The problem of waste disposal in the modern world is one of the most acute. Every second, cities with millions of inhabitants dump cubic meters of waste water contaminated with household chemicals and solid waste into the sewer system. As a result, chemical compounds are formed that can not only pollute, but also fatally poison underground water sources, soil, and air. On a planet with an increasing number of inhabitants, such waste of environmental resources is an unacceptable luxury. Ever wonder where polluted water goes? We study sewer drains.
Journey down the funnel pipe
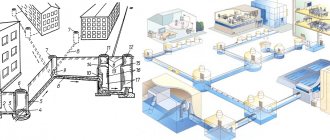
After the dirty water has flowed down the drain, it ends up in the sewer system. First, to the house building: there, the drains of different apartments are connected in collectors. Then the flow of sewage becomes larger and passes through a whole bunch of collectors, combining flows from different houses and neighborhoods.
Water flowing into the sink drain hole
Along their route, rivers of household wastewater flowing in main sewer pipes under sidewalks and roads are replenished with industrial wastewater, as well as rain and melt water flowing into storm sewers. In the end, everything ends up in sewer basins, divided by district. And then - to treatment facilities, depending on the size of the settlement - regional or city. For example, the wastewater treatment system of the St. Petersburg Vodokanal treats more than 2.1 billion m³ of wastewater daily at 3 treatment stations.
Reservoirs of a biological wastewater treatment plant
This is how the sewer system of any settlement works. The main element in it is treatment facilities
Because disposing of wastewater is half the battle, it is important to treat contaminated water to the point of safe return to natural water basins
Anyone who drinks water has a vested interest in ensuring that it is clean and safe—free from hazardous chemicals and pathogens. The owner of the cottage must realize that the quality of the water that his child pours into a glass from the kitchen tap depends on how he cleans up what has flowed into the toilet.
What happens to wastewater after it enters the sewer system?
sewer
The first receiver of household waste from each apartment is a sewer pipe. Then the water flows through the common building riser into the city sewer. The diameter of the pipeline here is large enough to accommodate an average of 2 million m3 of sewage per day. Often a city highway has a diameter of 70 cm or more.
Along the way, domestic contaminated water is combined with storm waste in the city sewer. They are either transported by gravity when the terrain is favorable and a slope has been created, or they continue to flow through the collector using powerful pumps.
All collected waste flows into sewer basins in the districts and is then sent to a treatment plant. As a rule, it is arranged outside the boundaries of a populated area. The point here is not about sharp specific odors, but about the scale of the enterprise. The station covers an area of up to several km2.
The length of the urban sewer depends on the size of the settlement and can be more than 5,000 km in total (for cities with a population of over a million).
The city wastewater treatment system does not accept wastewater from industrial enterprises. These polluted waters have their own purification systems.
Where does the sewer go?
It’s unlikely that anyone wonders where the waste that we flush down the sewer pipes goes to. And they have a long journey ahead of them.
First of all, it must be said that enterprises use their own individual cleaning system. That is, waste from large factories is not connected to the citywide sewerage system.
As a rule, such a system has a cycle: water is used for technical purposes, then it goes for cleaning, and then returns to the workshop for the next use.
Everything is clear here. What about the city sewerage? We decided to take Moscow as an example of interesting facts about cities.
Nowadays, one can often hear outrage that the Moscow River will soon turn into a swamp due to the fact that millions of tons of sewage waste from the city and even enterprises flow into it almost directly.
In reality, everything is not so simple. If this were true, then the Moscow River would have long ago become a real septic tank, and everyone who swims there would be infected with various diseases.
It must immediately be emphasized that waste from human everyday life in liquid form flows into special treatment facilities that exist in every city. This is the key point.
Where does the sewer flow? Interesting facts
Inquisitive minds often ask questions that not every average person would think of. For example, where does the sewer flow? But this is really extremely interesting.
There are all sorts of rumors about this. Someone says that all the city sewerage flows directly into the river, so swimming on city beaches is not recommended.
Others claim that liquid waste goes underground through special drains and is absorbed into the depths of the soil.
note
However, if you just imagine how many millions of cubic meters the residents of Moscow allocate every day, there won’t be enough soil to “suck” it into itself.
We have prepared for you interesting facts and photographs about what happens to the sewer after it leaves our home.
Where does the sewer go?
It’s unlikely that anyone wonders where the waste that we flush down the sewer pipes goes to. And they have a long journey ahead of them.
First of all, it must be said that enterprises use their own individual cleaning system. That is, waste from large factories is not connected to the citywide sewerage system.
Everything is clear here. What about the city sewerage? We decided to take Moscow as an example of interesting facts about cities.
Nowadays, one can often hear outrage that the Moscow River will soon turn into a swamp due to the fact that millions of tons of sewage waste from the city and even enterprises flow into it almost directly.
