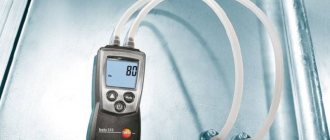
A pressure gauge is a measuring device that allows you to determine the value of excess pressure acting in a pipeline or in the working parts of various types of equipment.
Such devices are widely used in heating systems, water supply, gas supply, and other utility networks for municipal and industrial purposes. Depending on the operating conditions of the meter, there are certain restrictions on the permissible limit of its error. Therefore, it is important to know how to determine the accuracy class of a pressure gauge.
What is the accuracy class of a pressure gauge and how to determine it
The accuracy class of a pressure gauge is one of the main values characterizing the device. This is a percentage expression of the maximum permissible error of the meter, reduced to its measurement range.
The absolute error is a value that characterizes the deviation of the readings of the measuring device from the actual pressure value. The main permissible error is also distinguished, which is a percentage expression of the absolute permissible value of deviation from the nominal value. The accuracy class is associated with this value.
There are two types of pressure meters - working and standard.
Workers are used for practical measurement of pressure in pipelines and equipment. Exemplary meters are special meters that serve to verify the readings of working instruments and allow one to assess the degree of their deviation. Accordingly, standard pressure gauges have a minimum accuracy class.
The accuracy classes of modern pressure gauges are regulated in accordance with GOST 2405-88. They can take the following values:
- 0,15;
- 0,25;
- 0,4;
- 0,6;
- 1,0;
- 1,5;
- 2,5;
- 4,0.
Thus, this indicator has a direct relationship with the error. The lower it is, the lower the maximum deviation that the pressure meter can give, and vice versa. Accordingly, this parameter determines how accurate the meter readings are. A high value indicates less accurate measurements, while a low value indicates increased accuracy. The lower the accuracy class value, the higher the price of the device.
Finding out this parameter is quite simple. It is indicated on the scale as a numerical value, preceded by the letters KL or CL. The value is indicated below the last scale division.
The value indicated on the device is nominal. To determine the actual accuracy class, you need to perform verification and calculate it. To do this, several pressure measurements are carried out using a standard and working pressure gauge. After this, it is necessary to compare the readings of both meters to identify the maximum actual deviation. Then all that remains is to calculate the percentage of deviation from the measuring range of the device.
Measuring pressure range
In practice, the following types of pressure are distinguished: absolute, barometric, excess, vacuum. Absolute is a measure of pressure measured relative to a complete vacuum. This indicator cannot be below zero. Barometric is atmospheric pressure. Its level is influenced by the height above the zero mark (sea level). At this height it is generally accepted that the pressure is 760 mm r.s. for pressure gauges this value is zero. Gauge pressure is a measurement between absolute and brometric pressure. This is especially true when absolute pressure is relative to barometric pressure.
Vacuum is a value that shows the difference between absolute and barometric pressure, provided that barometric pressure is exceeded.
That is, vacuum pressure cannot exceed barometric pressure. In other words, vacuum measuring instruments measure the vacuum of the vacuum.
Devices for measuring pressure can be divided into several groups:
- Pressure meters, they are used to measure pressure up to 40 Pa.
- Traction meters, they are designed for measuring vacuum pressures up to 40 kPa.
- Thrust pressure meters, these devices have a two-sided scale with measurement limits of ±20 kPa. Differential pressure gauges are used to measure pressure differences.
Determination of error
Owners of measuring instruments are interested, first of all, in the maximum error characteristic of a pressure gauge. It depends not only on the accuracy class, but also on the measurement range. Thus, to obtain the error value, you need to make some calculations. For example, for a pressure gauge with a measurement range of 6 MPa and an accuracy class of 1.5, the error will be calculated using the formula 6*1.5/100=0.09 MPa.
It should be noted that only the main error can be calculated in this way.
Its value is determined by ideal operating conditions. It is influenced only by the design characteristics, as well as the assembly features of the device, for example, the accuracy of the graduation of divisions on the scale, the friction force in the measuring mechanism. However, this value may differ from the actual value, since there is also an additional error determined by the conditions in which the pressure gauge is operated. It can be affected by vibration of the pipeline or equipment, temperature, humidity level and other parameters.
