The principle of electric arc welding is based on the use of the temperature of the electrical discharge that occurs between the welding electrode and the metal workpiece.
An arc discharge is formed due to electrical breakdown of the air gap. When this phenomenon occurs, gas molecules are ionized, its temperature and electrical conductivity increase, and it transitions to the plasma state.
The burning of a welding arc is accompanied by the release of a large amount of light and especially thermal energy, as a result of which the temperature rises sharply and local melting of the workpiece metal occurs. This is welding.
general description
An arc occurs between the electrode and the metal workpiece being worked with. The formation of this discharge occurs due to the fact that electrical breakdown of the air gap occurs. When such an effect occurs, gas molecules are ionized, not only its temperature increases, but also its electrical conductivity, and the gas itself turns into a plasma state. The welding process, or rather the burning of an arc, is accompanied by such effects as the release of large amounts of heat and light energy. It is precisely because of the sharp change in these two parameters towards their large increase that the process of metal melting occurs, since in a local place the temperature increases several times. The combination of all these actions is called welding.
Application Methods for Electrical Carbon Steels
Carbon steels are divided into groups depending on the percentage of carbon in the alloys:
- High carbon – 0.6-2.07%;
- Medium carbon – 0.25-0.6%;
- Low carbon – less than 0.25%.
Depending on the group, the arc welding procedure is carried out. But there are also general approaches to the process. Butt seams in this case are often welded when the parts are in a suspended state. The equipment is aimed at ensuring that the seam is firmly welded, but without burning through the metal. Electric arc welding allows work to be done on both sides; seams can be applied in several layers. If the parts are thick enough, then this type of work will be suitable. But the hanging of products and sheets leads to defective work. To eliminate it, use the electric arc method again:
- The metal at the defect site is removed;
- Edges and surfaces are cleaned;
- Defective areas are re-welded.
If the electroslag method is chosen, then staples are used. They secure the parts and are then welded from above at the entry point into the metal parts. Sometimes strips are welded to close the seam using this method. They secure the seam, eliminating the possibility of tearing the structure.
Arc Properties
In order for an arc to appear, it is necessary to briefly touch the workpiece with which you want to work with the electrode. Thus, a short circuit occurs, as a result of which a welding arc appears, its temperature rising quite quickly. After touching, it is necessary to break the contact and establish an air gap. This way you can select the required arc length for further work.
If the discharge is too short, it is possible that the electrode will stick to the material being processed. In this case, the melting of the metal will take place too quickly, and this will cause the formation of sagging, which is extremely undesirable. As for the characteristics of an arc that is too long, it is unstable in terms of combustion. In this case, the temperature of the welding arc in the welding zone will also not reach the required value. Quite often you can see a curved arc, as well as severe instability, when work is carried out with an industrial welding unit, especially if work is carried out on parts with large dimensions. This is often called magnetic blowing.
Magnetic blowing
The essence of this method is that the welding arc current is capable of creating a small magnetic field, which may well interact with the magnetic field that is created by the current flowing through the element being processed. In other words, the deflection of the arc occurs due to the fact that some magnetic forces appear. This process is called blowing because the deflection of the arc from the outside looks like it is due to strong wind. There are no real ways to get rid of this phenomenon. In order to minimize the influence of this effect, you can use a shortened arc, and the electrode itself must be located at a certain angle.
Arc structure
Currently, welding is a process that is discussed in sufficient detail. Thanks to this, it is known that there are three arc burning regions. Those areas that are adjacent to the anode and cathode are the anode and cathode sections, respectively. Naturally, the temperature of the welding arc during manual arc welding will also differ in these zones. There is a third section, which is located between the anode and cathode. This place is usually called the arc column. The temperature required to melt steel is approximately 1300-1500 degrees Celsius. The temperature of the welding arc column can reach 7000 degrees Celsius. Although it is fair to note here that it is not completely transferred to the metal, however, this value is enough to successfully melt the material.
