What kind of oil to fill in a piston air compressor
Not everyone knows what kind of oil to put in a piston air compressor or whether it needs maintenance. To clarify this issue, let's start with the concept: what is an air compressor?
Technologically, this is the complete opposite of the internal combustion engine. We are talking about a piston design, because membrane compressors operate on a completely different principle.
Any mechanical unit requires lubrication, otherwise its service life will tend to zero. To simplify the analysis, compare the compressor with a conventional internal combustion engine.
A piston engine works on the following principle: pressure is generated in the cylinders (due to the combustion of the air mixture), the pistons move, and with the help of the crankshaft they transmit torque to the power take-off shaft.
In a compressor, everything is the other way around: the shaft rotates (using an external drive), the pistons move in the cylinders, and pressure is created. For the sake of it (pressure) the whole structure works.
Compressor life
Manufacturers often forget to indicate this parameter, and deliberately so. After all, the duration of operation of the unit can only be determined experimentally. However, there are indirect signs of determining the motor resource. In piston models, this is the crankshaft rotation speed. The faster the shaft rotates, the more the head heats up and the faster it wears out. It is correct to compare compressors of the same performance.
Belt driven compressors last longer. Belt drive provides high performance at low speeds. Compressors with belt transmission of torque belong to the semi-professional class and are capable of creating up to 16 atm.
Changing the oil in the compressor must be done. It is quite difficult to calculate how many hours a unit has worked, especially if it works daily. It is recommended to change the oil twice a year. During this time, it usually manages to change color.
Good day to all. I have this compressor
The instructions say to use L-DAB 100 oil. Can anyone tell me what can replace it with? The compressor is completely new and needs to be filled with oil.
Why pour oil into the compressor?
At first glance, it may seem that the pistons in the compressor can operate without oil. There are modern materials that have a minimum coefficient of friction (Teflon, fluoroplastic, etc.).
For example, piston-type automotive compressors do not use separate lubricant. However, there is a huge difference in the volume of air pumped. Let us remember the elementary laws of physics: when gases are compressed, a large amount of thermal energy is released.
Simply put, the piston group gets very hot during operation: the higher the pressure in the receiver, the stronger the heating. It is for this reason that the compressor cylinders are equipped with air cooling fins.
- Oil has good thermal conductivity (albeit less than ordinary water), so washing the piston group to some extent helps remove heat.
- No matter how low the coefficient of friction of the piston rings, heating still occurs. If you leave the compressor without lubrication, the metal may become hot, it will “lead”, and the geometry will be disrupted.
- In addition to the pistons and cylinders themselves, the piston group consists of many elements: connecting rods, crankshaft, and possibly a gearbox. These elements require lubrication, and according to the classical method (as in an internal combustion engine). That is, the compressor has a crankcase in which lubricant splashes.
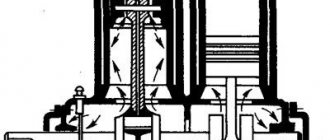
To understand the principle of operation of a piston compressor, consider its structure:
The crankshaft (1) rotates freely using bearings (2) . The need to lubricate these components is not even discussed: without it, work is impossible. The connecting rod (3) and piston pin (4) do not have rolling bearings. Just like in an internal combustion engine, liners are installed. If these friction pairs are not lubricated, the compressor will seize within a few minutes.
To prevent air compressor oil from leaking out of the housing, a seal (8) . What about the piston (5) ? If the rings are not sealed, fumes from the lubricant will enter the working chamber (6) . And then through the valves (7) the contaminated air will enter the working line.
With such a lubrication system, the cylinder walls are sufficiently washed with oil to ensure normal sliding and additional cooling. To clean the air from possible vapors, filters are installed.
It is usually a porous material that retains any liquids. To obtain breathing air (for example, when filling scuba tanks), more advanced cleaning systems are used.
There is another design of the piston group, which is used in compressors with guaranteed purity of the pumped air. Only the crank mechanism is lubricated; a slider is installed between the piston and the crankcase, guaranteeing complete dryness in the working chamber.
True, such systems cannot provide high performance: loads are contraindicated.
Oil for air piston compressor
Oil performs various important functions that ensure stable operation of the compressor. Failure to do at least one of them reduces productivity and sometimes causes breakdowns. Let's list its functions :
- lubrication of rubbing parts;
- cooling of parts that heat up during operation;
- sealing gaps;
- reduction of detonation;
- creating tightness in compression chambers.
