Application
The induction furnace is widely used in large and small enterprises for melting metals (non-ferrous and ferrous). In induction casting furnaces, a metal or alloy is heated until its state of aggregation changes.
At the same time, channel furnaces, despite their higher efficiency, are used much less frequently - mainly for the production of high-quality cast iron and alloys, the melting point of which is relatively low, as well as for the melting of non-ferrous metals. Such furnaces are not used for steel, since its melting temperature greatly reduces the durability of the lining (protective finish). Also, low-grade rock, shavings and small rock should not be melted.
Crucible furnaces are used much more often due to their ease of operation and greater process control capabilities, including the possibility of irregular and intermittent operation. They are good both for the production of large quantities of castings of several tens of tons, and for small portions measured in tens of grams.
Crucible furnaces are used to melt alloy steels and other alloys that require special purity of the chemical composition and homogeneity.
- Induction furnace 350 kg Ulyanovsk
- Induction furnace 500 kg Chelyabinsk
- Induction furnace 1 ton Arkhangelsk
- Induction furnace 1 ton Minsk
Self-assembly of the stove
There are many technologies and schematic descriptions of this process presented on the Internet and magazines, but when choosing, it is worth choosing one model that is most effective in operation, as well as affordable and easy to implement.
Homemade melting furnaces have a fairly simple design and usually consist of only three main parts housed in a sturdy casing. These include:
- element generating high frequency alternating current;
- a spiral-shaped part created from a copper tube or thick wire, called an inductor;
- crucible - a container in which calcination or melting will be carried out, made of refractory material.
Of course, such equipment is not often used in everyday life, because not all craftsmen need such units. But the technologies found in these devices are found in household appliances that many people deal with almost every day. This includes microwaves, electric ovens and induction cookers. You can make various equipment using diagrams with your own hands if you have the necessary knowledge and skills.
In this video you will learn what this oven consists of
Heating in this technique is carried out thanks to induction eddy currents. The temperature rise occurs instantly, unlike other devices of a similar purpose.
For example, induction cookers have an efficiency of 90%, but gas and electric cookers cannot boast of this value, it is only 30-40% and 55-65%, respectively. However, HDTV cookers have a drawback: to use them you will have to prepare special dishes.
Transistor design
There are many different schemes for assembling induction melters at home. A simple and proven furnace made from field-effect transistors is quite easy to assemble; many craftsmen familiar with the basics of radio engineering can handle its manufacture according to the diagram shown in the figure. To create the installation, you need to prepare the following materials and parts:
- two IRFZ44V transistors;
- copper wires (for winding) in enamel insulation, 1.2 and 2 mm thick (one piece each);
- two rings from chokes, they can be removed from the power supply of an old computer;
- one 470 Ohm resistor per 1 W (you can connect two 0.5 W each in series);
- two UF4007 diodes (can easily be replaced with the UF4001 model);
- 250 W film capacitors - one piece with a capacity of 330 nF, four - 220 nF, three - 1 µF, 1 piece - 470 nF.
Before assembling such a stove, do not forget about the tool.
Assembly takes place according to the schematic drawing; it is also recommended to check the step-by-step instructions, this will protect you from mistakes and damage to elements. Creating an induction melting furnace with your own hands is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Transistors are placed on fairly large heatsinks. The fact is that circuits can get very hot during operation, which is why it is so important to select parts of the appropriate size. All transistors can be placed on one radiator, but in this case you will have to insulate them, preventing them from coming into contact with metal. Washers and gaskets made of plastic and rubber will help with this. The correct pinout of transistors is shown in the picture.
- Then they start making chokes; you will need two of them. To do this, take copper wire 1.2 millimeters in diameter and wrap it around rings taken from the power supply. These elements contain ferromagnetic iron in powder form, so it is necessary to make at least 7-15 turns, leaving a small distance between them.
- The resulting modules are assembled into one battery with a capacity of 4.6 μF, and the capacitors are connected in parallel.
- Copper wire 2 mm thick is used to wind the inductor. It is wrapped 7-8 times around any cylindrical object, its diameter should correspond to the size of the crucible. The excess wire is cut off, but rather long ends are left: they will be needed for connecting to other parts.
- All elements are connected on the board, as shown in the figure.
It is recommended to use a 12 V, 7.2 A/h battery as a power source. The amount of current consumed during operation will be 10 A; such a source will last for about 30-50 minutes.
