Welding is perhaps the most effective way to join metal parts.
To carry it out, various types of welding machines are used, among which inverter-type devices have recently become widespread.
The reasons lie in its compact size, low weight, as well as the fairly high quality of the weld, which has led to its widespread use by home craftsmen.
In fact, a welding inverter is a modified apparatus for welding metals, which, since its inception, has almost completely replaced the bulky devices of the transformer and rectifier type that are familiar to everyone.
Voltage converter 12-220 (Inverter). Types and parameters
Just recently, no one even imagined that it was possible to have a household electrical network in a car. But with the advent of modern electronic devices based on PWM controllers, such an element of comfort in a car has become possible. For this purpose, a 12-220 V voltage converter has been developed. Its efficiency can reach 95%. This makes it possible to efficiently use the energy of a car battery.
Chinese online stores are replete with various models of such car inverters. But usually Chinese devices do not have the high parameters that are indicated on their packaging or case.
Varieties
Car inverters are divided into types based on various factors.
According to the type of sinusoid created:
- With a normal (constant) sinusoid. They work without deviations, all operational parameters are observed with high precision and can be used to connect any electrical devices designed for a voltage of 220 volts.
- With modified sine wave. In such models there are slight deviations in voltage. This does not have a big impact on the functioning of ordinary household appliances, except for medical and complex measuring equipment.
By power:
- Inverters up to 100 watts. Such car inverters operate from the cigarette lighter and are not able to withstand heavy loads. They are suitable for powering chargers of household appliances.
- From 100 watts to 1.5 kilowatts. Such models are widely used to power many devices operating from a household network. They are connected from a car battery, and are supplied with auxiliary accessories: cables, cords, adapters, etc.
- More than 1.5 kilowatts. Serve to provide power to a microwave oven, iron and other high-power household devices.
By design features:
- Compact.
- Stationary.
- Automotive.
When choosing a car converter, experts recommend purchasing a device with some power reserve.
When going to nature or a country cottage where there is no electricity, there is often a need for lighting in the dark. The simplest method is to connect LED lamps or flashlights to a 12-220 V voltage converter, although this is not an economical option in terms of battery energy consumption, since its efficiency decreases with increasing load.
A stationary voltage converter 12-220 V with pure sine wave is suitable for using electricity from solar cells or wind generators. Such sources provide low-voltage power from 12 to 36 volts, which can be used for the converter.
Compact converters are unpretentious in terms of the type of power source, and can operate at voltages from 12 to 50 volts. In automotive design, they look like chargers that operate from a cigarette lighter.
Technical specifications
Converters from 12 to 220 volts have standard output parameters of 220 V, 50 hertz, which corresponds to the characteristics of a home network. Such parameters are compatible with household electrical devices.
In addition to standard parameters, such inverters have other characteristics:
- Rated power.
- Type of output sinusoid.
- Overheating and short circuit protection.
- Supply voltage.
- The highest current consumed at the input.
- Electricity consumption at idle.
- Passive and active cooling.
- Efficiency.
All modern inverters are assembled on the basis of pulse controllers, providing high efficiency. This parameter often reaches 95%; the rest of the energy is dissipated by heating the device body.
Inexpensive inverter models have a modified rectangular sine wave at the output. Expensive inverters produce a pure sine wave, similar to that found in a household electrical network.
Rated power
When connected, some electrical appliances consume significantly more energy than indicated in the data sheet. For example, an electric drill at the moment of startup consumes power that is twice the nominal value. This must be taken into account when choosing a voltage converter.
The real power value of inexpensive Chinese converters can be underestimated several times. Manufacturers indicate with large symbols on the device body the peak short-term power at which the converter can operate for only five minutes, and then the protection will turn it off due to overload and overheating.
For home use, you can purchase stationary models with a power of up to 5 kilowatts. For a passenger car, a voltage converter of 12-220 V with a power of 100 to 1500 watts is suitable. At higher power, additional preparation of the vehicle will be required.
When choosing an inverter, you should clarify exactly what power is indicated: rated or peak, designed for a short time. When calculating the load, you should make a power reserve of about 20% so that the device does not operate at extreme loads that reduce its service life. Expensive devices from well-known brands have such a power reserve, and cheap Chinese inverters do not even reach the standard.
It is better to entrust the connection of the inverter to a specialist, since the current consumption for the battery will be about 50 amperes. If the work is carried out carelessly, you can damage the vehicle's electrical equipment or burn wires. Therefore, it is better to install an auxiliary fuse or safety interlock. On jeeps they even install a special mass switch for this purpose.
