What is a press fitting
Press fitting is a device for permanently sealed connection of metal-plastic pipes with each other or with metal elements of the system. Such devices make it possible to easily and quickly install a system using metal-plastic pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene, and connect it to a metering unit, threaded pipelines, heating devices or mixers.
Elements for copper pipe connections
Copper fittings, which are used to connect copper pipes, are presented on the modern market in a wide variety of sizes and designs. The most well-known types of such connecting elements are:
- threaded fittings for copper pipes;
- self-locking connecting elements;
- compression or crimp fittings;
- so-called press fittings;
- capillary type connecting fittings.
Of all the listed types of connecting elements, in our time, press fittings for copper pipes are the least used, which is explained by the following reasons: their installation requires the use of complex and expensive equipment: special presses. The design of press fittings was originally developed in order to connect plastic and metal-plastic pipes with their help, so their use for the installation of copper products is not always advisable.
Press fitting pliers
In order for a pipeline in the construction of which copper parts are used to serve as long as possible and be highly reliable, it is advisable to use elements made of homogeneous materials during its installation. Connecting copper pipes with fittings that are made from other raw materials should only be done in rare exceptions.
If it is not possible to avoid the use of fittings made of dissimilar materials when installing pipelines, then this process must be carried out by adhering to the following simple rules:
- copper pipes in communications, for the creation of which elements from different materials are used, are always installed after products made of ferrous metals: in the direction of fluid movement;
- copper parts of pipelines cannot be connected to fittings made of galvanized steel; failure to comply with this requirement will lead to electrochemical reactions occurring in such systems, which will significantly accelerate the corrosion process of steel parts;
- copper elements of pipe structures can be connected to parts made of acid-resistant steel, but if there is such a possibility, it is better to replace such parts with fittings made of polyvinyl chloride.
Device and purpose
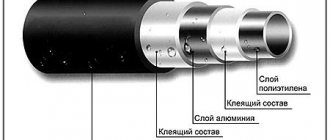
Traditionally, the part consists of a housing, an outer press sleeve and a seal. Housing - an internal liner with a thrust ring and threads for connection to a metal part of the system or other fitting. When crimping, the press sleeve compresses the metal-plastic blank, fixing it between the liner and the outer sleeve.
The second type of fittings is slide-on. In them, the inner liner is a “ruff” with teeth, and the upper sleeve slides onto the inserted tube, deforms it, squeezing it very tightly and hermetically.
All press connectors used in household engineering systems are made of stainless steel or brass - a material that is strong, but at the same time soft enough to be deformed when compressed. There are combined products - a brass body, a stainless steel ferrule (for example, from Tiemme).
Press fittings are designed for installation of metal-plastic engineering systems - heating, water supply, heated floors, gas and steam pipelines. When installing home systems from HDPE or RE-X pipes, there is practically no alternative. They are easy to install without the help of specialists, not too expensive, and very reliable.
How to install
To install a fitting connection at home, you need to have a pipe, a fitting, scissors or a hacksaw for metal, and a deburring knife.
In production they use a pipe flaring machine, but at home you can do without it. Place the nut on the pipe, insert the spacer ring, insert the fitting and tighten the union nut with a wrench.
Each type has its own installation methods, which we will consider below.
Compression
All types of compression fittings are assembled the same way. The tightness is ensured by a crimp ring, which creates pressure on the metal-plastic pipe. To ensure a strong connection, tighten the union nut until it stops.
Monitor the presence of a Teflon insulating gasket and two rubber rings in the housing.
Crimping
This type of sealing works on the principle of uniform compression of a pipe with a metal ring from the outside to the inside. To create a strong connection, you must adhere to certain rules:
- cut pipes at right angles;
- clean burrs from the inside and outside;
- use a calibrator;
Before assembly:
- Put the nut on.
- Remove burrs with sandpaper or a knife.
- Flare the hole with a calibrator.
- Put on the clamping split ring.
- Insert the fitting body into the pipe.
- Tighten the nut first with your hands and then with a wrench.
A strong connection is ready.
