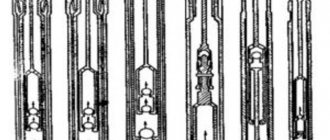
A vane pump is a rotary volumetric hydraulic machine in which the displacers are two or more blades (vanes). It is often called gate or rotary-plate. Having good characteristics and a practical design, it has won a wide range of applications in various industrial sectors. Its design is used in the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries.
Vane pump
Technical data:
- Used in various machine tools and hydraulic power steering;
- Nominal outlet pressure up to 12.5 MPa;
- Efficiency up to 85%;
- Torque 30 rpm;
Double or double acting vane hydraulic machines
The main feature of a double-acting vane pump is that its stator is oval in cross section. Moving along the inner surface of such a stator, each rotor gate performs two strokes per shaft revolution. A double-acting vane pump operates according to the following algorithm.
- Temporary working chambers (the transported medium is pumped into them and then displaced into the discharge line) are formed by such elements as the outer surface of the rotor, the oval inner surface of the stator, two adjacent plates and side disks. In this case, temporary working chambers of the smallest volume are created in that place of the internal cavity of the vane pump where the gap between the rotor and the stationary part of the engine is minimal.
- The high tightness of the temporary working chambers is ensured due to the fact that the plates, sliding their end part along the inner surface of the stator, are tightly pressed against it.
- After the plates pass the area with a minimum gap between the rotor and stator, the volume of the temporary working chamber increases. This leads to the fact that the pressure in it sharply decreases, which means that an area of rarefaction of air is created. When passing the section of the inner surface of the stator, where the side disk is located, the slots in which are connected to the suction line, the temporary chamber is filled with the pumped medium.
- When the temporary working chamber, already filled with the pumped liquid, passes the next section with a minimum gap between the rotor and stator, the pressure of the working medium increases in it, which helps to displace the latter into the slot of the second side disk connected to the discharge line.
- Thus, due to the oval shape of the stator cross-section, the entire process described above occurs twice during one revolution of the rotor shaft.
Operating principle of double acting vane pump
The force of pressing the end part of the working plates against the inner surface of the stator as they slide along it is influenced by the pressure of the pumped liquid exerted on the rear surface of such elements. The force with which the plates are pressed against the inner surface of the stator during sliding can be calculated by multiplying the pressure of the fluid acting on the rear surface of such elements by the area of their end part. When pumping liquids with poor lubricating properties under a certain pressure, situations may arise when a thin film of the working medium does not form between the end surface of the plates and the inner walls of the stator. Operation of a vane-type pump under such conditions contributes to intensive wear of its working elements.
If a vane pump is planned to be used for pumping liquid that enters the suction pipe under a pressure exceeding 150 bar, then to solve such problems, select models of pumping devices, the design of which is equipped with double plates. In such cases, the pumped liquid is supplied through an opening in the rear end of the vane pump and enters the space between the paired plates, which allows one to compensate for too much liquid pressure exerted on the working blades.
» data-lazy-type=»iframe» src=»data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7″>
This is interesting: Diaphragm (diaphragm) pumps: principle of operation, types, application
Single acting devices
The cross-section of the rotor of vane pumps operating on the single-acting principle is cylindrical. The change in the volume of the temporary working chamber (this is a necessary condition for the effective operation of vane-type pumping equipment) is ensured due to the fact that the rotor, relative to the stationary part of the engine, performs rotational movements along an eccentric trajectory.
The operating principle of single- and double-acting vane pumps, despite the differences in their design, is the same.
Operating principle of a single type vane pump
Adjustable type hydraulic machines
In variable-type vane pumps, the position of the stator ring can be changed. Adjustment of the spatial position of the stator relative to the rotor rotating inside it, for which there are three screws in the pump design, is carried out as follows.
- Using the feed limit screw, you can change the eccentric path along which the rotor moves. Thanks to this, the flow level of the vane pump is regulated.
- Using the support position adjustment screw, you can change the spatial position of the stator in the vertical plane. The dynamic characteristics of the pump and the noise level it produces during operation depend on this parameter.
- The maximum pressure adjustment screw allows you to control this parameter by changing the degree of compression of a special spring.
Design of a vane pump with adjustable displacement
The operating principle of a variable-type vane (vane) pump is as follows.
