Time does not stand still; instead of steel and cast iron, modern materials, especially plastic, are becoming increasingly popular. HDPE pipe is now most often used. The abbreviation HDPE stands for “low-density polyethylene”. Pipes made from this material are a durable and flexible plastic structure. The main advantages are lightness, durability, and the absence of the risk of corrosion and salt buildup.
Properties of HDPE
What is PND? This material is high-density polyethylene. It has an affordable price and is distributed everywhere. The international abbreviation looks like HDPE - stands for high density polyethylene (translated: high density polyethylene). The conditions for manufacturing the material are contained in its name - “low pressure”.
Polyethylene granules - raw materials for the production of HDPE pipes
The characteristics of PDN include its resistance to solvents at room temperature and chemical inertness. When placed in an alkaline or acidic solution, this polyethylene remains intact (with the exception of 50% nitric acid, chlorine and fluorine). The polymer density is 0.94-0.96 g/cm³. The color of the unpainted material is white, thin sheets are transparent.
Advantages:
- It can be used in the food industry for storing food and water. This material is absolutely harmless to people and animals.
- Low temperature resistance – can withstand -60°C and below.
- Plastic and durable.
- Chemically inert.
- Quite inexpensive to produce.
Disadvantages of polymer:
- Does not tolerate high temperatures well: at 70-80°C it loses strength.
- Not tolerant of ultraviolet radiation.
Application area
The gas pipe is marked with a yellow stripe.
Eighty years have passed since ethylene was first polymerized. This discovery has been widely used in various fields. Cheap and practical material with high density is used for industrial and domestic needs. It is made from:
- Containers and containers. These are containers for storing food products, plastic bottles, canisters, barrels, containers for transporting bulk materials. Large tanks for water storage and treatment facilities are also made from HDPE.
- Films for greenhouses, vapor and waterproofing, bubble; dense for packaging and thin for food products; tape and bags.
- Household and household items: buckets, boxes, pots, dishes, toys. Decorative details: accessories for furniture and tailoring. Interior elements - chairs, chests of drawers, tables, etc.
- Equipment for children's playgrounds.
- Boats, as well as cabinet products for small equipment, household appliances and equipment.
- Pipes and their connecting parts - for gas and water supply, drainage, sewerage, alkalis and acids, casing for drilling wells. They also produce pipes for aggressive environments in production. But low-density polyethylene is incompatible with solvents.
- Anti-corrosion coating for steel pipes. In particular, HDPE is used to make the outer lining of large-diameter oil pipelines (intended for transporting gas and oil products).
- Insulating material for wiring and equipment.
- Insulating material – foamed polyethylene foam (including foil).
- Adhesive (hot-melt adhesive).
Low pressure polyethylene pipe
Let's look at its pros and cons.
- Long service life. The only condition is the absence of ultraviolet radiation and extremely high pressure. The first introduced products have already been in use for fifty years.
- Durability . Pipes are capable of recovery after deformation and withstand hydraulic shocks.
- Plastic. The pipeline may have slight bends. When heated, the HDPE pipe can be bent up to 90 degrees. If water freezes inside, the pipe endures pressure, and after thawing it returns to its original shape.
- Easier to transport and install . The material is light in weight. The weight of the PDN pipe is 8 times less than its metal counterpart.
- Easy to assemble and install , mounted using connecting elements, butt or electrodiffusion welding, easy to cut or bend.
- Corrosion resistance . Plastic does not require constant processing and painting.
- Low level of surface adhesion - due to the smooth wall from the inside, magnesium and calcium salts are not deposited during use, which means the pipeline does not become clogged.
- Chemically inert material . The water in such pipes is not saturated with foreign tastes or odors, and their resistance to aggressive environments allows them to be used in production and in the petrochemical industry.
- Safety for consumers and environmental friendliness , because they can be recycled.
- It does not tolerate ultraviolet radiation well , so pipes made of low-density polyethylene are laid exclusively indoors or in the ground, but not in open areas.
