Recently, an updated procedure has been established for how the composition and properties of wastewater are monitored. The main document that lists the updates is Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 728 dated May 22, 2020. In addition, this Decree introduced some changes to certain regulations. Without a doubt, this is a fairly significant change in environmental legislation; there are many questions.
The question remains relevant of how the control of wastewater sent to the centralized wastewater system (CSS) will now be carried out, because the previous Rules have lost force. We have studied the innovations and in this material we will try to pay attention to the main aspects of this issue.
- Who controls the composition and properties of wastewater?
- What has changed in drainage in 2021?
- What does monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater include in 2020?
- Frequency of water disposal control
- Fines for water users
Who controls the composition and properties of wastewater?
On May 22, 2021, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 22, 2020 No. 728 was adopted, which amended the rules for cold water supply and wastewater disposal and approved new rules for monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 30.3 of the Federal Law of December 7, 2011 No. 416-FZ “On Water Supply and Wastewater Disposal”, the organization that carries out wastewater disposal is responsible for monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater. Or another organization authorized by it.
The subject of control is the composition and properties of wastewater, which are physical and legal. persons who have entered into a water supply and sanitation agreement are sent to the central sewerage system (CSV).
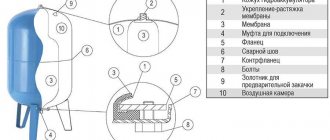
The principle of operation of water drainage and sewerage in a country house
The system consists of mandatory elements with the help of which the waste liquid is transported.
Stock receivers. The openings of sinks, drainage hatches, toilet bowls, and drains serve to receive and further direct liquid into the sewer pipes. Devices and fittings for them consist of materials that can withstand the aggressive environment of wastewater. These are cast iron, ceramics, steel, and some types of plastic. The devices discharge the used liquid to the gutters.
Sewage pipes, gutters. Wastewater from receivers is directed through pipes or gutters into storage wells and treatment structures.
Asbestos cement is suitable for internal drainage elements and gutters, if the system is not threatened by mechanical damage.
Pipes made of metal, ceramics, and non-galvanized sockets are also suitable for laying sewers. Elements of the system can pass on the surface of the earth and underground.
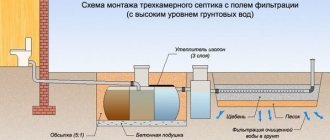
System of storage wells and treatment facilities. Internal sewage effluents end up in special storage tanks such as:
- 1.sealed wells
- 2.drainage wells
- 3.settling tanks
- 4.septic tanks
- 5.biological (natural) treatment station.
Different storage systems have varying degrees of cleaning ability. Wells with a filter bottom purify liquid up to sixty percent; wastewater is further purified using bacteria in the soil.
Cleaning septic tanks do a better job; the water gets into the ground, which is safe for the environment.
The operation of the station is provided after cleaning with industrial water for irrigation of the site, and sludge as fertilizer.
Containers can be plastic, concrete, metal . When choosing a plastic container, you will have to specially equip a place for it, create a pit with reinforced walls or a metal casing to prevent deformation of the structure due to the soil.
Concrete storage wells are used when constructing a drainage system or storm sewer system. Concrete is inferior in durability compared to plastic. Metal storage tanks are coated with paint to prevent corrosion due to contact with wet soil and runoff fluid. The disadvantage of metal structures is their weight; it will not be possible to install such a container alone.
What has changed in drainage in 2021?
It is known that until June 3, 2021, the Rules for monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 21, 2013 No. 525, were considered valid.
Now, the previously existing rules have been replaced by new rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 22, 2020 No. 728.
The main difference between the new rules and the already outdated ones: previously, subscribers were divided into two categories:
- Subscribers for whose objects the VAT of pollutants (PS), or other substances and microorganisms is established in the CSV;
- Subscribers for whose facilities standards for permissible discharges into the central water supply system are not established.
Now the composition and properties of wastewater discharged by all subscribers in the sewer system are subject to control; subscribers are not divided into categories “with VAT” and “without VAT”. Previously, control was carried out in accordance with a special program for monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater. It was developed in accordance with Rules No. 525. This program included a list of subscribers for whose facilities standards for permissible discharges were established (by subscriber category).
Maximum permissible discharges into water bodies
The new Rules No. 728 no longer contain the development and approval of a program for monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater. Thus, VAT is not established for subscribers who have facilities that discharge into the central heating system. There is no need to develop and approve a program for monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater.
