GOST R 51613-2000 — Pressure pipes made of unplasticized polyvinyl chloride. Technical conditions.
| Designation | GOST R 51613-2000 |
| Name | Pressure pipes made of unplasticized polyvinyl chloride. Technical conditions. |
| Title | Pressure pipes made of unplasticized polyvinylchloride. Specifications. |
| Application | This standard applies to pressure pipes made of unplasticized polyvinyl chloride - uPVC without a socket and with a socket, intended for pipelines transporting water, including for domestic and drinking water supply, at temperatures from 0 to 45 ºС, as well as other liquid and gaseous substances. The standard does not apply to pipes for electrical installation work and transportation of flammable gases intended as raw materials and fuel for industrial and domestic use. |
The text of the standard is provided for informational purposes and does not replace the official publication.
Types and sizes
Pipes are manufactured in the following types:
- without bell;
- with a socket for connection with an elastic sealing ring of a special section or other similar ones - P;
- with a socket for adhesive connection - RK.
Pipe with socket for adhesive joint
Pipes are manufactured in straight sections with a nominal length of 4 to 12 m with a multiple of 0.25 m. The maximum deviation of the length from the nominal length is no more than 25 mm. Allowed in a batch of pipes in sections of up to 5% of pipes of shorter length, but not less than 1 m.
By agreement with the consumer, it is allowed to manufacture pipes of other lengths and other maximum deviations.
Pipe symbol
The symbol for pipes consists of the word “pipe”, the abbreviated name of unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (UPVC 100, UPVC 125), type of socket, standard dimensional ratio (SDR), dash, nominal outer diameter, nominal pipe wall thickness, purpose of the pipe: domestic and drinking water use denoted by the word “drinking”, in other cases - “technical” and the designations of this standard.
Examples of symbols
PVC-U pipe 100 without socket, SDR 26, nominal outer diameter 63 mm and nominal wall thickness 2.5 mm, for drinking water systems:
PVC-U pipe 100 SDR 26-63x2.5 drinking water GOST R 51613-2000
UPVC pipe 125 with socket for O-ring connection, SDR 17, nominal outer diameter 225 mm and nominal wall thickness 13.4 mm, for pipes not used for drinking water systems:
PVC-U pipe 125 R SDR 17-225x13.4 technical GOST R 51613-2000
PVC-U pipe 100 with socket for adhesive joint, SDR 33, nominal outer diameter 140 mm and nominal wall thickness 4.3 mm, for drinking water systems:
PVC-U pipe 100 RK SDR 33-140x4.3 for drinking GOST R 51613-2000
Technical requirements
Pipes are made from a composition based on suspension polyvinyl chloride with a K value of at least 67 (GOST 14040).
Pipes for domestic and drinking water supply are made from compositions approved for use by health authorities of the Russian Federation.
By agreement with the consumer, it is allowed to produce pipes for technical purposes using secondary raw materials of the same composition, generated during the in-house production of pipes according to this standard.
Recommendations for choosing pipes for transporting various media
The selection and calculation of the maximum operating pressure of pipes for transporting various liquid and gaseous media, except water, to which unplasticized polyvinyl chloride, the material of the sealing rings and the adhesive are chemically resistant, is carried out on the basis of regulatory documents for the installation and operation of the corresponding pipelines.
The reduction coefficient for the maximum operating pressure at a temperature of water transported through the pipeline up to 45 °C for a service life of 50 years is given in the table.
| Operating water temperature Trab, °C | Pressure reduction coefficient Ct |
| Up to 25 | 1,00 |
| 26-30 | 0,88 |
| 31-35 | 0,78 |
| 36-40 | 0,70 |
| 41-45 | 0,64 |
Classification according to GOST and marking features
When choosing pipes, it is important to be able to correctly decipher the markings on PVC-U pipe products. The alphanumeric code printed on the walls of the pipe contains all the data about the material, type, size, date of manufacture and technical conditions.
The first letters in the marking indicate the material of manufacture - the letters PVC-U or PVC-U.
Numbers - pipe sizes:
- diameter;
- wall thickness.
The letters TU and numbers are data on the technical operating conditions of the product.