If necessary, you can build a housing for the unit; for this purpose, only heat-resistant materials, such as textolite, are used. The power of the device can be adjusted, for which it is enough to change the number of turns of wire on the inductor and their diameter.
There are several variations of the induction furnace that can be assembled
With graphite brushes
The main element of this design is assembled from graphite brushes, the space between which is filled with granite, crushed to a powder state. Then the finished module is connected to a step-down transformer. When working with such equipment, you do not have to worry about electric shock, since it does not need to use 220 volts.
Manufacturing technology of an induction furnace from graphite brushes:
- First, the body is assembled; for this, fire-resistant (fireclay) bricks measuring 10 × 10 × 18 cm are laid on tiles that can withstand high temperatures. The finished box is wrapped in asbestos cardboard. To give this material the desired shape, it is enough to moisten it with a small amount of water. The size of the base directly depends on the power of the transformer used in the design. If desired, the box can be covered with steel wire.
- An excellent option for graphite furnaces would be a 0.063 kW transformer taken from a welding machine. If it is designed for 380 V, then for safety reasons it can be subjected to winding, although many experienced radio technicians believe that this procedure can be abandoned without any risk. However, it is recommended to wrap the transformer with thin aluminum so that the finished device does not heat up during operation.
- A clay substrate is placed at the bottom of the box so that the liquid metal does not spread, after which graphite brushes and granite sand are placed in the box.
The main advantage of such devices is considered to be the high melting point, which can change the state of aggregation of even palladium and platinum. The disadvantages include the transformer heating up too quickly, as well as the small furnace area, which will not allow smelting more than 10 g of metal at a time. Therefore, every master should understand that if the device is assembled to process large volumes, then it is better to make a furnace of a different design.
It is not recommended to melt brass in such furnaces. This material is characterized by a high content of zinc, which begins to burn out at high temperatures and produces caustic smoke that is very harmful to the body.
Lamp-based device
A powerful melting stove can be assembled from electronic light bulbs. As can be seen in the diagram, to obtain high-frequency current, beam lamps must be connected in parallel. Instead of an inductor, this device uses a copper tube with a diameter of 10 mm. The design is also equipped with a tuning capacitor in order to be able to regulate the power of the furnace. For assembly you need to prepare:
- four lamps (tetrodes) L6, 6P3 or G807;
- trimmer capacitor;
- 4 chokes at 100-1000 µH;
- neon indicator light;
- four 0.01 µF capacitors.
To begin with, the copper tube is shaped into a spiral - this will be the inductor of the device. In this case, a distance of at least 5 mm is left between the turns, and their diameter should be 8-15 cm. The ends of the spiral are processed for attachment to the circuit. The thickness of the resulting inductor should be 10 mm greater than that of the crucible (it is placed inside).
The finished part is placed in the housing. For its manufacture, you should use a material that will provide electrical and thermal insulation for the filling of the device. Then a cascade is assembled from lamps, chokes and capacitors, as shown in the figure, the latter being connected in a straight line.
It's time to connect the neon indicator: it is needed so that the master can find out when the device is ready for work. This light bulb is connected to the furnace body along with the handle of the variable capacitor.
Hydraulic induction furnaces
The basic delivery set includes two hydraulic melting units, a thyristor converter and a hydraulic station.
Melting units are placed on a pre-prepared foundation and require lining before starting. Each charge uses its own lining mass. We recommend using a cooling tower as a cooling system. The induction furnace is in demand among medium-sized industrial enterprises with a productivity of 2000 tons/year.
more details
- Induction furnace 250 kg Ekaterinburg
- Induction furnace 250 kg Chelyabinsk
- Induction furnace with a capacity of 250 kg Krasnoyarsk
- Induction steelmaking complex 250 kg Chelyabinsk
- Induction furnace 250 kg Moscow
- Induction furnace 250 kg Ekaterinburg
- Induction furnace 1 ton Kurgan
- Induction furnace 2 tons Ulyanovsk
Gearbox induction furnaces
The basic delivery set includes two melting units on the gearbox, a thyristor converter and related equipment such as gearboxes, flexible conductive copper cables.
