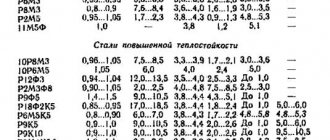
Learning to identify copper and distinguish it from other metals and alloys
Chemically pure copper has three distinctive characteristics. It is a colourful, ductile and corrosion resistant metal. The latter property is due to the formation of a thin oxide film. This layer makes the copper chemically inert in a non-corrosive environment and also adds a red tint to its golden pink color.
The best way to accurately identify copper is spectral analysis, which requires expensive equipment - a metal analyzer, while identifying copper at home is a task with a limited set of tools. Here the best instruments are the senses, easily accessible chemicals, fire and improvised devices.
Briefly about element No. 29
Pure copper (Cu) is a golden-pink metal with high ductility, thermal and electrical conductivity. Chemical inertness in an ordinary non-aggressive environment is ensured by a thin oxide film, which gives the metal an intense reddish tint.
The main difference between copper and other metals is color.
. In fact, there are not so many colored metals: only gold, cesium and osmium are similar in appearance, and all elements included in the group of non-ferrous metals (iron, tin, lead, aluminum, zinc, magnesium and nickel) have a gray color with varying intensity of shine.
An absolute guarantee of the chemical composition of any material can be obtained only through spectral analysis. The equipment for carrying it out is very expensive, and even many expert laboratories can only dream of it. However, there are many ways to distinguish copper at home.
with a high degree of probability.
How to distinguish copper from other metals by eye?
Visual perception is the simplest, but not always quite accurate method. However, in most cases it works and it is not difficult to distinguish copper scrap from other non-ferrous metal scrap. Indeed, despite the name of the category non-ferrous metals, only the following are equally colored:
- copper;
- gold;
- cesium;
- osmium.
The remaining metals are characterized by a gray tonality and differ mainly in the intensity of their shine. Therefore, color is an excellent “means of identification” in such matters as distinguishing copper from aluminum, zinc or nickel.
Pure copper with a characteristic copper color
The natural color of the pure element Cu is red-pink. It is recommended to look at metal in natural light. Artificial lighting, with the exception of LED lamps with warm color temperatures, changes the hue towards a yellow-green tone.
The second rule for visual identification of copper is that the surface oxide film must be removed. Oxidation creates a greenish-blue coating on the metal surface. Therefore, to determine by color that you have copper, preferably by fresh sawing or by processing the material with a file. The situation with copper alloys: brass and bronze is much more complicated. It is also visually difficult to distinguish between Cu and copper-plated aluminum.
personal-ua.com - all about working in Ukraine!
Copper is characterized by three distinctive parameters: color, high ductility and corrosion resistance. The anti-corrosion properties of the material are provided by a thin oxide film covering its surface.
Pure copper has a pinkish-red color. It is advisable to examine metal in natural light. Artificial lighting gives copper a yellow-green tint. The exception is LED lamps with warm color temperatures - they do not change the color of copper.
An important point: before inspecting the product, remove the oxide layer that gives the bluish-green tint.
The visual method of copper identification is by far the most accessible. However, unfortunately, it is not always effective. Copper-enriched aluminum, which has a yellowish color, is characterized by a color similar to copper. Difficulties may also arise when identifying tinned copper (it has a silver color). By the way, both alloys are used to make cables. Therefore, if, for example, a situation arises when you need to find out what the cable is made of, visual analysis will not help.
The easiest way to distinguish copper from aluminum is by measuring resistance. A hundred-meter copper wire has a resistance of 4-8 ohms, and an aluminum wire has a resistance of 12-20 ohms. The main advantage of this method is the absence of damage to the cable.
You can also distinguish copper from aluminum by testing the product for strength. If you bend and straighten a copper cable several times, nothing will happen to it, but an aluminum cable will break due to similar actions.
Another method is to hold the product on fire. Aluminum begins to melt already at 600 °C, while the melting point of copper is 1083 °C. By the way, when heated, copper will quickly change color because it will be covered with an oxide film. Therefore, using this method, you can distinguish copper from aluminum by color.
An alternative method for copper identification is the use of nitric acid. Pour a few drops of the reagent onto the surface of the object. If the product under study consists of copper, then in the contact zone it will turn blue-green. Aluminum is resistant to nitric acid.
How to distinguish copper from bronze How to distinguish copper from brass How to distinguish copper Sell cast iron for scrap Classification of non-ferrous metals
Information for the applicant: Post your resume so that the employer can find you: create a resume | post your resume on the Internet for free
Note to the employer: To increase the efficiency of searching for candidates who meet the requirements of the vacancy, be sure to post a vacancy : post a vacancy ad | add a vacancy and view your resume
How to distinguish copper from brass and bronze
The first metal is a Cu-Zn alloy. The zinc content varies in the range of 4 – 45%. When an alloy is characterized by a high addition of a major impurity, it is easy to distinguish it from pure metal by color. The color of copper is pink-red, brass is lighter, but scrap brass may have a dirty surface. The more zinc in the alloy, the more its color shifts from red to yellow. Therefore, visual perception is unacceptable for high-copper brasses, where the presence of impurities is at the level of 10%. In this case, there are 3 options left for how to distinguish copper from brass without using a tool:
- By sound. It is advisable to have an ear for music here. When struck against metal, soft copper sounds muffled, while brass sounds loud. The method works well for massive, oversized products - pipes, for example.
- Along the fold. The ductility of copper allows the metal to be easily bent. Harder brass is not as malleable.
- By weight. The density of Cu9 g/cc is higher than that of Zn (7.1). The resulting characteristic value for brass is on average 8.6 g/cc. The difference is small, but if you have accurate scales, it is possible to distinguish metals.
Visual difference between copper and bronze and brass
A good identifier of copper, relative to brass, is shavings. In pure metal it is spiral-shaped. On the contrary, the brass shavings are straight and needle-shaped.
A more complex approach involves the use of chemicals, namely hydrochloric acid. Chemically inert copper does not react in solution, whereas when brass is immersed, a white coating forms on the surface of the metal. This is zinc chloride, the result of the reaction of this metal with an acid.
Video – copper and brass:
How to distinguish between copper and its alloys?
Copper alloys are widely used in industry. Over many years of research, it has been possible to obtain many materials with unique properties: high ductility, electrical conductivity, chemical resistance, strength (all depends on alloying additives). The most common are bronze (with the addition of tin, aluminum, silicon, manganese, lead and beryllium), brass (with the addition of 10-45% zinc), as well as copper-nickel alloys (nickel silver, cupronickel, copel, manganin).
Only bronze and brass are difficult to identify, since copper-nickel alloys differ significantly in color due to their low copper content.