The final numbers are the date of manufacture of the pipe.
| GOST R 51613-2000, TU 22.21.21-034-73011750-2017 | Pressure pipes are used to build water pipelines that can even transport drinking water. Maximum t - up to + 45°C. |
| GOST R 54475-2011 with TU 2248-050-73011750-2016 | Gravity pipes with traditional and reinforced rings are mainly used for the construction of communications - sewerage, sewerage, industrial wastewater. Not suitable for drinking water supplies. The maximum operating temperature is 60°C. It is allowed to transport substances at a temperature of 90°C, but for no more than a minute. |
How to choose a pressure PVC uPVC pipe for water supply, what you should pay attention to.
UPVC – unplasticized polyvinyl chloride. For brevity, the letter "N" is often omitted from the abbreviation.
1) The pipe must be accompanied by permits confirming its compliance with the requirements of regulatory documents (DSTU, TU, technical certificate), as well as the corresponding permit from the Ministry of Health:
a) certificate of conformity and/or technical certificate; b) conclusion of a sanitary and epidemiological examination (for drinking water).
2) Visually, compliance with standards can be determined by the following criteria:
a) Pipe color – gray (various shades are allowed); b) There is a factory-applied marking - clear and clearly visible against the background of the pipe, durable, not erased; c) The marking contains the following information: • Trademark and/or name of the manufacturer; •name of material (PVC or PVC-U); •serial number (S); •nominal outer diameter; •nominal pipe wall thickness; •purpose of the pipe (“drinking” or “technical”); •nominal operating pressure (PN) of water in the pipe at 20°C with the designation of the unit of measurement (bar); •designation of a normative document; •batch number; •Date of issue; •additional information is allowed, such as manufacturer contacts, production line number, etc.
Example of correct marking: TOV KaTZ UPVC S12.5-160 x 6.2 pitna 10.0 bar DSTU B V.2.7-141:2007 P.007 12/17/12 12:22 L No. 2 tel...Decoding: Explanation: Production pipe Kalushsky Pipe Plant made of PVC-U, serial number S12.5, nominal outer diameter 160 mm, nominal wall thickness 6.2 mm, intended for drinking water supply, nominal operating water pressure not more than 10.0 bar, manufactured in accordance with DSTU B V.2.7- 141:2007, batch: P.007, date and time: 12/17/12 12:22, line No. 2, contact phone. d) The pipe must not have visible abrasions or deep scratches on the outer or inner surface; e) The outer and inner surface of the pipe must be uniformly colored, without inclusions of a different color, stretch marks, traces of “bubbles”, light spots, stripes, etc.
Pay attention to the color of the bell - here the color shade (compared to the color of the main part of the pipe) should also not change. If the shade of the bell is lighter, there is a high probability of violation of the technology of its formation (bell).
3) Check by touch:
a) The external and internal surface of the pipe must be smooth, without roughness or burrs; b) The rubber O-ring located in the socket of the PVC pressure pipe must sit very tightly in its seat. To manually remove the ring from the “correct” pipe, you need to apply a lot of force.
4) Conduct a strength experiment: the PVC pressure pipe must be very rigid and durable. You can safely stand on it and even jump, no deformation is allowed.
5) Inquire about the prices for PVC-U pipe raw materials - a high-quality pipe should cost more than the raw materials by weight.
6) Simplify your life - choose a well-known manufacturer and a reliable supplier that you can trust.
Tips on how to choose
The choice of pipes primarily depends on the purpose and operating conditions: for pressure or non-pressure systems, at depth or laying in basements, ducts, buildings.
Electrical, telephone or Internet networks are laid in pipes or corrugated pipes; often the communications are not sealed.
The second important factor is the working pressure in the water supply or soil pressure on free-flow networks. The choice of pipe design (smooth-walled, corrugated, double-layer corrugated, bell-shaped) depends on these factors. In addition, the temperature regime is taken into account - overheating of the ground in summer, freezing in winter.
The choice of ring stiffness class for a PVC-U sewer pipeline depends on the density and thickness of the soil layer above the communication. If the depth is greater or the sewerage system is located under a road or parking lot, strong corrugated pipes with a two-layer wall are used. Corrugation is also used for water pipes with high pressure or with a very massive screed over a heated floor system.
Estimated cost
The cost of the most common types of uPVC pipes in private construction - socket elements Ø 110 mm - is 110 rubles per meter pipe, 315 rubles for a three-meter pipe. Pressure bell-shaped round products with PN 1.6, 6 m long, cost from 1,750 rubles. A corrugated pipe for sewerage Ø 110 mm with SN6 costs from 170 rubles per meter.
