Galvanizing is one of the most effective ways to protect metal structures from corrosion. There are several methods by which the result is achieved, ranging from electrochemical deposition to thermal gas spraying. However, the most popular and simplest is cold galvanizing of metal - a method suitable for processing parts of any size, profitable and affordable even for use at home.
General information
Galvanization is the process of coating the surface of a metal part or an entire structure with certain substances that protect it from external destructive forces (not physical, but only chemical). Zinc is added to the base of the substance. It is he who has the above properties. Hence the name of the technology. Advantages of processed products:
- increased strength, however, this will not save you from impact;
- less susceptibility to temperature changes;
- aggressive substances (chemicals, detergents, solvents) do not cause much harm;
- extended operational period without loss of quality;
- no oxidation and rusting.
Video: Garage galvanizing
Zinc Treatment Process
It is in demand all over the world and is used in large-scale and small-scale production, and many people who want to extend the shelf life of purchased products try to create a specialized solution themselves to cover all the necessary surfaces. This is done primarily in order to create a barrier between the metal and oxygen. It is this that oxidizes the top layer, which subsequently leads to the appearance of rust.
The procedure can be hot or cold; we’ll talk about the methods below. But in general, it is low-cost due to the ease of coating, as well as the low cost of the chemical.
Why is a layer of zinc applied to steel?
When operating in high air humidity (for example, any car), the first corrosion processes occur. Galvanized coating can prevent this. The explanation is as follows: the element in the solution with which the surface is coated creates a galvanic couple with the steel product, among which the first substance will be dominant, since it has more negative electrons in its charge.
During chemical oxidation processes (the reaction still occurs), this top layer suffers, but not the steel itself; in fact, the impregnation takes the blow. But since any protection tends to deteriorate, galvanizing also has a shelf life. But this is a long process. And if there is a small gap, then upon contact with water another reaction will occur, where zinc hydroxide will appear in its place, which performs the same barrier functions. In addition to providing a barrier against interaction with moisture and air, the solution protects against electrochemical influence.
Video: Galvanizing metal at home
Popular materials for galvanizing
Cold galvanizing is performed using various materials, which are selected depending on a number of factors. Popular compositions suitable for both industrial use and home work include:
- the preparation “Galvanol”, which has good adhesion to products made of ferrous metals and is characterized by ease of application, the possibility of use in the temperature range of –30°C – +50°C and galvanizing even rusty surfaces;
- “Tsinotan”, used for processing tanks for storing petroleum products, pipes and tanks of the hot water supply system, power line supports and hydraulic structures;
- paint for cold galvanizing "AnticorZinc™", characterized by resistance to petroleum products, solvents, fresh and sea water, high adhesion to the metal surface, mechanical strength and good aesthetic characteristics;
- “Master AK-100” is a composition suitable for corrosion protection of automotive parts, including body elements, building and railway structures and supports for power lines;
- “Cinotherm” is a solution used in combination with any paint and varnish materials, which allows not only to protect the metal, but also to change the color of its surface;
- “ZVES” is a paint whose compositional features (the inclusion of zinc powder and ethyl silicate) allow it to be used to increase the protective properties of alloy steel.
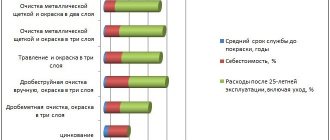
Almost all substances used for cold galvanizing are characterized by the same gray color and consumption in the range of 0.25–0.3 liters per 1 m2.
And when choosing a specific product, you should pay attention to their price and specified characteristics such as service life, drying time to a strength level suitable for applying the next layer and temperature range of use.
Another important parameter is the zinc content in the material, which is in the range of 85–96%. While the service life can reach 10 years, the drying period is from 0.5 to 6 hours, and the processing price is 1 sq. m of surface starts from 55–60 rubles.
Cold galvanizing technology, video:
Metal galvanizing technology
Complete coverage with the solution is possible in the presence of a container and equipment constructed from a material that can withstand an aggressive environment. The procedure occurs in several stages:
- Preparation. The surface is completely cleaned, processed, all grease and other stains are removed, and, if necessary, cleaned or sanded to a smooth surface. Then the surface layer is removed by etching (using electrolysis or an acidic environment - sulfuric acid). These manipulations create a film of oxides on the top of the part. It combines well with zinc. Then you need to thoroughly dry the workpiece.