Copper or brass?
Brass can contain from 10 to 45% zinc, a silver-gray metal. Naturally, the more zinc, the paler the alloy. However, high-copper brasses, in which the amount of additives does not exceed 10%, differ little in color from the copper sample. In this case, you can only trust your feelings: brass is much harder and more difficult to bend (for greater reliability, a comparison with a reference sample is advisable). You can try to remove the shavings: copper shavings will have a curl shape, brass shavings will be straight, needle-shaped. When the samples are placed in a solution of hydrochloric acid, no reaction with copper is observed, and a white coating of zinc chloride forms on the surface of the brass.
How to distinguish copper from bronze
It is not always possible to determine which metal is in front of you by color. Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin, also characterized by a pink-red hue; scrap bronze can be found in anything. In this case, the main distinguishing characteristic is the ductility of the pure metal. By pressing on the copper with a hard object, we get a notch on the surface. Deforming bronze is much more difficult.
Items made of bronze are very difficult to distinguish visually from copper
An alternative way to distinguish copper from bronze at home is a saline solution. Add 200 grams of table salt to a metal container containing 1 liter of water. The solution is heated to a temperature above 50 °C. Next, the metal is placed in the heated liquid and kept for about 15 minutes. The color of copper changes. Bronze remains insensitive to the effects of saline solution.
The next method is patination of copper. Oxidation of pure metal over time in air is an inevitable process, leading to the formation of a greenish-blue coating. Bronze is not subject to patination.
How to identify copper?
| Copper scrap price per kg in Moscow | wholesale | retail |
| Copper Mix is not graded | 570 | 550 |
| Copper Mix tin | 475 | 450 |
| Lump copper from 3 mm. not el.tech. "D" | 575 | 560 |
| Copper Varietal burnt from 0.5 mm “F” | 575 | 560 |
| Copper Electrical copper shiny from 0.5 mm “A” | 590 | 510 |
| Electrical copper busbar “G” | 588 | 560 |
| Copper shavings | 415 | 395 |
| Copper radiators | 335 | 310 |
| Copper rod "K" | 480 | 467 |
| SCRAP Enamel wire from 0.5 mm. | 465 | 455 |
It is difficult, but possible, to distinguish pure copper from alloys with high copper content.
If brass contains more than 80% copper, then both metals are similar in color and reaction to moisture: they become covered with a patina - a protective green film. The cost of such non-ferrous metal is quite high and you can hand over copper scrap at the LOMTSVETMET collection point
In order not to mistake bronze, brass and alloys for pure copper, you need to know its basic properties:
- Color. Before us is red-brown metal, when struck, a muffled sound is heard. A fresh cut or cleaning the surface with a file allows you to examine the original texture in daylight.
- Plasticity and malleability. Copper is a soft metal; wire made from it bends but does not break. To ensure that there are no foreign matter, press lightly on the test item. Copper products are malleable to change in shape, while brass is a hard metal that is not subject to change without firing.
- Rust resistant. Even in a humid environment, copper products are not susceptible to corrosion.
- Reaction to a magnet. Pure metal is indifferent to magnets. This trick allows you to determine the authenticity of metal at home.
- Habitat. Spare parts and tools are rarely made from copper, but it is often used in the production of electrical wires. This soft metal is a good conductor of electricity.
Method for determining the authenticity of copper:
- physical;
- chemical.
The first group of methods is based on the physical properties of the metal, and the second is based on the use of chemicals. You can determine pure metal at home by:
- Marking. Brass products are marked with the letter “L”, and copper ones with “M”. In the EU, both metals are designated C, so the subsequent designations have the final say. For copper, the first 4 letters of the Latin alphabet are used.
- Heating. Heat part of the product with a lighter. When exposed to fire, copper first tarnishes and then turns black.
Chemical methods for determining copper:
- Use of nitric acid. One drop of the substance will color copper blue-green.
- Hydrochloric acid will strip pure copper of its patina, but will cause zinc chloride to appear on the surface when exposed to brass.
- Using analyzers.
Knowing the properties of copper makes it easy to distinguish it from bronze and brass, but it is impossible to identify the metal under the light of an incandescent lamp.
When comparing copper and high copper content brass, consider the labeling and use nitric or hydrochloric acid. The surest way is to contact specialists who will help determine copper using express analysis.
DO YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS???
LEAVE A REQUEST AND WE WILL CONSULT YOU FOR FREE!
Similar articles:
- How to distinguish copper from brass?
- What products contain copper?
- Recycling of non-ferrous metals
- Classification of non-ferrous metal according to GOST
- Application of non-ferrous metals
How to distinguish copper from aluminum
Naturally, metals are easy to distinguish by color. The situation becomes more complicated when it is necessary to determine what the cable cores are made of. Tinned copper takes on a silvery tint, while copper-plated aluminum takes on a yellow tint. The result is that it is extremely difficult to distinguish metals from each other by color.
Tinned copper in cables
The best option is to measure the resistance. For a copper twisted pair cable about 100 meters long, the parameter value reaches 4–8 ohms. The resistance of a similar aluminum cable is significantly higher: 12 – 20 Ohms. This method is good because there is no mechanical impact on the metal.
How to distinguish copper from Cu conductor in UTP?
Manufacturers of twisted pair cables (UTP\FTP) use three types of conductors when producing them, these are:
1. UTP with CCA;
2. Cable with copper-plated steel core;
3. Cable with Cu conductor;
There is also a fourth type of vein, the Chinese call it “ MIX ” - this is an alloy of copper with a secret component, in fact the most natural fake of copper.
In the first point, when you have a cable with CCA, everything is not difficult - first of all, it is the weight of the package - (for the standard, so to speak, we use an internal twisted pair 4P * 2 core 0.5 - from the Ekkon factory ) - the package is 305 m., ( standard packaging), weighs about 7 kilos. – 6.9 kg. Copper is always heavier - about ten kg, a coil of 305 meters.
Clean the wire with a blade and lightly scrape it, a silver-colored core will appear - what you see will be Al (aluminum) or steel. You can also use a magnifying glass to look at the cut edge, it is clearly visible - the core of such a wire will be steel-colored. Without a doubt, electrical engineering. You won't notice any copper core.
Let's try to determine - is the base steel wire or aluminum? This is quite simple - you can determine this by breaking the conductor with your hands - steel is stronger and more elastic than aluminum. But there is a much more primitive method and its reliability = 100%. Fridge magnet. If the wire is attracted by a magnet, this means it is steel, but if not, it means aluminum wire.