Cost of uPVC communications
The cost of uPVC communications is low. Only thermistor fittings and collapsible couplings are relatively expensive. But when installing non-pressure sewer networks, they are rarely needed. When installing water pipes of small diameters for a private house, they are also not necessary; the usual bell-shaped structures are used.
Decoding and using PVC
Abbreviation
PVC pipes for sewerage are made from the limestone material of the same name, which, after undergoing heat treatment, has the peculiarity of retaining its shape. The abbreviation PVC means vinyl chloride polymer. The main constituents of PVC pipes are materials such as ethylene and stabilized chlorine.
And by using auxiliary additives you can achieve the best qualities. PVC pipelines are used in the construction of wastewater networks due to the ease of installation work and low price. And also, thanks to its good technical characteristics, this type of pipe can be used in pressure systems. Its features include good dielectric properties and resistance to aggressive chemical environments. It is not susceptible to corrosive formations, is not afraid of humidity and ultraviolet radiation. Thanks to these qualities, polyvinyl chloride pipes are widely used both in industry and in everyday life.
Exploitation
PVC pipes are used in such areas as:
- construction of a swimming pool, fountain, water park;
- chemical production;
- food industry;
- Agriculture;
- in the construction of a wastewater system.
- Polyvinyl chloride pipelines are used for these types of waste systems: internal networks;
- external; external pressure systems;
- with gravity drainage.
They are practically eternal. Probably, the manufacturer gives a guarantee of fifty years of service for every plastic pipe product. Also, polyvinyl chloride is environmentally friendly and absolutely harmless. For the customer, this type of pipe is more interesting than any other plastic pipe due to its reliability and cost.
Currently, these materials are the most profitable option for wastewater systems, not taking into account the not very simple manufacturing process. For example, low-density polyethylenes are simply poured into an extruder; raw materials for PVC pipes undergo a complex multi-composition process and have a limited shelf life
Nowadays, it is widespread to use PVC plastic pipes in the construction of waste systems. They are gradually replacing classic cast iron ones. Plastic has many good properties, which makes it different from its metal counterparts.
Range of uPVC sewer pipes
First of all, uPVC sewer pipes are distinguished by their scope of application. Exist:
- PVC-U pipes for internal sewerage;
- PVC-U pipes for external sewerage, organized on the principle of gravity flow;
- pipes for external pressure sewerage.
Pipes for indoor and outdoor use differ in color. The former have a gray light, the latter are red or brownish-red.
It is important that the pipes used are suitable for the application. For example, uPVC pipes for internal sewerage cannot be used outdoors, since they are simply not designed for high loads and atmospheric exposure
It is possible to use external sewer pipes for installation around the house, but it is irrational, since their prices are higher.
Standard sizes
Pipe sizes are designated by outer diameter. For internal sewerage systems, uPVC pipes are produced in the following diameters: 25, 40, 50, 110, 110, 150 mm. Pipes intended for external installation in the ground have diameters of 110, 125, 150, 160 mm. For laying industrial drainage systems, pipes with a diameter of up to 1 m are used. PVC-U sewer pipes are sold in sections of different lengths from 300 mm to 6 m.
uPVC pipe wall
The wall thickness of the pipes also varies depending on the purpose. The thickness of the material in PVC-U pipes for interior work is 3-3.5 mm. This thickness is due to insignificant physical loads on the pipeline, and the achieved tensile strength is sufficient. For the outer part of the sewer system, pipes with a wall thickness of up to 15 mm are used. Often external pipes have complex multi-layer walls. Between two layers of PVC is foam, aluminum or carbon fiberglass. This design is designed to improve thermal insulation performance, reduce the weight of the pipes, and increase their strength.
PVC-U sewer pipes have an indicator of ring strength, which characterizes the ability of the pipe walls to withstand compressive loads. For each type of pipe this indicator has its own designation. The “weakest” pipes for indoor use are marked SN2. The ring strength of external sewer pipes is 2 and 4 times higher and is marked SN4 and SN8, respectively. SN8 uPVC pipes are laid under busy roads and in areas with increased soil mobility.
Performance characteristics
Today, sewer pipes made from unmodified polyvinyl chloride have almost completely replaced cast iron, ceramic and concrete pipes.
