Cold galvanizing. Process technology
Compositions for cold galvanizing include: • highly dispersed zinc-containing powder (80% and above), • binding components (organic or inorganic).
To form a uniform layer during cold galvanizing, the powder used includes a mixture consisting of fine particles of pure zinc ranging in size from 5 microns to 15 microns. The smaller the zinc components, • the better the interdiffusion connection between the applied layer and the base (metallic Zn-Fe bond), • the higher the elasticity of the protective layer, • the less roughness of the coating (the surface is even and smooth).
cold galvanizing technology
, polymer organic compounds are most often used as a binding element The main characteristic of the binding components is the ability to “harden” (harden), forming a waterproofing coating. 1. Hardening of epoxy and polyurethane compounds occurs due to the occurrence of chemical reactions that are irreversible. 2. Zinc silicate compositions harden in air due to the pre-hydrolysis reaction with moisture. 3. Some zinc-rich coatings (thermoplastic) “harden” as a result of solvent evaporation.
Cold galvanizing is a technological process that results in a coating with high anti-corrosion properties. Protection of the matrix base from destruction is carried out in two ways: • barrier (waterproofing), • protective (cathode).
comparative diagram of the protective mechanism of paint and varnish and zinc-filled coatings
During cold galvanizing, the protection of the processed product proceeds from the tread type to the barrier type.
Barrier type of protection is typical for paint and varnish coatings. It is based on creating an insulating layer on the surface of the workpiece.
The protective method is based on the work of the galvanic couple zinc - iron (Zn is the anode in relation to Fe). When exposed to aggressive conditions, zinc protects the steel coating by dissolving. The products of destruction of the protective layer are sparingly soluble oxides that fill the damaged areas. The main components of tread protection are: • the concentration of zinc-containing pigment (the higher the zinc content in the powder, the higher the galvanochemical activity), • the porosity of the workpiece and the applied material.
After cold galvanizing, the zinc-rich coating can be used 1) as an independent protective coating, 2) for preliminary priming treatment, 3) as interoperational, repair protection.
Application of a protective layer during cold galvanizing can be done by dipping the workpiece into a prepared technological solution or by painting using special sprayers (spray guns) or brushes and rollers.
methods of applying zinc-rich coating
The thickness of the layer obtained after cold galvanizing can reach up to 120 microns.
The whole truth about cold galvanizing
- home
- Articles
- Cold galvanizing
Corrosion is combated using various methods: applying compounds, hot-dip galvanizing, galvanization and others. Each method has different costs, method of application, pros and cons. Cold galvanizing is a common, easy to use and economical method. However, it is he who raises many questions that we will answer in this article.
What is cold galvanizing?
Cold galvanizing
– application to the prepared metal surface of a special composition with a zinc content of 92-96%. The composition is available in cans and is applied like regular paints and varnishes, with a brush, roller or spray gun. After application, the composition forms a durable coating on the metal surface that protects against corrosion using a barrier method (does not allow moisture and oxygen to pass through) and a protective coating using an electrochemical method (if moisture does seep into the metal).
Why is the composition based on zinc?
Iron, when interacting with moisture and oxygen, oxidizes and forms a fragile, loose film on the surface. Such unreliable protection continues to allow moisture and oxygen to penetrate deep into the iron and destroy it. But zinc, tin and aluminum, when interacting with moisture and oxygen, form a durable film that prevents further destruction. That is why a thin layer of these metals is used to protect other metals that are more susceptible to corrosion.
Special offer for new clients
Additional discount of 350 rubles when ordering through the website.
Zinc stands out among this group of “durable” metals in that it provides further protection from moisture and oxygen even if the coating is damaged, while the protection of tin or aluminum weakens or even begins to promote corrosion if the integrity of the layer is compromised. Two methods of protection with zinc are called barrier (passive) and cathodic (active, sacrificial, electrochemical).
What is cathodic or sacrificial protection?
Zinc, when applied to iron, forms a galvanic couple with it, in which iron is a less active metal, and zinc is a more active one. When in contact with moisture and oxygen, the zinc anode reacts first, donating its electrons to fight corrosion, and the iron cathode accepts electrons, is protected and remains virtually untouched by rust. The protective process continues until the zinc layer is completely depleted. 1 layer of 40-60 microns is enough for 10-25 years.
Why is cathodic or electrochemical protection needed?
Any coating with the composition is not 100% sealed, but has defects and pores. The zinc coating can also allow a certain amount of oxygen to pass through at the initial stage of operation. It is then that it protects metals from rust using a protective or electrochemical method. During operation, the coating structure becomes compacted, the zinc compounds are completely dissolved, and barrier protection takes effect, as with hot-dip galvanizing.