Low tightness or seals reduce the efficiency of the compressor, but in the absence of lubrication or cooling of parts, an expensive unit quickly fails due to wear of parts, so the oil level in the air compressor must always be at the proper level.
Is it possible to fill the compressor with motor oil?
Traditional oils are not suitable for several reasons:
- Compressor oil has higher environmental standards. Air can enter the operator's respiratory tract, even if he is a mechanic using pneumatic tools.
- The composition must ensure fire safety. That is, lubricant vapors, if mixed with air, should not pose a risk of ignition. And in such temperature conditions the risk is very high.
- The viscosity characteristics are fundamentally different.
- The compressor can run longer than the car engine (other terms for replacing used oil).
An amateur's experience or what will happen if you pour engine oil into a compressor - video
In addition, uniform standards have been established for oils that can be poured into the compressor. Each manufacturer (of equipment) sets its own requirements, but the approach remains the same.
- Minimum coke number. This means that during thermal decomposition of the lubricant (if it occurs), the amount of solid precipitation should tend to zero.
- Requires high thermal conductivity not available with traditional motor oil.
- When temperature and pressure increase (normal conditions for an air piston compressor), the physico-chemical properties should not change. This is especially true for the parameters of dripping, melting, solidification and flash. Although for this type of oil it is more correct to use the term “discharge temperature”.
495 rub.
with VAT - 1 l. Stock. Rosneft VDL-100 compressor oil (formerly TNK VDL100) is produced on the basis of highly purified mineral base oils with an imported package of functional additives. The additive package includes additives that provide high anti-corrosion and antioxidant properties, and high resistance to sedimentation. Oils of this series are developed taking into account all the requirements for oils by domestic and foreign manufacturers of compressor equipment, fully comply with the requirements of DIN 51506, category VDL, and other world standards in this area. Rosneft oil has a number of approvals from equipment manufacturers and positive recommendations from large operators of compressor equipment.
Characteristics:
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Kinematic viscosity at 40°С, mm2/s | 101,7 |
| Kinematic viscosity at 100°С, mm2/s | 11,1 |
| Color on the CNT colorimeter, units | 2,5 |
| Ash content, % | 0,01 |
| Density at 20°C, g/cm3 | 891,3 |
| Acid number, mg KOH/g | 0,2 |
| Flash point in an open crucible, °C | 232 |
| Pour point, °C | -24 |
| Tribological characteristics for ChShM: | |
| scuff index, N (kgf) | 53(54,8) |
| wear indicator, mm. | 0,31 |
Attention! If the compressor is filled with a different brand of oil, it is necessary to drain the remaining oil and fill in new one. Mixing different brands of oils is not recommended.
695 rub.
with VAT - 1 l. Stock. Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 100 is a mineral oil designed for the lubrication of air compressors. Distinguishing properties: highly refined oil based on paraffin oils; excellent thermal stability, exceptional oxidation resistance; minimal formation of sediments and deposits, guaranteeing the cleanliness of all mechanical parts; prevents the risk of fire or explosion; excellent anti-corrosion properties; low volatility. Applications: air compressors, oil injection rotary compressors, dry rotary and centrifugal compressors, closed hydraulic systems using ashless oils.
Characteristics:
| Property | Method | Unit | Result |
| ISO class | 100 | ||
| Viscosity at 100°C | D 445 | CSt | 10,56 |
| Viscosity at 40°C | D 445 | CSt | 91,56 |
| Viscosity index | D 2270 | 97 | |
| Density at 15°C | D 1298 | kg/m? | 888 |
| Flash point COC | D 92 | °C | 216 |
| Pour point | D 97 | °C | -25 |
Attention! If the compressor is filled with a different brand of oil, it is necessary to drain the remaining oil and fill in new one. Mixing different brands of oils is not recommended.
116 euro including VAT - 20 l.
High quality oil for piston air compressors. Shell Corena P 100 is a high quality reciprocating air compressor oil. Developed from a mixture of specially selected base oils that bring the product's performance properties closer to the level of synthetic oils.
Application area:
Piston air compressors. All industrial piston air compressors operating with discharge air temperatures up to 220°C.
