Red electrodes are used for electric arc welding of copper.
- Blue electrodes are used for processing heat-resistant elements.
- Yellow electrodes are used for workpieces made of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant steels.
- Gray electrodes can be used for processing non-ferrous metals.
Gas method of copper welding
Gas welding technology.
If you follow the technology, then copper can be easily welded using acetylene cylinders. A welded joint of excellent quality can be obtained by forging the seam.
Copper has a high level of thermal conductivity, so welding it will require a high-power flame, 150 l/hour if there is material less than 10 mm thick, and 200 l/hour if there is material more than 10 mm thick. If you are welding thick copper, you will need to use two torches. One of them is for heating, and the other is for welding parts.
To reduce heat dissipation, asbestos sheets will need to be laid on the lower and upper parts of the element. In this case, it is recommended to use a reducing flame, the core of which is oriented to the edges of the copper at almost a right angle.
To reduce the formation of metal oxide and prevent the appearance of high-temperature cracks, it will be necessary to join metals at maximum speed, without interruptions.
During the process, it is necessary to strictly monitor the conservation of the reduction flame.
Why roast copper and how to do it
Russian legislation provides for several federal laws, articles of the Criminal Code and the Code of Administrative Offenses, as well as government regulations that prohibit the lighting of fires, burning of garbage and burning of wire. For different categories of offenses, different punishments are expected, from monetary fines to real terms. In order not to fall under the articles of the law, it is important to familiarize yourself in advance with the list of legislative acts that control the burning of waste, and in particular the burning of copper and aluminum. The main prohibiting and controlling articles are the following:
- Code of Administrative Offenses – Article 8.2.3;
- Article 51 of Federal Law No. 7 on environmental protection;
- Code of Administrative Offenses – Article 20.4;
What punishment these articles provide for and what they prohibit should be examined in detail so that there are no difficulties with the law when trying to dispose, process or transport scrap metal.
Article 8.2.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation – Failure to comply with rules and requirements for waste management, improper processing of industrial waste, including illegal disposal, accumulation and transportation. The article provides for punishment in the form of a fine of 1,000 to 2,000 rubles (for legal entities up to 250 thousand, for officials up to 30 thousand rubles). According to Article 8.2.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, those actions with garbage that have resulted in epidemics, infections, or harm to the environment and the health of citizens are unlawful. This article does not include offenses that are criminal offenses.
Adopted in 2002, the 7th Federal Law “On Environmental Protection”, article 51 of which specifies the requirements for citizens who process and dispose of waste and garbage, has been revised several times. For 2021, the following prohibitions are relevant:
- It is prohibited to throw garbage and waste from a fire (for example, burnt plastic after burning copper), into water, bury it in the ground, or near urban and rural settlements.
- It is prohibited to place and store garbage (including metal waste) near urban and rural settlements, as well as near recreational areas, on animal migration routes, and fish spawning areas;
- It is prohibited to create a danger to humans and the environment by burning and disposing of waste.
The Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation also contains Article 20.4, which regulates the organization of fires, including for the purpose of roasting copper. According to this article, violation of fire safety requirements is punishable by a fine of 4 to 5 thousand, or arrest for up to 90 days. A place for making a fire must be equipped by insulating the fire pit. You should not light a fire in windy weather, and it is also important to properly dispose of waste - by burning or roasting it in barrels. The Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides for punishment only for those actions that entailed the death of a person or caused serious harm to the health of citizens (Article 219).
What equipment is used
Copper undergoes two types of heat treatment:
- annealing to reduce remaining stress;
- recrystallization annealing.
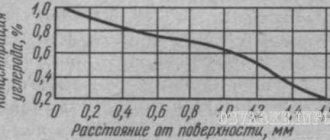
The temperature regime for recrystallization of oxygen-free copper is 200–240°C, and that of electrolytic copper is 180–230°C. Metal containing oxygen is treated in a neutral environment to reduce losses after oxidation.
