Choosing a local treatment plant that is productive and works stably for many years is a responsible task, which is complicated by the variety of septic tanks available for purchase. The eternal question of the abundance of offers on the market: which septic tank for a summer residence is better?
But the question of choice is not the only thing that worries future users of local treatment plants. Many people are interested in the features of the internal structure and the essence of the operation of a sewage treatment plant - how it works, and how a high degree of purification is achieved, such as, for example, in Eurolos septic tanks.
What is a cesspool and how is it constructed?
A cesspool (sewage) is the simplest device for collecting sewage, consisting of a tank with a sealed or absorbent structure. The bottom of the pit is filled with a cement-sand mixture, and the walls are erected from concrete rings, brickwork, or made monolithic.
Finished products made of metal and plastic, which are called cesspool septic tanks, can also be used. Plastic containers are most widespread due to their good tightness and resistance to aggressive environments. The volume of such tanks for a country house or cottage usually varies from 1 to 5 m³, but can reach 60 m³.
Plastic containers for cesspools are made single-chamber. There is an inspection hole at the top. The most widely used materials are polypropylene and polyethylene.
Expert opinion
Ilya Kozhevnikov
Design engineer. 10 years of experience
Ask a Question
If the groundwater in the area is close to the surface, formwork may be required when digging a pit, which increases the cost of installation by at least 20 tr.
Is it possible to make a cesspool without a bottom?
A cesspool without a bottom can only be used in cases where groundwater is deep. Such a pit cannot be installed closer than 15 meters from the house.
The base of the pit is covered with filter materials (sand, gravel, crushed stone), and the walls can be made of different materials (concrete rings, brick, etc.).
Methods of wastewater treatment
Autonomous treatment facilities can be passive, energy-independent, or active, operating under the influence of biological, chemical or physical processes.
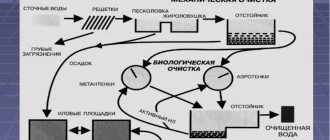
There are several ways to clean sewage:
- Mechanical - based on filtration and sedimentation of wastewater. For its application, various filters, gratings, sieves, traps and settling tanks are used. Using mechanical cleaning, you can get rid of sand, soil or debris. The disadvantage of this method is the impossibility of removing organic impurities and chemical compounds.
- Biological —works under the influence of aerobic microorganisms that can feed on organic waste. The principle of biological treatment is used in aeration tanks, gabion structures or bioponds.
- Chemical - cleaning is carried out under the influence of reagents that react with various pollutants. The resulting chemical compounds settle as insoluble precipitates.
- Physico-chemical - consists of removing finely dispersed inorganic and organic substances using various methods: electrolysis, flotation, electrocoagulation, etc.
Obtaining 100% pure water can be achieved through a comprehensive combination of various methods and subsequent disinfection by chlorination, ozonation or ultrasound.
When choosing a cleaning method, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- seasonality of operation of buildings and structures;
- number of permanent residents;
- geological features of the land plot;
- depth of groundwater.
Paying attention to the cost of constructing treatment facilities, it is necessary to take into account the costs of further operation.
You might be interested in
Rain inlet HL 600N with swivel joint DN100 made of PP, top part made of plastic
RUB 11,840
Order
Rainwater inlet HL 600NG with swivel joint DN100 made of PP, top part made of cast iron
In stock RUB 20,861.
Buy in cart
ACO Self rain inlet made of polymer concrete with a cast iron grate with a galvanized steel edging...
In stock RUR 9,358
Buy in cart
Attachment for ACO Self rainwater drain to increase height without grille
In stock RUR 3,135
Buy in cart
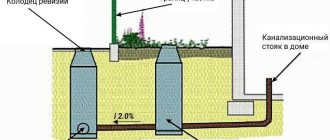
Septic tanks and their varieties
A septic tank is a sewerage element that serves for partial filtration (clarification) of wastewater. Based on their operating principle, they are divided into:
- flow type;
- local wastewater treatment plants (WTP);
- aeration units (AU).
The main differences between septic tanks are the filtration method. This can be settling, or processing by microorganisms (bioseptics).
Bacteria are loaded artificially into pumping treatment stations, and in aeration plants they are bred thanks to specially created conditions.
Flow septic tanks have the simplest design. They consist of several cameras (usually 2 or 3), and according to the production method they can be either factory-made or home-made.
Principle of operation
Sewage flows through pipes or trays into the tank, accumulating until it is completely filled.
Solid components settle to the bottom of the tank, and clarified water, through overflow or through collectors, sequentially enters the following structures. Subsequent purification can occur under the influence of active microorganisms, chemical reagents or various physical processes in special units.