In reality, everything is not so simple. If this were true, then the Moscow River would have long ago become a real septic tank, and everyone who swims there would be infected with various diseases.
It must immediately be emphasized that waste from human everyday life in liquid form flows into special treatment facilities that exist in every city. This is the key point.
What happens to the sewer in the end?
In a nutshell it can be described as follows. When liquid waste from city sewers flows into wastewater treatment plants, it undergoes a primary stage of treatment, which results in the precipitation of sludge.
You will be surprised, but this is a really interesting fact: from this sludge they then make... gas.
Schematically, the sewage waste treatment process is as follows:
So, at the very beginning, sewage enters the treatment system through giant pipes. Traffic is approximately 2.5 million cubic meters per day:
Important
Next, the first stage of cleaning is filtration with special gratings of waste larger than 10 mm:
Now the water enters the first settling tank, where it remains for exactly two hours. During this time, the settled organic matter is sent for biogas production, and the rest goes further through the system:
This is the second sump:
In general, there is a constant analysis of water coming from the city’s drains, tap water and purified:
And only after such thorough purification does water enter the Moscow River directly from this reservoir:
Now you know where all the Moscow sewers flow and what happens to wastewater and other sewage. All cities in the world operate on approximately the same cleaning principle.
Otherwise, the very existence of megacities would be impossible.
By the way, read interesting facts about Russia - you will learn many amazing things. We also recommend subscribing to InterestnyeFakty.org. It's always interesting with us!
Did you like the post? Press any button:
Where do the poop go? Where does the shit go from the toilet?
The previous answerers(responders?) are right, but there are alternatives. Different countries have different requirements for wastewater quality.
In theory, household wastewater ends up in the sewer system (if we are talking about cities), and then through it to a treatment station. Wastewater has many characteristics - solids content, VOC (Volatile organic compound) - indirectly characterizes the amount of organic matter in the water, salt content, etc. In principle, purifying water from poop is a fairly simple process. It is much more difficult to purify the water from those remnants of drugs and other chemical nastiness that end up in drains either passing through people, or like washing powders and stuff like that - such pollution is very dangerous for fish and crabs and stuff like that. For example, in Seattle, due to the high content of medications in wastewater, salmon in the bay began to get sick and generally feel unwell. Another big factor is where the waste is dumped - river, lake, ocean.
(if you eat now, quickly finish the juice; the juice will be about poop)
Now about the feces itself. We must be aware that by the time wastewater reaches the treatment plant, this water is a fairly homogeneous liquid - water and all sorts of organic things float in it. In appearance, it is a dark, opaque liquid with a strong, strong, very strong odor. The first stage of cleaning is the settling tank. There, large pieces of “organic matter” settle to the bottom - we’ll call it silt (we’ll come back to it later). After this, the water is just a cloudy yellow-green color with the same, rather intense smell. The next stages of treatment can be either aerobic or anaerobic, using activated sludge, etc. The end result is a little more sludge and water with a low VOC (why this is important is a separate question), but there are still bacteria, chemical contaminants, salts, the pH may shift. The next stages of cleaning can handle this, and we return to what settled at the bottom in the first two stages of cleaning.
Where does purified water flow from septic tanks in a private house?
Many people are interested in the question of where purified water flows from septic tanks in suburban areas.
There are several options for where to discharge treated sewage water:
- Filtering field. Such fields are a platform of sand and gravel; passing through it, the water undergoes final purification. Water from the septic tank is transferred to such fields through pipes using a pump or by gravity.
- Filtration well. It may represent a third septic tank. Water is drained into it from the previous container. At the bottom of such a structure lies a thick layer of sand and gravel, passing through it, the wastewater is additionally filtered.
- Artificial biological ponds. Already purified water is drained into them. Here it undergoes additional filtration.
- Cassette filter systems are used infrequently, as they occupy a large area. In this case, special trenches are created with several layers of natural filter.
Artificial systems into which purified water is drained have a service life of no more than 10 years. After this, the filter layer will have to be completely replaced.
Where does the sewerage flow in Nizhny Novgorod? What is a modern septic tank?
A septic tank is usually understood as an autonomous treatment facility, which includes a plastic tank, inside of which there are special chambers. Depending on the model of the structure, there may be two, three or more cameras. They carry out gradual filtration of sewage water.
Sewage flows into the septic tank, is successively cleaned of contaminants and discharged into the filtration field. The degree of purification, in this case, can reach 98%. Water purified in this way is quite suitable for country farming (for example, irrigation).
The main elements of a modern and reliable septic tank:
- a receiver where all household sewage flows, clearing large debris;
- anaerobic chamber where biological decomposition occurs;
- a settling tank in which small particles settle.
Such a system is an ideal solution for a country cottage or summer cottage. Plastic septic tanks have many advantages over traditional sewage systems (cesspool, bio-toilet, etc.). This is why residents of Nizhny Novgorod and the Nizhny Novgorod region are increasingly deciding to install a septic tank.