Compressors that produce breathing air. Shell Corena P can be used in compressors producing compressed breathing air, providing additional cleanliness to the equipment used, ensuring that the air produced is breathable. Shell Corena P 150 is approved for use in BAUER breathing air compressors.
Advantages:
Long service life. The oil provides a significant extension of the intervals between maintenance of valves and pistons. This greatly extends the period when the compressor can be operated with high efficiency.
Safety of overhead lines. Rust particles dispersed in carbon deposits in compressor discharge lines, when exposed to the heat of compressed air, can cause an exothermic reaction leading to explosions and fires. Shell Corena P helps to minimize the occurrence of such hazards.
Excellent antioxidant properties. The oils are resistant to the formation of carbon deposits (carbon deposits) and varnish formation on valves and piston heads caused by corrosion products (iron oxides and hydroxides) at high operating temperatures and pressures. These deposits can cause serious damage, reduce compressor efficiency and increase operating costs.
Excellent anti-corrosion and anti-wear properties. Effectively protects all metal surfaces from corrosion. Protects all critical equipment parts, such as casings, valves, bearings, from wear and extends maintenance intervals.
Very good deaeration and anti-foam properties. Careful selection of additives ensures rapid air separation without excessive foaming.
Good demulsifying properties. Shell Corena P easily separates water and excess water can be easily removed from the oil circulation system. This helps prevent corrosion and maintain effective lubrication, and also helps separate oil from condensate in oil/water separators and dryers.
Specifications and approvals:
DIN 51506 VDL ISO 6743-3:2003 DAA standard conditions.
Corena P150 is approved for use by BAUER and is included in the BAUER reference oil list for breathing air compressor lubricants.
Compatibility with sealing materials:
Shell Corena P is compatible with all sealing materials commonly used in air compressors.
Recommendations:
Recommendations for the use of lubricants in applications not specified in this data sheet can be obtained from your Shell representative.
Health and Safety:
When good personal and industrial hygiene is observed and when used properly in recommended applications, Shell Corena P does not pose a health or environmental hazard. More complete information on this issue is contained in the product safety data sheet.
Protect the environment:
Used oil must be sent to specialized disposal points. Do not dispose of used oils into sewers, soil or bodies of water.
Typical physical and chemical characteristics:
| Index | Method | Shell Corena P |
| ISO viscosity grade | ISO 3448 | 100 |
| Standard | DIN 51506 | VDL 100 |
| Kinematic viscosity, mm²/s at 40°C at 100°C | ASTM D 445 | 100 9,2 |
| Density at 15°C, kg/m³ | ASTM D 1298 | 899 |
| Flash point in open crucible, °C | ASTM D 92 | 240 |
| Pour point, °C | ASTM D 97 | -33 |
| Neutralization number, mg KOH/g | ASTM D 974 | 0,3 |
| Sulfate ash content, wt.% | DIN 51575 | 0,06 |
| Oxidative stability (change in coke residue mass), % | DIN 51352-2 | 2 |
| Properties of the fractionation residue (20%) coke (according to Conradson), wt.% kinematic viscosity at 40°С, mm²/s | DIN 51551 DIN 51562 | 0,3 160 |
| Corrosion protection (steel) | ASTM D 665 | withstands |
| Demulsifying properties, min. at 54°C at 82°C | ASTM D 1401 | — 20 |
Characteristics that determine which oil can be poured into the compressor
It is the discharge temperature that is one of the main parameters (relating to the safety of the compressor).
- category 1 – gentle operating conditions, up to 160°C;
- category 2 – standard operating conditions, up to 180°C;
- category 3 – heavy duty for continuous operation of compressor stations, up to 200°C;
- category 4 – harsh working conditions, including in aggressive environments, over 200°C.
- Oil is supplied under pressure using nozzles. This is an entire system that has a separate capacity (replenishment and replacement are carried out directly during operation). Viscosity is selected in strict accordance with operating conditions, including ambient temperature.
- Discharge using an internal gear pump also requires low viscosity, but is not dependent on the degree of oil heating.
- Natural splashing from the crankcase oil bath does not require special characteristics; standard values for transformer oils are sufficient.
As an example, an illustration of the parameters of Lukoil KS-19 motor oil.