Such popularity of these pipes is explained by the ratio of their advantages and disadvantages. Among the advantages are, firstly, the low weight of the pipes, which significantly reduces the cost of loading and transportation. In addition, lightweight pipes are easier to work with, which significantly reduces the time for installing sewer systems. Secondly, uPVC pipes are not susceptible to corrosion and are not affected by most chemically active substances. Thirdly, their service life can be 50 years or more.
The disadvantages of uPVC pipes include the vulnerability of most types of pipes to rodents, which can damage the pipelines in the house. A significant disadvantage of such pipes is their small operating temperature range from -5 to 60 ° C, so the external sections of sewer systems have to be laid deep into the ground below the freezing level.
If we compare all the pros and cons, then PVC-U sewer pipes can be concluded that this material is very practical and easy to use. And if we take into account all the technical limitations, then sewer systems installed using these pipes will cope with their function perfectly and will last a very long time.
Differences from PVC pipes
Many people believe that pipes made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and unplasticized polyvinyl chloride are the same thing, but in reality they are not. The presence of one letter in the name, in fact, completely changes the characteristics of the products.
To obtain PVC, plasticizers are added to the polyvinyl chloride composition, which change the properties of the material - making it plastic, soft, viscous, which simplifies processing and, as a result, reduces production costs. PVC is convenient to use, but due to the presence of chlorine in the composition of the substance, it cannot be called completely environmentally friendly: chlorine, albeit in small quantities, begins to be released into the environment during operation.
While uPVC is the safest and most durable plastic, which is also called rigid PVC.
Pros and cons of unplasticized polyvinyl chloride casing pipes
Casing pipes for wells, the manufacturing material of which is uPVC (unplasticized or unmodified polyvinyl chloride), have a number of advantages:
- meet all necessary sanitary and hygienic requirements;
- have high resistance to chemically aggressive environments;
- withstand long-term operation (PVC casing pipe can last more than half a century);
- have high strength with a relatively low specific gravity;
- provide exceptional tightness, since, as a rule, casing pipes are made of PVC with threads;
- have high resistance to the formation and development of corrosion;
- easy to install;
- transported without problems (as mentioned above, uPVC products are lightweight);
- have the ability to successfully withstand mechanical loads that casing products made of metal can withstand;
- do not emit harmful substances (UPVC is an inert material with respect to water);
- do not overgrow over time and are practically not subject to wear;
- have a relatively low cost when comparing PVC casing pipes with similar products made of metal.
Areas of application
PVC-U products are used in all areas of the national economy, from construction and industry to residential buildings and urban engineering infrastructure. The widest area of application is the installation of sewer systems in residential, office, public, and industrial buildings. PVC-U pipes are used for drainage and as storm sewers.
In second place is the use of uPVC communications in industry for transporting water and chemically aggressive liquids at low temperatures.
It is also worth mentioning the construction of wells for water supply using casing pipes - socket pipes with an internal thread in the socket and an external thread at the other end of the pipe.
Use in sewer systems
In household utility networks, uPVC pipes are used mainly for non-pressure external sewerage systems in the form of bell-shaped structures and fittings. Inexpensive, durable, short-lived uPVC pipes and fittings for them are produced in a very large assortment, which allows you to assemble utility networks of any complexity.
Use of uPVC pipes for external sewerage
For sewer lines, uPVC pipes are used both at the reconstruction stage and for laying new mains.
It is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of the operation of external sewer systems
It is extremely important that the material of pipe products matches the conditions in which it operates. External lines must be resistant to ultraviolet radiation, temperature and pressure changes, and not deform from possible water hammer
In this sense, pipes made of unplasticized polyvinyl chloride fully comply with the requirements for an external sewer network:
High strength. Withstands external pressure up to 160 atmospheres (depending on wall thickness), internal pressure up to 25 bar, and is resistant to hydraulic shocks. Light product weight
Despite this, a pipeline submerged in water does not float, which is important for land-based networks. Low hydraulic resistance and, as a result, reduced likelihood of blockages. Simplicity and ease of installation. No special equipment required. Products are easy to cut. Minimum labor costs for maintenance and repair of ready-made networks. UV resistance
Suitable for open laying method. Long service life, 50 years or more.
Disadvantages include a serious deterioration in strength characteristics at subzero ambient temperatures, as well as the inability to use the material for transporting working media with temperatures above +40°C. When heated above 50°C, the pipe material begins to release chemical compounds hazardous to health.