Mandatory wastewater compliance criteria are now:
- Actual indicators of the composition and properties of wastewater, which are included in the Declaration on the composition and properties of wastewater
and/or
- Standards for the composition of wastewater, requirements for the composition and properties of wastewater discharged to the central wastewater treatment plant, established by the Rules for cold water supply and wastewater disposal, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 29, 2013 No. 644.
Thus, for CSV subscribers, the requirements for parallel sampling have been transformed, and requirements for “visual inspection” have been established. The old Rule No. 525 has been permanently repealed. In addition, the Rules for charging fees for the discharge of wastewater and pollutants into the sewerage systems of populated areas have been abolished. Significant changes have also affected the Rules for cold water supply and sanitation.
What is the difference
Let's look at the difference between sewerage and wastewater disposal. First of all, you need to understand what tasks they perform. The first complex is used for the collection, disposal and purification of wastewater, while the second only ensures the removal of liquids from residential or industrial areas.
It is necessary to take into account that there is no precise definition of one or the other system in the regulatory documents. The reason for this was the wide variety of types of networks, noticeable differences in the configuration and composition of the equipment. Modern installations are capable of operating autonomously or creating large public complexes. They can combine household, stormwater and industrial lines into a single assembly. In such conditions, it is difficult to determine the boundary between the concepts of “sewage” and “sewage”, what is the difference between them. It's difficult to even compare these terms because their meaning depends on the context. When it comes to technology, there is not much difference. But, if we consider the difference in terms of design and equipment used, it is necessary to understand exactly where each section is.
However, as already mentioned, there is no fundamental need for this. It is much more important to understand, for example, how sewerage differs from water supply. One system removes wastewater, and the other, on the contrary, supplies clean water to the premises, i.e. they perform opposite functions.
If we compare these elements, it is important to understand their unity. The first is a general network, including initial wastewater reception areas and purified water discharge points. Wastewater is part of this network. It does not treat wastewater, only removing liquids from places of water consumption. If we consider the wastewater treatment system as a separate independent complex, then the differences between the concepts of “drainage” and “sewerage” become minimal. Therefore, one of the signs of sewerage as a system can be considered the presence of treatment facilities.
Some types of storm drains can discharge water into bodies of water without treatment. This is allowed in case of peak loads during heavy rainfalls. Liquids are considered conditionally pure, so they can be immediately sent to a reservoir. In such cases, the system can be classified as a drainage line, since no cleaning is performed.
What does monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater include in 2021?
After Regulation No. 728 came into force, wastewater control includes the following steps:
- Conducting wastewater sampling;
- Further analysis of collected wastewater samples;
- Visual control (more precisely, this means checking objects for compliance with the requirement to prohibit discharge into a centralized drainage system).
Please note that visual control is a new stage. It is carried out in accordance with Rules No. 644 and Rules No. 728 on substances, waste, wastewater, for which verification of compliance with the requirements for banning said discharge is possible without sampling wastewater and further analyzing it. This procedure is carried out if prohibited discharges into the central heating system can be visually detected. These substances are in the list of Appendix No. 4 to Rules No. 644.
The actual indicators of wastewater are determined using special sampling equipment, which is installed by the organization carrying out wastewater disposal.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with what the wastewater sampling report form is.
Visual inspection, wastewater sampling and analysis of collected wastewater samples
We propose to dwell in a little more detail on what visual control is, as well as such control stages as wastewater sampling and analysis of already collected samples.
Who is responsible for each stage of wastewater control?
- Visual control is carried out by the wastewater disposal organization;
- According to special requirements, wastewater sampling is carried out by an accredited laboratory or wastewater disposal organization;
- Also, an accredited laboratory analyzes already collected samples.
Requirements for subscribers:
- Provide the opportunity to conduct visual inspection and sampling of wastewater;
- Provide free access to water for monitoring;
- Give the wastewater organization free access to the sewerage system;
- Provide places for sampling wastewater and install special signs that will identify control sewer wells (they should not interfere with the installation of equipment);
- The subscriber or his representative must be present during visual inspection.
The form of the act of detecting the fact of discharge of substances that are prohibited for discharge into the water supply center.
on the use of residential premises and the equipment located in an apartment building, at the address: Saratov, st. Razina S.T., house 54.