Basic requirements for the characteristics of compressor oil
Due to the fact that compressor lubricants must be separated from the gases pumped into the cylinders, volatility is an important parameter. This characteristic is measured when the liquid is heated to operating temperature, which occurs after 10-15 minutes of operation of the unit. Characteristics of Ravenol compressor oil - video
- When creating oils, manufacturers are forced to compromise. On the one hand, a minimum viscosity is required, on the other hand, oil that is too thin is prone to evaporation. Therefore, binders must be added to the composition.
- Another requirement that compressor manufacturers make is a low oxidation coefficient. With prolonged use, the oil may burn. Soot and soot are formed, which gets on the cylinder walls and leads to the formation of scratches and scoring.
- The degree of wear resistance characterizes the ability to maintain specified characteristics until the oil is changed. If the parameters gradually decrease, it is impossible to ensure stable operation of the compressor.
- After short-term heating to a critical temperature, the basic indicators should return to their original state.
- Additives must be added to prevent foaming. The crank mechanism works like a mixer. The oil will simply whip up in the crankcase without creating a strong working film.
The complex of properties of compressor oil, from any manufacturer, must ensure:
- reliable start-up of equipment regardless of external temperature;
- if possible, reduce energy costs for operating units;
- at high loads on the piston group, there should be no prerequisites for jamming of the rubbing pairs;
- prevention of emulsion formation: with a sharp change in pressure in the piston group, condensate forms, which must be bound by demulsifiers.
How to replace compressor oil?
If you adhere to the technical requirements, replacement is not provided. That is, there is no alternative among other types of lubricants. However, based on experience in using low-power compressors, it is possible to fill in engine oil for diesel engines with a viscosity of SAE 15W40.
This may not be profitable from an economic point of view: branded compressor oil is cheaper. And given the availability of these materials, there is no point in experimenting with the equipment.
Source
Question answer
“What screw units are used in Remeza compressors?”
Remeza screw compressors are equipped with oil-filled units manufactured by the German company GHH Rand. This brand is a division of the American corporation Ingersoll Rand Company. It is considered a world leader in the production of oil and oil-free screw blocks.
“How to choose rings for a compressor?”
Piston compressors are equipped with two types of rings - compression and oil scraper. The selection of these parts must be carried out
- depending on the piston diameter. Aircast compressors use two sets of piston rings:
- set of piston rings F65 (catalog number 21145003). It fits models LH-20-2, LH-20-3, LB-30-2, LB-40-2;
- set of piston rings F80 (catalog number 21145004). It fits LB-50, LB-75 models.
- compressors with gray receiver. They are AirCast series equipment. The equipment is equipped with a pump assembly made of cast iron produced in France;
- compressors with a red receiver. This is Fiac series equipment. It is equipped with a pump assembly made of silumin produced in Italy;
- compressors with blue receiver. This group includes oil-free and mobile Remeza compressors.
You can also order high and low pressure rings for W-95 and W-115 compressors from us. They are supplied not in sets, but individually.
“Why are Remeza compressors painted different colors? What is the difference between equipment with a gray, blue and red receiver?
produces three model ranges of piston compressors. For the convenience of buyers and users, they are painted in different colors:
Knowing these features, you can easily choose and buy the appropriate model.
“What are the reasons for the appearance of additional noise during operation of a piston compressor?”
The appearance of extraneous noise during operation of the unit can be caused by several reasons:
- crankshaft deformation,
- bearing damage,
- insufficient clearance between the cylinder and the piston,
- plate valve wear.
To eliminate the source of noise, it is necessary to replace deformed and damaged parts.
“How to choose the right compressor equipment?”
When choosing a compressor, the type of equipment and its performance are primarily taken into account. Piston units are purchased for periodic use with the possibility of transportation. Oil-free coaxial models are inexpensive, supply clean air, but are not suitable for high loads. Oil compressors have higher performance, but require maintenance and are not designed for continuous operation. Belt models have high efficiency and a long service life, but are characterized by a high noise level. Low-noise screw compressors are in demand for large volumes of work. They can be used around the clock, but are expensive.
The performance of the model must exceed the power of the pneumatic tool.
“What is the difference between cold and hot regeneration?”
Dryers with cold regeneration (without heating) of the adsorbent use part of the dried air to remove the moisture found on its granules, the pressure of which is increased until it exceeds atmospheric pressure. Air is passed through the adsorber and, after it has absorbed moisture, released into the atmosphere.