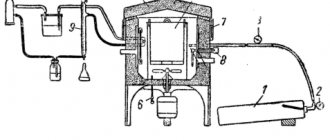
For annealing heat treatment, a shaft-type convection oven is used. In addition, the equipment is in demand for annealing wire, rope, rods, steels, and metal balls.
The oven has the following advantages:
- improved accuracy of temperature control;
- automation of heat treatment;
- the fan at the bottom of the device ensures stable heat transfer;
- processing error is +/-5C;
- heating is carried out from electricity;
- ammonia and pure nitrogen protect the metal from oxidation;
- capacity - 8–36 tons;
- ease of operation and installation.
The furnace lid is equipped with a special pneumatic device, which is responsible for opening and closing during the annealing process. The emergency valve operates automatically when the pressure rises to high or drops to low.
Annealing furnace
How much does 1 kg of roasted copper cost?
The value of scrap after heat treatment is determined by the appraiser. It takes into account batch size, contamination and the presence of impurities. You can find out during the purchase how many criteria the appraiser is guided by.
| Type of cable scrap | Cost per kg. | |
| For metal content | By gross | |
| Burnt copper cable and wires Type of cable scrap metal | 330-365 rub. Per metal content (kg) | On request |
Processing principle
Annealing is a heat treatment procedure for copper that produces a stable, strong metal structure, free from residual stresses. Annealing technology goes through several stages:
- Loading metal into equipment.
- Installing the muffle and purging with protective gas to remove air.
- Heating to 650–700 degrees.
- Rapid cooling up to 100 degrees when immersing the product in water.
- Giving the required shape.
- Reheat to 350–400 degrees.
- Air cooling and unloading.
The last stage of the technology is carried out twice as slow. The treatment ends when the annealing temperature of copper reaches a value at which it can be exposed to air without oxidation. It is prohibited to expose workpieces to high-temperature air. Duration: 1–2 hours.
Welding wire: brands, markings, types
Welding work is carried out with any materials - it can be cast iron, steel or non-ferrous metals. Technologies make it possible to perform these works on productive automatic and semi-automatic machines. The functionality of this equipment is ensured by consumables in the form of wire. Application The main purpose is to use consumables on semi-automatic machines in an atmosphere of protective gas. In cases where self-shielding wire is used, welding is performed without gas. The wire is used as surfacing.
Source
Required temperature for melting copper
Copper is not a fusible metal
People found the use of copper back in ancient times, when it was mined in the form of nuggets. Due to the low temperature required for the melting process, it began to be widely used for the manufacture of tools and hunting, nuggets can be melted over a fire. Nowadays, the technology for producing metal is not much different from that invented in ancient times; only furnaces are being improved, the firing speed and processing volumes are increased. A pertinent question here is what is the melting point of copper? The answer to this can be found in any textbook on physics and chemistry - copper begins to melt at a heating temperature of up to 1083 °C.
Boiling copper reduces its strength
In the process of thermal exposure of a metal, its crystal lattice is destroyed; this is achieved at a certain temperature, which remains constant for some time. At this moment, metal melting occurs. When the process of crystal destruction is completely completed, the temperature of the metal begins to rise again, and it turns into a liquid form and begins to boil. The melting point of copper is much lower than the one at which the metal boils. The boiling process begins with the appearance of bubbles, similar to water. At this stage, any metal, including copper, begins to lose its characteristics, which is mainly reflected in strength and elasticity. The boiling point of copper is 2560 °C. During cooling of the metal, a similar picture occurs as when heating - first the temperature drops to a certain degree, at this moment solidification occurs, which lasts for some time, then cooling continues to its normal state.
Soldering copper pipes
Copper has been used by mankind since ancient times, although its use for laying heating and water supply pipes on a large scale is officially considered to be the beginning of the last century.
One of the main processes for joining copper pipes is soldering, which involves heating the pipe ends and couplings, causing the solder to melt and form a sealed joint.