Key benefits:
- septic tanks are installed in the ground and take up minimal space;
- there is no sewage smell at all;
- you can use the toilet and water without restrictions (if you choose the right equipment model based on the needs of a country house);
- the plastic construction, if installed correctly, is very reliable and durable;
- the system is relatively cheap, you can choose equipment at a suitable price;
- operation is also inexpensive and easy;
- environmental Safety.
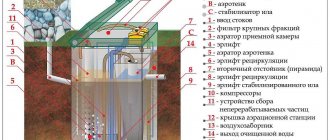
What is a septic tank and how does it differ from a metatank or aeration tank?
Anaerobic treatment devices
Devices in which biochemical reactions occur with the participation of anaerobic bacteria include a septic tank. This is an element of treatment facilities, which is a sealed container made of plastic, concrete or metal. In the septic tank, the primary purification of wastewater and its settling takes place: what has a higher density than water precipitates at the bottom, lighter contaminants float on top, forming a crust.
Installation of an autonomous deep wastewater treatment plant
Depending on the design of the septic tank, its internal volume can be divided into 3 sections by partitions. After the wastewater passes through the drain pipe, it enters the first chamber, where the settling process begins. The chamber is gradually filled with wastewater, a sediment of activated sludge and insoluble debris accumulates at the bottom, a crust forms on top, and the liquid flows into the next section, where the processes continue. Thus, in the first part of the septic tank the largest particles of contaminants fall out, closer to the outlet the layer of activated sludge decreases, and the wastewater becomes increasingly clearer.
At the exit from the septic tank, wastewater contamination is about 65% of the original level. Effluents with this degree of contamination are sent for soil treatment - in filtration fields, irrigation fields, biological ponds, filter wells or cassettes - depending on the specific design of the treatment plant.
Thus, a metatank is a septic tank: the processes in it release methane, which is released into the atmosphere through ventilation. This type of artificial treatment plant imitates natural conditions that occur deep underground or in swamps.
Aeration treatment plants
If the activity of aerobic forms of microorganisms is used to purify wastewater, then their life requires a constant supply of oxygen.
Aeration treatment facilities. Photo from the site novostroi.spb.ru
Aero tanks are more complex devices; they require a constant connection to electricity for the compressor to operate. This means they are more expensive and difficult to operate. Aeration treatment plants are used if the volume of wastewater is large or a higher degree of water purification is required, for example, to discharge clarified wastewater into a reservoir - the sanitary requirements in this case are more stringent. In aeration tanks, conditions similar to natural reservoirs are created for bacteria.
Indoor networks
The first place where water from the sewer goes is the horizontal part of the system inside the apartment (the sun lounger). All plumbing fixtures are connected to it. At the end it is connected to a vertical pipeline - a riser, through which wastewater and organic matter go into the basement of the sewer system. It must be taken into account that the riser belongs to the common property of the house, while the sun lounger is the property of the apartment owner. Responsibilities for maintenance and upkeep of these elements are assigned accordingly.
After the wastewater is discharged into the underground part of the system, it goes to neighborhood lines, which then merge into citywide mains. The predominant part of the systems is gravity, the liquid moves through them independently. To achieve this, the pipes are laid at a slight slope. There are systems where the supply is provided by special pumps. Such lines are called pressure lines. They are used where it is impossible to ensure pipe slope. In addition, pressure lines are used when it is necessary to drain wastewater into a tank located at a higher level than the pipeline system.
Answers from experts
Alexei:
It's different in different regions. Somewhere, passing through treatment facilities, it is drained back to where it came from, somewhere it is drained immediately, and in regions with water shortages, it settles in pools, undergoes purification with chemicals and bacteria and is again sent to the water supply or to irrigate fields.
Pavlik:
This is the water cycle in nature.
Xoma:
Through wastewater, it ends up at a local treatment plant, where it is treated with bleach and waste is screened out, and then again into the tap.
Artem:
It goes into settling tanks, where it is treated with chemicals, passes through filters and is again supplied to the water supply system.
But this is not everywhere.
Oleg Avdeenko:
through sewer drains to water treatment plants. after mechanical and chemical cleaning it goes back into the reservoir (for example, in my case, into the Volga). and then through water intakes and pumping stations back to the tap...
Kirovpromventilation:
goes into the sewer, then undergoes treatment and is drained. It does NOT become drinkable. Drinking water - intake from a reservoir (river) - purification - pumping into the water supply system
Magomed Tagirov:
Our water goes straight into the sea))
Timonok:
I was once at a sewage treatment plant where sewage flows. There were square settling basins everywhere, 3-4 meters long, filled with thick, black, stinking slurry per kilometer. In general, they explained to me that this slurry settles, separates from the water and pours out into the river, I can’t say for sure it was a long time ago.
telemaster:
So, does everyone here drink water from the sewer?? ? For example, all our drinking water is artesian. The average depth of water intake from wells is 200 meters.