As for point four “mix” - it differs from copper wire in the color of the core, it is brownish-brown and very soft; if you scratch with a simple blade, the wire is cut and not scraped off. This means you have the most unfortunate purchasing option, since - if you purchase copper-plated aluminum or a pair based on copper-plated steel wire and this is officially designated by the seller, you are able to pre-predict the UTP resistance and, based on these indicators, predict cable sections without compromising the conductivity of electrical signals .
When it is a “mix” and the supplier sells it to you as a copper conductor, which is very often, the characteristics of “this” are not fully accessible to him or he does not even know about the composition of the wire himself.
The best way is to find out the price list of electrical equipment before ordering. copper on the international market (approximately 00 tons), then check the weight of the coil from the seller, and then use a calculator to add up the import price, customs duty and seller’s income. When the amount received makes you wary, be careful with your purchase.
Other cases of fire and acid testing
Exposure to flame is used not only to identify metal relative to aluminum. For these purposes, a gas stove, lighter or fire is sufficient. Heating copper leads to the formation of its oxide, which affects the color change. The surface of the metal gradually becomes dull until it acquires a completely dark shade.
Nitric acid is another identifier for copper at home. It is also important to be careful here. It's better to just drip the liquid onto the metal. Pure copper at the point of contact will turn blue-green.
Video - how to distinguish aluminum from copper:
Twisted pair: copper or bimetal (copper)?
Demand gives birth to copper - the law of a market economy.
The impetus for writing this article was the noticeable interest of some consumers in such a new product on the market as twisted pair cables with a bimetallic (copper-clad) conductor, which were previously traditionally produced with conductors made of pure copper. This article will provide a rationale for the appearance of copper-clad cables on the market, and will also reveal their disadvantages compared to “copper” twisted pair cables. Basically, we will talk about cheap UTP twisted pair - unshielded, 4 pair, 5e category made in China/Taiwan.
Where do the “legs” of a copper-bonded twisted pair cable come from?
Copper-clad twisted pair appeared relatively recently. It should be noted that copper-plated twisted pair is not at all a competitor or an alternative to high-quality and expensive cables that are used in the installation of SCS (structured cabling systems). By the way, on the Internet there is a very interesting resource about SCS , which is maintained by a market expert. “Omednenka” is rather a competitor to the cheapest twisted pair , but it is currently wrong to say that copper-coated cables are rapidly replacing copper ones. It should be noted that copper appeared in the segment of 2 and 4 pair UTP . proposals on the market for copper-clad multi-pair cables yet, and this has its own logic, because historically there was only demand for 2 and 4 pair cheap cables.
The appearance of copper-clad cables is not associated with innovations and technological breakthroughs in cable production. Copper plating of the conductor was widely used in the production of television coaxial cables, the most inexpensive of which were bimetallic (copper-coated steel core). The appearance of copper-clad twisted pair cables is primarily due to economic reasons. Let's see this together by studying the fluctuations in wholesale prices for one of the popular copper cables (UTP cable 4 pairs, category 5e , solid, 305 meters) in the period 2003-2008.
Diagram. Wholesale prices (in USD UTP cable 4 pairs 5 e category
Due to the growth in the number of local computer networks and the popularity of regional Internet providers (home networks), wholesale prices for UTP cables began to slowly fall and reached their minimum - 33.6 USD per 305 meters (2003 on the diagram). At this minimum level, the price for them lingered for about 1 year, then there was a smooth increase from year to year. As a result, from 2003 to 2006 the price doubled!!! Of these 3 years, the most dramatic was 2006, during that year alone the price of twisted pair cable increased by 50% contrary to market expectations. The main reason for the increase in the price of copper twisted pair cables was and remains the increase in copper prices. The graph of the growth in the price of copper completely repeats the graph of the growth in the price of UTP cable for this period of time.
The key consumers of cheap twisted pair copper are Internet providers who connect their subscribers using Ethernet technology. For example, such a Moscow Internet home provider as the Mig-Telecom company purchased 200-300 bays monthly, and there were many like this company. By the way, many companies know Mig-Telecom from the odious, bearded and loud-mouthed supplier Leonid, who, one might say, has become a living legend in the Moscow IT market. He was known in almost all companies. Someone now remembering him will smile, and someone’s hands will automatically reach for a baseball bat... Personally, we remember him with a smile.)
At that time, serious competition was unfolding in the ranks of home providers. If one of the providers in the area announced a free connection, then the others automatically did so. Against the backdrop of this “war” for freely connected clients, home providers “squeezed out” the lowest prices for twisted pair cables in order to somehow reduce their investments in a new client. Naturally, in such conditions, home providers were looking for the best price, and suppliers, in turn, squeezed discounts from their Chinese manufacturers.
When there is demand for something, the only question is how quickly supply will arise. Apparently at some point in time, engineering flexibility was shown at one of the Chinese factories, and a solution was found - copper-plated twisted pair. That is, the high demand for cheap twisted pair cables has generated a corresponding supply in the market.
Types of bimetallic twisted pair cables.
The location of copper in the outer layer, and aluminum or steel inside the structure, and not vice versa, is very important: on the one hand, with alternating current, a higher conductivity of the entire wire is achieved in general, on the other hand, copper protects the metal located underneath it from corrosion. Aluminum oxidizes very actively and becomes covered with a thin oxide film with high electrical resistance. This film protects aluminum from further corrosion, but creates a high contact resistance at the contact points of aluminum wires and makes it impossible to solder aluminum using conventional methods. Aluminum has lower properties compared to copper - both mechanical and electrical. With the same cross-section and length, the electrical resistance of an aluminum wire is 1.63 times greater than that of a copper wire!!!
Currently, two types of bimetallic UTP cables :
1. copper-plated steel conductor ( CCS = C opper C lad S teel)
2. copper-plated aluminum conductor ( CCA = C opper C lad A luminium)
Twisted pair with a copper-clad steel core ( CC S ) is a rather rare offer; mainly CCA . In our opinion, of the two types of copper-clad cables, CCS is the worst option.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
| Low cost | Brittle, the conductor breaks at small bending radii. |
| A light weight | The RJ-45 connector does not crimp well |
| The core does not hold well in the connector (floating contact) | |
| Short segment length | |
| Unpredictability of impedance in the contact area when terminating a cable into an IDC connector of a socket or patch panel | |
| As a rule, the thinner core is on the blue (4-5) and brown (7-8) pairs | |
| In most cases only supports 10Base-T (i.e. only 10 Mbps) | |
| Unpredictable changes in characteristics during subsequent cable relaying |
For those who want to get acquainted with the real experience of using copper-plated cable, I strongly recommend that you read the reviews on one popular website.