Melting units are placed on a pre-prepared foundation and require lining before starting. Each charge uses its own lining mass. To cool the inductors of the melting units, we recommend using a cooling tower. The induction furnace is in demand among small industrial enterprises with a productivity of 2000 tons/year.
more details
- Induction furnace 5 kg Orenburg
- Induction furnace 15 kg Orenburg
- Induction furnace 20 kg Chelyabinsk
- Induction furnace 50 kg Perm
- Induction oven 60 kg Kazan
- Induction furnace 100 kg Chelyabinsk
- Induction furnace 100 kg Lugansk
Induction Furnace for Steel
The induction furnace for steel operates at medium frequency (0.5-2.4 kHz). Steel is melted in a lining that can withstand from 10 to 40 melts. IST induction furnaces come in different loads and capacities; they are equipped with two types of converters: thyristor and transistor. IST furnaces are highly productive, so up to 6 heats can be produced in one shift. Thanks to the lining wear control system, unforeseen situations and accidents can be avoided.
Let's get to the stove: what you need to know
An electromagnetic field (EMF) affects the human body, at least warming it up in its entirety, like meat in a microwave. Therefore, when working with an induction furnace as a designer, craftsman or operator, you need to clearly understand the essence of the following concepts:
PES – electromagnetic field energy flux density. Determines the general physiological impact of EMF on the body, regardless of the frequency of radiation, because The PES of an EMF of the same intensity increases with increasing radiation frequency. According to sanitary standards of different countries, the permissible PES value is from 1 to 30 mW per 1 sq. m. of body surface with constant (more than 1 hour per day) exposure and three to five times more with a single short-term, up to 20 minutes.
Note: the United States stands apart; its permissible power consumption is 1000 mW (!) per square meter. m. body. In fact, Americans consider the beginning of physiological effects to be external manifestations, when a person already becomes ill, and the long-term consequences of EMF exposure are completely ignored.
The PES decreases with distance from a point source of radiation by the square of the distance. Single-layer shielding with galvanized or fine-mesh galvanized mesh reduces the PES by 30-50 times. Near the coil along its axis, the PES will be 2-3 times higher than at the side.
Let's explain with an example. There is a 2 kW and 30 MHz inductor with an efficiency of 75%. Therefore, 0.5 kW or 500 W will go out of it. At a distance of 1 m from it (the area of a sphere with a radius of 1 m is 12.57 sq. m.) per 1 sq. m. will have 500/12.57 = 39.77 W, and per person - about 15 W, this is a lot. The inductor must be positioned vertically, before turning on the furnace, put a grounded shielding cap on it, monitor the process from a distance, and immediately turn off the furnace when it is completed. At a frequency of 1 MHz, the PES will drop by a factor of 900, and a shielded inductor can be operated without special precautions.
Microwave – ultra high frequencies. In radio electronics, microwave frequencies are considered to be so-called. Q-band, but according to microwave physiology it starts at about 120 MHz. The reason is electrical induction heating of cell plasma and resonance phenomena in organic molecules. Microwave has a specifically targeted biological effect with long-term consequences. It is enough to receive 10-30 mW for half an hour to undermine health and/or reproductive capacity. Individual susceptibility to microwaves is extremely variable; When working with him, you need to regularly undergo a special medical examination.
It is very difficult to suppress microwave radiation; as the pros say, it “siphons” through the slightest crack in the screen or with the slightest violation of the grounding quality. Effective combating of microwave radiation from equipment is possible only at the level of its design by highly qualified specialists.
Fortunately, the frequency range in which induction furnaces operate does not extend to microwaves. But if it is poorly designed or used, the oven can enter a mode in which parasitic microwave frequencies appear. Of course, this should be avoided at all costs.
Induction furnace for cast iron
The IChT series is most suitable for melting and overheating (used to increase strength) of cast iron. These furnaces use metalworking waste to produce high-quality synthetic cast iron. An induction furnace for cast iron is economical because it operates at industrial frequency current. Thanks to a multi-stage protection system from external influences and ease of maintenance, this type of furnace occupies a leading position in the Russian market.
Induction furnace for aluminum
A series of induction furnaces designed for aluminum and its alloys - IAT comes in two types: power frequency and medium frequency. The second type is used to obtain pure metals, which is achieved by maintaining the surface oxide film during the melting process. Thyristor frequency converter. Power is regulated by manually switching transformer steps.