There are several conditions that must be created to ensure a stable arc. A stable current with a strength of about 10 A is required. With this value, you can maintain a stable arc with a voltage from 15 to 40 V. It is worth noting that the current value of 10 A is the minimum, the maximum can reach 1000 A. The voltage distribution across areas is uneven and most of all it in the anode and cathode. Voltage drop also occurs in an arc discharge. After carrying out certain experiments, it was found that if welding is carried out with a consumable electrode, the greatest drop will be in the cathode zone. In this case, the temperature distribution in the welding arc also changes, and the greatest gradient occurs in the same area.
Knowing these features, it becomes clear why it is important to choose the correct polarity when welding. If you connect the electrode to the cathode, you can achieve the highest temperature of the welding arc.
Aluminum surfacing
Very often it is not necessary to weld parts, but to repair them. During operation, parts wear out, and additional metal beads need to be added to individual parts. Surfacing is required in various situations:
- Broken fastening parts;
- Appearance of attrition;
- Broken edges;
- Chips;
- Destruction of the edges of metal-cutting tools;
- Worn bearing bushings and internal surfaces.
Surfacing in welding terminology is the process of restoring lost shapes and original dimensions. Surfacing is convenient in that it can be placed on any surface, its thickness and volume can be changed, and worn-out and defective equipment can be repaired.
Temperature zone
Regardless of the type of electrode used for welding, melting or non-consumable, the maximum temperature will be at the column of the welding arc, from 5000 to 7000 degrees Celsius.
The area with the lowest temperature of the welding arc shifts to one of its zones, the anodic or cathodic. These areas experience 60 to 70% of the maximum temperature.
Where is metal heated welding used and what equipment is needed?
The base material is most often subjected to preheating at a distance from the welded joint. Let's look at an example. A is a specific area of a fillet weld.
To calculate the distance from it to the place where preheating should be carried out, two problems will need to be solved:
- When the metal thickness is equal to or less than 50 mm, the calculated value should not be more than 50 mm from the welded joint.
- When the material thickness is more than 50 mm, the distance from the seam for preheating is taken to be less than 75 mm. This is indicated in the certification instructions for workers performing quality control of welded joints - CSWIP 23.4.
Today, manufacturers offer several types of different equipment for determining the control, indication and measurement of metal preheating temperature. It is used in a number of commercial industries.
Let's consider the main measuring instruments and temperature sensors used for this purpose:
- Contact thermometer – used to measure temperatures not exceeding +350 °C. The device is based on a “thermistor” - a temperature meter. The resistance of the latter decreases when heated, therefore, it is inversely proportional to temperature. The difficulty with this device is the “periodic calibration” that must be carried out to obtain accurate measurement results.
- Thermal pencil and thermal paste, which contain a material that changes color and melts under the influence of different heating temperatures. Their advantages are low cost and ease of use. The disadvantage is that the measurement result is not very accurate.
- Thermocouple. The principle used in this device is the calculation of the thermoelectric potential difference between the material being welded and the heated weld metal in order to calculate the temperature. The device should be used during and after welding, as well as for heat treatment. It continuously monitors cooling and heating temperatures over a wide range. However, it requires regular calibration, which is considered a rather big drawback.
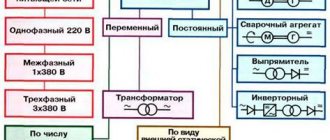
AC Welding
Everything described above concerned the procedure for welding with direct current. However, alternating current can also be used for these purposes. As for the negative aspects, there is a noticeable deterioration in stability, as well as frequent jumps in the combustion temperature of the welding arc. One of the advantages is that you can use simpler, and therefore cheaper equipment. In addition, in the presence of a variable component, such an effect as magnetic blast practically disappears. The last difference is that there is no need to select polarity, since with alternating current the change occurs automatically with a frequency of about 50 times per second.
It can be added that when using manual equipment, in addition to the high temperature of the welding arc with the manual arc method, infrared and ultraviolet waves will be emitted. In this case, they are emitted by a discharge. This requires maximum protection for the worker.
Installation modes
Arc welding is divided into modes:
with coated electrodes – MMA mode;
For argon arc welding using non-consumable electrodes - TIG.
Both modes involve operation on direct current - DC and alternating current - AC.