Cooling system
The degree of heating of the inverter depends on its total power and the size of the connected load. An aluminum housing with developed fins is used as a cooling element for better cooling. This type of cooling is called passive .
At high power, a fan is additionally installed that cools the device with air flow. This is called active cooling, which does not operate all the time, but only when the case temperature is higher than the set value. This process is controlled by a thermal sensor, which turns the fan on and off at the right moments. In a car, the fan may not work, as there is a high probability of it becoming clogged with dust.
Additional protection
A high-quality 12-220 V voltage converter always has protection against overheating, current overload and short circuit, and a fuse must be installed. The power of devices that are connected to the inverter varies, and children can mistakenly connect, for example, an iron to it, which will simply damage the inverter. To prevent this from happening, the current protection must react quickly and de-energize.
A short circuit can cause a large current to flow, causing the wiring to quickly heat up and catch fire. The protective block is designed to quickly turn off the converter output and keep it in this state until the short circuit is eliminated.
There is a type of protection such as blocking against incorrect polarity of connecting the device, as well as against very low or too high input voltage. Auxiliary indicators and voltmeters will show these parameters and help identify and eliminate the malfunction in advance.
The presence of thermal protection in the inverter can be determined by the presence of a temperature sensor installed on the radiator for cooling powerful transistors.
Typically, a 12-220 V voltage converter is connected in a car.
With careless handling or inexperienced connection, the cigarette lighter fuse, which has a load limit, most often burns out. Low-power devices, such as a tablet or cell phone, can be connected without worry.
Features and principle of operation of the welding inverter
In recent decades, inverter welding has increasingly replaced traditional transformers and rectifiers, not only in industrial production, but also in domestic use. This became possible thanks to the creation of a reliable element base for frequency converters, as well as a significant reduction in the cost of power electronic components. The rising cost of energy and copper, which is used in inverters by orders of magnitude less than in other welding machines, also played a role.
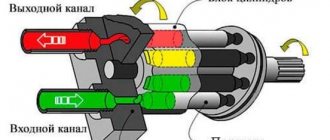
The operating principle of a modern welding inverter is based on the conversion of low-frequency mains current into high-frequency pulses with the subsequent formation of various types of welding currents with adjustable parameters (see figure below).
Figure 2 - Operating principle of the welding machine
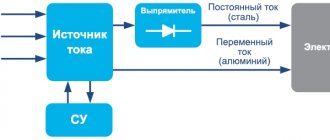
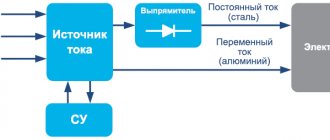
Single-phase or three-phase alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz and a voltage of 220 or 380 V is supplied to the input rectifier, after which it is smoothed out by large capacitors.
The rectified current with a significant level of ripple is supplied to the input of the inverter, which converts it into high-frequency alternating current. This current is then supplied to the high-frequency transformer, where its voltage is reduced to the no-load value. Then it passes through a rectifier, after which, due to the high frequency, ripple smoothing is no longer required. The rectified current is supplied directly to the welding electrode. Its characteristics are monitored by current and voltage sensors connected to the inverter control unit, so the frequency and duty cycle of the pulses can be changed in real time. The number of turns of the primary winding is inversely proportional to the frequency of the current, so in high-frequency transformers there is orders of magnitude less copper than in conventional ones. This dependence is nonlinear: at a frequency of 10 kHz, the mass and size decrease by 3 times, and at a frequency of 50 kHz - by approximately 15 times (see the transformer in the figure below).
Types of inverter converters
Inverters can be dependent or operating autonomously. Dependent models include grid-driven, Grid-tie, and similar models. Inverter converters are also classified into single- and 3-phase. Single-phase devices are:
- with an input signal in the form of a pure sinusoid - such inverter converters are indispensable for equipment that has an electric motor or transformer at the input, or works strictly with a sinusoidal signal;
- with a simplified signal type - close to a sinusoidal version, suitable for most devices.
Three-phase devices are used primarily to produce 3-phase current to power asynchronous electric motors and other equipment. The motor windings are directly connected to the output of the inverter converter. In terms of power, inverter converters are selected according to the peak power value for a specific consumer.
Selection criteria and calculation of a voltage inverter
The most important characteristics of the inverter:
- voltage converter frequency and voltage shape. It is advisable to purchase a device that produces a pure sinusoidal signal. Even highly sensitive equipment can be connected to such a converter;
- rated power. It must be higher than the total load of all connected consumers;
- maximum peak power. This value determines the maximum load the device will withstand when connecting equipment with a low cos f value. Such equipment includes electric motors, pumps, compressors;
- value of input/output voltage and electric current.