Separately, I would like to comment on one common misconception that, supposedly, when a copper-clad core is embedded in an IDC connector, a bimetallic contact is formed. Apparently, those who hold this opinion, making similar statements, believe that the blades of the IDC connector are copper and in the case of introducing a “copper” blade into the aluminum core of the conductor, this so-called bimetallic pair is formed. However, it is not. Bimetallic contact is normal for this type of connection, even when using standard components. For example, the material of IDC connectors 110 type from LANMASTER is a phosphor-bronze alloy coated with tin (Phosphor Bronze with Tin plated), i.e. in any case, a bimetallic pair is obtained.
Since we have delved so deeply into the topic of contact between the core and blades of the IDC connector, it would be appropriate to highlight in detail one of the shortcomings, which is formulated as follows - “the unpredictability of the wave resistance (impedance) in the contact area of the cable cores in the IDC connector of a socket or patch panel.” So, we embed a copper-aluminum conductor into a 110 type IDC connector, the connector blade cuts through the insulation (PE) of the conductor and is embedded in the body of the conductor. Next, 2 options are possible: 1) The knife is in contact only with the copper part of the copper-aluminum core, 2) The knife has cut through the copper layer and has electrical contact with the aluminum core of the wire.
| Contact IDC knife with copper conductor | Contact IDC knife with aluminum core CCA core |
In the first case, we have a completely familiar situation, as in the case of a regular copper conductor - the impedances are matched. In the second case, due to the contact 110 of the knife with the aluminum core, we have unmatched impedances, because copper and aluminum have different characteristic impedances. It is impossible to know in advance which part of the core the IDC connector will contact. Unmatched impedances in one pair or in different pairs, in the case of copper-clad cable, significantly affect the operation of active equipment, which leads to numerous errors and unstable operation.
Conclusion:
It should be noted that all of the above disadvantages very often lead to significant losses of time, both on the part of the subscriber and on the part of the service provider, which from an economic point of view does not justify the use of copper-clad cables.
We recommend:
| [~model=38968~] | [~link=38968~] | [~sum=305*38968~] |
PS There are still very few articles on the Internet on the above topic, so it would not be amiss to provide links to them here.
- Are Copper Clad Aluminum Wires (CCAW) in Data Cables a Great Idea? Just at First Sight!
- Beware of fakes - “copper-plated” UTP cable category 5e
Chemical methods
Using various chemical compositions, you can influence the breakdown of molecules and atoms of a substance and isolate its constituent parts. Chemical methods include the electrolytic method of measuring the copper part in alloys of other metals; it is carried out using the following elements:
Scrap copper is also treated before use
- acetylene;
- tartaric acid;
- aqueous ammonia;
- ammonium nitrate;
- disodium salt;
- ethanol;
- Cuprizone.
To begin with, the copper composition (sample) is weighed, then sent into a prepared reagent solution, in which the sample should completely dissolve. The resulting liquid is heated, which removes nitrogen oxides, the purified solution is diluted with water and heated again to 40 °C.
After this, the mass is ready for the electrolysis process - electrodes, usually made of platinum, are immersed in the solution, a current of 2.2 V is connected, and with constant stirring, the process of copper separation begins.
Cleaning copper coins with chemical solutions
To control, you can repeat the electrolysis process; for this, the electrodes are lowered into the liquid, below the level of the isolated copper, and the current is connected. If the initial process was completed correctly, then during the control procedure no metal deposits will form. The copper cathode obtained as a result of this splitting is washed with water without disconnecting the electric current, then treated with ethyl alcohol and dried. The resulting copper cathode is weighed, and the result is compared with the original weight. Thus, the specific gravity of copper in the substance is calculated.
Various chemical methods for determining copper differ in the composition of solutions, the feasibility of which is determined depending on the expected impurities of foreign substances, but the principle of operation is the same.
What are copper and bronze?
Copper is a natural mineral, i.e. a pure non-ferrous metal that occurs naturally in nature. This metal has high thermal and electrical conductivity, therefore it is actively used in the production of conductive elements. Another property is its resistance to corrosion, which is why it is used in the production of plumbing pipes.
This metal is soft and ductile when in its pure form. Various impurities are often added, resulting in the formation of copper alloys. This is done to achieve certain performance characteristics that metal in its pure form does not possess.
One of them is bronze - an alloy of copper and tin (about 12%). Depending on the desired properties of the final material, other impurities are also added: zinc, aluminum, manganese, etc.
How to distinguish bronze from copper by color?
Copper has a characteristic reddish tint, which can have a pink tint. With high humidity, a greenish patina may appear.
The color of bronze directly depends on the content of pure metal in it. If there is a lot of it, the color will be similar (red-brown). Shades range from brownish to gold (the more tin in the alloy, the easier it will be for you to determine by eye).
Areas of application
These non-ferrous metals have different performance properties, so they are in demand in the production of various products. Typically, copper is used to make cables, roofing and plumbing fixtures. This is explained by good electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
Bronze is resistant to sea water, so it is actively used for the production of mechanisms for boats and shipbuilding. Another area of application is the production of musical instruments, badges, medals, etc.
Distinguish copper from bronze
Bronze is an alloy of copper with tin and other elements, most often has a reddish-brown color. These two metals are also very similar in appearance. Remember that all its alloys, compared to copper, are always much harder.
To determine, you need to prepare a hot saline solution. Then either pour it onto a previously cleaned surface, or dip copper wire into the solution for a while. The same should be done with a bronze product. When exposed to hot salt water, the shade of copper will become much darker compared to bronze.
You might be interested in
- Cleaning bronze and brass at home
- How to remove rust from metal - folk remedies
- How to clean a gas stove from old grease and carbon deposits
Important differences
Copper and bronze are very similar in color. When scrap is delivered, alloys are assessed in laboratory conditions. It is not difficult to make distinctions, if necessary, given the characteristic features of the bronze alloy. These include:
- more ductile copper has a red-pink or red-brown tint, the color of bronze depends on the dominant element: magnesium, beryllium, aluminum, which give it reddish-gold, grayish-brown, pink, yellow-pink shades;
- when exposed to a saline solution, objects made of copper change color and darken, while bronze remains unchanged;
- due to its elastic properties, copper wire or plate is simply bent by hand; when drilling, ornate chips are formed; when drilling a hard and brittle alloy, chipped sawdust, thin and small, is formed;
- Bronze products, depending on the composition, are quite difficult to bend; they can even exceed steel in strength;
- During the process of natural patination, copper products become covered with a greenish coating upon prolonged contact with air; this reaction is not typical for bronze products.
Quantitative methods
There are many types of chemical solutions for cleaning copper products.