Why is this method more profitable than others?
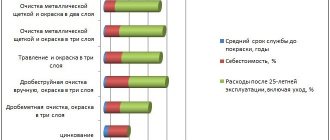
Cold galvanizing provides the same protective characteristics as other methods such as hot galvanizing. But, unlike them, it is much easier to apply on site where structures are used, costs less and lasts longer.
Who uses cold galvanizing?
Forges and artistic forging need galvanizing - galvanized products are more readily purchased, and having protection, they increase in price.
Anyone who uses metal structures or products themselves if they want them to last for decades and not require constant processing.
How does the process itself happen?
The process consists of 6 points:
- surface preparation
- preparation of the composition
- coating
- applying further layers
- quality control
- drying before use
How to prepare the surface for applying the composition?
It is necessary to carefully examine the surface, thoroughly clean and degrease. Wait until it dries completely, prepare everything for application and get to work.
How and what to apply?
The compositions are applied like regular paints - with a brush, roller, spray gun or dipping (convenient for small parts). The equipment is ordinary, no different from what is needed for applying paint and varnish.
Where is it used?
The compositions are used in civil and industrial construction - for the foundations of residential and work buildings, in the electric power industry - for power plants and power transmission line supports, in the construction of road fences and bridges, the construction of hydraulic structures, for equipment for oil production and storage, protection of trucks, railway cars, air and water transport. The method is completely safe for people and animals, has no contraindications and can be used in any area.
Is a solvent needed?
The solvent is used during application as a thinner for a more liquid consistency, for degreasing the surface and cleaning tools.
Can zinc coating be repaired or restored?
Cold zinc coating is easy to repair. To do this, you do not need to completely renew the coating of the entire structure; it is enough to treat the damaged area. By the way, this ability distinguishes cold galvanizing from other methods of galvanizing.
How to make the coating more attractive?
If you want to make a metal structure or product not only protected, but also attractive, apply colored enamel on top. Compositions for cold galvanizing are compatible with almost any paints and enamels, but it is better to use special anti-corrosion enamels, which will extend the protection period of metal structures.
Can it be used in winter?
Coatings can withstand negative temperatures down to -40°C continuously and up to -60°C with short-term drops. By the way, it also withstands high temperatures: +150°C constantly and up to + 200-400°C with short-term increases (depending on the specific composition).
Under what conditions should it be applied?
The compositions can be applied outdoors or indoors, ventilate well during the process. It is allowed to apply at temperatures from -35°C to +40°C and relative air humidity of no more than 85-90%. It is worth considering that at low temperatures the composition will become thicker and more viscous, and the coating will take 2 times longer to dry, but no protective qualities will be reduced.
Is this method of protecting metals expensive?
The compositions are 3-4 times cheaper compared to other methods of anti-corrosion protection. The method is durable for up to 25 years, which means it will not require repeated use for a long time. Coatings are applied by hand directly at the site of operation, without the involvement of third-party specialists and are not transported anywhere. All this allows you to save significantly.
See how metal structures coated with cold galvanizing compounds look in the cold galvanizing reviews section.
Our store offers a wide selection of different anti-corrosion coatings, among them you can choose the one that is optimal for you.
You have questions? Call or write to us!
We will help you choose the coating that is optimal for you!
- Moscow: +7
- Saint Petersburg: +7
- Russia: 8
(Toll free number) - Email: [email protected]
Call right now and purchase our products at the best price!
To the list of articlesNext >
Difficulties in applying zinc coating using cold galvanizing
1. When applied, zinc powder must always be in a suspended state, otherwise it may settle and stick together, which can lead to defects in the resulting coating and the impossibility of the technological process. 2. When cold galvanizing, high demands are placed on surface preparation before applying a protective layer (the surface must be clean, dry and porous, which improves chemical adhesion).
cold galvanizing defects
3. When applying zinc-rich coating by spraying, special requirements are placed on special equipment (spray gun). 4. The technological process is sensitive to the thickness of the applied layer (the larger the layer, the higher the likelihood of peeling).
Application of material
The working composition is applied to a cleaned and degreased surface no later than after 12 hours if the metal structures are located outdoors, and 48 hours if the metal is located indoors. Regardless of the chosen method of applying the composition to the prepared surface, welds, as well as places that are difficult to reach with painting equipment, should first be painted with a brush. If there are cracks and hidden voids after welding, exclude the possibility of moisture getting into these places (by any waterproofing methods that do not pollute the surface). The GALVANOL® material can be applied to the surface to be treated using a brush, roller, spray paint or dipping.