Purified water can be used for technical purposes or for irrigation. Sludge processed by microorganisms is used to feed plants.
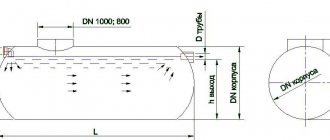
Rice. 2. VOC diagram.
Flow-through septic tanks and what is Shambo sewerage
They consist of several chambers connected to each other by overflow pipes. When solid waste accumulates in the primary tank, it is also necessary to pump it out with a sludge sucker, but this is done much less frequently. One of the representatives of flow-through septic tanks is the Shambo cesspool.
Wastewater enters the first chamber, where heavy fractions settle at the bottom, and light fractions float to the surface and form a film. In the middle part, clarified waste is collected, which, when replenished, flows into the next chamber. After passing through 2-3 sections, the wastewater is purified up to 60%, but at the same time retains an unpleasant odor and requires additional soil treatment. Therefore, from the last container, liquid waste is transported through pipes to the filtration fields. There they undergo soil purification with a layer of crushed stone and sand, and end up in the ground.
It is possible that the last container of the Shambo septic tank is made without a bottom and serves as a filter well. In this case, the lower surface of the septic tank pit is filled with gravel, and rings are installed on top.
The advantage of flow devices is energy independence. They can be used in houses with non-permanent residence and in summer cottages. However, over time (on average from 2 to 5 years), the soil and drainage layers become silted and stop allowing drainage to pass through, which is why it is necessary to change the layer by adding another ring. Therefore, this method of arranging a shambo pit is considered undesirable.
Number of users
Calculation of the station's volume according to SNiP 2.04.01-85 (Appendix 3) assumes 2 hundred liters per day for each person. Example: for a family of 5 people, a septic tank for a 3-day stay in it requires a volume of 3 m3. An additional performance requirement is the volume of the so-called salvo discharge. It shows the maximum possible volume of wastewater that the tank can process over a certain period. It is assumed that wastewater will be discharged from several sources (showers, bathtubs, toilets, bathroom sinks and kitchen sinks). If the volume of salvo discharge is exceeded, the quality of water purification will deteriorate.
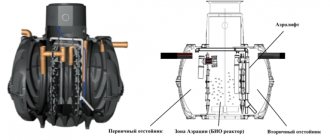
What are VOC AND AU
Local treatment facilities (LTP) are a deep biological treatment station that uses bacteria. Microflora can be created naturally or started artificially. They are characterized by compactness and a high degree of purification: up to 95-98%.
VOCs and aeration units are the most effective devices for autonomous sewerage. The high degree of purification allows the discharged water to be used for washing cars and watering lawns. Their common drawback is energy dependence.
Local treatment plants can be used periodically. Long breaks in operation do not affect their filtering ability, and even after six months of inactivity, VOC can effectively clean wastewater.
ACs are more demanding in terms of operating conditions. Just 8 hours of lack of electricity can lead to the death of biobacteria, after which the installation will return to normal mode for about a week.
All this time, the wastewater will not be treated enough to be discharged onto open ground. But if the correct operating mode is observed, their degree of purification is higher than that of VOCs.
Also, aeration units need to be preserved for the winter (if they are not planned to be used).
Expert opinion
Ilya Kozhevnikov
Design engineer. 10 years of experience
Ask a Question
When choosing a local treatment plant, you should take into account not only its productivity, but also the maximum permissible burst discharge, which is limited due to the small size of VOCs.
Pumping of local treatment facilities
Local sewerage needs to be pumped out once every 6 months. At the Topas, Yunilos Astra, Biodeka, Genesis, and Eurobion stations there is a special airlift for pumping out sludge. With its help, you can perform pumping yourself. A more effective pumping method is using a drainage pump, which is lowered into a sludge stabilizer. The sludge is pumped into a bucket or other suitable container.
After pumping, the local treatment facility must be filled with water. If you leave the septic tank empty, it will float or be crushed by the soil.
Local treatment plants with a receiving chamber for settling (BioPurit, Tver), as well as pumping wastewater through a biofilter (Evrolos, Kolo Vesi), are serviced by a sewer truck.
Station maintenance is not just pumping out sludge. It is necessary to disconnect and wash the airlifts, check the condition of the electrics and other equipment. To perform this work, it is better to call a service engineer who will quickly and professionally perform the service. When purchasing a local cleaning station from the Zagorod company, you can enter into a service agreement with us. Maintenance under a contract is cheaper than one-time maintenance.