Methods for quantitatively determining the mass of copper in the total volume of metal are used mainly for alloys with nickel, bronze and zinc. In the process of exposure to a substance, copper is deposited and in this form it can be measured. Inorganic and organic elements are used for precipitation. Inorganic substances used to determine copper include:
- ammonium tetrarodanodiamine chromate, also called Reinecke's salt, this reagent is not used for alloys containing mercury, thallium and silver;
Reinecke's salt reagent for cleaning copper surfaces
- Potassium thiocarbonate precipitates copper when heated to 80 °C;
- acetic acid is used to precipitate copper oxalate.
- hydroxyquinoline-8, it precipitates copper in combination with ammonia and alkaline solutions; when the precipitate is heated, copper oxide is formed. This method is used for complex alloys that contain aluminum, tin, lead, arsenic, chromium, iron;
- α-benzoinoxime in an alcohol solution is capable of precipitating metal in the form of flakes; this method is not applicable if nickel is present in the composition;
- Potassium iodide, it is used in neutral and acidic environments; it is not used if the alloy contains iron, antimony and arsenic.
Organic substances that are used in the quantitative determination of copper include:
Before using any method, it is necessary to determine the composition of the alloy in advance; this can be done experimentally, by heating (the metal changes color), evaporation (the metal precipitates), and using filters.
How to distinguish aluminum from other metals
Business July 24, 2018
We welcome everyone who, being a real owner, draws knowledge and experience from our website. This suggests that today for some reason you are interested in the question of how to distinguish aluminum from stainless steel. But really, it’s not that simple.
Features of aluminum
Why is aluminum so valuable? This is a pure metal classified as non-ferrous. It is lightweight, durable, has a good degree of deformation, and is resistant to aggressive environments and corrosion.
All of the listed advantages allow it to be used in a variety of areas from industry and construction (except for industries where high-strength structures are manufactured) to domestic use.
The demand for the valuable metal is great, so it is important to know how to accurately distinguish it from other similar metal alloys.
Aluminum or stainless steel: methods of determination
There are several ways to help you do simple research on your own at home. Find out how to distinguish aluminum from stainless steel - advice from forum members and experts.
- Using a magnet. Aluminum of any grade will not stick to a magnet. Stainless steel also has this property. But there is an exception to the rule. If it contains nickel in sufficient quantities, the tested products will have some attraction. If there is a lot of chromium or copper in a stainless metal, it will not have any effect on the magnet.
- Marking on stainless steel. Some stainless steel products have identification markings. This already gives a hint on how to distinguish aluminum from stainless steel. If there are markings, for example, “STAINLESS” and the like, this is not aluminum.
- Plain paper won't lie. The method is very simple. Experiment conditions: you need white, as thick paper as possible (printer paper will also work). Use a thick cloth to remove dirt from the edges of the products being tested. Move the cleaned areas one by one with some pressure across the sheet. There will be no traces left of the stainless steel. Aluminum will draw gray stripes.
- How to distinguish aluminum from stainless steel by the color of the metal? The surface of the object has a shiny, colorless hue that does not change over time - it is stainless steel. The matte surface of a product that has a grayish or whitish color is aluminum. It will not be polished with sandpaper to a high gloss finish. Check it out.
- Under mechanical load. Another simple way will help you understand how to distinguish aluminum from stainless steel. Hit the product against the surface of any hard metal in the dark. Aluminum will never spark, unlike stainless steel.
- Thermal conductivity, melting. Compare where the water heats up faster. Of course, in an aluminum container. This metal has much better thermal conductivity. But it is not used on the burner of a gas furnace; the melting point is 660 °C. Stainless steel cannot be melted in the usual way (melting index is above 1800 °C).
- Testing for copper sulfate. An option available to everyone. Copper sulfate, after exposure to aluminum, will leave cloudy stains and traces on it, but will not appear on stainless steel.
- Alkaline solutions. Any housewife knows that it is impossible to boil aluminum cookware in alkaline solutions. It will darken and lose its appearance. Conclusion: aluminum products are afraid of alkali, both sodium and potassium. The same cannot be said about stainless steel.
- Acid test. All acids, starting with the usual citric acid and ending with more aggressive ones, will leave marks when they get on the aluminum surface. You won’t see them on stainless steel; it doesn’t react with acids.
Duralumin – an alloy of aluminum with transition metals
The industry is not able to provide itself only with pure metal, and duralumin comes to the rescue here - various combinations of manganese, copper and magnesium in an alloy with aluminum.
In addition to all the above properties of its older brother, the transition metal has:
- high degree of strength;
- long service life;
- plasticity;
- high hardness.
It accumulates fatigue properties more slowly and is resistant to cracking.
The disadvantage of products made of duralumin is susceptibility to corrosion, which can be prevented by anodizing, applying a thin layer of paints and varnishes, aluminum.
The choice between the two metals depends on the end use. We pay tribute to their advantages, but also foresee their disadvantages. The domestic sector leaves the choice to aluminum, while the industrial sector votes for the strength that duralumin has.
Naturally, the question arises of how to distinguish aluminum from duralumin. It is almost impossible to determine by eye which metal is which. The chemical laboratory will give you the exact answer. But experts on the forums have their own opinion on this matter.
- Follow the markings.
- The color of the alloy is steel gray.
- Scratches leave clear marks.
- A ringing sound is heard from the impact.
- During processing, the chips will break without ductility.
- The structure of the alloy is fine-crystalline.
You can determine the type of material by conducting an experiment. Apply a drop of sodium hydroxide to duralumin and aluminum samples for 10 minutes. After removing the substance, we learn about the metal from the resulting stains: the dark one is duralumin.
If you place a piece of aluminum in an acid with added alkali, it will dissolve, forming a white powdery precipitate. In the experiment with duralumin, blue copper granules will be present.
Unlike aluminum, the main characteristics of the alloy are lack of ductility, brittleness and hardness.
Everything can be learned by comparison; examine the parts of two samples several times, pick them up and compare the weight. Such familiarity will help you subsequently simply recognize metals.
Silumin - a twofold relationship
Products made from silumin, an aluminum-based alloy with the addition of silicon, literally flooded the market. Why does it attract the buyer and how to distinguish aluminum from silumin?
Advantages of silumin
Of course, this alloy of two materials has its “fans”. They call the following positive features of silumin:
- light in weight;
- highly durable;
- resistant to wear and corrosion;
- cheap price.
Cons of silumin
Silumin products should be treated with caution, unlike aluminum ones. in silumin, aluminum production waste, silumin-containing alloys, and metal powder do not have an exact proportion. It cannot be called high quality, since the manufacturer produces cheap products under the name of some brand.
The disadvantages of the alloy include:
- design flaws;
- they are unsuitable for food products;
- dangerous to health.
You can distinguish silumin from aluminum visually. The products have a glossy smooth gray surface.