Principle of operation
The fundamental principle is the transformer type transmission. A workpiece is placed inside the solenoid inductor (or nearby). Alternating current is supplied to the inductor, resulting in a changing magnetic field that penetrates the heated object, inducing a vortex field (closed lines of force). This field injects eddy currents, as a result of which the workpiece heats up (Joule-Lenz law).
Types of induction boilers
There are the following types of induction heating boilers, designated both by the principle of operation and by the manufacturer’s brand:
- SAV is a type and at the same time a trademark of new generation boilers with a power from 2.5 to 100 kW, produced by the Russian company since 2007;
- VIN - the abbreviation is not only an abbreviation for the name of a type of induction device (vortex induction heaters), but also a patented name for boilers produced by Izhevsk.
Induction heaters SAV
Operation of SAV units does not require the use of an inverter; a current of 50 Hz is supplied to the inductor. The electromagnetic field induced by the primary winding causes the formation of vortex flows in the secondary winding, the role of which in boilers of this type is played by a section of a closed circuit of pipes with coolant. This section of the pipe - the secondary winding - is intensively heated under the influence of Foucault currents and transfers heat to the coolant, which is forced to circulate in the heating system using a circulation pump.
The heating system is constructed using radiators or in a labyrinthine manner, reminiscent of baseboard heating, in order to increase the total area of the outer surface (heat transfer) of the pipes - the heating circuit, at a minimum, should not be minimal in length.
SAV boilers are manufactured for voltages of 220V and 380V. They use water as a coolant (pure or with antifreeze additives), as well as antifreeze. It takes about 5-20 minutes for the unit to reach full operating power (depending on the volume of coolant), the efficiency of the heaters of such devices is at least 98%. For efficient heating of a room up to 30 square meters. An induction device with a power of 2.5 kW is sufficient, the purchase of which, complete with automation and control systems, will cost approximately 30 thousand rubles.
VIN heating units
Boilers of this type are more advanced in operating principle and design, which naturally affects their cost. To operate VIN devices, an inverter is required - a device for increasing the frequency of the incoming current. High frequency current causes the formation of an electromagnetic field of high intensity, which, in turn, causes the occurrence of more powerful eddy currents in the secondary winding. In addition, the heat exchanger and boiler body are made of ferromagnetic alloys that have their own magnetic field. The result of all these processes is a high heating intensity of the heat exchanger and, naturally, the coolant.
A VIN unit with a power of 3 kW is enough to heat a room with an area of 35-40 square meters. (depending on climatic conditions and the quality of thermal insulation of external building structures).
Due to their greater productivity, VIN units can be used not only in residential heating systems, but also for hot water supply. To do this, additional storage tanks equipped with automatic protection are installed into the coolant circuit, the capacity of which is calculated depending on the number of hot water intake points. These containers are provided with hot water by circulating it in a system with direct-flow heating by an induction heater.
Specifications
The main characteristics of induction furnaces include:
- - name of the metal to be melted;
- — capacity in tons;
- — power in kilowatts;
- — voltage and frequency of the supply network, rated current and number of phases.
The technical documentation also indicates: the overheating temperature of the metal, the frequency of the current and the number of phases of the circuit network, productivity, the rate of melt production and overheating with specific electricity consumption, the power of the supply transformer, the flow rate of water cooling the inductor and other data.
Our company’s specialists provide in their instructions for induction furnaces a complete list of technical characteristics with detailed diagrams and recommendations.
Lining
Lining is a protective finish that protects an object from all kinds of damage. The performance and reliability of induction furnaces largely depends on the quality of the lining.
Its choice is especially difficult for channel-type furnaces. Their most important element, the hearth stone, needs special protection, since it contains ring-shaped channels, always filled with liquid metal, and in the center there is a hole into which the middle rod of the core with the primary coil of the transformer is inserted. To protect such a composition, a very careful calculation is required for each furnace, taking into account all the properties of the materials used.
The lining of an induction crucible furnace is simpler and more reliable. It consists of the crucible itself, the hearth (the lower part that forms the bath), ceramic fiber and coating. In general, there are many types of linings for induction furnaces, which take into account all the features of the melted material.
Thus, for ferrous metals there is a lining based on silica, or fused magnesite, or alumina. For aluminum - heat-resistant concrete. To sinter the lining mass at the time of heating, borax, boric acid, liquid glass, clay, etc. are used.
It is imperative to constantly carry out preventive monitoring of the lining and, if necessary, repair it and promptly replace worn crucibles as soon as the thickness of its walls decreases by 30%.