- Applying zinc coating to metal. The alloy is melted to a homogeneous liquid state by heating it to a temperature of 450 degrees (which is slightly higher than its specific heat of fusion). Then the product is immersed in this container-pool. You can only pull it out after you make sure that even the smallest holes, corners, and crevices have been treated. Because otherwise, destruction will begin with them.
- Drying. Exposure to warm or cold air is not recommended. It is best if the workpiece dries in room conditions.
Since you can galvanize metal at home with your own hands only if you have a special bath, which should be able to quickly connect the current, we will divide them into:
- large-sized;
- mid-size;
- small-sized.
Galvanizing at home
The technological process of galvanizing involves the deposition of metal cations on the anode. A similar chemical reaction occurs in a bath of electrolyte when exposed to electric current.
Where to find electrolyte
Any solution of zinc salts can be used as an electrolyte. The most popular and easily accessible are zinc chloride and hydrochloric acid. Also, an electrolyte with the necessary properties can be obtained by etching zinc in sulfuric acid. This reaction must be carried out very carefully. It is accompanied by the release of a large amount of thermal energy and explosive hydrogen.
Pickling of zinc in sulfuric acid with the release of hydrogen and obtaining zinc salts
How to get zinc
To galvanize at home, you need to prepare zinc, which can be obtained in the following ways:
- using regular salt batteries;
- fuses from the times of the Soviet Union;
- any parts with zinc coating;
- pure metal, which can be found in appropriate stores where chemical reagents are sold.
Scheme for obtaining zinc from batteries
Preparing for the procedure
To create a high-quality metal coating, several preparatory operations should be performed:
Galvanizing process
- prepare a galvanic bath. Any glass or plastic container can play its role;
- install stands for the anode and cathode;
- the electrolyte should not contain undissolved salt crystals , for which distilled water is additionally introduced;
- The role of the anode is performed by a zinc plate. The larger its area, the better the quality of the coating;
- The plus from the power source is connected to the anode. There can be several of these elements if desired;
- A minus is connected to the cathode. Zinc particles will be deposited on its surface;
- The cathode must be cleaned of rust and any contaminants. Before processing, it is additionally dipped in an acid solution;
- the cathode must be at the same distance from the anode to ensure uniform coverage on all sides;
- with a constant current output is used as a power source
- the greater the current and voltage, the faster the reaction will occur and the looser the protective film will be;
- when using a car battery, an incandescent light bulb of up to 20 W is included in the circuit to reduce the current.
Device for galvanizing at home
Technology for creating zinc film
To create a high-quality protective coating on the metal surface, after the preparatory operations have been carried out, the current source is connected to the network, and the cathode is dipped into a galvanic bath. This process should take place without violent boiling. If this is observed, you may suspect too much current in the system. To reduce it, several additional consumers are connected to the electrical circuit.
Gradually, a metal coating will form on the surface of the cathode. The longer this process takes place, the thicker the protective layer on the metal will be.
How does it rust?
The rusting process consists of three influences: air, water and aggressive environments. At the same time, they enter into chemical reactions, destroying the integrity of molecular bonds. As a result, small, invisible holes first appear, which may look like roughness, and then holes form. In this case, it is necessary to distinguish between oxidation - this is the initial stage on the upper layers, and corrosion, that is, more serious damage to the structure, the appearance of holes.
The stronger the moisture and the more aggressors, the faster the process occurs; this will only prevent galvanizing of metal in domestic or industrial conditions. Let's consider the advantages of using the method.
Local galvanization of the body
There is an old tried and tested method of applying a protective zinc coating to steel parts at home. It is called galvanic or electrolytic zinc coating. Its essence is simple and known from chemistry lessons. A solution of zinc salt, zinc sulfate or zinc chloride is taken. If there is no ready-made solution, it can be obtained by dissolving zinc in sulfuric or hydrochloric acid, respectively. Ready-made zinc chloride is sold under the name “soldering acid” in radio parts stores. Sulfuric acid can be bought at an auto parts store; it is an electrolyte for acid batteries. If you can only find acid and zinc, then to prepare a solution, you simply need to dissolve it in acid. According to the rules, you need to put the zinc in an acid-resistant container and carefully add the acid. Zinc should be taken at a rate of approximately 400-450 grams per liter of acid. Of course, it is not necessary to prepare so much solution. When zinc dissolves, a chemical reaction will occur, releasing hydrogen, which is flammable and can cause an explosion. So it is better to do this outdoors away from fire. If the zinc has completely dissolved in the acid, you need to add it a little more to make sure that the acid has been completely developed and the reaction with the release of hydrogen bubbles no longer occurs. The resulting solution must stand until clear, then it must be drained from the sediment.
