Wire ESAB OK AristoRod 12.50. Photo 220Volt
To perform one-time welding work at home, you need to decide on the amount of consumables that will need to be purchased in the store. In industrial conditions, the amount of welding wire consumed will affect the final price of the product produced and, ultimately, customer demand.
Wire Features
Wire consumption is influenced by many factors , including the human factor in the context of whether the welder has the required qualifications. However, the most objective is the value of the deposition coefficient .
Stainless steel welding wire Alfa Global ER 347Si. Photo Welding Technologies
This indicator determines the amount of deposited metal per unit of time at a current of one ampere. The value of the coefficient is influenced by the composition of the wire material, the organization of protection of the welding zone (gases, flux), as well as the type of current (alternating, direct) and its polarity. The value of the deposition coefficient, depending on the type of wire and the method of conducting the technological process, can vary from 5-7 to 18-20 g/A*h . There are several types of wires: titanium, copper, alloyed, polished, stainless, steel, aluminum, copper-plated, powder. The coefficient is determined mainly experimentally.
Reference. The deposition coefficient, as well as other technical characteristics of popular brands: PANCH-11, SV08G2S, ER70S-6, VT1-ooSv are presented in the relevant articles.
Wire consumption rates
The presence of wire consumption standards, which are presented as the amount of consumable material in units of mass per linear meter of weld , allows you to navigate the amount of wire to perform a specific type of welding work. With a mechanized welding method (automatic, semi-automatic, common argon-arc welding technology), the consumption rates are significantly less than with manual welding.
Table of material consumption per meter of seam when welding with semi-automatic welding
Edge cutting options
When developing a welding process, recommendations are given on the cutting of edges and gaps in the welded joint. They are based on the design documentation base, where the dimensions of the workpieces and the type of welded joint (lap, butt, corner, etc.) are determined.
Further, in state and industry standards and technical conditions for welded joints, the required dimensions of the weld are found. Calculating the theoretical cross-sectional area with modern computer technology is not difficult.
Such calculations are especially in demand in the construction industry , where welding work is carried out in large quantities and it is necessary to have a good understanding of the varied quantities and range of consumables. In the document VSN 416-81 “General production standards for the consumption of materials in construction” in the section “Welding work” the consumption standards for welding materials are given. These standards, depending on the type of work, are presented in tables by type of connection.
An example of one of the tables for mechanized butt welding in carbon dioxide for a one-sided butt joint without beveled edges:
Table. Standards for 1 meter of seam.
| Line code | Thickness of parts, mm. | Carbon dioxide, kg. | Welding wire, kg. |
| 01 | 1,0 | 0,027 | 0,05 |
| 02 | 2,0 | 0,049 | 0,091 |
| 03 | 3,0 | 0,052 | 0,099 |
| 04 | 4,0 | 0,056 | 0,105 |
| 05 | 5,0 | 0,085 | 0,161 |
| 06 | 6,0 | 0,09 | 0,17 |
Here it should be taken into account that the consumption rates are given for a seam located in the lower position . In other situations, according to document VSN 416-81, a correction is applied in the form of the following coefficients:
- vertical position – 1.12;
- horizontal position – 1.13;
- ceiling - 1.26.
Gas consumption rates are calculated in the table when supplied with a specific flow rate of 6 l/min. If the feed is increased, then correction factors are introduced accordingly:
- for 8 l/min – 1.3;
- for 10 l/min – 1.6;
- for 12 l/min -2.0.
Important! All normative data are theoretical. In reality, it is necessary to take into account the work associated with preparatory welding operations (performing tack welds, temporary welds, etc.), additional consumption of welding wire when the arc is interrupted, sealing minor defects, dependence on the qualifications of the welder, and others. Therefore, you should always make a reserve, based on the experience of specialists.