Natalya Kozykina:
and then through water intakes and pumping stations back to the tap....
Zwanka:
As a result of daily human activities in everyday life and at work, various types of waste, refuse, garbage, remains of raw materials, products, food, etc. are accumulated. Mixing with water, these contaminants form wastewater, which should be immediately removed outside populated areas and industrial enterprises. Contaminated rainwater from the territories of some industrial enterprises must be removed outside populated areas.
Sewerage is a complex of engineering structures, equipment and sanitary measures that ensure the collection and disposal of contaminated wastewater outside populated areas and industrial enterprises, as well as their purification and neutralization before disposal or discharge into a reservoir. Before discharge into water bodies, wastewater is purified by mechanical, chemical and biochemical (biological) methods.
To neutralize and destroy pathogenic bacteria, purified water is disinfected before being discharged into a reservoir. The sludge collected at treatment plants is dried naturally on sludge beds or artificially dewatered (in large volumes) and used for fertilizer.
In some cases, specially prepared land plots - irrigation fields - are used after wastewater treatment on them for growing crops, ornamental and fruit trees. If the fields are used only for wastewater treatment, they are called filtration fields.
You can read more here
oracle:
Much closer!! ! To the nearest river, having previously undergone purification and filtration.
Where does sewage waste go? Where does everything that we flush down the toilet go to?
When there were far fewer people on the globe than there are today, used water and waste were diverted from homes and industries through sewer pipes and discharged into large bodies of water.
Sewage disposal in those days involved allowing the effluent to mix with salt or fresh water, which would dilute it. Today, in our overpopulated, highly developed world, wastewater must undergo a purification process in order not to contaminate the world's water supplies. During the decomposition (decay) of waste - under the influence of bacteria - a large amount of oxygen is consumed, and if such decomposition occurred in a river or lake, then the plants and animals living in them would lack the gases necessary for life - oxygen and carbon dioxide. Some types of waste, such as human and animal excrement, also contain harmful bacteria. If such bacteria accumulate in large quantities and people come into contact with them, it can cause infectious diseases.
So when you flush a toilet or pour dirty water down a drain, the wastewater is sent to a wastewater treatment plant. This is done to protect you and the environment. Wastewater from your home is piped into larger diameter sewer pipes located underground—sometimes so large that the wastewater flows through it like a river. (It happens that accumulated groundwater and storm water are also discharged into the sewer network.) On the way to the treatment plant, wastewater from residential buildings and industrial enterprises of the settlement is merged into one stream.
(In some communities, where homes and businesses are or were once located far from each other and where it is practically unprofitable to maintain a sewerage system, wastewater is often discharged into huge septic tanks - colossal tanks installed underground near each household. Most sewage decomposes in septic tanks under the influence of bacteria, but these tanks have to be emptied and cleaned quite often.)
When wastewater enters the treatment plant, it is filtered through a large metal screen. This grid separates large items that cannot be recycled. Small stones and sand are also filtered out. After cleaning and drying, these materials can be used in construction and road repair. After this, the “fragrant”, soup-like wastewater, passed through a grate, enters a huge settling tank, where the solid particles eventually sink to the bottom. This dirty sludge enters a special treatment tank where bacteria feed on it, turning it into harmless substances.
This decomposition process produces methane gas. This gas is used as fuel to produce steam, which powers the pumps running a wastewater treatment plant. The resulting sludge from these processes is rich in nutrients and can be used as fertilizer. The liquid part of the wastewater, after separating the sediment, is fed to the filter loading, where it undergoes purification. Here, cleaning occurs in this way: water seeps through a layer of loading - stones covered with bacteria, and the bacteria eat all the remaining waste. The clean water that results from this entire process is discharged into rivers, lakes or seas.
From your own home
Quite often, people begin to think about where the polluted waste goes, having bought their own home without amenities. City dwellers, accustomed to using a toilet in an apartment, are racking their brains about how to drain waste according to all the rules and where to dispose of wastewater?
There are several cleaning options for autonomous sewage systems, after which it is possible to discharge the purified liquid into nature. When installing the system, be sure to take into account the depth of underground sources, the nature of the soil on the site and other features.
Septic tanks
To set up an autonomous system, you can use a septic tank, which is a large sealed container, and the drains are cleaned using bacteria.
The water entering the container settles, solid particles and bacterial waste products settle to the bottom. Over time, it needs to be cleaned by pumping out solid sediment using a sewer truck.
Varieties:
- An aeration tank using aerobes requires constant operation of a compressor pumping air into the tank.
- A digester tank using anaerobes requires the removal of methane gas, which is formed as a result of the activity of anaerobic microorganisms.