In this article we will look at how to solder copper pipes, their types, advantages and disadvantages.
Types of pipe materials
The industry produces two types of pipe products: annealed and unannealed copper pipe, what are the differences? The manufacturing process for both varieties involves processing copper ore. All unwanted impurities are removed from the resulting blister copper by blowing oxygen through it. The result is metal ingots of high purity. Further, the production technology of each type is sharply different.
- Unfired copper pipe is obtained by rolling and stamping the resulting ingots.
As a result of these operations, products with high hardness and strength are obtained. The release is carried out by separate straight rods 5 and 3 m long. The absence of heat treatment does not lead to damage to the internal structure of the metal. At the same time, the product becomes very durable. For unfired products, the tensile strength indicator can be from 340 to 450 MPa, the permissible elongation value is 6 percent. - Copper pipe, annealed or soft. Manufacturing is carried out by annealing, which is reflected in the name of such products. The process is based on a special heat treatment, in which the products are heated to 700 degrees, followed by gradual cooling. The pipes are supplied in coils of 50 and 25 m. When annealed, the natural plasticity lost during rolling or stamping is returned to the material.
Annealed pipes, while inferior to the first type in terms of strength indicators, are significantly superior to them in ductility. In case of accidental freezing, the high plasticity of annealed water pipes guarantees them against rupture.Their possible elongation reaches 60%, which allows bending, if necessary, in a cold state, subject to a certain ratio between the radius under which the bend is made and the diameter of the pipe (R = 3...8d).
Annealed products are highly resistant to operation in conditions of high humidity and sudden temperature changes.
Pipe materials with thick walls successfully withstand high pressure; when a polymer layer is applied to the surface, heat losses are significantly reduced and condensation does not form in cold water pipelines. Such products are especially popular when installing heating systems and hot water pipelines.
Solid, unannealed pipes in a cold state can be bent using a pipe bender only with diameters up to 18 mm; if it is necessary to bend larger sizes, it is necessary to first soften the products by heating up to 500 degrees.
What if you add a copper additive to your oil?
You can find these additives in a jar on sale. No approvals, no standards, no certificates. Everything is based on trust. At one's own risk. In my opinion, it is better not to experiment.
You can find these additives in a jar on sale. No approvals, no standards, no certificates. Everything is based on trust. At one's own risk. In my opinion, it is better not to experiment.
Any additive manufacturer always presents its products in the most favorable light. Typically, the emphasis is on improving several of the above characteristics of the oil, while the rest are supposedly “not worsened.” However, manufacturers of miracle potions based on copper often promise fuel savings of as much as 12%, an increase in power by the same amount, a reduction in noise by 18 dB (and that’s a lot!) and, most importantly, an increase in service life by 30 times! From these statements alone one can understand that either the Nobel Prize cannot find a laureate in any way, or it is all a fake.
ESAB welding wire
Consumable material in the form of welding wire is widely used in various welding technologies. The presence of this product in the range of manufacturers with influence in the welding materials market is a prerequisite. ESAB, as a world leader, is distinguished by its production of wide-purpose wires, covering all possible areas of its application. Areas of application ESAB welding wire is in demand in oil and gas, shipbuilding, mechanical engineering, chemical and other industries. IN.
What is roasted copper?
Buyers bring various types of cable scrap. Burnt copper (“F”) is a conductive wire core with a cross-section of 1 mm, which was obtained after heat treatment of illiquid goods. This category includes scrap contact cable.
Requirements for roasted copper:
- no traces of oil or paint;
- clogging content no more than 0.5%;
- absence of braid parts;
- normal background radiation;
- no traces of tinning.
The cost of baked copper is affected by the content of foreign impurities and total weight. Buyers work with retail and wholesale clients. They offer a high cost of copper per kg. Guaranteed immediate payment.
Conditions for obtaining burnt copper:
- burning of waste wire;
- manufacturing defect;
- burning of illicit cable.