Carbon dioxide consumption per 1 kg of material
Semi-automatic welding of stainless steel indoors
The consumption of carbon dioxide should not be less than a certain level, after which the quality of the weld will begin to decrease. But large expenditures are not economically feasible. The choice of the optimal value depends on the thickness of the workpieces being welded, the diameter of the wire and the value of the welding current.
The factor of the place where welding is performed is also taken into account . When welding in the open air, the gas evaporates faster and the flow rate should be increased. This is especially true when there is strong movement of air masses (wind).
It is necessary to monitor the purity of the gas . Gas consumption is influenced by the quality of the gas mixture.
The qualifications of the welder greatly influence gas consumption .
Calculation of consumption of welding materials
The consumption of welding materials (electrode wire, shielding gas) is calculated for each weld size. The calculation is made for the total length of the seam of each standard size in accordance with the recommendations.
NE consumption rate
(kg) of welding wire per product is determined based on the length of the seams
lsh
(m) and the specific consumption rate of electrodes
Ge
per 1 m of a weld of a given standard size:
;
In general, the specific consumption rate is calculated using the formula:
;
;
where mн
– calculated mass of deposited metal in
kg/m
;
kр
– consumption coefficient, taking into account the inevitable losses of electrodes and wire;
ρ=7.8 g/cm 3
-density of deposited metal;
Fн
– cross-sectional area of the deposited weld metal in
mm2
.
2. Consumption rate of protective gas for the NG
l, determined by the formula:
,
where QГ
– specific rate of gas consumption per 1 m of weld of a given standard size in l:
,
where qГ
– optimal flow rate of protective gas according to the rotameter in l/min;
to
– machine (basic) time for welding 1m of seam per minute.
QDOP
– additional gas consumption for preparatory and final operations: preparation of gas communications before welding, setting welding modes:
,
where tP.Z
– time for preparatory – final operations, min.
The main time when welding with a consumable electrode can be determined by the formula:
where αн
– deposition factor in
g/Ah
;
Seam No. 1:
Welding method: semi-automatic welding in shielding gases;
Seam type: T1-∆5; tee, single-sided, without beveled edges
1. Determine the length of the seam:
2. Determine the calculated mass of the deposited metal:
3. Specific rate of wire consumption:
where kр=1.05
– loss coefficient for a consumable electrode in a CO2 environment
4. Wire consumption rate:
5. Basic welding time:
Deposition coefficient: αн=18.6 g/Ah;
6. Specific gas consumption rate:
The main consumption of shielding gas per 1 meter of seam: qG = 16 l/m
;
7. The rate of consumption of shielding gas for welding a given seam:
Additional shielding gas consumption: Qadd = 0.5 l;
Seam No. 2:
Welding method: semi-automatic welding in shielding gases;
Seam type: T7, tee, one-sided, with a bevel of one edge, with an underwelding seam;
1. Determine the length of the seam:
2. Determine the calculated mass of the deposited metal:
3. Specific rate of wire consumption:
where kр=1.05
– loss coefficient for a consumable electrode in a CO2 environment
4. Wire consumption rate:
5. Basic welding time:
Deposition coefficient: αн=18.6 g/Ah;
6. Specific gas consumption rate:
The main consumption of shielding gas per 1 meter of seam: qG = 16 l/m
;
7. The rate of consumption of shielding gas for welding a given seam:
Additional shielding gas consumption: Qadd = 0.5 l;
Seam No. 3:
Welding method: semi-automatic welding in shielding gases.
Seam type: T6, T-joint, one-sided, with one edge beveled.
1. Determine the length of the seam:
2. Determine the calculated mass of the deposited metal:
3. Specific consumption rate:
where kр=1.05
– loss coefficient for a consumable electrode in a CO2 environment
4. Consumption rate:
5. Basic welding time:
Deposition coefficient: αн=18.6 g/Ah;
6. Specific gas consumption rate:
The main consumption of shielding gas per 1 meter of seam: qG = 16 l/m
;
7. The rate of consumption of shielding gas for welding a given seam:
Additional shielding gas consumption: Qadd = 0.5 l;
Didn't find what you were looking for? Use the search:
Best sayings:
A scholarship can buy you something, but nothing more.