The main disadvantages are its high cost and difficulty in installation. However, once installed, the service life is unlimited.
Filter field
According to sanitary rules and regulations, it is strictly prohibited to drain sewage from a septic tank into the environment. If it flows into a neighboring river, you may be fined by the sanitary and epidemiological station. Water can only be freely drained into a ditch or pond from storm drains.
For additional purification, use a filtration field, one or more. The filtration field consists of pipes through which liquid flows from the container and is poured onto the surface or deep into the prepared soil filter. Such a filter is made from a large layer of sand and gravel, taking into account the absorption capacity of the soil and other features.
Well
For final filtration, you can use a vertical well with walls lined with stone or brick. A filtration layer of sand and gravel is laid at its bottom and pipes from the septic tank are supplied. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the volume of discharge and correctly calculate the size so that the well can successfully cope with any incoming volumes. And also: soil absorption capacity, groundwater level, soil freezing depth and other features.
Instead of a well, you can use a deep filter trench, which is arranged according to the same principle as a well.
Ponds
Such biological filter ponds are used if it is possible to place them at a considerable distance from the house, since the smell of septic tank waste will not improve your relations with your neighbors.
Plants that vigorously consume liquid are planted around the pond. For example, young birches or other trees. This will speed up the filtration. In addition, special algae are cultivated in such ponds, which additionally purify the water from excess nitrogen and phosphorus (the waste products of bacteria in the septic tank).
Cassette filtration
Filter cassettes are used if the soil is clayey and does not absorb moisture in the required volume. They are bulk filters into which liquid from the septic tank flows through pipes. Next, the water is collected in a drainage collection system. Filtered using the cassette method, it is used to irrigate crops or for other technical needs.
Any artificial system becomes unusable after some time. Average service life is from 8 to 10 years. After this, you will need to clean the walls and completely replace the filter layer. Or build a new building.
As a result, we can say that water from the sewer still ends up in nature. Therefore, every person who uses sewerage must remember that the purity of drinking water depends on him as well. This is especially true for owners of their own houses, whose waste water goes into a local river, reservoir, or lake.
From a city apartment
Directly from city apartments and houses connected to the city sewerage system, waste water goes into the collector system.
The entire city is riddled with large and small highways of underground pipes through which contaminated liquid waste flows. Drains from industrial enterprises, household waste, rain and melting snow, which enter the system through storm grates, are drained here. Then the sewerage is combined in large sewerage basins, and from there it is sent to treatment facilities - stations. At stations they undergo several stages of thorough cleaning. The main methods used at all stations:
- mechanical;
- chemical;
- biological.
After all stages, having passed strict control, the water can be used for the technical needs of the city or discharged into settling tanks.
Mechanical
This method is used at all treatment plants - it can be called preliminary. It allows you to get rid of the garbage that people, without thinking, dump into the system.
The official application from the bookmaker 1xBet is absolutely free and you can click on the link and place bets on sports.
To filter solid particles, discharges are passed through sieve-shaped coarse and fine mesh filters. They get rid of large and small insoluble mechanical particles. Filters capture everything from polyethylene to pieces of bricks and construction sand.
The final stage - after settling, the liquid passes through a sand trap filter, which removes even minor mechanical impurities.
Naturally, this method is not final; after it, several more methods must be used to improve the result to the maximum possible.
Chemical
A certain reagent is added to the settling tanks, which helps get rid of harmful chemical compounds and neutralize them. These compounds are bound by the reagent and precipitated into the sludge. The chemical method also includes the use of adsorbents, which adsorb harmful compounds on their surface and sink to the bottom of the sump. This method has significant disadvantages:
- Requires a large sludge tank;
- High-quality reagents are quite expensive;
- The reaction can slow down significantly during the cold season;
- It takes time to react.
However, this method is the best for getting rid of harmful chemicals, and therefore is used in large industrial enterprises and wastewater treatment plants.
Biological
The most effective and environmentally friendly method is with the help of bacteria that utilize fine organic matter. In this way, the quality of sewer discharges can be improved by 90%.
For the private sector, special septic tanks have even been invented that allow you to filter the wastewater of a private home and make it suitable for irrigation or other technical needs.
Selecting a storage tank for sewage
The disadvantages are:
- Inability of bacteria to clear chemical compounds;
- Their sensitivity to chemical compounds. Using household chemicals can destroy the population in the container, so from time to time you need to replenish it by flushing the bacterial culture down the toilet.
There are two types of cleaning using bacteria: aerobic and anaerobic. In the case of anaerobic, organic matter is utilized by bacteria, whose vital activity takes place in an oxygen-free environment. The efficiency of this process is up to 70%. In addition, additional grease traps and settling tanks are installed, and solid sediment is regularly pumped out.
Aerobic culture, on the contrary, reproduces better in the presence of oxygen. This cleaning method is considered more effective and simpler; aerobes more actively utilize organic matter. It also requires pumping out solid waste, but much less frequently than the previous method.