What is uPVC
PVC is a thermoplastic polymerized vinyl chloride. Other names for this plastic are vinyl, PVC, polyvinyl chloride, vestolite, jeon and many others.
The plastic is colorless and transparent, durable, unpainted, not resistant to ultraviolet radiation, and odorless. But it is resistant to alkalis and most acids, organic solvents, and oils. It practically does not support combustion in an air atmosphere, but at high temperatures it decomposes, releasing harmful substances.
PVC is produced in two types:
- unplasticized rigid PVC, called vinyl plastic (PVC-U, uPVC);
- plasticized soft plastic compound (PVC-P).
The difference in types of polyvinyl chloride is determined by the use or non-use of plasticizers. Up to 50% plasticizers are added to the plastic compound; it is used where plasticity and elasticity are required from PVC - for linoleum, films, hoses, wire insulation, in medical equipment, for blood transfusion systems, artificial leather, oilcloth, seals, wallpaper, posters, banners. Plastic compound is easier to process into various products; there are many options for its use.
Unplasticized PVC is made without the use of plasticizers. The scope of its application is determined precisely by its hardness and strength - for pressure and free-flow pipes, plastic doors, windows, some garden structures, gramophone records, souvenirs, toys, containers, air ducts, fan parts, laboratory and chemical glassware, equipment, etc. uPVC has some ductility but has neither flexibility nor elasticity.
For pipelines of engineering systems, storm sewers, and drainage, durable and rigid uPVC is used.
Decoding the abbreviation
The abbreviation UPVC stands for unplasticized polyvinyl chloride.
Performance characteristics
The density of uPVC is 1.35-1.43 t/m3. Melting point – 150–220 °C. When heated to temperatures above 60 °C, it softens and loses strength; above 110 °C, it begins to release hydrogen chloride (hydrochloric acid). It ignites poorly, has the ability to self-extinguish, the ignition temperature is 500 ° C.
It has dielectric properties and can be used to insulate conductive parts of equipment. They have low thermal conductivity. Becomes brittle at temperatures below -75 °C (below the glass transition temperature).
Unpainted PVC is subject to destruction (decomposition) under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, so it is painted with opaque paints. In this case, destruction affects only the outer layer 0.05 mm thick.
Most often, sellers and buyers do not go into these details and consider PVC to be UV resistant. In my articles I also do not overload the reader with this information, since it has no practical significance.
Polyvinyl chloride is resistant to solutions of acids, alkalis, salts, alcohols, fat emulsions, most hydrocarbons (including gasoline, kerosene, mineral oils). Limited soluble in acetone and benzene, soluble in dichloroethane and some other chlorinated and aromatic hydrocarbons. Has low gas permeability. The tensile strength of PVC sheet is 40 MPa or more.
Types of pipes for well construction
Drilling a well is only part of the problem that must be solved in order to provide your summer cottage or garden plot with water coming from underground sources. To raise water to the surface, you need a pump, and first you need to lower a casing pipe into a hole drilled in the ground.
Construction of a well with casing pipe
As mentioned above, products made from metal, asbestos cement and PVC (UPVC) can be used. For use as casing metal and asbestos-cement pipes, lifting equipment is required, since they are heavy. In addition, rolled metal pipes are quite expensive, so their use is associated with significant financial costs.
Asbestos-cement products are more affordable, but they are inconvenient to install and are very susceptible to mechanical loads. When using asbestos-cement pipes as casing, situations often arise when they burst under the influence of external loads, which leads to erosion of the well and its subsequent clogging. Restoring it in this case is almost impossible, so the solution is new drilling. This naturally leads to additional financial costs.
Socket connection of uPVC pipes
How to calculate the casing diameter size
Before purchasing materials and constructing a water well, its size should be determined. Manufacturers offer a wide range of casing materials for wells.
The minimum diameter of products is 90 mm, the maximum is 225 mm. Wall thickness varies from 7 to 20 mm. For a domestic well, a common size is casing pipes 125 mm in diameter. Thick-walled products are used for installing deep artesian wells.
When choosing the size of a well, one should be guided by considerations of practicality. The dependence here is this: the more water is required daily, the more power the pump will use. When calculating the diameter of a well, the depth of its drilling also matters; the larger it is, the more powerful the pump will be required to lift it to the surface.