I. General requirements.
Owners bear the burden of maintaining the premises by paying fees for the maintenance and repair of residential premises, which includes fees for services and work on managing an apartment building, maintenance and routine repairs of common property in an apartment building. The owner of the premises also bears the costs of major repairs of common property.
When living in residential premises and using non-residential premises, Consumers are obliged to:
a) comply with the rules for using residential premises;
b) use the residential premises for their intended purpose and within the limits established by the Housing Code of the Russian Federation;
c) use the residential premises taking into account the rights and legitimate interests of citizens and neighbors living in the residential premises;
d) ensure the safety of the residential premises, prevent the performance of work in the residential premises or the commission of other actions leading to its damage;
e) maintain the proper condition of the residential premises, as well as common areas in an apartment building (apartment), improvement facilities, maintain cleanliness and order in the residential premises, entrances, elevator cabins, stairwells, and other common areas, ensure the safety of sanitary conditions technical and other equipment;
f) immediately take possible measures to eliminate detected defects in the residential premises or sanitary and other equipment located in it, and, if necessary, report them to the HOA;
g) carry out routine repairs of residential premises.
i) allow employees of the management organization and persons authorized by it (including emergency services workers), representatives of state control and supervision bodies, representatives of state control and supervision bodies to inspect the technical and sanitary condition of the residential premises, sanitary and other equipment located in the premises at a pre-agreed time. it, as well as to perform necessary repair work - at any time;
j) not carry out reconstruction and (or) redevelopment of residential premises in violation of the established procedure;
k) in the event of fires, accidents on in-house engineering systems, as well as other violations that occur during the use of utility resources, immediately report them to the HOA or the emergency service;
l) ensure the safety of seals on metering devices;
m) at a time previously agreed upon with the contractor (no more than once every 6 months), provide access to take meter readings.
II. Consumers are prohibited from:
a) use household machines (devices, equipment) with a rated power exceeding the maximum permissible loads determined in the technical characteristics of in-house engineering systems specified in the technical passport of the residential premises;
b) drain the coolant from the heating system without the permission of the HOA;
c) unauthorizedly join in-house engineering systems or join them bypassing metering devices, make changes to in-house engineering systems without making changes in the established manner to the technical documentation for an apartment building or residential building or to the technical passport of the residential premises;
d) unauthorized increase the heating surfaces of heating devices installed in a residential premises beyond the parameters specified in the technical passport of the residential premises;
e) unauthorizedly break the seals on metering devices, dismantle metering devices and carry out actions aimed at distorting their readings or damaging them;
III. Composition of common property in an apartment building
The common property includes:
1) premises in the house that are not parts of apartments and are intended to serve more than one room in the house, including inter-apartment landings, stairs, elevators, elevator and other shafts, corridors, technical floors, basements in which there are utilities;
2) other premises in the house that do not belong to individual owners and are intended to meet the social and everyday needs of the owners of the premises in the house;
3) roofs enclosing load-bearing and non-load-bearing structures of the house, mechanical, electrical, sanitary and other equipment located in the house outside or inside the premises and serving more than one room;
4) the land plot on which the house is located, with elements of landscaping and improvement, other objects intended for the maintenance, operation and improvement of the house and located on the specified land plot.
IV . Engineering systems
In-house engineering systems for cold and hot water supply and gas supply.
The common property includes in-house engineering systems for cold and hot water supply and gas supply, consisting of risers, branches from the risers to the first shut-off device located on the branches from the risers, the specified shut-off devices, common house meters for cold and hot water, the first shut-off and control valves on branches of intra-apartment wiring from risers, as well as mechanical, electrical, sanitary and other equipment located on these networks.
In-house engineering drainage system.
The common property includes an in-house engineering drainage system, consisting of sewer outlets, fittings (including bends, transitions, pipes, revisions, crosses, tees), risers, plugs, exhaust pipes, drainage funnels, clearings, branches from risers to first butt connections, as well as other equipment located in this system.
In-house heating system.
The common property includes an intra-house heating system, consisting of risers, heating elements, control and shut-off valves, common house heat energy meters, as well as other equipment located on these networks.
In-house power supply system.
The common property includes an in-house power supply system, consisting of incoming cabinets, input distribution devices, protection, monitoring and control equipment, general house electrical energy metering devices, floor panels and cabinets, lighting installations in common areas, electrical installations of smoke removal systems, automatic fire alarms of internal fire water supply systems, freight and passenger elevators, automatically locking devices for the doors of apartment building entrances, networks (cables) from the external border, apartment electricity metering devices, as well as other electrical equipment located on these networks.