- The need to maintain temperature conditions . The recommended limit for operating pipes without additives is from 0°C to +40°C. For a short period of time it can withstand heating up to +80°C. With intense overheating, long sections of the pipeline may “lead.”
- The need to withstand limited pressure , as a result of which the use of HDPE pipes is impossible in some areas of production. The permissible value is 2.0 MPa.
- Aesthetics : Color (bright blue or black stripes) is often inappropriate in indoor spaces.
The material from which it is made and its features
Continuing to answer the question of what a HDPE (low-density polyethylene) pipe is, it would be useful to familiarize yourself with the production methodology. They are made using special technology using the extrusion method. Its essence lies in the fact that the polymer melt is pressed through a nozzle with a special shape. The production technology consists of the following stages:
- The prepared raw material (polyethylene granules) is automatically fed into a special extrusion hopper. There it is heated to a melt state. Additives of chemical origin, appropriate to the type, are added to this mass to give the final product the appropriate performance properties.
- This hopper maintains the required pressure necessary to compact the molten mixture. As a result, ethylene molecules join together, creating a strong crystalline network.
- The alloy is then passed through an extrusion head equipped with cooling elements. As it cools, the hot mass takes on a tube-like shape.
- Next, the product is rolled on a special calibrating machine. Here it is formed into a product of the required diameter and length.
- The last stage is labeling. After which the finished product is sent to a workshop with a color cutting line. In order for the user to understand what a HDPE pipe of a particular batch is.
LDPE (high-pressure polyethylene) pipes are also produced using a similar technology. Both the raw materials and the methodology are similar, the only differences are in the pressure at the stage of melting the granules. Therefore, the performance characteristics and scope of use of these materials are different.
LDPE is a more elastic material, sold in coils of 100 meters. HDPE pipe what is it? This is a pipe with a high level of rigidity, does not bend, and is sold in lengths. This is where its features lie.
Marking
Pipes must be marked. In this case, the maximum permissible interval of inscriptions is 1 meter. Identification labels contain the following information:
- manufacturer's name;
- designation of manufacturing standard;
- international name of the product brand (for example, PE-63, PE-100, PE-80);
- dimensions: external diameter, as well as wall thickness (in mm);
- pressure recommended for work;
- date of manufacture;
- batch number.
HDPE pipe marking. Blue stripe - water pipe
Marking with colored stripes
In order to easily recognize the purpose of pipes, they are usually painted in certain colors, namely:
- products intended for gas supply are usually black with a yellow stripe, sometimes just yellow;
- for technical purposes – black (without stripes);
- for drinking water - blue or black with a blue stripe;
- for drainage - green;
- for sewerage - gray, white or black;
- intended for installation of external sewage systems are usually bright red in color;
- casings of electrical cables (corrugated products) are red.
Markings, sizes and diameters
HDPE pipes for water supply are available in a wide range of lengths and diameters (from 10 to 2000 mm):
- In straight sections, the length of products varies in the range of 3-24 m.
- In coils or coils, the length of pipes can exceed 500 m.
- With a diameter of 180 mm and above, HDPE pipes are produced only in sections.
Density of polyethylene
| HDPE | PVD | |
| Density | 910 – 925 kg/m³ | 941 – 965 kg/m³ |
Such a small difference in the density of materials is only insignificant at first glance. In fact, the higher the density coefficient, the stiffer and stronger the product, and its shell is more resistant to gas penetration.
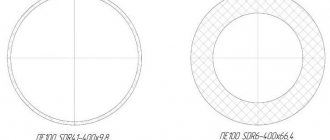
Diameter of HDPE pipes and what is SDR
The standards indicate the following standard sizes of HDPE pipes:
- Outer diameter – from 10 to 160 (for PE 32) and up to 2000 mm (for PE grades 63, 80 and 100).
- Wall thickness – from 5 to 53.3 mm.