Induction Crucible Furnace Frame
The frame (casing) of the furnace serves as a structural basis for fastening all the main elements of the furnace. At the same time, two main requirements are imposed on it: ensuring maximum rigidity of the entire furnace structure as a whole and minimal power absorption by the frame elements, since they are located in the magnetic stray field of the inductor. Currently, the following basic frame schemes are used in crucible furnaces:
- A frame in the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped, the ribs of which are made of non-magnetic material (for example, from a duralumin corner or non-magnetic steel), and the edges are covered with an asbestos cement sheet. Small-capacity furnaces (less than 0.5 tons) and laboratory furnaces are made with such frames. In order to reduce the heating of the metal corners of the frame, its individual metal elements are isolated from each other with insulating gaskets to eliminate ring currents in the frame frame. The inductor in such a frame is usually attached to the lower and upper asbestos-cement slabs.
- The metal frame is usually cylindrical in shape, made in the form of a continuous winding of thick steel sheet with cutouts (“windows”) for access to the inductor or in the form of a “squirrel cage” formed by vertical metal posts welded to the upper and lower support posts. Between the posts there is access to the inductor. Such frames are mainly used in medium- and large-capacity ovens.
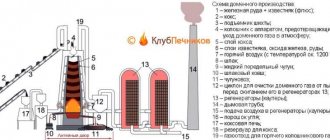
Scheme
The basis of the channel furnace circuit is a closed electrically conductive ring, consisting of a multi-turn inductor mounted on a closed steel core, and a lining placed around it with an annular channel in which liquid metal is constantly located. There are many designs of such furnaces: single-phase and multi-phase, with different numbers of differently placed channels.
Basic circuit for induction crucible furnaces:
- - inductor - a coil through which a current of a given frequency flows;
- — behind the coil there is a dielectric layer (for example, a brick);
- - then the crucible in which the melting is carried out.
To prevent the coil from overheating during operation, the cooling system is water.
The inductor of a crucible furnace is the primary winding, and the molten metal itself, loaded into the crucible, into the center of the inductor is the secondary winding. This is very convenient, and sometimes the crucible itself is not even needed.
Detailed diagrams for crucible furnaces are all different, because there are many different designs with completely different operating parameters.
Device
The furnace in question is a kind of transformer, but it does not have a secondary winding; it is replaced by a metal sample placed in the inductor. It will conduct current, but the dielectrics do not heat up in this process, they remain cold.
The design of induction crucible furnaces includes an inductor, which consists of several turns of a copper tube, coiled in the form of a coil, with coolant constantly moving inside it. The inductor also contains a crucible, which can be made of graphite, steel and other materials.
In addition to the inductor, the furnace has a magnetic core and a hearth stone, all of which are enclosed in the furnace body. It includes:
- induction unit casing;
- bathroom casing;
- frame.
In high-power furnace models, the bath casing is usually made quite rigid, so there is no frame in such a device. The housing fastening must withstand strong loads when the entire oven is tilted. The frame is most often made of shaped beams made of steel.
A crucible induction furnace for melting metal is installed on a foundation into which supports are mounted; the axles of the tilting mechanism of the device rest on their bearings.
The bath casing is made of metal sheets, onto which stiffeners are welded for strength.
The induction unit casing is used as a connecting link between the furnace transformer and the hearth stone. To reduce current losses, it is made of two halves, between which there is an insulating gasket.
The halves are connected using bolts, washers and bushings. Such a casing is made cast or welded; when choosing a material for it, preference is given to non-magnetic alloys. The two-chamber induction steelmaking furnace comes with a common casing for both the bath and the induction unit.
In small ovens that do not have water cooling, there is a ventilation unit that helps remove excess heat from the unit. Even if you install a water-cooled inductor, you need to ventilate the opening near the hearth stone so that it does not overheat.
Modern furnace installations not only have a water-cooled inductor, but also provide water cooling of the casings. Fans powered by a drive motor can be installed on the furnace frame. If such a device has a significant mass, the ventilation device is installed near the stove. If an induction furnace for steel production comes with a removable version of induction units, then each of them is provided with its own fan.
Separately, it is worth noting the tilt mechanism, which for small ovens comes with a manual drive, and for large ones it is equipped with a hydraulic drive located at the drain spout. Whatever the tilt mechanism is installed, it must ensure that the entire contents of the bathroom are completely drained.