External boundary of networks.
The external boundary of electricity, heat, water supply and sewerage networks, information and telecommunication networks (including wired radio broadcasting networks, cable television, fiber optic networks, telephone lines and other similar networks) included in the common property is the external boundary of the wall apartment building, and the boundary of operational responsibility in the presence of a common building metering device for the corresponding utility resource is the point of connection of the common building metering device with the corresponding utility network included in the apartment building.
The outer boundary of the gas supply networks that are part of the common property is the point of connection of the first shut-off device with the external gas distribution network.
V. Reconstruction and redevelopment of residential premises
Reconstruction of a residential premises is the installation, replacement or transfer of utility networks, sanitary, electrical or other equipment that requires changes to the technical passport of the residential premises.
Redevelopment of a residential premises is a change in its configuration, requiring changes to the technical passport of the residential premises.
Reconstruction and (or) redevelopment of residential premises are carried out in compliance with legal requirements
A person who unauthorizedly rearranges and (or) replans a residential premises bears the responsibility provided for by law.
VI. Features of using indoor equipment and in-house engineering systems.
Use of an in-house heating system.
Heating appliances and pipelines in apartments must be securely fastened.
When preparing premises for winter, Consumers are required to install sealing gaskets in the vestibules of window and door openings, and cover window frames if double-glazed windows are not installed.
It is not allowed to increase the surface or number of heating devices without special permission from the HOA board
It is prohibited to switch to heating residential premises in apartment buildings using individual apartment sources of thermal energy (domestic gas, electricity)
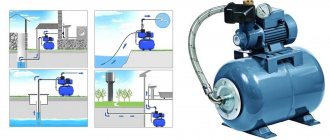
Use of water supply and sewerage.
Consumers are required to comply with the following rules:
a) keep toilets, sinks and washbasins clean;
b) prevent damage to sanitary fixtures and fittings installed in the apartment;
c) do not pour flammable liquids and acids into toilets, sinks and washbasins;
d) do not throw sand, construction waste, rags, bones, glass, metal and wooden objects into toilets;
e) prevent non-productive consumption of tap water, constant flow during water use, and leaks through water fittings;
f) do not use sanitary fixtures if there is a blockage in the sewer network;
g) immediately inform the operating personnel about all malfunctions of the water supply and sewerage system;
h) protect sanitary fixtures and openly laid pipelines from impacts and mechanical loads;
i) protect plastic pipes (polyethylene sewer risers and cold water connections) from high temperatures, mechanical stress, shock, scratching the pipes, paint polyethylene pipes and tie ropes to them;
j) to clean the outer surface of the plastic pipe, use a soft, damp cloth; it is strictly prohibited to use metal brushes;
k) when polyethylene sewer pipes are clogged, it is prohibited to use steel wire; plastic pipelines should be cleaned with a piece of polyethylene pipe with a diameter of up to 25 mm or a rigid rubber hose.
Using the ventilation system.
If condensation is detected on water supply and sewerage pipes in sanitary facilities and kitchens, frequent ventilation of the premises should be carried out with the ventilation openings fully open. If the above measures are insufficient, it is recommended to insulate and waterproof the pipelines.
Consumers are prohibited from:
Seal exhaust ventilation grilles or cover them with household items, and also use them as fastening lines for drying clothes.
Carry out unauthorized repairs and alterations of ventilation ducts.
Use of balconies and loggias.
If signs of damage to the load-bearing structures of balconies are detected (destruction of the edges of the balcony slab or cracks between the balcony slab and the wall), loggias, canopies and bay windows, the consumer is obliged to report this to the board of the partnership.
The consumer has the right to install flower boxes on balconies only in accordance with the design instructions.
Changing the design of balconies and installing new brackets for attaching flower boxes is allowed only according to the project and agreement with local authorities.
It is not allowed to place bulky and heavy things on balconies and loggias, to litter or pollute them.
The use of balconies and loggia is prohibited if they are in poor condition.
Use of gas-using equipment.
