Unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (UPVC) is a polymer based on vinyl chloride and does not contain plasticizers. It is denser than ethylene, due to which it has higher mechanical strength. This material is used for the manufacture of sewer pipes, for which strength and resistance to external influences are important.
You can often hear the name “PVC sewer pipes for external sewerage.” The omission of the letter “H” at the beginning, which indicates the absence of plasticizers, is incorrect: it is precisely because this type of polymer does not contain additives that it is so durable, non-flowing, and dense. Modified PVC is soft and is not used for sewer or water pipes.
Advantages and disadvantages of polyvinyl chloride pipes
PVC pipes for sewerage have the following advantages:
- low specific gravity, facilitating installation;
- wide operating temperature range;
- environmental Safety;
- resistance to corrosion and chemicals;
- immunity to fungus and mold;
- minimal thermal conductivity;
- noise absorption;
- durability;
- flexibility and elasticity;
- wear resistance;
- smooth walls that do not form plaque;
- presentable appearance.
The disadvantages of PVC sewer pipes include fragility and a high coefficient of thermal expansion.
Operational Features
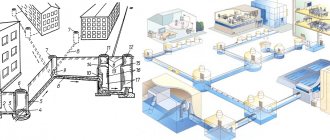
Today, sewer pipes for external sewerage made of uPVC are actively “penetrating” into all spheres of economic activity, replacing concrete, steel, and cast iron.
Advantages of uPVC pipes for external sewerage
- Resistance to corrosion, formation of oxides, films, overgrowing of the working clearance.
- No cathodic protection required.
- Resistance to aggressive environments, including acids, alkalis, abrasives.
- Stable throughput until the end of its service life.
- Less weight compared to cast iron and steel.
- Estimated service life 50 years (no longer estimable due to recent use).
- Reduced costs for loading, unloading and delivery.
- Easy installation without the use of heavy equipment.
- Lighter requirements for installation personnel.
- Availability for networks of any purpose and complexity.
- Adaptability when connecting to equipment due to a wide range of shaped products.
- Hygienic and environmentally friendly - in a stable state they do not emit harmful substances and do not form rotting products.
- Not subject to deformation at low temperatures.
Disadvantages of uPVC pipes
- Small operating temperature range (from -5 to -600C for most brands)
- Susceptibility to damage by rodents.
- Release of toxins when melted.
There are significantly fewer disadvantages, which makes this option attractive. With a little skill, an external PVC pipe can be installed independently on a small scale.
Purpose of PVC pipes for sewerage and their main characteristics
Plastic sewer pipes have a wide range of applications.
Products are used to create the following engineering structures:
- underground pipelines;
- transportation of technical liquids at enterprises;
- drainage channels around buildings;
- drainage of wastewater from consumers in apartments and offices;
- indoor and outdoor sewerage;
- ventilation ducts;
Pipes are made from vinyl chloride, plasticizers and dyes. The products can withstand external pressure up to 50 MPa and are capable of passing media under pressure up to 16 bar. To connect individual fragments, there are shaped parts at their ends; the dimensions of the shaped parts ensure the creation of a highway from parts having different outer diameters.
Indoor and outdoor
Depending on the installation location, plastic drainage systems are divided into internal and external.
Internal lines are assembled from gray products. They are laid in shafts, grooves, along walls or floors. The diameter varies between 32-160 mm. The standard diameter of the sewer riser is 100 mm. The purlins are not designed for heavy loads and require careful handling.
Products for external gaskets are painted orange. The pipes are more durable and have a diameter of 110-500 mm. They are used for draining industrial wastewater at enterprises and transporting liquid waste within a populated area.
Pressure and non-pressure
Non-pressure systems are installed in buildings where liquid flow is expected to flow by gravity. The internal diameter of the house sewer drain pipe varies between 32-110 mm. The wall thickness does not exceed 3 mm. An example of non-pressure communications are outlets from bathtubs, sinks, and toilets, when all communications are discharged into a common riser.
Pressure systems are designed for forced transportation of organic and chemical compounds. The wall thickness of the products is 3-30 mm depending on their diameter. The parts are connected using glue or welding.
Corrugated
Corrugated pipes are used to connect water consumers with horizontal sections. Corrugations are used to drain wastewater from toilets, sinks, washbasins, washing machines and dishwashers. The diameter of the products varies between 25-120 mm depending on the purpose and location of the pipeline.
Double-layer products are reinforced with steel wire and have a smooth inner surface. They can be laid directly in the ground, as they are designed for high mechanical impact.
Decoding and using PVC
Abbreviation
PVC pipes for sewerage are made from the limestone material of the same name, which, after undergoing heat treatment, has the peculiarity of retaining its shape. The abbreviation PVC means vinyl chloride polymer. The main constituents of PVC pipes are materials such as ethylene and stabilized chlorine.
And by using auxiliary additives you can achieve the best qualities. PVC pipelines are used in the construction of wastewater networks due to the ease of installation work and low price. And also, thanks to its good technical characteristics, this type of pipe can be used in pressure systems. Its features include good dielectric properties and resistance to aggressive chemical environments. It is not susceptible to corrosive formations, is not afraid of humidity and ultraviolet radiation. Thanks to these qualities, polyvinyl chloride pipes are widely used both in industry and in everyday life.