This solution will be the electrolyte. Now the workpiece is taken and the “minus” of the current source is connected to it. "Plus" is connected to a piece of zinc metal. Both of them are placed in an electrolyte, at some distance from each other, and voltage is applied. 12 volts from a car battery or charger will be enough for it. Under the influence of current, zinc will be deposited on the steel part, and a piece of zinc will dissolve and go into solution. It is important that only the piece of zinc is immersed in the solution, but not the wire that is connected to it. Otherwise, the wire will also dissolve and precipitate on the steel, and ruin the whole thing. If everything goes correctly, the steel will be covered with a uniform layer of gray color; if the current is too high, the process will go too quickly and you will end up with a dark, loose coating. Usually a current of 0.5-1 A is enough. After treatment, the part should be rinsed well with water, or better yet, with a solution of baking soda to neutralize any remaining acid.
When it comes to galvanizing a car body, the question arises, how to place it in this solution of ours? We will not place the car in the solution; this is done only in production. The technology for processing small areas of the body is as follows: Completely clean the area from rust with sandpaper. In no case is it phosphorus or a rust destroyer. When using an existing battery, connect the wire that goes to a piece of zinc to its plus. It is very convenient to use clamps for “lighting”. The minus of the battery remains on ground, that is, it is, as expected, connected to the body. The zinc needs to be wrapped in a piece of cloth several times to make it thicker. The fabric should not touch either what you are holding this zinc with or the wire. Now you just need to dip the zinc wrapped in a cloth into our solution and move it over the area that we want to galvanize. Zinc will be deposited on the body material. After treatment, the part must be rinsed well with water, or better yet, first with a solution of baking soda to neutralize any remaining acid. All that remains is to thoroughly dry the treated area, after which it can be primed and painted.
automobile-help.ru
pros
- Smooth surface, no roughness, shine even without topcoat.
- Long period of operation.
- There will be no rusting for a long time.
- The ease of processing in this way does not require complex equipment, high electrical voltage or expensive components.
But it must be remembered that inhaling zinc vapor or entering the body in another way can lead to poisoning. Therefore, you cannot heat drinking water in galvanized buckets (you can carry it, but only without increasing the temperature) or perform other manipulations with food (for yourself or animals), while heating the product.
Video: DIY galvanizing
Types and methods of galvanizing metal
Efficiency will be determined by such a concept as adhesion, that is, the ability of the zinc coating to attach to the top metal layer. Not every material has the ability to adhere to zinc, so different procedures are used for different alloys. The choice also depends on:
- operating conditions;
- required protective properties;
- thickness of the formed layer.
Let's take a closer look at the options.
Cold galvanizing
Over the past decade, this has become an innovative development because it has made it possible to obtain high-quality results without additional financial costs. The absence of the need for expensive equipment has led to the fact that you can galvanize metal parts at home with your own hands - galvanizing will be done using the cold method. This became possible when Zinconol was invented. It is a solution, a coloring substance that contains more than 90 percent zinc. And the remaining parts contain ingredients responsible for the fact that it will remain in a liquid state before application, and then set soon enough.
You can paint the part manually - with a brush, roller, or spray gun. The latter is the optimal method when you need to protect static structures that are difficult or impossible to remove from rust. Often "Zinconol" is used in car services for restoration work on the body. The results of zinc coating at home will be good, the only difference is insufficient resistance to mechanical stress, but this can be compensated for by a layer of paint.
Hot galvanized
This is the oldest method, and it is also the most effective. We discussed its stages above; the main task is to melt the substance and immerse a metal structure in it. The highest technical qualities are achieved, but the method is used less often than cold. This is due to the negative impact on the environment. Another drawback is that in order to completely process large one-piece structures, a very massive bath is required, as well as a lot of raw materials. But most power lines are covered in this old way.