The consumer is obliged:
a) pay for the consumed gas on time and in full;
b) immediately notify the gas supplier about damage to the seal(s) installed by the gas supplier at the point where the gas meter is connected to the gas pipeline, damage to the seal(s) of the gas meter installed by the manufacturer or the organization that carried out the verification, as well as about a malfunction of the device gas metering;
c) ensure that the gas meter is presented within the established time frame for verification;
d) inform the gas supplier of information about the readings of the gas meter within the period established in the contract, unless another way for the gas supplier to obtain such information is established by the contract;
e) install and operate gas-using equipment that meets the technical requirements established for it, immediately notify the gas supplier of changes in the composition of gas-using equipment;
f) ensure the safety of gas meters and seals, use gas-using equipment in accordance with the established requirements for its operation;
g) immediately report to the emergency dispatch service about accidents, leaks and other emergency situations that arise when using gas;
h) ensure access for representatives of the gas supplier to gas metering devices and gas-using equipment for inspection;
i) ensure the proper technical condition of in-house gas equipment, timely conclude an agreement on the maintenance of in-house gas equipment and emergency dispatch support.
Electric stoves.
Electric stoves must be connected to the electrical network using a special plug connection with a grounding contact. Maintenance of electric stoves must be organized by the owner of the premises once a year.
During maintenance the following is carried out:
measuring the potential between the body of the electric stove and the grounded plumbing equipment in the kitchen;
measuring the insulation resistance of the electric stove and the power cable in a heated state (the cable is tested together with the plug);
checking the operation of the burner and oven power switches;
inspection of busbars and wires, tightening of fasteners.
VII. Fire safety requirements.
Entrances to staircases and technical areas. floors, as well as approaches to firefighting equipment and inventory, should not be cluttered.
Placing household items, equipment, inventory and other items on staircase landings is not permitted.
In apartments of residential buildings, it is prohibited to set up various types of production and storage premises in which explosive, explosive and fire-hazardous substances and materials are used and stored, as well as to change the functional purpose of these apartments and rooms, including when renting them out.
In apartments and living rooms, storage (use) of no more than 10 liters of flammable liquids and gases in closed containers is allowed. Flammable liquids and gases in quantities of more than 3 liters must be stored in containers made of non-flammable and unbreakable materials.
Not allowed:
storage of flammable gas cylinders in apartments and living rooms, as well as in kitchens, on escape routes, in basements, basements and attics, on balconies and loggias.
operation of gas appliances during gas leaks;
connecting parts of gas fittings using a spark-producing tool;
checking the tightness of connections using open flame sources (including matches, lighters, candles);
Practical tips on how to prevent fires in residential premises:
Maintain electrical switches, sockets and plugs in good technical condition. Operation of electrical wiring with damaged or dilapidated insulation is prohibited.
Do not leave switched on electric heating and gas appliances unattended.
Do not install electric heating devices near flammable objects.
Do not independently connect additional household electrical appliances that exceed the permissible rated power of energy consumption.
Attention!
Operating electrical appliances in excess of the permissible power can lead to overload and fire.
When operating electric irons, electric stoves, electric kettles, use fireproof stands.
Do not use homemade fuses (“bugs”) to protect the electrical network.
Don't smoke in bed - it's dangerous, it can cause sunburn and carbon monoxide poisoning.
Do not leave children unattended, do not entrust them with supervision of gas stoves, electrical appliances and heating devices that are turned on. Do not leave young children alone in the apartment; hide matches in places inaccessible to them.
Remember
that drying clothes over a gas stove is dangerous; it can catch fire. If you smell gas in the apartment or in the entrance, be sure to call “04”; before the emergency gas service arrives, do not use fire, do not turn on or off electrical appliances, as sparking and, as a result, a gas explosion are possible. Be sure to ventilate the room. Do not attempt to repair a gas stove yourself.
Do not use open flames when checking for gas leaks - this will inevitably cause an explosion. It is best to use a soap solution for this purpose.
If you discover a fire, you should immediately call “01”. Indicate the exact address of the fire location and what is burning. Warn your neighbors and begin evacuating people. If the fire is small, take measures to extinguish the fire.
It is advisable to have a fire extinguisher in the apartment.
Before leaving, make sure that the gas or electric stove and other electrical appliances are turned off. Check if cigarette butts are extinguished if there are smokers. Close windows and vents so that the wind does not scatter cigarette butts or be carried from higher floors.
REMEMBER!
Burning electrical wiring and electrical appliances can be extinguished with water only after first turning off the power using the switch in the electrical panel. If the TV catches fire, immediately unplug the cord from the socket and only then extinguish the fire with water or cover the TV with a thick cloth. A burning flammable or combustible liquid can be extinguished by covering it with a blanket of thick fabric, sand, or soil from a flower pot.