Differences between a septic tank and a cesspool
- The first difference between a septic tank and a cesspool is wastewater treatment. If a cesspool-type sewer system serves only to store sewage, then septic tanks or VOCs (even better) can process household waste.
- Sewage pits are a source of unpleasant odor, while many bioseptic tank designs make it possible to neutralize it through the use of microorganisms.
- In terms of environmental impact, septic tanks also differ for the better.
- Sewage cesspools require periodic cleaning with vacuum cleaners. Flow-through septic tanks, by the way, are also susceptible to this drawback. But they need to be pumped out much less often. But VOCs or ACs process sewage into sludge, which has no toxic effects and can often be removed without the involvement of outside help.
Why is domestic wastewater treatment needed?
Domestic wastewater is wastewater from kitchens, dining rooms, baths, toilets and shower rooms, laundries, hospitals, as well as those generated when washing floors, premises, etc. Mineral substances in them make up about 42%, organic substances - 58%.
The entry into reservoirs of water that has not been purified contributes to a lack of oxygen, the accumulation of hydrogen sulfide, and “blooming” of water (the active proliferation of blue-green algae and cyanobacteria). Such processes poison aquatic organisms, especially commercial fish species. A high amount of organic substances has a toxic effect on the soil - it creates a reducing environment in it, which is favorable for the formation of silt water, which is saturated with hydrogen sulfide, metal ions and ammonia. This type of water should absolutely not be used for drinking and recreational needs.
Detergents, which contain surfactants (surfactants) and additives (peroxide compounds, neutral and alkaline electrolytes, substances that prevent the resorption of pollutants), are added in large volumes to contaminated water of this type.
Detergents, when released into the aquatic environment, disrupt the processes of biological oxidation of organic substances and oxygen metabolism, cause foaming, deteriorate organoleptic qualities, have a detrimental effect on fauna, and complicate the biological treatment of wastewater.
You also need to understand that various bacteria and pathogens of infectious diseases can multiply in untreated waters.
Which is better - a septic tank, a cesspool or concrete rings
The only advantages of sewer pits are their simplicity and low financial costs for construction. But still, comfort and cleanliness of the environment are much more important. And the efficiency of a pit or septic tank is only imaginary. During operation, the costs of pumping out wastewater with vacuum cleaners significantly exceed the costs of maintaining an autonomous sewer system without a cesspool.
If we compare the material from which the septic tank is made (from rings or plastic), then plastic has better tightness. Concrete rings, in turn, have higher rigidity and strength.
A ready-made plastic container for a pit is easier to install, but from the rings you can build a cesspool with individual parameters, taking into account the terrain. But then you will need to hire heavy equipment. In addition, concrete or brick structures require additional waterproofing. Installation errors can be costly later (contamination of soil, groundwater, etc.). It is much easier to install a factory-made plastic tank, and to speed up the installation process it is recommended to contact specialists. The average cost of installing a septic tank is 15 - 25 thousand rubles, not counting the price of the septic tank itself.
A drainage pit is inferior to septic tanks or new autonomous sewerage devices in terms of convenience and environmental friendliness, so we can safely say that a septic tank is better, especially VOC or AC.
So which sewer treatment plant should you choose for your site? We will conduct a comparative analysis and evaluate the characteristics of each type of sewerage device.
Comparative analysis of septic tanks and biological treatment stations
The advantages and disadvantages of different types of septic tanks and VOCs are given in the table:
| Type of septic tank | Design Features | Operating principle and degree of purification | Cost of equipment without installation | Advantages | Flaws |
| Cumulative | Works on the principle of “cesspools” Have one block and a pipe leading to it Require frequent pumping with a sewer truck | Accumulates Degree of purification 0% | 15 000 – 70,000 rub. | -Budget option -Possible independent device | -Not environmentally friendly -Expensive to operate (often requires pumping with a sewer machine) -No wastewater treatment |
| Settling tanks (overflow) | They have a multi-stage design consisting of several containers with overflow pipes. Requires installation of additional cleaning systems. | Accumulates and defends. Degree of purification up to 60% | 25 000 – 80,000 rub. | -Relatively budget option -Not difficult to use - Does not require electricity | - Requires the installation of soil water purification - Possible release of unpleasant odors. |
| VOC | A single sealed multi-section unit with inlet and outlet pipelines. Performs wastewater treatment. Requires electricity. | Accumulates, defends and cleanses Degree of purification up to 98% | 45 000 – RUB 250,000 | -Environmentally friendly -High degree of purification -No unpleasant odors | -Initial cash outlay required -powered by electricity |