During hot regeneration, heated air is supplied for drying, which removes water not only from the surface of the granules, but also from the deep layers. After this, the adsorbent’s ability to regenerate increases significantly, and the adsorption phase between regeneration processes increases to 4–8 hours. There is no need to compress the air.
“How to calculate the air requirement when replacing an old compressor?”
The calculation of the required flow rate is determined by the performance of the pneumatic tool used. The compressor output output should be 20–25% higher. It should be taken into account that manufacturers usually indicate input performance, so the rating characteristics must be multiplied by the efficiency. For piston models it is 0.65–0.76, for screw models it is 0.95.
“The technical specifications of compressors from different manufacturers use different units of measurement. How to compare such characteristics?
Equipment productivity in accordance with the SI standard is measured in m3/min. However, very often manufacturers indicate this characteristic in l/min. This unit of measurement is a thousand times smaller than the standard one, and is used to avoid indicating values in decimal fractions. In the English measurement system, performance may be expressed in cubic feet per minute (CFM). In this case, the calculations are more complex, since 1 CFM = 28.32 l/min. When converting pressure from Pascals to atmospheres, bars and millimeters of mercury, it is recommended to use the appropriate tables.
“What is the optimal operating mode for a screw compressor?”
In this type of compressor equipment, air is compressed under the influence of a screw pair rotating in an oil tank. During operation, heat is effectively removed as the friction coefficient is low. The equipment operates almost silently, has high performance and has an unlimited service life. It is advisable to use it for round-the-clock operation in order to recoup the considerable investment upon purchase.
“How often should compressor oil be changed?”
Oil coaxial compressors require regular maintenance. Their moving metal elements require a film of oil to be maintained on the surface. The oil change procedure must be carried out in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. Depending on the model, for piston compressors the interval ranges from 500 to 1000 hours. Screw compressor equipment is replaced on average every 4000 hours.
“What is the service life of piston and screw compressors?”
Piston compressors have a shorter service life compared to their screw counterparts. Thus, household and semi-professional devices from the first group are designed to operate for 1,000–3,000 hours. Industrial piston-type compressor units are more durable and can operate up to 8,000 operating hours (up to 3 years). However, maintenance of devices of this design should be carried out every 500 hours.
Screw compressors have a huge service life (up to 40,000 operating hours), which also depends on the modification of the device. In time terms, the service life of industrial installations of this type reaches 12 years of operation (before MTBF).
“What kind of oil should I put into a screw compressor?”
For screw compressors, it is recommended to use only the special oil provided by the manufacturer. It must have resistance to aging, increased anti-corrosion properties, hydrophobicity and lack of foaming. The ignition temperature of such oil must be at least 180 °C, and the kinematic viscosity must be from 7 cSt. Perfect for these purposes:
- Dicrea sx 46,
- Kraftmann Kraft-oil,
- Agip Dicrea 46 and others.
This lubricant is designed for fairly high loads to which it is subjected in screw compressors. In addition to lubricating rubbing parts, it performs cooling, sealing and filtering functions.
“What is compressed air quality?”
The quality of compressed air is determined by the technical requirements specified in regulatory documents. It is expressed in the quantitative content of various impurities per unit volume. These include:
- mechanical microparticles (present in the air when it is taken);
- tiny drops of machine oil (occur during operation of a lubricated mechanism);
- odors (present in air masses initially and added upon contact with the compressor);
- the presence of moisture vapor, which, when compressed, turns into water (characterized by the “dew point” temperature).
The fewer these impurities, the better the quality of the air.
“How to install a compressor correctly?”
Installation of the compressor is carried out only by specialists and in strict accordance with the project. The unit is installed on a solid reinforced concrete foundation, to which unhindered access is provided from all sides. During installation, the following requirements must be met:
- efficient room ventilation, especially for air-cooled compressors;
- fire safety;
- isolation from other equipment (if the installation power exceeds 100 kW, then a separate room is required).
Most piston-type installations cannot be installed near crowded places. This is due to the increased sound pressure of these units.
“What types of compressor output connectors are there?”