VIII. Resource saving.
Heat saving.
Energy saving of thermal energy inside a residential premises can be achieved through the following measures:
installation of air dampers on windows with regulation of the flow area;
replacing conventional glass on windows with low-emissivity glass;
installation of heat-reflecting films on windows;
sealing and sealing window blocks or installing plastic energy-saving double-glazed windows;
glazing of balconies and loggias;
installation of thermostatic and shut-off valves on radiators;
sealing interpanel and expansion joints;
installation of modern pre-insulated pipelines, fittings and heating devices;
insulation of external walls.
Saving water.
Saving cold and hot water can be achieved by performing the following measures:
installation of metering devices;
timely repair of taps, mixers, shower heads and toilets. Two to three drops of water per second
from a loosely closed tap leads to losses of
30 liters of water per day
.
Replacing a worn gasket
in a dripping faucet can reduce water loss by
15 liters per day;
replacing conventional faucets with contactless ones (an infrared sensor is installed in the faucet. The consumer sets the water temperature he needs. When he raises his hands, the sensor is triggered and the water is mixed automatically to the set temperature. Water savings range from 30% to 50% . );
installation of faucets equipped with a water saving system, which saves water up to 30 - 40% .
These faucets have 2 water flows: economical and full. With economical, 60% of the total water is consumed;
installation of lever mixers; they are more economical than with two taps;
the use of taps with aerators, in which water is mixed with air, also helps to save water;
installation of special attachments on the faucet that allow you to turn the water supply on and off with one click;
using a front-loading washing machine;
using a dishwasher;
replacing toilets with more modern, economical models (2-mode).
Saving electrical energy.
Saving electrical energy can be achieved by performing the following measures:
Lighting control from several places is carried out using pulse relays. This makes it possible to turn the light on and off from a distance;
installation of dimmer switches instead of conventional switches. This device allows you to set the desired intensity of light radiation;
use of static energy-saving devices (energy-saving device). Energy savings of 15–45% are achieved by improving and normalizing the structure of the electrical flow, dynamic absorption or release of reactive power, reducing harmful harmonics and harmful electromagnetic waves, reducing resistance losses, eliminating power surges in the network;
timely disconnection of unused electrical household devices from the network;
the use of dimmable halogen lamps saves up to 30% energy;
the use of fluorescent lamps provides at least fourfold energy savings. A modern energy-saving lamp lasts 10 thousand hours, while an incandescent lamp lasts an average of 1.5 thousand hours, that is, 6-7 times less. But at the same time its cost is approximately twice as much. The 11 W compact fluorescent lamp replaces the 60 W incandescent lamp. The costs are recouped in less than a year, and it lasts 3-4 years. In addition, do not neglect natural light. Light curtains, light wallpaper and ceiling, clean windows, a moderate amount of colors on the window sills will increase the illumination of the apartment and reduce the use of lamps;
use energy-saving lamps; they last 10 times longer than conventional incandescent light bulbs, and energy savings reach 80%;
When cooking, do not use pots whose diameter does not match the size of the burners on the stove. This leads to a loss of up to 20%. Dishes with a curved bottom can lead to excessive energy consumption of up to 40-60%. Cover the pan with a lid. This will save up to 30% energy;
Do not place the refrigerator near a heat source, as the freezer will use more energy to cool. The refrigerator should be placed in the coolest place in the kitchen, preferably near the outer wall;
Use A+ class refrigerators/freezers. This refrigerator consumes 2 times less energy than old refrigerators produced 10 years ago. In addition, any refrigerator will use less energy if you regularly defrost it and wipe dust from the back wall;
Buy stoves with induction burners; they work faster and save energy. Unlike traditional cast-iron and glass-ceramic ones, only the pans heat up, and not the burners themselves. Consequently, virtually no heat is wasted. After boiling food, it is better to switch to low-temperature cooking mode;
Use irons with economy mode. The secret to saving energy is the automatic energy saving feature, which you can use when you press the handle of the iron. When the device is turned on, but is not moving (raised or just standing on the surface of the ironing board), steam generation automatically stops, which leads to less energy consumption;
Save energy when ironing. Leave the laundry a little under-dried; to iron over-dried laundry, you need a hotter iron, which means more energy consumption;
Remove scale from the electric kettle in a timely manner, because scale has low thermal conductivity. Therefore, the water in such a kettle heats up slowly. Pour the amount of water needed for a cup of tea in the morning, for example a quarter of a teapot.