To calculate the required power of a DC/AC converter, you must:
- Add up the power consumed by the connected equipment. It is taken from the passport data for the equipment. For example, a refrigerator - 200 W, a washing machine - 1500 W, a vacuum cleaner - 1000 W. Total in total: 200 + 1500 + 1000 = 2700 W.
- Consider peak load. To do this, we multiply the resulting amount by a factor of 1.3 (for the example under consideration: 2700 * 1.3 = 3510 W).
- Take into account the coefficient cos f to obtain the result in volt-amperes. Its value for different equipment varies within 0.60. 0.99. For calculation it is better to take the minimum value. 3510/0.6 = 5850 VA ≈ 6 kVA. It is this value that you should focus on when choosing an inverter.
Types of inverters
What types of inverters are there? To answer this question, these voltage converters must be considered in terms of several parameters in which there may be significant differences.
Voltage form
Inverters may have different conversion circuits, and therefore the voltage form at the output of the device may differ. From this point of view, two types of inverters can be distinguished. The first is inverters with the correct sinusoidal voltage. These devices use a rather complex conversion circuit, which makes their price slightly higher. In return, you receive an output signal that is identical in shape to the network signal, only the accuracy of maintaining the voltage is higher (the network is characterized by voltage drops, but inverters are not). This type of inverter can be used with any consumers without any restrictions. Their alternative is inverters with a modified sine wave voltage. What are the differences between a modified sine wave and a correct one? In this case, the concept “modified” does not indicate any superiority. The modified sinusoid (also called approximated) has a stepped shape. The conversion circuit is implemented much simpler, which means the price is much lower, for which, judging by the reviews, buyers often prefer just such inverters. The modified signal shape imposes some restrictions on the use of this type of inverter, however, most devices will work perfectly thanks to the presence of a switching power supply. The exception is consumers such as boilers, pumps, compressors and other consumers whose design includes transformer power supplies or AC motors. If you want to buy an inverter for a specific consumer and are unsure whether it requires the correct sine wave to operate, consult our specialists. In addition, you can personally check the operation of this or that type of inverter directly at our retail outlets opened in Kyiv, Kharkov, Dnieper and Odessa.
DC circuit voltage
When choosing almost any electrical product, it is extremely important to determine the power. This also applies to the inverter. The number of potential consumers depends on the choice of power. A high power inverter requires a suitable direct current (DC) circuit, which may consist of one or more batteries. If the inverter has low power, then it is reasonable to increase the capacity of the DC circuit by connecting several batteries in parallel. In the case of high power, in turn, it may be necessary to connect the battery in series to sum the circuit voltage. For example, the Leoton XT36A inverter requires a 24V DC circuit to operate, which is quite logical, since this reduces the current output by half compared to a 12-volt circuit. Also, many powerful inverters require a 48V DC circuit. Whatever the requirements of the inverter regarding the DC circuit, in our online store you will find the best traction batteries in the right quantity, which can be purchased together with the converter.
Method of connecting to the battery
In the process of considering the types of inverters, we will not dwell long on the methods of connecting to the battery, since there are only two of them. The most common of them is a direct connection to the battery terminals. Almost all inverters use standard crocodiles for this. However, there is a separate type of inverter, which, judging by reviews, is popular among lovers of traveling and outdoor recreation. These are car inverters, which are characterized by connection through the cigarette lighter. In this case, you don’t even need to buy a traction battery, since the cigarette lighter is powered by the generator when the car engine is running. When the engine is stopped, long-term use of the inverter is not recommended, since lead-acid car batteries are very susceptible to discharge below 40-50%. And the risk of subsequently not starting the engine increases significantly.
Features of storage and maintenance
To understand how to properly store and maintain a DC welding inverter, you need to know what it is constructed of. We have already said above that the basis of all modern inverters is compact, high-performance transistors such as IGBT or MOSFET. It was thanks to them that we were able to significantly reduce the dimensions of the welding machine and add more functionality. Also at the heart of the inverter there are many microcircuits and a cooling system.
The technical equipment of the inverter is much superior to that of a classic transformer. This means that with great functionality you will have to put up with the peculiarities of storage, maintenance and operation of such a device.
Most often, breakdowns occur due to dust settling on the inverter components. Dust and dirt enter the housing through the ventilation holes. Add to this high humidity and the device will definitely not last long.