9123 – | 7290 – or read all.
95.47.253.202 © studopedia.ru Not the author of the materials posted. But it provides free use. Is there a copyright violation? Write to us | Feedback.
Disable adBlock! and refresh the page (F5)
very necessary
Calculation: formula
When performing a one-time job, you can independently calculate the approximate wire consumption. By increasing the resulting result by the technological losses required in the work, you will receive a guaranteed supply of welding wire for welding work.
The calculation is carried out using the formula N=G*K ,
- where N is the wire consumption rate;
- G – mass of deposited metal in the weld;
- K is a coefficient that takes into account the increased consumption of material to create the existing surfacing.
To calculate the mass of the deposited metal, the most difficult thing will be to accurately determine the cross-sectional area (F) of the deposit. Here you will need to use formulas from geometry to calculate the areas of various figures.
The density (γ) of the deposit depends on the type of material of the welding wire. The formula F*γ is used to find the mass (G) of surfacing for 1 meter of weld. The K coefficient depends on the spatial position of the weld, the shielding gas used and other features of the parts. This calculation will make it possible to avoid wasted time during welding work.
How to calculate consumption
The consumption of welding materials for argon-arc welding or the consumption of wire for semi-automatic welding per meter of seam is made according to the following formula:
N = G*K
Where “N” is the desired parameter or, in other words, the rate of wire consumption per 1 meter, which we need to calculate. “G” is the mass of deposit on the finished weld, again one meter long. And “K” is the correction factor, which depends on the mass of the deposited material to the metal consumption required for welding. To find out the value of G (weight of deposit on a welded joint), we need this formula:
G = F*y*L
The letter "F" indicates the cross-sectional area of the joint in square meters. The letter “y” is the density of the metal from which the wire is made.
Note! "y" value is extremely important because each brand of wire can vary significantly in weight due to the metal used to make it.
The value “L” is automatically replaced by the number 1, since we are calculating exactly 1 meter. If you need to calculate more or less than a meter, then use a different figure. Using these formulas, you can calculate the wire consumption during bottom welding. For other welding methods, you need to multiply “N” “K” , other than 1.
"K" value changes according to the position:
- In the lower position, “K” is equal to the number 1
- With semi-vertical - 1.05
- When vertical - 1.1
- With ceiling - 1.2
If you are welding metal using a semi-automatic machine, consider the shielding gas used in the work, the characteristics of your welding machine, the diameter of the wire and the features of the parts.
Thanks to these simple calculations, you can easily find out the amount of wire needed to weld parts when using argon arc welding or any other type of welding work. Take into account all the features of the type of welding and the wire used so that the calculations are accurate.
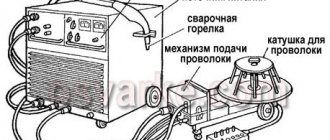
Material feeding mechanism
The feed mechanism is responsible for a stable supply to the welding zone, in accordance with the specified parameters in the semi-automatic machine . It allows you to adjust the wire feed speed over a wide range of values.
Semiautomatic welding machine Blue Weld MEGAMIG 500S with wire feed mechanism. Photo VseInstruments.ru
Depending on the design of the semi-automatic device, the mechanism can be located both inside the device body and outside it.
- If the mechanism is located in the housing, the operating principle is based on pushing the wire into the welding zone. The consumable material is transferred to the burner nozzle through a flexible metal channel, as a result of which there are restrictions on the length of such a guide device.
- The mechanism can be located on the burner itself . Then he will perform a pulling action, pulling the wire towards himself. The advantages of this method are the use of sleeves of sufficiently long length. However, a welding head with increased weight and dimensions creates significant inconvenience in the work of the welder.
- Feed mechanisms with a combined design have a right to exist, but are used extremely rarely.