Washing machines.
Washing machines use the most energy when heating water. Therefore, some manufacturers have developed models of washing machines that can be connected directly to hot water. Which helps save up to 72% of energy compared to devices designed to supply only cold water (washing at 40 degrees). In addition, the automatic load sensor ensures that only the right amount of water is supplied to achieve the best washing results - thus reducing energy consumption.
If this is not possible, then you can reduce consumption by using special programs using various powders and additives that allow you to wash even very dirty things at a temperature of about 40-60 degrees. Reducing water heating from 90 to 40 -60 degrees gives up to 25% savings.
Vacuum cleaner.
When using a vacuum cleaner one-third full, the dust collection bag deteriorates suction by 40%, and accordingly, energy consumption increases by the same amount. Clean your vacuum cleaner's dust container more often.
Any household equipment left in standby mode (not unplugged) will consume electrical energy. A TV with a medium-sized screen (with a diagonal of 20-21 inches) consumes 297 Wh per day in standby mode, and almost 9 kWh per month, a music center - about 8 kWh per month, a VCR - almost 4 kWh per month
A cell phone charger left plugged in will become hot, even if there is no phone there. This happens because the device still consumes electricity. 95% of energy is wasted when the charger is always plugged in.
Switching off unused devices from the network will reduce electricity consumption by an average of 300 kW/h per year.
Board of Homeowners Association "Almaz-09"
Frequency of water disposal control
Control can be planned or unscheduled. Let's look at its differences.
Scheduled control is carried out no more than once per calendar month and less than once per calendar year. An exception is for subscribers whose facilities discharge a volume of less than 30 cubic meters per day in general (if wastewater is discharged into the sewer system). The frequency of planned control in this case cannot be more than once a calendar month.
As for unscheduled control, it is mandatory if:
- An accident has occurred, or the central heating system or its elements have failed;
- During state environmental supervision, violations were identified and orders were received to eliminate them;
- The water body was contaminated by the water supply system at the point where wastewater was discharged into it.
Linear drainage
Linear drainage is one of the types of storm drainage. The installation of linear drainage does not require serious surface preparation; it is enough to make flat slopes on both sides to the drainage line. As a result, the likelihood of soil subsidence is reduced, the length of storm drainage channels is reduced, and the catchment area is increased. Linear drainage is a system of buried trays (drainage channels, gutters) and sand traps - containers in which sand and small debris carried out by the flow of water are retained, serving as a link between surface drainage and underground storm drainage. From above, drainage trays and sand traps are covered with protective and decorative drainage gratings.
Rice. B. Point drainage
Fines for water users
View fines for water users
The size of fines for water users depends on the nature of the violation. Water pollution can even threaten the water user with criminal liability. Fines will not affect you only if you comply with environmental legislation and have all the permits required by the enterprise. EcoPromCenter specialists will help you with any issue of water use!
At the time of writing, changes are still being made. For subscribers with wastewater disposal of less than 30 cubic meters per day, the fee is 20,000 rubles/month. In addition, it is planned to introduce a new service regarding payment for environmental damage to wastewater networks. It should be taken into account that it is necessary to wait for the final results of the changes to fully understand how water users will have to report.
Installation stages
Different types of waste removal systems are installed as follows:
- Roofing. The trays are attached along the entire perimeter of the roof with a slope towards the drain pipe.
- Linear storm drain. Prepare trenches, the bottom of which is compacted. Then pour a layer of sand and compact it. A concrete mixture 5-7 cm thick is poured over the sand cushion. After it dries, trays are laid. They are also filled with solution on the sides. Protective grilles are placed on top.
- Drainage drainage. Channels are prepared for drains below the groundwater level. Sand is poured into the bottom of the trenches, followed by a layer of fine crushed stone. Perforated pipes in geotextile are laid on it. The top is again covered with crushed stone and the channels are buried.
- The household drainage system is installed sequentially. First the inner part, then the outer part. The minimum diameter of pipes for drainage in an apartment is 50 mm. From the toilet - 110 mm. The central riser has a cross-section of 110-150 mm. The outer pipes are taken with a cross-section of 160-220 mm. All drainage elements are connected to each other using fittings, adapters, and tees.
Any of the systems must have a bias towards the common house riser or private septic tank. The calculation is made depending on the cross-section of the pipes. The larger it is, the smaller the slope can be.