Exploitation
PVC pipes are used in such areas as:
- construction of a swimming pool, fountain, water park;
- chemical production;
- food industry;
- Agriculture;
- in the construction of a wastewater system.
- Polyvinyl chloride pipelines are used for these types of waste systems: internal networks;
- external; external pressure systems;
- with gravity drainage.
These pipes are light in weight, which undoubtedly facilitates easy installation and transportation. The smoothness of the inner surface does not allow the formation of blockages. They were used at temperatures from -15 to +60 C. They produce pipes of the following diameters: 110, 160, 200, 250, 315, 400 and 500 mm. To avoid cutting to fit a specific size.
They are practically eternal. Probably, the manufacturer gives a guarantee of fifty years of service for every plastic pipe product. Also, polyvinyl chloride is environmentally friendly and absolutely harmless. For the customer, this type of pipe is more interesting than any other plastic pipe due to its reliability and cost.
Currently, these materials are the most profitable option for wastewater systems, not taking into account the not very simple manufacturing process. For example, low-density polyethylene is simply poured into an extruder; raw materials for PVC pipes undergo a complex multi-composition process and have a limited shelf life.
Nowadays, it is widespread to use PVC plastic pipes in the construction of waste systems. They are gradually replacing classic cast iron ones. Plastic has many good properties, which makes it different from its metal counterparts.
Features of the diameter and size of sewer pipes
The production of PVC pipes is carried out in accordance with GOST 51613-2000.
Product parameters are determined by the following indicators:
- length;
- outside diameter;
- inner diameter;
- bell section;
- bore diameter;
- wall thickness.
Based on their strength class, structures are divided into the following categories:
- light – SN2 with wall thickness up to 2.3 mm;
- medium - SN4 with walls 2.5-12.3 mm;
- heavy - SN8 with walls 3.2-15.3 mm.
The wall thickness increases in direct proportion to the diameter of the products.
Diameter of PVC sewer pipes
This indicator determines the throughput of the highway. This takes into account the likelihood of large objects getting into the line that could cause a blockage.
Based on the size of the internal cross-section, structures are divided into the following categories:
- Small – 25-50 mm. Used to drain wastewater from household consumers.
- Medium – 60-160 mm. Such products are used to make a common sewer riser and a drain pipe from the drainage gutters on the roof.
- Large – 200-500 mm. They are used to drain wastewater from the house to the central collector and lay underground city communications.
PVC sewer pipe size chart
The table shows the ratio of the diameter and wall thickness of polymer pipes that are used in private and commercial construction:
| Inner diameter (mm) | Wall thickness (mm) | Section length (cm) | Throughput (l/s) |
| 25 | 1,2-1,8 | 200 | 0,8 |
| 32 | 1,5-2,0 | 200 | 1,2 |
| 50 | 1,8-2,4 | 200 | 2,0 |
| 62 | 2,0-2,5 | 200 | 3,2 |
| 90 | 2,2-6,6 | 200 | 3,6 |
| 110 | 2,7-8,6 | 200, 300 | 4,5 |
| 160 | 4,0-9,5 | 200-500 | 6,0 |
| 225 | 5,5-13,4 | 200-500 | 8,5 |
| 315 | 7,7-18,7 | 200-800 | 10,2 |
| 400 | 9,8-23,7 | 200-1200 | 13.6 |
| 500 | 12,3-23,9 | 200-1200 | 15,0 |
Comparison of plastic and cast iron sewer pipes
First, let's fully understand the differences between polymer materials and cast iron. Both options have pros and cons. Let us list them first for metal pipes.
The advantages include:
There are more disadvantages and they are significant:
The era of plastic has come a long time ago. This synthetic material is used in all areas of life. It has a set of unique properties and reduces the cost of assembly and production.
PVC pipes for sewerage with rubber joint seals
Polymer pipes have the following advantages:
Pollution is observed to a lesser extent Return to contents
How to choose the optimal pipe diameter?
The optimal diameter of the sewer system is selected by calculating the volume of wastewater that will pass through the system at the time of maximum load. This indicator is determined by the number of residents in the house. Peak loads occur in the morning and evening hours.
For internal wiring, 50 mm links are used. The toilet bowl is connected to the tee with 110 mm corrugation. Risers for low-rise buildings are assembled from 110 mm sections. For high-rise buildings this figure increases to 160-200 mm. When choosing the diameter of the pipes, you should not act on a grand scale. Bulky structures will require additional costs and a reduction in usable area.
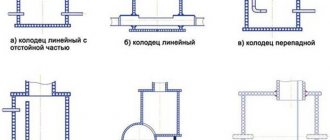
Types of components, fittings
The following types of components are used to assemble sewer systems:
- couplings;
- corners;
- contours;
- tees;
- plugs;
- crosses;
- angular and rotary compensators.
The internal dimensions of sewer fittings correspond to the external diameter of the products. The components are made of polyvinyl chloride. To make the connection, the straight end of the pipe is inserted into the socket of the fitting. Main pipelines are assembled using a circular welding machine.