- Weight per 1 linear meter – from 51 g to 700 kg (for PE grades 63, 80 and 100) and from 52 g to 8.13 kg (for PE 32).
SDR is an indicator of the ratio of the outer section of a HDPE pipe to the thickness of its wall. In fact, it is calculated by the formula:
On a note! The SDR index indicates the strength of the HDPE pipe: the lower the digital code, the thicker the pipe wall, and the stronger and greater the load it can withstand.
Pipe series and pressure rating
The pressure at which plastic pipes can operate without failure, and their actual purpose, depends on the brand of polymer and the SDR value.
Regulations
The production of HDPE water pipes is regulated by GOST standards 18599–2001.
Example of PE pipe marking
The terms of GOST require the mandatory inclusion of the following data in the labeling:
- Manufacturer's name or trademark designation.
- Polyethylene class.
- SDR index.
- Standard size (section, wall thickness).
- Nominal pressure.
- Temperature regime.
- Purpose.
- GOST, in accordance with which the products are manufactured.
Additionally, the date of manufacture, batch number, certification data and other information that the manufacturer deems necessary to convey to the consumer may be indicated.
In addition to alphanumeric designations, the manufacturer is required to apply a longitudinal color marking strip, which allows you to visually determine the purpose of the pipe:
- Products intended for organizing drinking water supply are indicated in blue.
- Yellow – for gas supply.
- A pipe without a marking strip is classified as technical.
On a note! To organize hot water supply, it is better to use HDPE pipes marked “PN”. This designation indicates a multi-layer product, in which one of the layers is made of fiberglass, foil or steel mesh and serves as reinforcement.
Types and varieties of low-density polyethylene pipes
By purpose:
- As a cold water supply . For this, blue pipes are used in basements (wiring) or underground. Mostly smooth structures are used. If the diameter is large, the elements are connected by welding, if small - fittings. However, these products are not used indoors.
- for installing drainage systems .
- When constructing pressure sewer systems, black pipes for technical purposes are used, which are installed using connecting elements or welding. If free-flow sewerage is assumed, socket-shaped products are used. Each subsequent element in such a design is inserted into the socket of the previous one. The sealant is a rubber seal. When the depth is sufficiently large, a two-layer corrugation with sockets is used.
- For electrical cables , Internet and communication lines, as well as sewer systems, corrugated or smooth red and black pipes are used.
- In order to protect the well from soil shedding, pipes made of low-density polyethylene are installed. At the same time, the depth of the aquifer can reach 50 m. A pump is placed in the well to draw water. There are restrictions for HDPE products: seismic hazard or threat of landslides.
- Industrial technological networks use corrugated or smooth black pipes for technical purposes.
When laying pipelines, the following grades of material are used: PE-100 with a maximum permissible pressure of 1.25 MPa, PE-80 with an indicator of 1.6 MPa, PE-63 - maximum pressure of 1.0 MPa.
Pipe Strength Ratio (SDR)
SDR is an abbreviation for Standard Dimension Ratio, translated as standard dimensional ratio. It is a method for assessing pipe strength as a function of pressure. It is defined as the ratio between the outer diameter and wall thickness (according to GOST 18599-2001). This indicator is a standard value.
Scope of application
The scope of application of HDPE pipes is determined by the brand of polyethylene (see table).
| Type of HDPE pipes | PE 100 | PE 80 | PE 63 | PE 32 |
| Pressure | Gravity | |||
| External and internal cold and hot water supply systems | + | + | — | — |
| External gas communications | + | — | — | — |
| Gravity sewers | + | + | + | + |
| Transportation of food and industrial liquids and gases | + | + | — | — |
| Pool equipment | + | + | — | — |
| Showers | + | + | + | + |
| Automation of irrigation systems | + | + | + | + |
| Protective casing (cable ducts) for fiber optic, electrical, television, telephone and other types of cables | + | + | + | + |
How to choose the right HDPE pipe
In order for the choice to meet your goals, you need to decide in which area the products will be used, and also consider operating parameters: depth in the ground, temperature conditions, aggressiveness of the environment.