Collet
The collet clamp works due to a split collet sleeve, which has petals. When screwed onto the body, the nut presses the split petals and thereby ensures tightness. The principle of operation of the collet is identical to the lead clamp in a mechanical pencil. When the metal sleeve moves onto the collet, the pipe is clamped. The connection principle is identical to crimp connections and is carried out in the same order.
Threaded
Threaded fittings are used to connect metal pipelines. Their only advantage is their low cost. To connect pipes, it is necessary to cut a thread at its ends with a clamp, weld or solder a bend. In order to connect two pipes, a coupling with a lock nut is screwed onto their ends. Sealing of the connection is ensured by winding flax tow onto the threads and coating with sealing paste. If it is not possible to cut threads directly on site, then you have to weld threaded bends at the ends of the pipes. Due to the complexity of the installation process, these connections are being replaced by others: compression, collet, crimp.
Features of installation of other types
To connect copper pipes, the capillary soldering method is used.
The difference is that: bends, tees, angles, bends-adapters, corners and couplings are immediately prepared for soldering and do not require flaring. During production, they already have the hole flared. You just need to insert a piece of copper tube and solder it. To do this, use a gas torch and solder. Despite the fact that soldering such connections requires special skills, copper piping is popular for heating installations.
With proper soldering, copper pipe systems can last up to 80-100 years.
Advantages and disadvantages
The biggest advantage of a press connector is reliability. The connection is permanent, sealed and does not require any maintenance (for example, tightening the nuts, like compression fittings). A metal-plastic pipeline connected using a press fitting can even be poured into a screed or covered with false plasterboard walls.
Other advantages of press fittings:
- Simple, reliable design ensures durability.
- Strength of the connecting node.
- Easy and quick installation using simple equipment - a hand press.
- A large assortment of different designs allows you to select press fittings for the installation of engineering metal-plastic systems of any configuration.
- Durability. The service life is approximately equal to the service life of plastic and is tens of years.
- Corrosion resistance of the base material – brass, stainless steel.
- Safety for people and animals.
- Environmental friendliness. After use, metal parts are simply melted down into new products.
- The connectors practically do not narrow the cross-section of metal-plastic pipelines and have low hydraulic resistance.
Flaws:
- Brass fittings are designed for operating pressure up to 1.6 MPa (16 atmospheres). But in practice, such pressure is usually not found even in high-rise buildings. In private homes, pressure rarely exceeds 2-3 atmospheres.
- Over time, brass products become covered with patina and darken. Therefore, they are often coated with chrome or nickel for decorative purposes.
- In a certain sense, the disadvantage of the fitting is that it is “disposable” - the permanent connection cannot be disassembled, the connector cannot be pressed in again, and if pressed in incorrectly, the press fitting will have to be cut off and thrown away.
Advantages of copper pipes and their disadvantages
At present, it is impossible to say for sure why copper pipes for water supply are used extremely rarely in the CIS. One of the likely reasons is the high cost of such products, although if we take into account the costs of repairs in one particular apartment, the difference is not so great.
Another factor is the huge variety of alternative options on the building materials market, which can be a worthy replacement for steel pipes, which are prone to oxidation and difficult to install. However, most likely the reason is still in long-rooted habits passed on from generation to generation.
Let's look at the main advantages of copper pipes:
- they are practically not subject to oxidation and corrosion;
- the threshold of permissible temperatures for pipe operation ranges from -110 ℃ to 250 ℃;
- the properties of the material make it possible to avoid the formation of any deposits on the internal walls of the pipes;
- The service life of copper pipes for water supply is quite long, and the costs of their installation and maintenance are extremely low.
However, it is impossible not to note some of the shortcomings of copper pipes for water supply:
- With some metals, in particular aluminum and steel, copper forms a galvanic couple. Therefore, if even a very weak current flows at the point of contact between the thread and the copper pipe, serious complications can occur.
- Copper is an excellent conductor, which in some situations can cause electric shock. This can happen even through no fault of yours - for example, if, as a result of a breakdown of your neighbors’ washing machine, a breakdown occurs between the phase and the ground to the water supply.
- Installing copper plumbing pipes and fittings is quite labor intensive. Although the principle of installing compression fittings will not differ from, say, working with metal-plastic pipes, however, much more effort will have to be applied (read: “How to install copper pipes correctly - expert advice”). If the joining of pipes is carried out using the soldering method, then consumables (solder, flux), a special tool (blowtorch), and also skills will be required.