Power
The power of induction furnaces is directly affected by the frequency of the alternating magnetic field, because the circulation of induced eddy currents, responsible for converting electromagnetic energy into thermal energy, depends on it.
If for channel furnaces with their high efficiency industrial frequency is sufficient, then in the case of crucible devices the absence of a steel core entails an increase in magnetic leakage flux, and too few lines of force penetrate the molten metal, and the natural power factor is very low. Therefore, crucible furnaces often require power supply with increased and high frequency current and the help of compensating capacitors.
Types of equipment
Only two types of furnaces are widely used: crucible and channel. They have similar advantages and disadvantages, the differences lie only in the method of operation used:
- In a crucible type furnace it is necessary to load each portion of the charge separately. The principle of operation of the device is as follows: the metal is loaded inside the inductor, after melting it is drained and a new portion is loaded. As a rule, such a model is purchased for small workshops when work is carried out with a small amount of raw materials.
- Channel ones differ in that they allow metal melting to be carried out continuously. The design allows loading of a new portion of metal and draining of already molten metal during operation. The only disadvantage is that difficulties arise at the time of draining, since the drain channel must be filled.
The most popular type of induction furnace is the crucible type. This is due to their high performance and ease of operation. In addition, if necessary, such a design can be made independently.
Homemade versions are quite common. To create them you need:
- Generator.
- Crucible.
- Inductor.
An experienced electrician, if necessary, can make an inductor with his own hands. This structural element is represented by a winding of copper wire. The crucible can be purchased at the store, but a lamp circuit, a self-assembled battery of transistors, or a welding inverter are used as a generator.
Using a welding inverter
An induction furnace for melting metal with your own hands can be created by using a welding inverter as a generator. This option has become the most widespread, since the efforts made relate only to the manufacture of the inductor:
- Thin-walled copper tube is used as the main material. The recommended diameter is 8-10 cm.
- The tube is bent according to the desired pattern, which depends on the characteristics of the housing used.
- There should be a distance of no more than 8 mm between the turns.
- The inductor is placed in a textolite or graphite housing.
After creating the inductor and placing it in the housing, all that remains is to install the purchased crucible in its place.
Application of transistors
Such a circuit is quite complex to implement and involves the use of resistors, several diodes, transistors of various capacities, a film capacitor, copper wire with two different diameters and inductor rings. Assembly recommendations are as follows:
- When using the scheme in question, the structure will become very hot. This is why efficient cooling should be used.
- The purchased capacitors are assembled into one circuit to form a battery.
- Throttle rings are used as the basis for the inductor. A previously purchased copper tube with a diameter of about 1 mm is wound onto them. The number of turns determines how powerful the homemade stove will be. The recommended range is from 7 to 15 turns.
- A second copper tube is wound around a cylindrical object, the diameter of which should be about 2 mm. It is worth considering that the ends of this tube should be left large, since they will be used to connect to the power source.
- A 12 V battery can be used as a power source.
The created circuit is placed in a textolite or graphite case, which are dielectrics. The circuit involving the use of transistors is quite complex to implement. Therefore, you should undertake the manufacture of such a stove only if you have certain work skills.
Lamp stove
Lately, lamp-based stoves have been created less and less frequently, as they require careful handling. The circuit used is simpler compared to the case of using transistors
Assembly can be carried out in several stages:
- 4 beam lamps are used as a current generator, which are connected in parallel.
- The copper wire used must be connected in a spiral. The coils created must have a diameter of 8 to 16 cm, with a distance of at least 5 millimeters between them. It is worth considering that you will need a fairly large amount of wire, since the crucible must fit inside the turns.
- The created spiral is placed in a housing made of a material that does not conduct electric current.
- The efficiency of the circuit can be increased by additionally connecting a trimmer capacitor.
The llamas used must be protected from mechanical impact.
Induction casting furnaces
Each induction casting furnace can be equipped with two types of converters, as a rule, a thyristor converter is cheaper and is equipped with high-power furnaces, and a transistor converter is more economical in terms of power consumption:
Thyristor frequency converters are used to power induction foundry furnaces; they operate on the usual two-stage principle:
- — the rectifier converts the alternating current of the network into direct current;
- - the inverter converts this direct current again into alternating current, but at the required frequency.