The more powerful the pump for pumping water, the larger its dimensions and the wider the well required to immerse it. Pumps with a flow of up to 8 mm have a casing diameter of up to 122 mm, which does not require a pipe larger than 125 mm.
PVC or cast iron pipes - which is better for sewerage
Looking ahead, we note that uPVC pipes are completely out of competition with their analogues. Why this is true will be clear from a comparison of the following:
- 1.Unlike cast iron pipelines, uPVC sewer systems do not rust or collapse. First of all, this is due to production technology. So, if in the first case metal was used for production, then for uPVC they use plastic, which is not afraid of corrosion and direct interaction with water. At the same time, polymer pipes are not afraid of chemical activity, which can be caused by the acidic base of food, as well as chemicals for washing tiles and dishes. This results in a big advantage of polymer pipes - the service life is 60 years, which is 3 times higher than that of cast iron analogues.
- 2. uPVC have a light, one might say airy, structure, which allows a small number of craftsmen to work with these pipes. Along with the low specific gravity, it is worth noting the simplicity of the design. In turn, the simplicity of the design allows you not to use a special tool for installation, which means it does not require specific skills. For example, to lay a sewer system from cast iron pipes, you need to have a welding machine, obtain a work permit, and notify neighbors about the work being carried out. At the same time, it is not a fact that you will definitely weld cast iron, because microscopic holes may remain through which an unpleasant odor will pass. In the case of uPVC, everything is much simpler. It is enough to simply combine two pairs of pipes, sawing off the required length if necessary. At the same time, the o-ring that is available simply will not allow you to make the joint incorrectly.
- 3. Low cost uPVC. Just imagine, plastic and metal. Of course, metal will cost many times more, despite the fact that its performance qualities are much worse.
- 4.High coefficient of resistance to high temperatures. This means that the polymer sewer system will never burst or leak, which will allow you to avoid unplanned repairs. In the case of cast iron, sooner or later the thermal expansion of the metal will lead to a violation of the strength at the welding site of two sections of the sewer. In this regard, it will leak and timely repairs will be required.
- 5.High coefficient of frost resistance. If you use cast iron outside, you will have to bury it one and a half meters or more. If uPVC is used, the sewer pipe can be buried 50 cm deep.
To summarize this article, we note that not all the positive qualities of uPVC pipes are listed here. But this is quite enough to draw conclusions in favor of polymer sewerage.
Features of installation and connection of PVC-U pipes
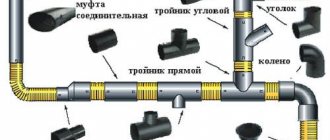
Methods for connecting polyvinyl chloride pipelines:
- using fittings for gluing;
- butt gluing (for structures with a wall thickness of at least 5 mm);
- bell-shaped structures are inserted at one end into the bell of the previous one.
Pressure communications are usually glued together using couplings, corners, transition couplings - simple or collapsible. During gluing using fittings, carefully prepare the ends of the workpieces - cut them evenly, clean them, remove dirt and shavings, degrease the end of the workpiece and the fitting.
Glue is applied to the workpiece using a brush or glue gun. Insert the workpiece into the fitting and turn it half a turn. Then forcefully press the workpiece into the fitting for 20-30 seconds and quickly wipe off any glue droplets that appear at the joint. The connection is left untouched for 24 hours to allow the glue to fully polymerize. At the entrance to the building, flanges are sometimes glued to the pipe and a valve is mounted between them.
Assembly of socket pipes
Much more often in a private house there is a need to assemble socket elements into a single sewer line. There is no particular difficulty in assembling elements with sockets - lubricate the end of the pipe with sealant and insert the pipe or fitting into the previous one. The main thing is that there is a seal in the socket.
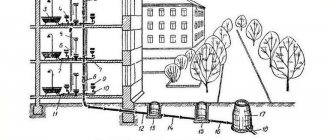
Installation features
Laying sewerage requires observance of the slope. If the slope is not maintained, the pipeline will have deflections and bulges - this contributes to the formation of blockages. When laying, the pipeline itself must lie on a 100-mm sand bed and be covered with sand from the sides and top. Wells should be installed in places where the pipeline turns.
If the communication is laid shallowly, the pipeline must be insulated. If the sewer freezes, it is almost impossible to repair the system in winter.