- The pressure of the pumped medium, depending on the value of the fluid resistance in the hydraulic system, acts on the inner walls of the stator, and through them on the adjusting spring. As long as the value of this pressure is less than the resistance force of the spring, the stator ring is in eccentricity with respect to the rotor.
- As the pressure of the working medium increases in the hydraulic system, the degree of its influence on the walls of the stationary part of the engine and the adjusting spring also increases.
- At the moment when the fluid pressure exceeds the counter pressure of the spring, the stator ring will begin to move from eccentricity to a concentric position. In this case, the volume of the temporary working chambers of the vane pump decreases, and, accordingly, the pressure of the liquid that it supplies to the discharge line decreases. As the pressure of the liquid entering the suction pipe increases further, the pressure of the working medium in the discharge line may approach zero (zero stroke of the pump). However, even in this situation, the pump will supply the pumped liquid to the discharge line, the volume of which will be equal to the amount of internal leaks of the device. The amount of fluid pressure in the supply line at which the above-described situation becomes possible is changed by the degree of compression of the control spring.
Operating principle of the pressure regulator
Variable vane pumps with a zero stroke option include a drainage system. Through it, all internal leaks are removed from the high pressure zone of the working chamber of the device. The presence of such a system in the design of a vane pump makes it possible to effectively remove heat from the rubbing elements of the device and also ensure their lubrication.
Features of a vane pump: principle of operation, application in production and advantages of equipment
The wide popularity of the vane pump is due to the structural features of the internal parts of the device; they have the form of flat or shaped plates. Back in 1974, Soviet designer Boris Grigoriev worked on the design of internal elements, and all manipulations turned out to be successful. After presenting his works to the whole world, the inventor from the USSR filed a patent in 29 countries around the world, which earned him great respect from his contemporaries. Today, vane pumps are used in many industries, but consideration must begin with the actual design of the equipment and its positive aspects.
The wide popularity of the vane pump is due to the structural features of the internal parts of the device; they have the form of flat or shaped plates. Back in 1974, Soviet designer Boris Grigoriev worked on the design of internal elements, and all manipulations turned out to be successful. After presenting his works to the whole world, the inventor from the USSR filed a patent in 29 countries around the world, which earned him great respect from his contemporaries. Today, vane pumps are used in many industries, but consideration must begin with the actual design of the equipment and its positive aspects.
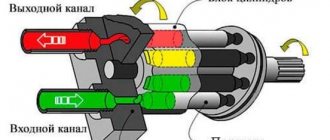
Indirect control units
The operating principle of such devices is identical to the operation of direct-controlled equipment. The only difference between them is the adjustment mechanisms. These units do not use adjustment springs (one or two), but pistons. These mounting elements are under pressure and control the movements of the stator.
Typically two pistons with different diameters are used. In this case, their surface area has a ratio of 2 to 1. The operating principle of the pump looks like this:
- A piston with a larger area is acted upon by a spring that regulates the maximum eccentricity of the stator at the moment of starting the pumping equipment.
- The smaller area piston is connected to the pressure line. Also, this pressure is interconnected through a special regulator with a larger piston.
- When the pressures acting on both positioning pistons are equal, the stator is positioned at the point of extreme eccentricity. This happens because the pistons have different areas.
A pressure regulator is used to determine the maximum pressure in the hydraulic system. It consists of the following parts:
Description of operating principle
The design of the pump affects the principle of its operation. In order for the entire system to work, it is necessary to provide a pressure difference. The increase in pressure at the outlet is due to the vortex effect, which is created by shifting the central rotational axis of the rotor.
Operating principle:
- An increase in pressure from the outlet side provokes a sharp decrease in pressure in the area of the stator inlet.
- During startup, this makes it possible to provide the necessary pressure difference so that water is sucked into the cavity of the device between the plates.
- Then the water comes out through the pump tubes and through the irrigation system of the garden or summer cottage.
A vane vane pump should be selected based on the tasks it will perform.
Some models, due to the fact that their axis of rotation can deviate, are used to regulate the volume of incoming liquid. Such a pump can be used not only for its intended purpose, but also as a good additional dispenser in a general water supply system.
Dry Oil Free Vacuum Pump
A dry oil-free vacuum pump is an air-based device that allows it to minimize the threat of overheating that can occur due to a lack of oil in the system. Recently, many have begun to lean towards dry vacuum pumps. The main reason for this is the new operating technology, which does not require constant lubrication or the addition of any liquid.