Also, the accuracy of pressure measurement depends on another characteristic of the pressure gauge - the magnitude of its variation, which is determined during verification. This is the maximum difference in meter readings identified from the results of several measurements.
The magnitude of the variation largely depends on the design of the pressure gauge, namely on the method of balancing, which can be liquid (pressure from a liquid column) or mechanical (spring). Mechanical pressure gauges have a more pronounced variation, which is often due to additional friction due to poor lubrication or wear of parts, loss of spring elasticity and other factors.
Technical parameters of the pressure gauge
The purpose of the device in question is to measure excess pressure in the system. Among the large number of design options, we will highlight the digital pressure gauge, since recently it has been installed on most equipment, including compressors. The electronic pressure gauge is characterized by the following features:
- Relatively small in size.
- High degree of accuracy of measurements.
- Provided the required operating conditions are met, long service life.
- Possibility of calibration.
In general, we can say that such a digital excess pressure meter is very common today. This can also be attributed to the relatively low cost of many models.
When choosing the most suitable version, attention is paid to the following points:
- Recommended operating conditions.
- Accuracy of measurements.
- Acceptable operating range of the digital pressure gauge in the system.
- The type of material used in the manufacture of the body and other elements.
- The degree of protection of the structure from environmental influences.
In addition, it is recommended to pay attention to the popularity of the brand under which the product is produced. As practice shows, products from well-known manufacturers last much longer and are characterized by increased reliability
Measuring pressure with a pressure gauge
Headings: Experiments , Crafts , physics , Experiments | Tags: Measuring pressure with a pressure gauge, Experiments, Crafts, physics, experiment | June 20, 2013 | Svetlana
To measure the pressure of air or gas inside a vessel with a pressure gauge, you need to attach its rubber tube to this vessel. Monitor the fluid level in both elbows of the pressure gauge. a) If the liquid is at the same level in both elbows of the pressure gauge, consider the gas pressure inside the vessel to be the same as the ambient air pressure. b) If the liquid level in the short leg of the pressure gauge is lower than in the other, consider the pressure inside the vessel to be greater than the ambient air pressure.
c) If in the short elbow of the pressure gauge the liquid is higher than in the other elbow, assume that the pressure inside the vessel is less than the pressure of the surrounding air.
If there is a difference in liquid levels in the pressure gauge tubes, the difference between atmospheric pressure and pressure in the vessel is calculated using the formula:
You can perform the following experiments using your pressure gauge. Place the end of the rubber tube of the pressure gauge firmly on the glass funnel and tighten its wide opening with rubber film. When the liquid in the pressure gauge has calmed down, lower the funnel into a bucket of water. Monitor how the pressure inside the water changes with the depth of the funnel. Having installed the funnel at a certain depth in the water, turn its hole in different directions, up and down, watching the pressure gauge reading. 2. Open the pipe near the stove that was heated shortly before the experiment. Insert the rubber tube of the pressure gauge into the oven. The water level in the short leg of the pressure gauge rises. Calculate the pressure of warm air in the furnace (during draft). 3. Inflate the rubber bag of the medical heating pad slightly with air and connect it tightly to the rubber tube of the pressure gauge. Lay the bag horizontally and place thick books (weight) on it one after another. The pressure gauge will clearly show the change in air pressure enclosed in the bag. 4. If you get a glass tube with a total length of about 1.7 m, you can make a pressure gauge to measure much greater excess pressure, for example, the highest air pressure when blowing with your mouth. In this way, the “power of the lungs” is controlled. You should not blow in jerks, but gradually increase the pressure.
5. The same device can measure the greatest vacuum created during suction by mouth. In this case, you need to draw air from the upper end of the tube with your mouth. 6. If in the device of the 4th experiment, instead of the short elbow of the tube, you insert a tube drawn to the narrowing, then when you blow into the long elbow, a fountain will flow from the short tube.
E.N. Sokolov “To the Young Physicist”