Video: Hot galvanizing of metal structures
Galvanic galvanizing of metal by electrolysis is impossible at home
Pros: high accuracy; before the procedure begins, you already know exactly what thickness the layer being formed will be. Another advantage is the attractive appearance of the product and exceptional smoothness. There are no air bubbles or other foreign interference.
Steel and zinc are connected at the molecular level, so their adhesion is complete, we can even talk about the diffusion of materials. The procedure goes like this. The bath is filled with electrolyte. The structure is placed in a solution that conducts current well. Electricity is connected. Here it is important to accurately select the voltage and duration of the session.
Thermal diffusion galvanizing
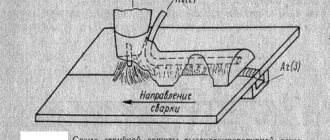
Abbreviated as TDC. Difficult to perform, possible only in production workshops, operation. The workpiece is placed in a closed box. Dry zinc is placed nearby. They heat the room up to 2600 degrees. At elevated temperatures, a change in the aggregate state of the substance occurs (from solid to vapor), and vapors settle on the walls of the product in a layer of more than 15 microns, which is more than with other methods.
How to coat metal with zinc using the gas-thermal method
The main technique is spraying. That is, the mixture that needs to be treated with the surface is dissolved in another gaseous substance so that it is applied to the workpiece together with it. The particles hit at high speed and seem to “stick” to the surface. At the same time, since this is all done unevenly and quickly, a smooth and even layer does not appear. On the contrary, it rather resembles scales and consists of small irregularities that are perceptible to the touch. For this reason, it is imperative to paint the part on top. This is a good option that retains its basic protective properties, but is used mainly when it is not possible to use hot-dip galvanizing or electrolysis.
Table 1. Comparison of zinc with other metals
| Properties of metals | Copper | Nickel | Lead | Tin | Zinc |
| Density, g/cm3 | 8,93 | 8,9 | 11,37 | 7,29 | 7,1 |
| Temperature | |||||
| melting, C | 1084 | 1455 | 327 | 231 | 419 |
| boiling point, C | 2360 | 3075 | 1755 | 2270 | 906 |
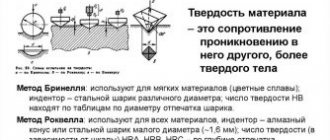
| Brinell hardness, kg/mm2 | 36,8 | 95 | 3 | 5 | 35 |
| Thermal conductivity, cal/cm.sec, deg | 0,94 | 0,14 | 0,08 | 0,15 | 0,27 |
Table 2. Comparison of zinc with non-ferrous metals
| Properties of metals | Copper | Nickel | Lead | Tin | Zinc |
| Density, g/cm3 | 8,93 | 8,9 | 11,37 | 7,29 | 7,1 |
| Temperature | |||||
| melting, C | 1084 | 1455 | 327 | 231 | 419 |
| boiling point, C | 2360 | 3075 | 1755 | 2270 | 906 |
| Brinell hardness, kg/mm2 | 36,8 | 95 | 3 | 5 | 35 |
| Thermal conductivity, cal/cm.sec, deg | 0,94 | 0,14 | 0,08 | 0,15 | 0,27 |
Principle of the method
Cold galvanizing of metal structures is a method of painting metal using a special composition containing a large amount of zinc (from 89 to 95%).
The result is the formation of a durable coating by drying paint. Moreover, the protection of the metal is not only physical, preventing mechanical stress, but also cathodic, preventing the development of corrosion by reducing the potential.
The technique is characterized by the following features:
- performing the process using a roller, sprayer or regular brush;
- ensuring a high level of water resistance, fire safety and electrical conductivity of the processed material;
- minimal probability of metal deformation due to high temperatures - when galvanizing, the surface heats up to only 5°C–40°C;
- the possibility of applying almost any paint and varnish material to the surface of the structure - the exception is alkyd paints, which have a risk of peeling;
- no need to move the workpiece.
Using this technique, bridge structures, pipes, elements of railway tracks and road barriers are protected. In addition, galvanizing provides protection for tanks, reservoirs and oil pipelines. And one of the most popular areas of application of the method is the processing of parts for passenger cars and trucks.