All the user needs to do is turn on the vacuum pump, after which it can work without any interruptions. But still, we should not forget that this is a technique and must be constantly looked after. By following all the necessary procedures for this device, you can be sure that it will serve you for many years and during this time its internal parts will remain in perfect order and will continue to provide the same high performance indicators.
Features of repair and replacement of elements
It's no secret that any technology sooner or later begins to fail. At the same time, the breakdown is not always some kind of major malfunction, and repairs can be done with your own hands. In any case, to repair a vane pump you need to have at least a little knowledge of mechanics and repair work.
Pump parts should only be purchased from trusted stores.
Types of repair work:
- Rotor failure. If the rotor wears out for one reason or another, experts recommend repairing it rather than replacing it. Replacing one rotor with another is much more difficult and expensive than repairing it. As a repair, it is necessary to restore the grooves so that their walls become parallel again, the necks and ends must be ground.
- Blades can also wear out from intense work over a long period of time. In this case, they are simply replaced with others. In this case, new blades can be made from a different, more durable material.
- Shakey. If the rotor journals are worn out, they are repaired by chrome plating or grinding.
As a rule, the journals of a rotary pump are repaired together with the ends, which must also be properly ground. Repair work on setting up gate-type equipment is quite labor-intensive and requires a lot of time and at least minimal knowledge in this area. And yet, despite this, minor defects and breakdowns are best corrected through repairs. For example, replace worn bearings or strengthen the oil seal.
In some cases, it is best to seek help from specialists, and in case of major breakdowns, replace the pump parts with new, more stable ones, or purchase a new device.
What is required for installation
A safety valve is installed to protect the hydraulic system and pump from overload. In this case, its settings must correspond to the nominal outlet pressure. The pipeline must have smooth bends and a good seal at the junction with the pump to prevent air from entering.
Before the first start, the working mass is poured into the mechanism, and the valve screw is unscrewed to zero settings.
Types of Vane Pumps
Vane pumps can be divided according to the principle of operation, as well as the design features of the working parts of the pump.
According to the principle of operation, vane pumps are divided into two types:
- Single action
These pumps only manage to provide suction and injection of liquid once during one rotation of the rotor.
- Double action
Double-acting pumps can respectively provide suction and discharge 2 times in one full revolution of the shaft and rotor.
According to the design of the main elements, vane pumps are divided into the following types:
- Vane pump
- Vane pump with flexible rotor (elastomer)
- Hanging Vane Vane Pump
- Roller vane pump
- External plate pump
This is interesting: Calculation of a pump for a heating system: selecting the optimal pump based on key parameters
Vane (vane) pump: design, types, principle of operation
Design features Double-acting or double-acting vane hydraulic machines Single-acting devices Adjustable-type hydraulic machines Adjustable indirect-acting vane pumps
For pumping media that tend to become more viscous and thick as the temperature decreases, a vane pump (or, as it is also called, a vane pump) is optimally suited. A design feature of vane pumps, which allows them to ensure a constant degree of viscosity of the pumped medium, is the presence of a special jacket in their body. The coolant, which is supplied from the outside and circulates in the internal cavities of such a jacket, heats the medium transported through the pump, preventing it from thickening.
Rotary pump device
Today, the rotary vane pump has undergone many changes and designs. But to understand the general principle of operation of such equipment, you can consider the design of a rotary pump of an adjustable single-action type with a constant direction of flow.
The pump performance is changed by moving the stator 1 , which rests on the needle bearing 2 .
A massive shaft 3 , on the splines of which a rotor 4 with inclined plates 7 , rests on bearings 5 and 6 and takes the load from the pressure of the working fluid on the rotor.
The shaft, rotor, stator and plates are made of heat-treated alloy steel.
When the pump starts, the plates are ejected by centrifugal force, and during operation the plates are hydraulically balanced.
The pumps use bronze distribution discs 8 , which distribute the working fluid and have windows for balancing the plates.
Such a vane pump has built-in controls that allow you to automatically change the eccentricity value depending on the load.
For this purpose, there is a spring 9 , which strives to install the stator 1 with minimal eccentricity, i.e. to the position corresponding to zero productivity.