The range of compressor connectors is quite large. Nevertheless, it is worth highlighting several particularly common types of compounds. These include:
- fitting-type connector for joining individual parts of the pipeline (consists of a special fitting, nut, coupling and gasket);
- ball valve (shut-off valve with a working body in the form of a steel ball rotating in the body around an axis);
- herringbone element (designed for quick connection of high-pressure rubber hoses);
- bayonet connection (special fittings for quickly joining the two ends of the air line).
“What kind of oil should I pour into a piston compressor?”
The oil specified by the manufacturer should be used. If only special oil needs to be poured into a screw compressor, then for piston analogues this requirement is not so critical. However, for piston-type compressor units, it is recommended to use a VCL or DIN51506 class lubricant with viscosity - SAE 30.
The following are quite suitable for filling into a piston-type compressor:
- Mobil Rarus 425,
- KS-19,
- Ravenol VDL 100 and others.
In these units, oil lubricates the crankshaft connecting rod and main bearings, cylinders and pistons with compression rings, and also removes heat and ensures sealing of the compression chamber.
“Where is it better to install the receiver: indoors or outdoors?”
The best option for installing an air receiver is an open area located away from crowded places. In this case, the container must be equipped with a condensate drain and a special heating element for heating.
According to safety requirements (rules “PB 03-581-03”), this equipment can also be installed in specially designated buildings. In this case, the compressor unit and the air receiver must be located in separate rooms. This set of equipment can be placed in one machine room in exceptional cases and only after permission from Gosgortekhnadzdor.
“When is it worth installing an air dryer on a compressor?”
This depends on the consumer’s requirements for the quality of the supplied compressed air. This equipment is designed to dry incoming air masses. Purpose: to prevent condensate from flowing through the pipeline into pneumatic tools or process equipment. Otherwise the following will happen:
- corrosion and premature failure of pipelines,
- breakdowns of pneumatic tools,
- deterioration in product quality.
Some compressors are immediately equipped with dryers. This is due to the fact that when air is compressed, moisture always condenses, which does not suit most consumers.
“What is the optimal loading mode for a screw compressor?”
The optimal mode for a screw compressor is a load of 75% of the rated power of the unit. This means that the enterprise’s peak demand for compressed air should be 25% less than the technical capabilities of the compressor unit. This principle should be taken as a basis when selecting power and purchasing a screw compressor.
“Is it possible to change the pressure in a screw compressor and how will its performance change?”
The compressor unit is supplied with factory settings and has optimal compressed air performance. If desired, the equipment can be adjusted both up and down. It is not recommended to perform these manipulations yourself. They should be entrusted to compressor repair (adjustment) specialists.
It is better to refrain from such experiments if the equipment was recently purchased and is under warranty. It must be remembered that changing the factory settings, as well as the design of the compressor unit, may violate the terms of the warranty.
“How to calculate the air requirement?”
The air requirement (P) can be calculated experimentally and analytically using a simple formula:
P = (Pmax – Pmin) × V / T,
Pmax and Pmin - readings obtained experimentally from the receiver pressure gauge during measurements (maximum and minimum pressure);
T is the period of time in minutes during which the experiment was carried out (it is recommended to perform it at the heaviest load);
V is the volume of the receiver (in our case, 500 liters).
For example, the maximum and minimum pressure on the pressure gauge is 8 and 4 atmospheres, respectively, and it dropped in 2 minutes. Calculation:
Demand = (8 atm – 4 atm) × 500 / 2 = 1000 l/min.
What should you pay attention to when choosing a compressor for a car service?
Compressors are used in tire shops and auto repair shops to operate pneumatic tools. This equipment prepares and supplies compressed air to impact wrenches, screwdrivers, paint guns and pneumatic drills. It is also used in tire inflation services.
The choice of a professional tool should be approached responsibly. High-quality equipment ensures stable operation of the car service, and incorrectly selected equipment guarantees unexpected failures and downtime in customer service.
The following types of compressors are distinguished:
- screw;
- piston;
- rotary-plate;
- membrane
The first two types are the most universal. The screw compressor is compact and reliable. Such equipment does not require water cooling and has a long service life. Compressors can be stationary, mobile or portable. They also differ in design - there is equipment with direct or belt drive. Choose the right type of compressor to avoid future problems with equipment and its maintenance!