Today, public dissatisfaction with plumbing products continues to grow due to the heterogeneous structure of the material with numerous internal stresses and voids. After 3-5 months, the water tap turns into dust, and the rotary steel ball rusts.
Bimetal and aluminum using radiators as an example
When replacing heating radiators, many are faced with the choice of which material to choose for the new design. Cast iron batteries are a thing of the past; manufacturers offer aluminum, steel and bimetallic ones.
While steel is easily recognizable in appearance, the problem with aluminum and bimetallic structures is that you can’t tell the difference by eye. Moreover, the latter option is in greatest demand.
In the store there is a chance not to buy a fake, but how to distinguish bimetal from aluminum at the market?
Visual recognition will not provide accurate results to the consumer. Both the aluminum and bimetallic systems have external fins made of aluminum. And it’s impossible to visually determine the weight of one section.
For reference: the aluminum section weighs 1–1.6 kg, the bimetallic radiator “compartment” weighs 1.5–2 kg.
You can use the “old-fashioned” method and arm yourself with a neodymium magnet, which has greater power.
Preliminary test. Place the magnet first on the steel, then on the aluminum radiator. The magnetic tester will attract the first option to the surface. The effect will be weaker for a bimetallic radiator. Its steel tubes are located under a diamagnetic material - aluminum. With a powerful neodymium magnet, it is possible to catch the attraction.
It is more difficult when the coolant tubes are made of copper, which, like aluminum, is impervious to the magnetic field.
Difference from other non-ferrous metals
It is known that metals have largely identical properties. But each element has its own distinctive characteristics. They allow you to understand how to distinguish metal from aluminum:
- copper is recognized by its bright reddish hue;
- iron and its alloys have high magnetic properties;
- You can recognize gold by its yellow color;
- Lead has high fragility and density;
- silver has a bright shine;
- Tin has high ductility.
The above methods are only estimates and approximate. More reliable information is available on the pages of special reference literature.
Distinguish copper from brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. Not surprisingly, visually they are very similar. The more zinc in the alloy, the lighter the brass. So copper is definitely redder. In addition, brass is a harder metal; it is difficult to bend without additional heat treatment (casting). So we try to bend it or check for a tooth.
Brass is also lighter. Electrodes for the plug of any electrical household appliance are made of brass. So at home there is always something to compare with.
How to distinguish copper from other metals at home
One of the main problems for those wishing to sell non-ferrous metal scrap is determining its type. In this article we will tell you how to distinguish copper from other non-ferrous metals at home. Copper is one of the oldest metals discovered by man. Due to its properties, it is widely used in a variety of fields, but is most widespread in electrical engineering.
Copper is mined in both nuggets and ore. When it comes to waste and scrap, copper alloys are often found. There are several ways to tell whether a metal is pure or an alloy. Let's look at each one separately.
Photometric methods
To determine copper in various material compositions, the photometric method is used; its advantages are a high level of accuracy in measuring the quantitative composition, ease of use, and does not require expensive equipment. This method can be used with various active substances:
Photometric analysis is carried out using special equipment. equipment
- cuprizone;
- Lead diethyldithiocarbamate.
The essence of the photometric determination of copper is to record the color intensity of the material that has passed through a concentrated solution. For such a solution use:
- ammonia;
- ammonium citrate solution;
- lead diethyldithiocarbamate;
- sodium sulfate.
The substance in which it is necessary to determine copper is passed through the above solutions, it is important to maintain the proportions, and then subjected to photometry. The single-beam photometer apparatus consists of a tungsten lamp, a movable diaphragm, a light filter, a photocell and a microammeter.
How to distinguish between the main copper alloys
The optimal method for accurate metal identification is spectral analysis. However, it requires complex, expensive instruments. If you need to distinguish copper on your own, you have to make do with improvised means.
Metallic copper has three distinctive features: a characteristic color, high ductility and corrosion resistance. Anti-corrosion properties are due to the thinnest layer of oxide covering the metal surface. This film ensures chemical inertness of the material and changes the light of the product.
How to identify copper by eye?
The visual method is the most accessible, although not always effective. The following metals have a color similar to copper:
- gold with impurities;
- cesium with impurities;
- osmium with impurities;
Others are painted in gray tones, making it easy to distinguish copper from most metals.
Pure copper has a pinkish-red color. The product must be viewed in daylight, otherwise the object may appear yellow-green.
An important point: you must first remove the oxide layer, which has a bluish-green tint.
Some difficulties may arise with copper alloys - brass and bronze, as well as copper-enriched aluminum.
How to distinguish copper from brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, the content of which ranges from 4 to 45%. With a significant proportion of zinc, the color of brass becomes yellowish. If zinc is less than 10%, the visual method will not help. In this situation, there are 3 solutions:
- Acoustic method. When struck, copper produces a muffled sound, while brass produces a ringing sound. A keen ear is required. This method is good for large objects.
- Mechanical method. Copper is ductile and, unlike brass, bends easily.
- Weighing. Zinc and its alloy are lighter than copper. For low zinc content and for small items, an accurate scale will be required. The density of copper is 9 g/cm3, zinc - 7.1 g/cm3, the density of brass depends on its composition, but is always lower than that of pure metal.
There are other methods. For example, if it is possible to remove chips. In copper it has a spiral shape, while in brass it is straight and needle-shaped.
Another method is somewhat more complicated, since it requires hydrochloric acid. Copper does not react with this reagent, but brass reacts to form zinc chloride, which forms a whitish coating.
How to distinguish copper from bronze
Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin. It is painted almost the same as pure copper. The visual method will be ineffective in such a situation. The most common identification method is based on the high ductility of copper.
Pressing a hard object onto a copper piece will cause a dent to form. Bronze is much stronger. This method is suitable for scrap or technical products.
But it is not always acceptable to leave defects on an item.
Another method will require a solution of table salt, which is always available on the farm. Prepare a solution at the rate of 200 g of salt per 1 liter of water and heat to 50 degrees. or a little higher. Immerse the product under study in it and keep it there for a quarter of an hour. Bronze will remain inert, while copper will change color.
Another technique is patting. This is the process of formation of an oxide film under natural conditions. An old piece of copper is already covered with a bluish-green coating, but a newly minted or cleaned one will inevitably become covered with it for some time. Bronze is not patinated.
How to distinguish copper from aluminum
Pure metals are easily distinguished by color. However, quite often there is a need to identify tinned copper, which has a silvery color, or copper-rich aluminum, which has a yellowish color. Both alloys are used to make the cable, and in some cases it is important to know what it is made of. In such a situation, visual analysis will not yield results.