Read also: Jigsaw files for wood
Application with a brush: the brush should be made of natural bristles, clean from dust and other contaminants. Dilution of the GALVANOL® composition with thinners under standard conditions is not required.
Application by roller: the roller must be made of a material that is resistant to organic solvents, free from dirt and previously used paints. Dilution of the GALVANOL® composition under standard conditions is not required.
Application by pneumatic spraying: equipment must be clean of contaminants from previously used paints. If necessary, the “GALVANOL®” composition is diluted with solvent or xylene diluents in a ratio of up to 5% by weight. Air pressure 0.2–0.3 MPa (2–3 bar). Nozzle diameter 2.0–3.0 mm.
Application by airless spraying: equipment must be clean from contaminants previously used by paintwork materials. If necessary, “GALVANOL®” is diluted with solvent or xylene diluents in a ratio of up to 4% by weight. Pressure 8–12 MPa (80–120 bar). Nozzle diameter 0.015–0.025 inch or 0.38–0.63 mm. Application by dipping: dilution of “GALVANOL®”, if necessary, is carried out with solvent or xylene thinners, in a ratio of up to 15% by weight. Application from an aerosol can: when applying the composition, the can should be held vertically with the valve up at a distance of 25-30 cm from the surface to be protected. Apply at ambient temperatures from +5 C to +40 C.
The working composition "GALVANOL®" must be periodically mixed during the application process by any method (every 20-30 minutes). After finishing work, clean the valve: turn the cylinder over and press the nozzle until clean gas begins to come out. Remove any remaining composition on the valve with a swab soaked in a solvent (solvent, xylene). The material must be applied in layers, overlapping the edge of the previously applied strip. The total coating thickness should be min – 40 microns, max – 160 microns. When applied to structures whose mechanical deformations are insignificant, the maximum coating thickness can be increased to 200 microns. All work on applying the GALVANOL® material (except for the aerosol can) is carried out at temperatures from –30 C to +50 C and relative humidity up to 90%. The composition can be applied to a damp surface. In this case, there should be no moisture in the form of drops on the surface, and at low application temperatures, exclude the presence of an ice crust. It is recommended to use canopies when applying coating in precipitation conditions (snow, rain).
Cold galvanizing. Advantages
1. No restrictions on the overall dimensions of products (structures) when applying a protective coating. 2. The ability to carry out welding work on a galvanized surface; welding seams are galvanized in place.
advantages of cold galvanizing
3. Cold galvanizing is carried out in the temperature range from -20 degrees to + 40 degrees. 4. Surface preparation before applying zinc coating is carried out at the location of the structure (product). 5. Cold galvanizing technology makes it possible to obtain an elastic, corrosion-resistant coating that is resistant to ultraviolet radiation, radiation, and microorganisms. 6. Variety of application methods (dipping, spraying, painting). 7. Complete absence of hydrogen embrittlement, aging processes and depletion of the surface layer are not observed. 8. The resulting protective layer has high electrical conductivity, heat resistance, resistance to impact loads and abrasion. 9. The galvanized surface obtained after cold galvanizing is fireproof and not subject to fire. 10. Cold galvanizing technology is simple. 11. Low cost of the technological process.
In terms of their technological parameters, zinc-rich coatings are not inferior to the technological characteristics of protective coatings obtained by hot-dip galvanizing.
Compatibility with other coatings
The composition for cold galvanizing "GALVANOL®" is easily compatible with 99% of solvent-soluble finishing coatings. Guaranteed compatibility with polyurethane, urethane-acrylic, acrylic, epoxy, vinyl chloride, chlorinated rubber, and alkyd coatings. For ideal compatibility, it is necessary to wait after applying the GALVANOL® cold galvanizing composition for at least 4-5 hours so that the solvent evaporates and does not interfere with further adhesion. Can be used as a primer for powder paints. In aqueous salt solutions (pH=6-9), fresh and sea water, the composition for cold galvanizing “GALVANOL®” effectively protects steel from corrosion. The coating is not resistant to gasoline and a number of organic solvents, so it should be covered with a topcoat that is resistant to the environment.
Application areas of zinc-rich coatings
application of cold galvanizing
Cold galvanizing is actively used in the protection and repair of building metal structures, tunnels, bridge structures, pipelines, liquid storage tanks, lighting poles, and is used in the automotive industry. The effectiveness of the cold galvanizing is based on the simplicity of the technology, low cost, and quick return on investment.