Classification and types
Press fittings are divided into two types based on functionality: traditional crimp fittings and push-on push-on fittings. Types differ in design and scope.
The design of press connectors is:
- Couplings, tees, angles (bends) with press connections on 2 or 3 sides.
- Adapter elements with threads for twisting with metal pipeline elements. They have a connection for crimping plastic on one side, and a fitting with a thread or a “ruff” on the other side.
- Transition elements with couplings with internal threads.
- Transition elements with union nuts for screwing onto the threads of metal pipeline elements. They have a press connection for plastic on one side and an American nut on the other.
Crimping
Compression fittings have been around for a long time and are found everywhere. In them, the end of a metal-plastic pipe is tightly clamped between the sleeve and the inner liner, the connection is sealed using seals made of fluoroplastic-4 (Teflon) or EPDM rubber.
Press-on sliding
Such connectors appeared relatively recently. The upper crimp sleeve is forced onto the end of the workpiece, the liner has teeth - a “ruff”, the pipe material is very deformed, sealing the connection hermetically. Such elements are used not only for metal-plastic, but also for connecting thicker-walled water pipes made of low-density polyethylene.
Marking
The marking must include the name of the manufacturer and the parameters of the metal-plastic pipes being connected - outer diameter and wall thickness: for example, 16×2. The data is applied to both the body and the crimp sleeve.
Crimping rules
Despite the ease of installation of compression fittings, there are several subtleties that must be taken into account during operation. Press jaws have a set of inserts of different sizes. The crimping insert is selected according to the caliber (diameter) of the pipe. Provided that the positioner insert is selected correctly, after crimping, two identical annular strips are obtained. An insert that does not match the pipe caliber will not allow proper compression, as a result of which the joint will be leaky.
The coupling can only be crimped once. Repeated compression is prohibited. If during work the fitting was installed incorrectly, it will have to be completely dismantled and a new one installed.
The design of crimp connectors may vary slightly between different manufacturers. The main difference is the installation of the ferrule. In some models it is initially fixed to the fitting. Installation of such components is carried out in a slightly different sequence, since there is no need to install the sleeve on the end of the pipe. Immediately after calibration, the pipe is placed on the fitting and the compression process is carried out.
Differences from compression analogues
The main difference between press connectors for metal-plastic pipes and compression analogues is their inseparability. But this feature is the other side of the coin, because press connections are much more reliable than compression connections and do not require maintenance (inspection, tightening). When assembling a press connection, the metal-plastic pipe and connector are irreversibly deformed; it is impossible to disassemble the connection without destroying it. Accordingly, repeated compression is impossible.
But compression connections can, if necessary, be disassembled, repaired, and reassembled. This applies to both metal compression connectors and polyethylene push-in couplings and elbows.
To crimp press fittings you will need quite expensive press pliers; to tighten compression connections you will need only two wrenches.
Compressive tension
This is the easiest way to connect. To make such a connection, you do not need a special tool for press fittings; pipe cutting scissors, a calibrator (rolling tool) and a simple adjustable wrench are sufficient, and, moreover, no special work experience is required. You just:
- put on the tension nut and clamping ring;
- after this, insert the fitting onto the rolled edge of the product;
- pull the ring onto it;
- tighten the tension nut with a wrench.
The main problem with such a connection appears in the future. Due to periodic thermal expansion, the threaded connection has a certain movement and the tension weakens.
As a result, a leak may occur, which will lead to corrosion of the metal and its complete destruction. The long-term reliability of such a connection cannot be guaranteed.
Tips for choosing
The reliability of engineering metal-plastic systems in your home or apartment depends on the choice of quality products. Any significant leakage of cold, and even more so hot water will lead to wetting of the covering and structures of the floor, ceiling and, possibly, the ceiling and walls (including those of neighbors). Therefore, you need to choose reliable connectors, in a large store, with a receipt and certificate. There are many manufacturers of fittings, including in every region of Russia. It’s still worth choosing the best (see below).