Recommendations for choosing oil for screw compressors and operating conditions
Screw compressors are equipped with two counter-rotating shafts (rotors, augers). They work on the principle of displacement. One of the shafts is the drive shaft and the other is the driven shaft, both rotating in the same housing. The inlet zone has a large cross-section and volume. When both shafts rotate, the volume decreases and compression occurs. The compressed medium is then forced out of the housing through the outlet. The compressor has a convex helical cross-section, while the other screw has a concave helical cross-section. Rotors in screw compressors, lubricated by injection and immersion in an oil bath, and bearings constantly endure mechanical and thermal loads.
Taking into account the versatility of oil in screw compressors and the impact of high loads on it, we recommend using high-quality oils from well-known manufacturers, rather than oils that meet only the minimum standard requirements.
In screw compressors lubricated by lubricant injection, the oil performs lubricating, sealing and cooling functions. The oil is injected into the high-pressure chamber between the rotors at a pressure of 3-4 bar; it is constantly in contact with hot air compressible medium heated to 75-90°C. It forms a hydrostatic and hydrodynamic film. The compressed medium and oil mix well. Thus, the oil lubricates the coupled rotors and the plain and rolling bearings, which are part of the gear clutch. In addition, it seals the gaps between the rotor and the housing. The lubricant also helps absorb heat and dissipate it through radiators. Air/oil separators remove oil from the outlet air. The residual amount of oil in the air is 1-3 mg/m38 bar), the pressure can be used to re-inject the oil. . The separated oil is then deaerated, filtered and cooled to 50°. When the oil is on the discharge side of a screw compressor (eg at 8 bar pressure), the pressure can be used to re-inject the oil.
Along with the mineral oils used with additives to increase oxidative stability, aging resistance and corrosion protection, synthetic lubricants can also be used, which, of course, are preferable, but are much more expensive.
Since oil viscosity is of paramount importance for elastohydrodynamic lubrication and therefore for the mechanical stability of the film, it must be selected for the starting conditions and normal operation of the compressor. The viscosity of the oil changes depending on the temperature, so the recommendations given in the operating manual are valid only for standard conditions and can be changed during operation. The oil viscosity is most accurately selected based on the injection temperature:
| Injection temperature °C | up to 50 | up to 60 | up to 70 |
| ISO viscosity grade | VG32 | VG46 | VG68 |
| Viscosity at 40 C mm O2/s | 28,8 — 35,2 | 41,4 — 50,6 | 61,2 — 74,8 |
As a rule, ISO VG 46 oils meet the requirements of compressor manufacturers for a maximum viscosity of more than 10 mm2. at operating temperature and approx. 500 mm2 suitable for most applications in Eastern Europe. Higher viscosity ISO VG 68 oils or synthetic PAG esters or PAO-based oils are used in plants with high ambient temperatures. Recently, hydrocracking oils (so-called group III oils) have become widely used. /sec/s at startup. This range is also
In compressors that operate for a long time at very low speeds (main rotor peripheral speed less than 15 m/s), in contrast to the above table, a viscosity grade one step higher must be used. When selecting an oil that has special requirements, you should pay close attention to other criteria. These are low foaming, excellent deaeration ability and good demulsifying properties for separating condensed water. In order to largely avoid wear of rolling bearings and drive gears, only those oils that have the lowest ash content and contain wear-preventing additives that ensure at least FZG ? 11 for improved extreme pressure properties, minimal deposit formation, good corrosion protection. The most important rule when operating a compressor is to maintain oil with proper performance characteristics. The main processes that reduce the quality of lubricants are:
— Oxidation, in which the oil thickens and forms carbon deposits and varnishes. It occurs under the influence of oxygen and increases with increasing temperature. At the same time, the lubricating and cooling properties of the oil decrease, its ash content increases (“cokes”). Many manufacturers indicate the operating time before changing the oil at a temperature of 82-85 ° C, while operating temperatures can reach 90-92 ° C, and sometimes, under unfavorable operating conditions, up to 100 ° C or more, until a protective shutdown of the equipment is triggered. Under such operating conditions, more frequent oil and oil filter changes are required. There are fully synthetic oils with operating temperatures up to 105°C, but do not forget that after the temperature in the screw block reaches > 92°C in the air/oil separator, oil emissions begin to increase exponentially.