The easiest way is to measure resistance. For a hundred-meter copper wire this value is 4 - 8 Ohms, while for an aluminum wire it is about 12 - 20 Ohms. The advantage of this technique is that the cable is not damaged.
Another method is based on different bending strengths. If you bend and straighten an aluminum core several times, it will break, but a copper core will withstand such a test.
Finally, you can hold the cable in the fire. Aluminum melts already at 600 degrees, copper - at a much higher temperature. It is necessary to understand that when heated, especially over an open fire, copper will quickly become covered with an oxide film and change color. This can be used to distinguish copper from other alloys.
Another universal method is exposure to nitric acid. Gently drop the reagent onto the product. The metallic copper in the contact area will turn blue-green.
How to distinguish copper wire from aluminum
Types of twisted pair cable CCA, pros and cons of copper and aluminum wire, advantages and disadvantages of UTP CCA cable, differences between CCA Copper Coated Aluminum and CCA Cooper Clad Aluminum
Copper Aluminum Wire CCA (Bimetallic Twisted Pair)
In this article we will tell you what a bimetallic twisted pair is, what are the pros and cons of copper and copper-aluminum twisted pair, and we will explain the difference between CCA from different manufacturers.
CCA is a general designation for a copper-clad conductor strand with an aluminum core. A twisted pair containing two metals - copper and aluminum - is considered bimetallic.
The main advantages and disadvantages of copper and aluminum conductors
- low electrical resistance;
- elasticity and mechanical strength of the material and contacts;
- it can be soldered, tinned, welded and even twisted well;
- even after surface oxidation, the contacts have low contact resistance;
- during crimping or installation, surface lubrication is not required;
- high cost of copper and copper-containing products.
- three times lighter than copper;
- several times cheaper than copper;
- electrical conductivity is 1.7 times worse than that of copper;
- an amorphous material that “leaks” from the crimp over time;
- when oxidized, the surface significantly loses conductivity;
- welding is carried out in an inert gas environment, and soldering is impossible without special fluxes with solders;
- The contact area during connection should be cleaned and after connection (except welding) coated with a neutral lubricant.
Copper, optics and copper-clad twisted pair
The reason for writing this article was a question that customers often ask: “Are you using copper, optics or copper-bonded twisted pair aluminum?” With this publication we want to kill two birds with one stone: answer the question and justify our choice.
Copper vs twisted pair
Answering the question, we’ll say right away that at GreenBushDC we use optics and category 5 copper cable. Copper Clad Aluminum (CCA) was abandoned from the very beginning and here's why.
The main and, perhaps, the only advantage of copper-plated twisted cable is the price. It is 3-3.5 times lower than copper. Sometimes a little weight is given as an argument for CCA, but the argument is dubious. The difference in weight matters, if we talk not about segments, but about coils. So the difference between lifting and laying 5-6 bays of copper-plated and copper cable is not that great and the labor costs are approximately the same.
Copper-clad twisted pair in coils
Otherwise, CCA loses to copper on all fronts:
- Copper and aluminum make up a galvanic couple, so the copper-plated aluminum gradually oxidizes at the joints. In general, a bimetal bond always negatively affects the predictability and duration of network operation.
- On segments longer than 35-40 m the link begins to jump, and on longer segments stability problems often arise. At 70-100 m, network performance does not improve even with cables from trusted manufacturers.
- When relaying the cable, the characteristics change unpredictably.
- At small bending radii, aluminum breaks quickly.
- The cable is poorly crimped by the connector, because aluminum, as an amorphous “flowing” metal, requires regular tightening of the connections.
Moreover, taking advantage of rising copper prices, unscrupulous cable manufacturers have flooded the market with dozens of low-grade CCA types with low-quality conductive materials with undersized cross-sections, thin insulation and low copper content. It is impossible to distinguish a high-quality copper-plated wire from a low-quality one by eye, and the manufacturer/seller is not always ready to provide objective information on the category of the pair, the percentage and method of copper plating, and cable diameter. This worsens the already poor possibilities of using copper-clad twisted pairs in cable systems.
Does this mean that copper-plated aluminum absolutely cannot be used in IT infrastructure? No, when installing short communication lines or organizing temporary Fast Ethernet on a limited budget, for example, in an office, CCA can be used. But not in the data center, where stability and reliability are priorities.
Optics vs copper
The GreenBushDC data center cabling system is based on single-mode fiber. The main subsystem is built on OF-300 class fiber. This class of optics provides maximum reliability, has the necessary bandwidth and supports 10 GB applications. In some cases, we also use optics for horizontal subsystems - here optical solutions allow us to optimize the number of cables, which is extremely important when laying a network under a raised floor: the fewer wires, the more free space for supplying air to the cooling units.
Cable system under raised floor
The main advantage of optical fiber is its range. At distances of tens of kilometers, copper cable is no competitor to optics. In addition, optical fiber is resistant to electromagnetic interference, which means there is no need to organize shielding, grounding, or galvanic isolation. Given the advantages of fiber optics, the entire IT infrastructure of a data center could be built on optics...if not for the economics.
The main disadvantage of optical fiber is the high cost of installation and maintenance. It’s not so much the cable system itself that is expensive, but the network transmitters, installation and maintenance work. That is why we use copper cables of category 5 to lay cross-connections up to 55 m. Here, their technical characteristics are quite sufficient to meet the required power and throughput on horizontal connections, where traffic is distributed from the internal backbone to local lines. Here, copper twisted pairs provide both a high level of reliability and the ability to quickly connect new devices and hassle-free service.
Service
In general, the structure and composition of the IT infrastructure in a data center is determined by high connection density, complexity and strict requirements for reliability, flexibility, and scalability. For this reason, in critical areas of the network, we give preference to more expensive, but also more reliable solutions. This approach eliminates potential problems in network maintenance, expands the range of its capabilities and, ultimately, reduces operating costs.
Determination of copper in water and soil
The main methods for determining copper in waste, sewer, river, sea waters, as well as in soil, include:
- atomic absorption direct;
- atomic absorption using chelation
- atomic absorption with processing in a graphite furnace
To determine metal in soil, the most reliable method is using a graphite furnace.
Atomic absorption analysis for the determination of copper in water
The essence of this method is that a soil sample is placed in a graphite tube, dehydrated by combustion and sprayed. The sputtering process involves separating a substance into atoms, which are then filtered and extracted from them the desired metal. To evaluate a soil sample, any photometric method for determining copper can be used.
To determine the metal in water, the most accurate and comprehensive method will be the atomic absorption method using chelation; it allows you to analyze any water, even sea water, which is not possible with the direct atomic absorption method. The essence of this method is to dissolve metal particles using dithiocarbamic acid, water is evaporated from the resulting extract and placed in a spectrophotometer, which determines the presence of copper and its concentration by color.