At urban wastewater treatment plants, both methods are used, connecting reservoirs using pipes and various filters.
For your information. Recently, large wastewater treatment plants have introduced an innovation - ultraviolet disinfection. It helps disinfect water from pathogens.
How wastewater is treated
The city sewer network differs from the local sewer system of a private house only in its size. The local sewage system of a country house should also be equipped with treatment facilities. Let's figure out how wastewater treatment occurs.
In most cases, the process is based on a classical scheme consisting of two stages:
- mechanical cleaning;
- biological treatment.
In some cases (for example, if treated wastewater must be discharged directly into a reservoir), a physicochemical method is also used, as well as water disinfection.
Mechanical cleaning
The first stage of cleaning is mechanical
At this stage, using conventional mechanical filters - grids with different cells - waste insoluble in water is caught: pebbles, broken glass, plastic parts from hairpins or toys, earring rings - in general, everything that accidentally fell into the sink drain or toilet
Mechanical filter
Mechanical cleaning systems also include grease traps - grease traps, which, although organic, are very poorly processed by bacteria or are not processed at all. If there is not too much wastewater, then the mechanical cleaning stage is usually neglected.
Biological treatment
The biological method of wastewater treatment was developed in 1913 in England. It is based on the life activity of a whole army of microorganisms - various amoebas, ciliates, rotifers, zoogles and others. This whole company makes up the so-called activated sludge in wastewater treatment plants.
Microorganisms
What the sewage consists of serves as food for these microorganisms. With the help of enzymes located in their cells, they decompose organic substances, which mainly consist of household wastewater.
Biological processes of organic oxidation in wastewater treatment plants can occur with the participation of aerobic forms of bacteria - those that require oxygen for breathing, and anaerobic - those that do not require oxygen for their life. Aerobic bacteria decompose organic matter in wastewater into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water, and ammonia nitrogen and sulfates into simple substances, nitrogen and phosphorus. If there is no access to oxygen, then a community of anaerobic microorganisms develops, and biochemical processes proceed with the release of methane (CH4). All this biochemistry leads to the release of energy, which is used by bacteria for their existence and reproduction.
Similar processes involving the same company of microorganisms in nature occur continuously - aerobic microorganisms live in the upper layers of the soil and in water bodies, anaerobic bacteria live in the lower soil layers. The vital activity of plants is inextricably linked with the life of microorganisms found in the soil and natural reservoirs; thanks to them, humus and compost are formed. Therefore, the cleaning method is called biological.
Where does the water go after treatment facilities? Sewage drainage
Domestic sewage goes either to local treatment systems (for example, to a septic tank near a country house), or to the citywide sewer network, where it first goes to sewage pumping stations, and from there to city treatment facilities. In many cities, wastewater from industrial enterprises also flows into the city sewer system (with or without preliminary treatment).
The main element in this system is treatment facilities. They are designed in such a way that wastewater must go through several successive stages of purification. First, wastewater goes to mechanical treatment facilities. At this stage of purification, the largest and heaviest suspensions are separated. Next, the wastewater is cleaned of the bulk of undissolved contaminants, after which it goes for biological treatment. After this stage, disinfection (disinfection) of wastewater is usually carried out. Purified and clarified waters undergo sanitary control and flow into the reservoir.
An important function of treatment systems is the processing of sludge formed during the treatment process. For this, the following scheme is used. If the station has digesters (facilities for digesting sludge), the raw sludge after the primary settling tanks goes there.
In small sewer systems, there may be no digesters; the sludge after the primary settling tanks immediately goes to dewatering plants or flows into sludge ponds, where it undergoes biological treatment. At some stations, a chemical cleaning stage is added to the above scheme. In this case, chemical reagents for coagulation are added to the wastewater before the settling tank.
Biological treatment can be complete or incomplete, depending on the required degree of purification. The choice of a specific system (aerobic or anaerobic) depends on the throughput of the station, and the possibility of allocating land for irrigation fields is also taken into account. If there is not enough area for this, aeration tanks are used.
Why we abandoned the installation of local sewerage using a septic tank
When looking through options for installing a toilet familiar to a city dweller in a village house, we decided against a septic tank or another option for local sewerage. Why?
financial issue
To do everything correctly, taking into account sanitary standards, requires a decent amount of money. Even if you try to save money by using three concrete rings, Eurocubes or other containers instead of a ready-made septic tank, the amount of excavation work to install filtration fields is colossal. Especially considering the characteristics of the soil in our area - clay at the depth of a shovel bayonet and the groundwater level half a meter from the surface.