— Water in oil leads to breakdowns of the lubricant film. The process of moisture loss in the screw block always occurs, so it is important to choose oils with low foaming and good demulsifying properties. The formation of condensation occurs due to temperature changes and in small quantities does not affect the lubricating properties of the oil, quickly evaporating from it. However, with short cycles and/or low compressor load, and even in cold rooms, the moisture does not have time to evaporate and an oil flooding effect occurs, which leads to a lack of lubrication and increased corrosion not only in the unit itself, but also in the mating components. If it is impossible to “reload” the compressor and extend the cycles, then it is required to run it at least once a week with an operating temperature of at least 78°C.
— Oil contamination with mechanical impurities occurs both as a result of its oxidation and when air is sucked in from the atmosphere. When air is sucked in, any particularly fine dust (cement, paints, waste from welding and cutting metals, soot in boiler rooms, etc.) turns into abrasive impurities. Installing a suction filter with a finer degree of filtration and replacing it in advance along with the oil filter will help eliminate unwanted consequences.
- a change in the chemical composition of the oil and, as a result, a deterioration in its lubricating properties, in compressors installed at chemical industry enterprises, tanneries or close to the sea. For these cases, no recommendations can be made other than sampling and changing the oil as soon as possible.
Brief conclusion.
Be sure to use only oil that meets the above criteria with a service life of up to 4000 hours. on a mineral basis with synthetic additives or up to 8000 hours. on a synthetic basis. Monitor it at least 500 hours. If necessary, replace in advance.
Replace the oil filter at least every 2000 hours, and replace the air filter if it is dirty.
? The main thing is to keep the compressor and the room in proper condition.
LLC "REMEZA-BelTS"
www.remeza.by
Based on materials and recommendations
equipment and oil manufacturers.
Download PDF – Recommendations for choosing oil for screw compressors and its operating conditions
Device characteristics
- Productivity shows how many liters of compressed air the equipment produces per minute. For small auto repair shops, a compressor of 300 l/min or higher is sufficient. Such equipment makes it possible to connect 4–5 units of pneumatic tools.
- Power. The performance of the equipment depends on this indicator. It is measured in kW or horsepower. Give preference to equipment with more power, all other parameters being equal.
- Air pressure is an important indicator of functionality. It is indicated in the passport for the compressor. For most car services, models with values of 8–10 atmospheres are suitable. Manufacturers equip modern compressors with regulators to increase or decrease pressure depending on the situation.
- Voltage. Compact compressors are connected to a 220 V network, and large industrial compressors are connected to 380 V. If there is no need to connect to high voltage networks, choose small models - this is a universal option for a car service center.
- Receiver volume. For a professional auto repair shop, you will need a receiver with a capacity of at least 25–50 liters. The air collector helps to level out pressure surges that invariably occur when using the tool.
Choose a compressor for a car service center based on the characteristics you need. The company's catalog includes models of any type, power and volume. Each piece of equipment meets high requirements for quality and reliability.
Why is a screw compressor better than a piston compressor?
When choosing compressed air equipment, the buyer is forced to evaluate many models. The most common types of compressors are screw and piston. Let's understand the operating principles of the first type and find out why a screw compressor is preferable to a piston compressor.
Compressors are used in everyday life and professional activities to operate pneumatic tools. The equipment prepares air - cleans and compresses it due to a special design. The belt-driven compressor is equipped with an electric motor. The screw block admits air through the valve. There it is compressed due to the reduction in space between the driving and driven rotors.
Compressed air enters the tank of the air-oil separator, in which the primary separation of oil occurs. The liquid is discharged out through the valve. After this, the pre-cleaned air enters the cyclone separator, where it is re-processed - 99% of the oil remains here. The clean air enters the dehumidifier, where all existing moisture is separated and removed.
The process of air compression in a screw compressor
- Unprepared air enters through the suction valve into the open cavities of the rotors. After this, the inlet closes and the air begins to compress.
- The driving and driven rotors rotate in different directions, so the space between them decreases and the open cavities close. Due to this, the pressure increases.
- Simultaneously with the increase in pressure, oil enters the equipment. It seals the gaps between the housing walls and the rotors and helps remove heat.
- After compression and reaching the desired pressure, the air begins to be pumped into a special window.
Screw and piston compressors are divided into single-stage and multi-stage. If you want to find out how many stages the equipment should have, read our separate article on this topic.