The principle of operation of the mechanism is based on the feeding of wire pressed between rotating rollers. The main components of the mechanism are as follows:
- a stationary roller, which can only carry out rotational movements; the grooves on the roller are made in accordance with the diameter of the wire being pulled;
- a roller with a movable axis connected to a clamping device and mirror-image grooves located on the stationary roller;
- a clamping device that regulates the pressure on the wire;
- an electric drive with a worm gear drives a stationary roller;
- an electronic circuit that controls the parameters (change of feed rate, interruption for a given period of feed time, etc.) of the device;
- guide bushings with a diameter slightly larger than the diameter of the wire, installed before and after the device.
To create a more uniform pressure on the wire, a mechanism with four rollers, arranged according to the 2 x 2 principle, is used.
Reels and reel seats
Aluminum welding wire ER4043 (1.6 mm; spool 6 kg) ELKRAFT 93614. Photo AllInstruments.ru
Welding wire is wound onto reels, from which it is removed during operation. The reel is securely secured in semi-automatic machines using devices called reel holders. The devices for fastening the reels must correspond to those on the reel seat.
When the semi-automatic machine is turned off, the coil of wire tends to continue its movement, which can lead to the formation of loops on the wire. The design of the reel seat has a braking device , for example, in the form of a friction clutch. Adjusting it with a nut prevents the spool from unwinding freely and maintains the correct winding of the wire.
Example
To make it easier to apply all the formulas in practice, consider an example.
Let's calculate the amount of welded wire used in semi-automatic operation if the working material is steel.
To make the calculation correctly, the first step is to determine the mass of the weld deposit. We use the formula G = F*y*L.
G=0.0000055 (m2) * 7850 (kg/m3) * 1 (meter) = 0.043 kg
Next, let's proceed to the main quantity using the formula N=G*K
N = 0.043 * 1 = 0.043
How to refuel, installation on automatic and semi-automatic
How to thread welding wire into a semi-automatic machine is shown in the video. Here it is worth noting the key points that the author draws attention to.
- When putting on a new cassette, be sure to hold the end of the wire to prevent the coil from unwinding.
- The wire should fit into the groove of the roller.
- For pulling, use the electric drive idling (without gas supply) at the highest feed speed.
- Avoid getting caught in the sleeve or current collector.
The author of the video did not mention anything about adjusting the clamping device. The use of cored wire requires special attention. For welding with less spatter, a four-roll feed mechanism is recommended for flux-cored wire to better distribute the clamping force.
Calculating the consumption of welding wire per meter of weld (formula, examples, tables)
To start welding, you need the machine itself, accompanying materials, terminals, and wire at hand.
To start the process, you need to plug in the unit and create as long as you have the desire and inspiration to work. And related materials can run out at the most inopportune moment.
To avoid such unpleasant surprises, you need to know the relationship between the number of consumables and the amount of work.
It is necessary to calculate the expected consumption in advance. Each welder, before taking on an object, calculates everything down to the smallest detail and gives the customer an estimated cost.
Welding wire is sold in coils or reels. Sometimes it is treated with a solution to increase shelf life.
In our review, we will tell you in detail how to calculate the wire footage and show it clearly in the calculations.
Where can I buy
The sale of various types of consumables is carried out by companies collected in a separate section. Familiarization with the information presented will allow you to find out where to buy welding wire.
In addition to the possibility of purchasing products from suppliers, it is also recommended to familiarize yourself with the range offered by manufacturers. Leading global enterprises, for example, ESAB and DEKA, have a wide network of representative offices, which allows you to purchase consumables and be completely confident in the quality of the products.
Sections: Welding wire
Tags: alloy welding wires, copper welding wire, flux-cored welding wires, wire for argon arc welding, aluminum welding wire, copper-plated welding wire, polished welding wire, steel welding wire, stainless steel welding wire, titanium welding wire
Previous: Welding Wire Manufacturers Next: ESAB Welding Wire