Thyristor converters can operate with high current and voltage and at the same time withstand continuous load. Their efficiency is higher than that of converters based on IGBT transistors.
Transistor frequency converters. Transistor frequency converters are used to power induction furnaces, in which up to 200 kg of non-ferrous metals and up to 100 kg of ferrous metals can be melted in IPP-type furnaces. Such furnaces are most often used in laboratory conditions for experimental melting, when there is a need to quickly change the alloy.
Among the undoubted advantages of transistor converters are compactness, ease of operation and quiet operation.
Induction furnace for metal melting
An induction furnace is a heating device where the induction method is used to melt steel, copper and other metals (the metal is heated by currents excited by a non-alternating field of the inductor). Some consider induction stoves to be a type of resistance heating device, but the difference lies in the method of transferring energy to the heated metal. First, electrical energy becomes electromagnetic, then electrical again, and only at the very end it turns into thermal energy. Induction stoves are considered the most advanced of all gas and electric stoves (muffle, steel-smelting, mini stoves), thanks to their heating method. With induction, heat is generated within the metal itself, and the use of thermal energy is most efficient.
Induction furnaces are divided into two types:
- with core (duct);
- without core (crucible).
The latter are considered more modern and useful (heating devices with a core, due to their design, are limited in power). The transition from channel to crucible furnaces began in the early 1900s. At the moment they are widely used in industry.
However, at the moment, steel smelting is often carried out using a heating structure such as an arc steel-smelting furnace; it uses the thermal effect for melting, and it is more convenient and practical. You can make many simple heating structures with your own hands. For example, a homemade melting furnace is very popular. If you decide to build a mini heating structure with your own hands, you need to know its structure. There are many types of induction furnaces, but we will describe only a few of them. If necessary, you can use the necessary diagrams, drawings and video recordings.
Induction Furnace Components
For the simplest designs, there are only two main parts: an inductor and a generator. However, you can add something of your own, improve the unit, using the necessary circuits. Inductor The heating coil is the most important component. Absolutely the entire operation of the heating structure depends on it. For homemade stoves with low power, it is permissible to use an inductor made of a bare copper tube with a diameter of 10 mm. The internal diameter of the inductor must be at least 80 mm. and no more than 150 mm., number of turns – 8-10. It is necessary to take into account that the turns should not touch, so the distance between them should be 5-7 mm. Also, no part of the inductor should touch its shield.
Generator The second most important component of the furnace is the alternating current generator. When choosing a generator circuit, you should in every possible way avoid drawings that give a hard current spectrum
As something that does NOT need to be chosen, we present a popular circuit based on a thyristor switch.
Crucible furnace structure
Inside there is a melting crucible with a drain sock (“collar”). On the outer sides of the structure, an inductor is located in a vertical position. Next comes a layer of thermal insulation, and at the top is a lid. On one of the external sides there may be a supply of current and cooling water. At the bottom there is a device for signaling crucible wear.
How to make an induction oven
First you need to assemble a generator for the inductor. Here you will need the K174XA11 circuit. The transformer should be wound on a mini-ring with a diameter of 2 centimeters. The entire winding is made with a wire with a diameter of 0.4 centimeters and should be 30 turns. The primary winding is characterized by the presence of exactly 22 turns of wire with a diameter of 1 millimeter, and the secondary winding should contain only 2-3 turns of the same wire, but already folded four times. The inductor must be made of 3 mm. wires with a diameter of 11 mm. There should be exactly 6 turns. To adjust the resonance, it is best to install a regular or mini LED.
Installation Features
Each specific induction furnace is equipped, among other things, with detailed instructions containing detailed technical data and operating rules.
The most important of them include:
- — strict monitoring of temperature conditions during operation, since even a minor violation will destroy the lining;
- — the temperature of the water supplied to the inductor must be high enough for the given room, otherwise a large amount of condensation may form on the tubes of the water vapor inductor, and there will be a danger of electrical breakdown between the turns of the inductor;
- — overheating of water at the outlet of the inductor is also unacceptable, in order to avoid the formation of scale on the walls of the pipes, which disrupts heat exchange;
- — placement of equipment in enclosed spaces located no higher than 1 km above sea level, with a positive temperature, normal air humidity and without aggressive impurities.
The operation of induction furnaces must be monitored by qualified specialists, preventive inspections must be carried out and deficiencies must be corrected in a timely manner.