Repairing an inverter is never easy. Here you won’t be able to quickly fix everything with your own hands, as is the case with a transformer. You will have to take the device to a service center. And this is not cheap due to the high cost of parts.
What can you do to avoid all this? Properly store the device and maintain it on time.
Storage
If you use your inverter frequently and don't want to bother with storing it, then simply put it in the cardboard box it came in. Store the box itself in a dry, warm room. Do not leave the inverter in the open air; wipe off dirt, dust and moisture from the surface of the housing.
If you rarely use the device, then wrap the inverter in plastic wrap, make holes in it and place the device in the box. Do not leave the inverter in the country house or in an unheated garage. If you have the opportunity, take the device into your apartment and store it in a closet.
Service
Now about the service. Of course, it is best to carry it out at a service center. If you have a device from a well-known manufacturer and you live in a large city, then find an official service center and return the device for maintenance for a small fee. A specialist will not only check the performance of your inverter, but will also carry out professional cleaning with compressed air. Including from the inside.
If you do not have the opportunity to take the device to a service center, then you can perform the service yourself. Clean the device regularly with a cloth and check the reliability of all connectors. If there is a need to tighten something, tighten it. Pay attention to the speed of work and the smoothness of adjustments.
Inverter power plants.
Principle of operation
An inverter power plant
is based
on the conversion of alternating current
into direct current
, after which the oscillations of electrical waves are maximally stabilized, and then the direct current through the inverter circuit is again
converted into alternating current
, with a given frequency and voltage.
Electronic adjustment
in combination with the conversion circuit, it is the basis of the converter of the inverter power plant, due to which the output is high-quality alternating current with industrial frequency.
Such technologies are most common in gasoline-powered mobile power plants
.
The main advantages of an inverter power plant.
- savings
of 20-40% compared to traditional models due to an electronic conversion system and adjustment of engine speed depending on the load.
- Easy
engine starting without additional settings throughout the entire period of operation.
- The ability to control the operation of the power plant at low load
due to the presence of a function for switching the engine to an economical mode.
- Low noise level
allows use in places with high noise pollution requirements.
- Environmental protection due to lower content of harmful substances in the exhaust
, thanks to a highly efficient fuel combustion system and engine operation at lower speeds. What is impossible at power plants with a classic mode of electricity generation, where the frequency of alternating current (Hz) is strictly tied to the speed of the power plant (engine)
Application of welding inverters
This device is used to connect individual parts of metal structures or eliminate cracks and damage on the surface of metal products.
Depending on the complexity and volume of work at the dacha, in the private sector or at a work site, you can select a welding inverter of a certain format. There are three main types of devices on the market - household, professional and specialized.
Read what a welding rectifier is.
Household inverters
This is the best option for private use. Welding inverter for home and garden, designed for quickly solving everyday problems, from eliminating a crack in a bucket to connecting metal beams.
It is light weight and compact in size. It heats up quickly. To work with it you do not need to undergo special training. It is enough to read the instructions supplied with the device.
Its power is up to 4 kW, electrode diameter is up to 5 mm. No 380 V current is required to start.
The main advantages of a welding inverter for home:
- light weight;
- compact dimensions;
- wide power range;
- affordable price.
It can be carried from place to place without much effort. The main thing is to connect the inverter to a 220V network and monitor the speed and quality of its operation.
The disadvantages of a household inverter are fast heating and compliance with a number of storage and operating conditions. You need to treat the device with care in order to maintain its technical characteristics and extend its service life.
Professional inverters
Visually, they look exactly the same as devices intended for welding in domestic conditions. But they have a stronger technical base, and they emit a higher current. They also have protection from dust, moisture, and are resistant to mechanical damage and shaking. After several hours of operation, they practically do not heat up.
Professional inverters are purchased by construction companies, auto repair shops, companies that repair facilities and large household appliances.
Key advantages of professional inverters:
- economical consumption of resources;
- a light weight;
- compact size;
- simple operating rules;
- uninterrupted operation for a long time.
Among the disadvantages is the high price of the device and the parts necessary to complete it. Also among the disadvantages is the limited range of operating temperatures.
Specialized inverters
These are stationary devices that produce high quality current. They are used in factories, during construction or major repairs of large-scale facilities. Compared to the previous two types of devices, specialized inverters are more powerful.
Among their main advantages:
- working with thick layers of metal;
- low current consumption;
- high efficiency;
- impeccable quality of welding current;
- working with several posts, i.e. points where welding is needed.
Among the disadvantages are the large weight and dimensions of the device, installation in one place.