Before purchasing, you should carefully inspect the product, including the threads. There should be no jams, chips, nicks, or changes in geometric shape. In the markets, you can occasionally find counterfeits made of aluminum or its alloys - they can be distinguished by their weight; aluminum is several times lighter than brass and stainless steel. Markings should be engraved and not painted.
When choosing a material, you should not focus on stainless steel - brass is perfect for household systems. But uncoated brass will tarnish, so it is better to choose brass with chromium-nickel coating.
Best manufacturers and approximate price
The most famous manufacturers of press fittings for metal-plastic pipes: REHAU, PRANDELLI, VALTEC, OVENTROP, Tiemme, COMAP (France), ALTSTREAM (Russia), Henco (Belgium), UPONOR (Finland). Prices for VALTEC products start at 60 rubles (diameter 16 mm, wall thickness 2 mm), often fittings cost 150-200 rubles.
How to choose
The choice of fittings depends on several conditions, these are:
- terms of Use;
- maximum pressure requirements;
- operational service life;
- financial component.
For drinking water supply and for supplying industrial water, different connections from different materials are needed. Fittings should not be used for installing heated floors in drinking water supply systems. In order to navigate the choice, you need to consult with professionals. No theory will help here.
Difference in usage
In addition to different installation methods, there is also a difference in maintenance. Collapsible joints, especially those made of metal, require constant tightening. This applies to hot water supply systems and heated floors. Due to thermal expansion, connections can weaken. The difference between pipelines with compression and press fittings is that the former require maintenance, while the latter do not. Permanent connections are established once and for all.
Dimensions
All fittings, regardless of manufacturer, must meet the same standard. For threaded connections, fittings with a maximum diameter of 50 mm are used. For diameters greater than 50 mm, flange connections are used. In exceptional cases, couplings, locknuts and bends with a diameter of up to 100 mm can be manufactured to individual order.
Which ones are better
There is no clear definition of which is better. It all depends on the operating conditions. But if we compare metal threaded ones with modern compression, crimp and collet ones, they are an order of magnitude better. And the new product, fittings made of cross-linked polypropylene, gives everyone else a head start. True, the financial issue is a serious obstacle here. Fittings made of cross-linked polypropylene are more expensive than others and require expensive installation equipment for installation work.
When choosing fittings, you must be guided primarily by practical necessity and select the necessary ones depending on the situation.
Installation and replacement rules
Unfortunately, it is impossible to replace the press fitting after it has been crimped. You can only cut it, throw it away, lengthen the metal-plastic pipe using a press connector, and press in a new part. Therefore, during installation you must be careful and follow all the rules for crimping connecting elements.
It is very important to draw a communication diagram in advance, then accurately determine the length of the segments - after all, after pressing, it will not be possible to disassemble the metal-plastic connection.
In the walls, pipelines are carried out in sleeves made of plastic pipes of larger diameter. The metal-plastic pipeline must move freely in the sleeve - this will protect the system during thermal expansion. Therefore, before starting work, it is necessary to punch holes in the walls, insert sleeves, cutting them flush with the wall. After installation, the holes with the sleeve can be covered with decorative overlays.
The fasteners must be installed near the fittings - this will reduce the movement of the metal-plastic pipe during heating and cooling and increase the reliability of the connection. It is better to use factory fastenings - clips or clamps.
Installation technology
Any installation begins with the preparation of workpieces. The pipe is cut strictly perpendicular to the required size, and the burrs are carefully and carefully removed with a file. If the metal-plastic pipe has become too flattened and has become oval, it is necessary to calibrate it using a calibrator.
A special tool – scissors or a pipe cutter – will help you avoid additional manipulations. Then thoroughly wipe the ends of the workpieces with a rag to remove dirt, dust, and plastic filings. It is advisable to remove the chamfer.
Crimping the workpiece in a press fitting:
- Disassemble the fitting and place the press sleeve on the end of the pipe.
- Insert the housing (inner liner) into the pipe with the sleeve until it stops.
- Insert the assembled workpiece into the press jaws.
- Bring the press handles together.
- When bringing the handles together, you need to apply sufficient force; you need to bring them all the way - then the connection will be of high quality. Remove the press - distinct ring marks from the pliers clamps will appear.
Crimping using a sliding connector:
- The end of the pipe is prepared.