To do everything correctly, taking into account sanitary standards, a decent amount of money is required. Digression
high groundwater level
This means that we are doomed to build above-ground structures for soil filtration: we need to build a hill with an area of at least 30 meters and a height of almost 2 m. And the water itself will not flow upward - the septic tank is located in the ground, which means we need a pumping station . And this also means money and constant dependence on electricity.
water supply
Where do you think most of the water in a typical apartment goes? Until I did the math, I thought that most of the water was spilled in the shower. It turned out not: up to 45% of the total daily water consumption per person in a city apartment comes from the toilet.
Up to 45% of the total daily water consumption per person in a city apartment comes from the toilet
There is a lot of water in our area: you can dig a well almost without looking, anywhere. But the debit of such a well is small, and in the summer it decreases even more. It turns out that if we want to install a flush toilet, we need to spend another N amount of money on extracting water, half of which is literally flushed down the toilet, in order to then build complex and expensive structures to clean it.
The septic tank needs to be cleaned
Regularly - depending on the volume - remove the sludge accumulated in the sump. If it is not removed, it will eventually fill the septic tank compartment. And if removed irregularly, the degree of wastewater purification will decrease. To the point that the concentration of contaminants at the outlet will be greater than at the inlet: water flowing through a silted septic tank will wash away the settled substances and become dirtier than it was. Aeration treatment facilities need to be cleaned less frequently. But they also cost more.
The septic tank needs to be cleaned
filter field service life
The filtration field also has a shelf life of 8-10 years. Then the gravel and sand backfill of the drainage pipes silts up and stops cleaning the drains. The only way out is to make a new filtration field, this time excavating the second half of the site. Well, or in our case, dig up the hill, replace the filter backfill and fill the hill back.
adequacy of the event
And it’s not even a lack of extra money, although this fact is also important: after moving from St. Petersburg to the village, I had to change my occupation (it’s unlikely that my neighbors - Grandfather Anatoly or Aunt Dusya - need the services of an interior designer), and therefore change my level of income . The point is adequacy: our entire hectare and 3 acres, garden, house and outbuildings cost well, if a fifth of the estimate is for the installation of a local sewerage system. Looking for additional sources of income, working hard just to be able to habitually press the flush button after visiting the toilet? Why then did we leave the city and give up a decent job - there were no problems with the sewage system, and the toilet worked properly.
Considering all that has been said, we decided that local sewerage is not suitable for us. But this does not mean that we plan to use the yard toilet in a wooden booth in the garden. We want a completely civilized toilet. We simply opted for another system for disposing of human waste - a composting toilet. I talk more about it in the publication Continuous composting toilet: device, operating principle, advantages.
Determining the location of the blockage
A clogged sewer is not a problem, you just need to determine the root cause. As a rule, these are errors during installation work in the house or uncharacteristic slope of the pipes, the appearance of a large amount of corrosion or icing and, as a result, a decrease in the effective diameter of the pipes in winter. A harbinger of impending danger is a rather unpleasant smell that appears from communications. Therefore, if you smell an unpleasant odor, you should try to take all possible measures.
If the drain is clogged, what should you do? You need to try to find out the extent and cause of the blockage as early as possible. The blockage usually occurs in the house, local communications, but sometimes external pipes become clogged. To clean, you need to disconnect the sewer pipe that enters a private house or apartment, for which you should do the following simple operations:
- We place any free container (basin or bucket) under the pipe;
- We disconnect the pipe with a special wrench, that is, you need to pull the inner pipe out of the outer sewer pipe. If there is a threaded connection, then first we knock out the seal;
- We collect all garbage and leaking sewage in a separate container;
- We open the mixer to supply water in the right place and visually observe whether water flows from there or not;
- If the water does not pass, or the water pressure is much less than expected, then turn off the water and look for the blockage locally. If there are no problems in this area, then you need to look for blockages in external communications.
Moscow Central Sewage Pumping Station
| Comments: | |
| (Link) |
is this really about this station? As a child, we almost climbed inside, but the kind security dissuaded us :) they really didn’t let us on the excursion. I always thought that it was from the flooding of Zamoskvorechye or is it something else? (no subject) – simsun
Expand(no subject) –
alex_avr2
Expand
| From: mitia_baban 2016-07-08 04:17 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
Well, why are you doing this with the nameplate, now you need to wash the monitor... =) and so - it’s too much...
I’d like to look at the cross-section of the pump, at the real one, that’s interesting...
(no subject) – mitia_baban
Expand(no subject) –
iime
Expand
| From: undergroundfoto 2016-07-08 04:37 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
Interesting) Especially about the days of peak flows... one can see the tendency of people to wash before New Year and September 1
| From: alex_avr2 2016-07-08 04:52 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
Well, the head of the sewerage department said that he calls August 31st the day for washing children before school :) Like everyone is preparing for September 1st, they come from their dachas on vacation, etc. But only if September 1st is a working day. And December 31st, if it’s a working day, then everyone comes home in the evening and starts being active, and then it’s very difficult. And if it’s a day off, then they start in the morning and it’s fine
And the day with the least consumption is the day of Russia, suddenly
(Parent) (Thread) (Expand)(no subject) – wazawai_n2
Expand
| From: simsun 2016-07-08 04:41 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
By the way, not all the stations are on panels, offhand I immediately remembered, far from there: Runovskaya, I wouldn’t have known about her if it weren’t for the very strong smell nearby (no subject) – simsun
Expand(no subject) –
alex_avr2
Expand
| From: der_wilde_hund 2016-07-08 05:04 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
Thank you, very interesting material!