For example, if you plan to install a water supply system, only HDPE pipes with a blue stripe are suitable. The fact is that they are made from virgin polyethylene and are completely harmless to both animals and humans. The use of black technical pipes not marked with colored stripes for these purposes is strictly prohibited, since they are made from recycled materials, which means that harmful substances can be released into the water.
When sewerage is carried out, socket elements are used, drainage - perforated structures. In this case, it is worth considering the load on the product. It depends on the depth or thickness of the concrete screed above them. If the load level is high (for example, when the layer of earth above the communication exceeds one and a half meters, there is a massive screed or rocky soil), it is advisable to use two-layer corrugated pipes.
Smooth structures are suitable for casing structures, electrical cables, information communications, and pipelines.
It is recommended to use pipes of a color that corresponds to the intended purpose in any work. Then, in case of repair, it will be easy to determine the necessary communication, and when buried in the ground, the bright color of the structure will be easy to detect.
Characteristics and use of HDPE pipes
Guided by manufacturing standards and building codes, HDPE pipes are used in four specific areas:
- in water supply systems with cold (up to 40°C) drinking water;
- in water pipelines with cold (up to 40°C) technical water;
- for moving liquids or gases that do not destroy polyethylene, the temperature of which also does not exceed the specified value;
- as insulation or conduit for electrical cables.
It should be noted that, despite the modest operating temperature of HDPE pipes, these products, when used properly, are very durable - their service life is up to 50 years.
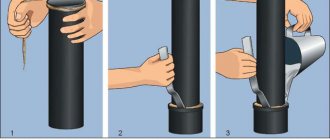
How to connect
Electric welded HDPE fittings have built-in heating elements for welding with pipes
The appropriate connection method is determined by the diameter of the products and the location.
- If the diameter does not exceed 315 mm, polyethylene compression fittings are used.
- Bell-shaped casing and drainage pipes are inserted into each other.
- If the wall is thicker than 5 mm, welding is possible.
- If it is necessary to install a large-diameter pipeline, the most suitable option is welding thermistor couplings. This connection method is the most expensive, but also the most reliable.
A short video lesson on connecting HDPE pipes
Technical characteristics depending on type and application
For an example of decoding technical characteristics, let's take one of the modifications.
| PE 100 pipe – explanation | |
| Density (kg/m3) | 950 |
| Maximum permissible temperature (+0C) | 40 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/mK | 0,41 |
| Working pressure (Atm) at (0C) | 20=10 40=4,5 |
| Linear expansion coefficient (mm/m) | 2 |
| Maximum strength temperature (-0C) | 50 |
| Hardness (mPa) | Hardness (mPa) |
| Elongation at break (%) | 250 |
| Fluidity (limit values in mPa) | 50 |
The diameter will depend on the scope of application and functional purpose.
| Purpose | Diameter (in mm) |
| Gas supply | 16-120 |
| Sewerage | 40-200 |
| Water wells | 125-200 |
Low-pressure polyethylene products - HDPE pipes - can also be deciphered using the GOST unified (PE80, 100, SDR13) marking. For example: drinking water GOST xxx:
- PE80 - the type of polyethylene used by the manufacturer;
- 40*1.2 – product diameter and wall thickness;
- SDR13 indicates the ratio of wall thickness in relation to the diameter of the product;
- labeling (drinking) indicates the scope of application of the product;
- GOST No. ХХХХ – designation of the technical passport according to which the product was manufactured;
- SDR – ratio of wall thickness and diameter – coefficients of ring strength.
The last parameter is very important for the choice of pipes in the creation of external sewerage and water supply. It indicates the pressure that the pipe can withstand during operation.
As you can see, you can decipher a HDPE pipe using different marking parameters in order to understand how suitable this type is for its intended destination. Despite the fact that products in this sector of goods are considered universal, it is still necessary to take into account the operating conditions and requirements for which they are designed.