- A sleeve is put on the end of the metal-plastic blank; the chamfer of the sleeve should be on the side of the end of the pipe.
- The sleeve near the end of the pipe is flared with a special device.
- The pipe is put on the fitting body, and the sleeve is moved further from the edge of the pipe.
- The half-assembled assembly is inserted into a special device.
- Using the device, the sleeve is pushed onto the fitting.
Technology of work execution
To connect pipes using press fittings, first of all, it should be understood that such a joint can only be made once. If you make a mistake with the length of the pipe or the choice of fitting, the part will be damaged and will have to be thrown away. Therefore, before performing this procedure, you need to accurately measure the required pipe length. For cutting, you should use special scissors that do not remove the pipe, making it oval.
After this, the cut edge of the pipe must be calibrated. This operation slightly increases the internal diameter of the communication, and the press fitting will be much easier to put on it.
For tension technology, this operation is necessary in order to increase not only the internal but also the external diameter of the pipe for the subsequent installation of a press ring. Calibration is performed with a special calibrator, for which attachments are provided for different pipe diameters.
After the press fitting is inserted onto the pipe, it is grasped with press pliers in the case of crimping technology. The second option is to stretch the ring onto it using a hydraulic press.
General description of couplings for crimping
A press fitting connection is one of the most reliable methods of joining metal-plastic pipes. As a result of this installation, the pipeline turns out to be one-piece, but very reliable. If after assembly you need to change its circuit, you will have to redo a lot from scratch, but leaks are practically excluded.
The reliability of the press connection is ensured by crimping the pipe around the fitting fitting with a special stainless steel sleeve. If the pipe needs to be replaced, the pressed section will need to be cut out
Press fittings are a permanent type of connection, obtained in this case by compressing a metal sleeve around an o-ring. In this case, as a result of the crimping performed, the ring is irreversibly deformed. It cannot be removed and then reused. The geometry of the pipe itself also changes slightly.
For metal-plastic pipes, fittings for crimping are made from:
- brass;
- of stainless steel.
The first option is more preferable. It is more reliable and durable in conditions of high humidity.
Unscrupulous manufacturers often use aluminum and other soft metals to make the fittings in question. They can be easily identified by weight. Brass is obviously heavier in the hands than these fakes. It is strictly not recommended to use such products for crimping metal-plastic pipes. By definition, they are not able to tightly compress the fitting and pipe plastic.
Fittings for press connections and metal-plastic pipes for installation of intra-house pipeline systems should be taken from the same manufacturer, otherwise you can forget about the absolute reliability of the joint
Each manufacturer of metal-plastic pipes recommends purchasing its own set of press fittings. And for good reason. Pipe products and fittings from different manufacturers can vary in diameter by literally a millimeter. Quite a bit, but this is enough to reduce the reliability of the connection. It’s better not to save money here, risking a break and leakage.
There is no single standard for the outlines and exact dimensions of fittings. Each manufacturer independently selects these parameters for their products. Some sellers offer universal press fittings, but this is a banal advertising ploy. The use of such connecting parts is inevitable and will result in leaks in the near future after installation.
Preparing pipes for processing with press jaws
It is recommended to store the device in a dry place, pre-packing it in a case or a special box, usually sold with the instrument.
Regular, complete, high-quality care and proper storage will extend the “life” of the instrument for a long time and ensure its impeccable performance
Electric and hydraulic units are somewhat more difficult to maintain and require professional maintenance. How to keep them in order can be found in the data sheet included with the equipment.
In addition to press pliers, assembling a metal-plastic pipeline will definitely require a pipe cutter, the specifics of the selection and application of which are given here. We recommend that you read this very useful information.
How to remove a fitting from a pipe
If a leak occurs or new components are added to the system, it is necessary to remove the fitting from the pipe if it is a detachable fitting or completely cut out the assembly if it is a press fitting. In the case of a compression (detachable) fitting, follow these steps:
- Turn off the water to the point where the pipe is disconnected.
- Using an appropriately sized adjustable wrench, unscrew the nut one turn.
- Hold the pipe and unscrew the fitting slightly.
- And turning alternately, first the nut, then the fitting, completely unscrew the fitting.