When choosing the type of device, evaluate which parameters are key: dimensions, weight, ability to move the device from place to place, power, quick connection. Also consider the volume and specifics of the work that needs to be performed. A household inverter is suitable for eliminating cracks, tears and other damage to household appliances and metal parts. To carry out larger-scale work, for example, connecting individual parts of a supporting metal structure, you will need a professional or specialized inverter.
No load voltage
After turning on the device, until the arc is ignited, the voltage at the tip of the electrode is significantly higher than during operation. And the higher it is, the easier it is to ignite the arc. But standards prohibit open-circuit voltage levels on devices delivering direct current above 100V.
To further reduce risks, the so-called VRD blocks. A device equipped with a VRD has only a few volts at the tip of the electrode before the arc starts. And only when you touch the metal, the no-load voltage is restored to the level necessary to ignite the arc.
All electrodes always indicate the polarity of the connection, the type of welding current (direct or alternating) and the minimum level of open circuit voltage required for ignition. For the vast majority of widely used electrodes, it does not exceed 60V.
The open circuit voltage, as well as the welding current, depends on the input voltage level. The lower the voltage in the power supply, the lower the open circuit voltage. Therefore, as the supply voltage decreases, ignition of the electrode becomes more and more difficult.
Differences between an inverter air conditioner and a conventional one
Inverter air conditioners outwardly do not differ much from conventional devices, but they have some features in design, operating principle and method of power regulation.
Design features of inverters: the external unit has an electronic power board. Conventional air conditioners do not have this part.
According to the principle of operation:
- Inverters provide stable operation with variable power.
- Conventional air conditioners turn on/off during operation depending on the temperature range reached. Their operating principle is alternating operation with constant power.
By adjustment method:
- In conventional devices there is a cyclic, step-by-step power control.
- In inverters - smooth, multi-stage.
Additional functions implemented on welding inverters
The use of microprocessor control of inverter equipment with effective feedback allows the implementation of additional options that facilitate the welding process. These should include:
- hot start, which provides a short-term increase in voltage during the initial period of welding, which facilitates ignition of the arc;
- anti-sticking, which sharply reduces the load when the electrode accidentally touches the welded edges, which avoids welding the electrode, which is a common problem for novice craftsmen;
- arc forcing, which prevents sticking of the electrode when a large drop of molten metal is separated from it due to a short-term increase in current strength.
All of the listed properties of inverter welding machines have a positive effect on the ease of working with them and the quality of the resulting seams.
Manufacturers of welding inverters
Another important question: which company to choose a welding machine (inverter).
The quality of the device depends on the choice of manufacturer. This rule works in 80% of cases. It is also recommended to pay attention to whether the manufacturer has:
- spare parts warehouse in your country. If not, how quickly spare parts are delivered upon customer request;
- does the manufacturer have a service department that troubleshoots problems and replaces inverter parts that have failed;
- does the manufacturer maintain a website where you can view the range of welding inverters and get acquainted with their characteristics;
- Does it provide online catalogs needed to explore products? If yes, how can you get them?
- Are there detailed instructions to make working with welding inverters easier? Description of the operating principle and characteristics of the device - important information for the buyer;
- availability of certificates confirming the quality of the device.
Among the manufacturers, we note the following: “Paton” (Ukraine), DECA and TELWIN (Italy), “KEDR”, “TORUS” (Russia). They produce welding equipment taking into account user requirements for the dimensions of the device, its functions, service life, and budget. These manufacturers have created a wide range of products, which includes welding inverters for both home and industrial facilities.
Our website presents inverters for welding from the following brands: AURORA, DENZEL, RESANTA, Fubag, KEDR, TORUS. You can select a suitable welding inverter from their range online. All characteristics of the devices are indicated in the product description.
Additional options
Also, when choosing a device, it is important to pay attention to the additional functions of the device. They speed up the work process and improve its quality.
If the model has the following options, then it will become indispensable for welding metal parts:
- “hot start”: it is responsible for quickly supplying an additional electrical pulse to the electrode, which ignites the welding arc and, accordingly, speeds up the start of the entire device. The speed of work depends on this indicator.
- “Arc forced”: it starts at the moment when the electrode almost comes into contact with the surface of the part being processed. And so that it does not “stick” to the product, a powerful current flow is launched onto it.
- “anti-sticking”: the essence of the function is simple. The current supply to the electrode automatically stops as soon as it has nevertheless connected to the surface being treated.
The presence of these functions has another advantage: if this is your first time working with an inverter, then the likelihood of making an error in operation is much lower. If the electrode “sticks”, the machine will stop, and you will be able to correct the texture of the weld and improve the quality of welding.