It would be great to see the consumption statistics. Look for non-trivial correlations. True, everything is probably very secret.
| From: wazawai_n2 2016-07-09 05:46 am (UTC) | (Link) |
“The pumps are driven by huge motors, each with a power of 1.6 MW. For comparison, this power is comparable to the power of one metro train or approximately 160 apartments.” Not the best comparison. The pump has operating mode S1 - its installed power is close to the consumed one. This is not the case with apartments and even electric trains. “The station has an impressively sized switchgear (integrated switchgear).”
Complete.
| From: drink_drunk_roo 2016-07-09 08:26 am (UTC) | (Link) |
Yeah, it turns out that an apartment uses 10 kW, but in my house, according to the standards, it’s 4 times less, so that’s already 640 apartments
| From: drink_drunk_roo 2016-07-09 08:32 am (UTC) | (Link) |
Cool! I love posts like this. At work, I came across 10 MVA synchronous motors that drive VOD-40 two-stage axial fans (sorry, I didn’t take a photo of the nameplate). Surprisingly, they are approximately the same in size as here in your photos, 1.6 MV, although I always believed that power and size are directly related.
(no subject) – drink_drunk_roo
Expand(no subject) –
alex_avr2
Expand(no subject) –
drink_drunk_roo
Expand(no subject) –
dimon_w
Expand(no subject) –
drink_drunk_roo
Expand
| From: snarkfog 2016-07-15 07:45 am (UTC) | (Link) |
Interesting. I have been to KNS, but much smaller ones. Are the grates not cleaned by hand here? And then at one of the stations I watched the work of a rake man, who every half hour went down and manually cleaned the grates with a rake.
Work is daily, in shifts. The salary was meager, but he worked there purely for the sake of his pension, because a year was counted as two years, and he had a couple of years left before retirement.
He says that it’s not so easy to get a job as a robber, there is a real competition among people of pre-retirement age :)
| From: vmulder 2017-09-14 05:46 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
Just a bomb! How I love this
Best answers
Len_Ka:
depending on which metropolis... in Europe everything is fair. settling tanks, treatment tanks, clean water - into the river. leftover poop goes to the fields
andrej suzdaltsev:
to the nearest body of water. after cleaning.
Svetlana:
There are huge treatment plants, and that’s where everything goes.
Ruslan Zakirov:
all roads lead to Rome
ashberry:
they undergo multi-stage purification and end up in a settling tank, and from there they go into the river below the city
Oleg))):
Is a million-plus city on the Volga a metropolis? If yes, then to the Volga. This is called spray cleaning. Sewage treatment plants in most cities do not remove or simply become dirty. What did you think?
Tatyana Teplova:
into our water pipes! Do you think anyone is concerned about our health to spend money on all sorts of water purification?
Evgenia Morozova:
To treatment plants, then to rivers.
Natalya Balbutskaya:
We have an AERATION station in St. Petersburg, where what is sifted out during cleaning using special methods is dried and pressed with a vacuum and sent for fertilizer, they say that foreign countries pay good money for this.
List of documents
When deciding to draw up the legal side of the issue yourself, you need to prepare the following papers:
- A site plan prepared by a surveying company, with the house marked on it and a diagram of the pipes for sewer services.
- Certificate of ownership of the house and plot.
- Documentation specifying technical requirements is prepared by an organization specializing in sewerage maintenance.
- A plan for connecting a private pipeline to a central network, developed by a qualified designer.
- The plan consists of a longitudinal profile, a master plan and a master network plan.
- Permission for sewerage in a private house, agreed in accordance with the architectural design.
- Application to the executive company.
During the last stage, you should collect a package of necessary papers, you need to start choosing a company that will be entrusted with the installation of sewerage in a private house to city communications.
Liability standards for draining sewage into a ditch or garden
SNiP clearly prescribes the rules for the collection, transportation and accumulation of human waste. If standards are violated, citizens will be held accountable. In accordance with the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, fines are imposed. According to Art. 8.2 for illegal drainage of sewage water:
- individuals are subject to a fine of up to 2,000 rubles;
- officials up to 30,000 rubles;
- for individual entrepreneurs, fines amount to up to 250 thousand rubles;
- Organizations not only pay fines, but can also stand idle for up to 90 days - the enterprise will simply be stopped until management eliminates the violations.
Loading …