Composite TPGs as a means of improving the economic parameters of the project and their main properties
A possible direction for improving the economic parameters of an object is the transition to bimetallic conductors (TCC) of twisted pairs. The essence of this solution is that the central part of the TPG is formed from aluminum, and the shell is left copper (the so-called copper-plated conductors). The transfer parameters of twisted pairs with this structure at high frequencies due to the surface effect do not differ from copper ones.
The cable formed from them turns out to be:
- cheaper (the price of copper is about 3 times lower);
- stronger;
- lighter (the specific gravity of copper is 3.5 times greater than that of aluminum).
Cables with composite TPG have the following disadvantages:
- The slightly higher resistivity of aluminum limits the capabilities of PoE remote power systems;
- the throughput of a cable with copper-clad wires with equal line length will be lower compared to a purely copper analogue.
The latter is determined by the data transfer rules adopted for Ethernet network interfaces - they operate in the so-called base band. Due to this, the throughput of the communication channel is determined by its parameters in the low-frequency region, in which composite TPGs give noticeably higher attenuation compared to pure copper ones.
Due to the preservation of the outer diameter of the wires, the twist pitch and the accuracy of its maintenance, the transient attenuation of cables with copper and composite TPGs has no differences. Thus, the noise parameters of the path based on cables of these types do not differ significantly.
Difference between metal and alloy
There are several methods to distinguish non-ferrous metal from its alloys. This can be done both without the use of special means and with the help of chemical reactions and tools. The best experts in metals are the people who work with them, as well as those who are well aware of their properties. So, a person who knows the difference between copper and brass is a foundry worker, a chemistry teacher, a scrap metal acceptor with extensive experience, a pawn shop worker, or a jeweler. All of them, to one degree or another, work with metals and know a lot about them.
Definition of color and sound
The main difference between a metal and its alloys is color. To determine what a product is made of, you need to:
- Clean it from the layer of dirt and patina.
- Examine carefully under daylight or under a white fluorescent lamp. Under no circumstances should the product be examined under the light emanating from an incandescent lamp.
- The best option would be to compare a brass or bronze product with a copper one. A piece of wire, which is always made of non-ferrous metal, is suitable as such an example.
The main differences between copper scrap metal
If there is a certain amount of copper-like scrap accumulated around the house, the question arises: is it possible to make sure that it is really Cu? Is it worth taking scrap metal to a collection point? Is it possible to sell copper in Moscow at a price that will provide a high income?
Scrap metal collection points willingly accept unlimited quantities of products made from pure copper and its alloys, paying for them at favorable prices.
Our prices for copper intake
Type of medicinePrice per kg, rub
| Scrap copper glitter | 360-370 |
| A piece of copper | 350-360 |
| Copper mix | 335-345 |
| Scrap copper burner | 335-350 |
| Scrap tinned copper, burnt waste | 315-320 |
Specialists in the field can quickly and absolutely accurately determine the composition of scrap using spectral analysis using special devices - metal analyzers.
What can you do at home when options for determining the chemical composition of scrap metal are limited?
Some methods may be available to us, in particular:
- using one's own senses;
- use of readily available chemicals;
- exposure to fire;
- use of simple devices.
How to visually distinguish copper from other metals?
First of all, the material is carefully examined to determine the main external distinctive features of copper:
- the color of the metal should be golden pink;
- There is usually an oxide film on the surface, adding a yellowish-red tint.
Only a few metals have a similar color, including gold (Au), cesium (Cs), and osmium (Os). However, since these chemical elements are rare in their pure form and are produced in small quantities, it is almost impossible to make a mistake during visual inspection and identification of Cu among the listed materials.
The material should be viewed in good daylight, as artificial colors tend to be distorted. It is also recommended to get rid of the oxide film. This is done mechanically using a file, which is used to clean the surface, or identification is performed using a fresh cut.
Many copper products are marked. If you try to carefully examine the surface and find the markings, then its presence will allow you to accurately identify the material from the reference book.
How to distinguish copper from brass?
The situation is somewhat more complicated in identifying the copper alloy - brass. Brass scrap is accepted at collection points somewhat cheaper, since in addition to Cu it contains the chemical element zinc (Zn) in an amount of 4 to 45% of the alloy weight.
- Color. The color of the alloy is lighter than Cu. Moreover, the greater the amount of Zn it contains, the more the color turns yellow. Although in the case of a small amount of alloying additive (up to 10%), it is still difficult to identify the metal visually.
- Sound. Brass rings when struck, while soft copper produces a muffled sound. This method is good to use with fairly large products as an example.
- Plastic. When bending Cu, this occurs easily due to its high ductility. In the case of brass, this is much more difficult to do: the hardness of the alloy is higher and, accordingly, the flexibility is less.
- Weight. The average density of brass is 8.6 g/cu. cm, copper – 9 g/cu.m. see. You can identify metal using precise scales (if you have them in your house).
- Shape of chips. After processing, copper shavings have a spiral shape, and brass shavings have a straight needle shape.
- Chemical method. When exposed to hydrochloric acid, a brass alloy forms a white coating on its surface. If you do the same with copper, then nothing will happen.
Methods to distinguish copper from bronze
Simple methods that make it possible to find the differences between Cu and its alloy with tin (Sn):
- Plastic. If you apply pressure to the copper with something hard, a notch will appear in this place. It will not be possible to deform harder bronze in this way.
- Oxidation. Over time, the Cu surface becomes covered with an oxide film, which changes the color of the metal. Bronze alloy does not oxidize in air.
- Chemical method. In a metal container, a saline solution is heated to 50 degrees at the rate of 200 g of table salt per 1 liter of water. If you place copper there for 15 minutes, its color will change. Bronze alloy will not react in any way to such conditions.
How to distinguish from aluminum?
Tinned copper and copper-plated aluminum (Al) are often used in cable and wire products. Metals can be identified in this way:
- Color. Copper-plated aluminum has a yellow tint, and the surface of Cu after tinning becomes silver.
- Plastic. Copper conductors are several times more stable when bent and unbent, while aluminum conductors break quickly.
- Resistance measurement. The resistance of copper twisted pair (100 m) ranges from 4 to 8 Ohms, aluminum - from 12 to 20 Ohms.
- Exposure to flame. Al begins to melt at 600 degrees. The temperature at which signs of Cu melting appear is much higher.
Other cases of fire and acid testing
When copper is exposed to an open flame, it begins to tarnish until it becomes completely dark.
If Cu is exposed to nitric acid, the surface at the point of contact will turn blue-green.
how to distinguish copper from other metals
Any questions?
Order a consultation with a manager for free!