At the same time, three strong springs 10 act through the differential piston 11 on the stator 1 , shifting it towards the highest eccentricity value.
The pressure of the working fluid, pumped by the pump and supplied through hole 12 , acts on the differential piston 11 and is perceived by springs 10 .
When, as the load increases, the increasing pressure of the working fluid in the pressure line overcomes the force of the springs 10 , the piston 11 rises, and the stator 1, under the action of the spring 9 , moves in the direction of decreasing eccentricity, as a result of which the pump performance decreases.
The shaft, rotor, stator and plates are made of heat-treated alloy steel.
Materials used in the production of pumping equipment
The body of the vane pump, as well as the main elements of its flow part, are made of gray or ductile cast iron, as well as carbon or stainless steel alloys. The pusher and rotor in a vane pump can be made from:
- polyetheretherketone;
- carbon graphite;
- NBR;
- EPDM.
The equipment model is selected taking into account the requirements for its temperature, abrasive and corrosion resistance. The shaft seal of pumping equipment can be cartridge or end-type. It is also possible to equip the shaft with a magnetic coupling.
Design Features
The design of the vane pump consists of:
- a housing with two pipes (suction and discharge), which is made of cast iron or steel alloy;
- drive motor (usually asynchronous type);
- a shaft with plates (rotor), which rotates inside the housing along an eccentric path (the working plates are located in special grooves of the rotor, in addition, on the surface of this structural element there are grooves that have different angles of inclination in those places where they extend to the faces of the shaft).
Main parts of vane pump
Vane pumps are divided into two broad categories: single- and double-action devices. Their main design difference lies in the cross-sectional shape of the stator - the element within which the rotor rotates.
The operating principle of vane (or vane) pumps, both single and double acting, can be described as follows.
- When the rotor rotates, the plates, which have the ability to move freely in the mounting slots in the radial direction, move out of them under the action of centrifugal force.
- The end part of the extended plates comes into close contact with the inner walls of the stator and begins to slide along them, moving the medium pumped by the device.
Operating principle of a vane pump
Depending on the scheme used to control the operation of a vane-type pump, such a device may refer to adjustable pumps:
- direct control;
- indirect.
Control circuits for variable vane pumps
Material execution
The main components of vane pumps can be made from a wide variety of materials to provide the required corrosion, abrasion and temperature resistance. The following main materials can be distinguished:
| Pump flow part: | Rotors and tappets | Plates |
| Gray cast iron | Carbon graphite | Carbon graphite |
| Ductile iron | PEEK (polyetheretherketone) | |
| Carbon steel | NBR (flexible rotor pumps) | |
| · Stainless steel | EPDM (flexible rotor pumps) |
Main areas of application: what tasks can vane pumps solve?
Vane pumps allow you to solve a whole range of specific problems:
- pump aerofuel;
- transport various aerosols;
- work with lubricants and fuels of different types;
- pump alcohols and solvents;
- transport ammonia and liquefied petroleum gas;
- used for transporting freon in refrigeration equipment.
The technology has found its application in the gas and oil industries, in the chemical industry and energy, in aircraft manufacturing, shipbuilding and shipping, and in the engineering sector.
#FORM#
Advantages and disadvantages of external gear pumps
Advantages:
- Pumping low-viscosity liquids at fairly high pressures
- Plate wear compensation
- Possibility of pumping solvents
- Ability to work “dry” for short periods of time
- Only one shaft seal
- Ability to create a good vacuum to absorb liquid
Flaws:
- Hard to maintain. Lots of spare parts
- Cannot work at high pressure
- Cannot handle high viscosity liquids
- Not very good resistance to abrasive liquids
Advantages and specifics of operating vane pumps
1.
Vane pumps make it possible to transport media with critically low viscosities. At the same time, they guarantee good pumping pressure.
2.
Plates made from carbon graphite are characterized by a high degree of wear, which eliminates the need for frequent maintenance and repair of equipment.
3.
Vane pumps can be used to pump solvents.
4.
In case of short-term cases of “dry” running, the equipment does not fail.
5.
The vane pump allows you to create an excellent vacuum for suction of medium in large volumes.
It should be noted that the equipment is not suitable for working at high pressure and requires serious maintenance in case of failure. The latter is due to the large number of spare parts in the design of the vane pump.
Video: operating principle of a vane pump