Burnt copper is highly valued if the heat treatment is carried out in accordance with GOST. There should be no traces of melted plastic left on the metal. The quality of copper “Zh” is inferior to electrical color. But roasting reduces the preparation time for processing and increases the cost of purchase.
Recycling collection points
Scrap acceptors purchase the following waste cable and wire products:
a) manufacturing defects, warehouse surplus;
b) used cable lines, production remains;
c) old uncleaned cable;
d) dismantled communications;
e) installation waste.
Acceptance is carried out according to several criteria, which determine the price per kg of scrap. The length of the conductor pieces, the percentage of scrap to insulation, and foreign impurities are taken into account.
It is recommended to hand over recyclable materials to collection points that have documents and permits to conduct this type of activity. Before weighing, the scrap is inspected and assessed by specialists.
By the way! To determine the weight of the metal without winding, the acceptance specialist cuts off a prototype conductor, strips it and weighs it.
Source
Annealing temperature
The choice of heating temperature is chosen depending on what properties of the part they want to obtain. To make it plastic, it is necessary to heat it to a temperature of 500-700 degrees, and then cool it sharply in water. In this case, the heating rate does not significantly affect the properties of copper. Cooling in water is preferable, since after this it is much easier to remove scale.
To reduce hardness, complete annealing is used. The workpiece is heated to 900 degrees Celsius and then slowly cooled, most often together with the furnace. The internal stress that arises during machining disappears.
After cutting the copper and obtaining the finished product, the part can be heated to a temperature of 400-450 degrees and cooled in air at room temperature (within 1.5 hours). This will return the hardness of the processed part.
Features of copper annealing
When heat treating copper and its alloys, two features of the material are taken into account: increased thermal conductivity and interaction with gases when heated. It is these factors that cause rapid and uniform heating of the metal along the perimeter of the section. Annealing copper is heating the metal followed by cooling, allowing you to change the properties of the material. Heat treatment makes the metal softer and more ductile. Copper is used in various fields where ductility is important.
Sequencing
If necessary, you can obtain products for decorative or practical purposes at home. Melting copper at home, step-by-step instructions are as follows:
- The raw material is crushed and then placed in a crucible. It is worth considering that by reducing the size of pieces of metal, the melting process is significantly accelerated.
- After filling the crucible, it is placed in an oven, which is preheated.
- The molten alloy must be removed from the furnace using special pliers. Due to the active oxidation process, a homogeneous film may form on the surface. Before casting from copper, it must be removed.
- The metal is carefully poured into the prepared container. It is worth considering that if the straightened alloy gets into exposed areas of the body, serious injuries may occur. In addition, some materials may ignite upon contact. Therefore, extreme caution must be taken.
When considering how to smelt copper at home, it is worth considering that you can use more than just furnaces. In some cases, a gas burner is used to heat the bottom of the crucible. The process is less productive, but it takes little time to prepare.
An ordinary blowtorch can be used as heating equipment. When using this technology, it is worth considering that contact of copper with air leads to the rapid appearance of oxide. In some cases, to reduce the intensity of oxidation, the surface is covered with crushed charcoal.
Popular methods for stripping insulation
When handing over a cable, the metal core of the conductors is of value. Before going to the receiving point, you need to strip the cable from the insulating winding. There are several ways to do this yourself:
- manual stripping with a knife or hammer is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process, suitable if the batch of scrap is small;
- roasting and melting - a fast process, but harmful to the environment, not recommended for thin-stranded scrap, the metal burns out along with the winding;
- the use of special equipment is the fastest and safest method; tools are used during the work.
Cleaning with a knife or hammer
A construction or stationery knife or pullers with hooks, adjusting screws, etc. are suitable for stripping wires. When working, carefully cut the winding along the core, then take it to the side and cut it.
When working with a hammer, they hit the cable with force until the insulation separates from the metal.
Firing and reflow
You can burn raw materials over a fire, but the method is justified for large volumes of raw materials. Perform work outdoors, observing safety precautions.