Both modes provide smooth regulation of the amount of incoming current, indication of arc current, and the ability to change modes. TIG performs long and short seams, purging of the gas passage, and a smooth reduction in current. Non-contact ignition on any type of current and regulation of arc capabilities are possible. It will melt and clean surfaces. The modes are easy to set and do not change without changing the settings by the welder.
Arc burning environment
Today, there are several different technologies that can be used during welding. They all differ in their properties, parameters and welding arc temperature. What methods are there?
- Open method. In this case, the discharge is burned in the atmosphere.
- Closed method. During combustion, a fairly high temperature is formed, causing a strong release of gases due to the combustion of flux. This flux is contained in the coating, which is used to process welding parts.
- Method using protective volatile substances. In this case, gas is supplied to the welding zone, which is usually presented in the form of argon, helium or carbon dioxide.
The presence of such a method is justified by the fact that it helps to avoid active oxidation of the material, which can occur during welding when the metal is exposed to oxygen. It is worth adding that, to some extent, the temperature distribution in the welding arc occurs in such a way that a maximum value is created in the central part, creating a small microclimate of its own. In this case, a small area with increased pressure is formed. Such an area can in some way impede the flow of air.
Using flux allows you to get rid of oxygen in the welding area even more effectively. If you use gases for protection, this defect can be eliminated almost completely.
Process technology
The principle of arc welding is based on the following actions: Current flows from the inverter to the electrode. It forms an arc by creating a closed circuit between the surface to be welded and the electrode. The arc melts the electrode, creating a weld pool. The whole process is precisely and strictly regulated. It is the same for all types of manual welding:
The electrode has a metal rod coated with silicate, flux, and glass. Any layer, when burned at high temperatures, forms a gas cloud and slag emissions. They protect against the penetration of air into the working environment, which destroys the metal. During the work, a connection is formed: the electrode - the part being welded. The rod melts, moving along the place of gluing or defect, forming a seam.
Classification by duration
There is a classification of welding arc discharges according to their duration. Some processes are carried out when the arc is in a mode such as pulsed. Such devices weld in short bursts. For a short period of time, while flashing occurs, the temperature of the welding arc manages to increase to such a value that is enough to produce local melting of the metal. Welding occurs very precisely and only in the place where the device touches the workpiece.
However, the vast majority of welding equipment uses a long-lasting welding arc. During this process, the electrode continuously moves along those edges that need to be connected.
There are areas called weld pools. In such areas, the arc temperature is significantly increased, and it follows the electrode. After the electrode passes the area, the weld pool leaves after it, which is why the area begins to cool quite quickly. When cooled, a process called crystallization occurs. As a result, a weld seam occurs.
What types of welding machines are there?
There are a lot of machines for metal welding on the market today. We have already written about this on the pages of our blog. Therefore, we will touch upon this topic briefly here. All of them are classified into 3 main types:
- semi-automatic;
- inverter;
- argon arc installations;
For example, the EWM Pico 180 puls model with pulse function is one of the best welding devices.
In addition to the machine itself, the welder should take care in advance of the availability of all consumables and accessories. This:
- electrodes;
- cored wire;
- connectors;
- clamps;
- ground terminals.
All these “little things” ensure comfort in work and high-quality performance of the production task.
Arc elasticity
During welding, it is necessary to monitor the length of the arc very closely also because such a parameter as elasticity depends on it. In order to obtain a high-quality and durable weld as a result, it is necessary that the arc burns stably and uninterruptedly. The elasticity of the welded arc is a characteristic that describes the uninterrupted combustion. Sufficient elasticity is visible if it is possible to maintain stability of the welding process while increasing the length of the arc itself. The elasticity of the welding arc is directly proportional to such characteristics as the current used for welding.
Volt-ampere characteristics
The graph shows the dependence of the power source voltage on the welding current, called the current-voltage characteristics of the welding process.
The red curves display the change in voltage between the electrode and the workpiece in the phases of excitation of the welding arc and its stable combustion. The starting points of the curves correspond to the open circuit voltage of the power source.
At the moment the welder initiates an arc discharge, the voltage drops sharply until the period when the arc parameters stabilize and the value of the welding current is established, depending on the diameter of the electrode used, the power of the power source and the set arc length.
With the onset of this period, the arc voltage and temperature stabilize, and the whole process becomes stable.