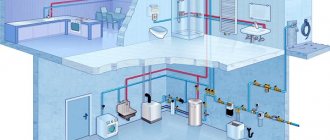
The rules for using public water supply systems are prescribed at the legislative level. They are presented in the form of a comprehensive document and are periodically edited and supplemented.
Rules for cold water supply and sanitation
Rules for using communal water supply and sanitation systems
SP 30.13330.2016 Internal water supply and sewerage
Normative base
All regulations relating to the rules of water supply and sanitation of residential buildings, both private and multi-apartment buildings, are regulated by several documents.
Attention! If you have any questions, you can chat for free with a lawyer at the bottom of the screen or call Moscow; Saint Petersburg; Free call for all of Russia.
General legislation of the Russian Federation:
- Constitution of Russia of December 12, 1993.
- Housing Code of the Russian Federation (Article 188 Federal Law) dated December 29, 2004.
- Federal Law No. 189 of December 29, 2009 “On the entry into force of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation.”
As well as Tariff regulation, Information disclosure standards and the Organization of water supply and sanitation of residential buildings:
- Decree of the Government of Russia No. 6 “On information disclosure standards in the field of water supply and sanitation” (dated January 17, 2013).
- FAS Order No. 792/17 “On approval of forms for providing information subject to disclosure by organizations providing hot and cold water supply and sanitation, and tariff regulatory authorities, as well as Rules for filling out such forms” dated 06/19/2017.
- Order of the Federal Tariff Service No. 2244-e “On approval of the Information Disclosure Regulations” dated December 16, 2014.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 13, 2013 No. 406 “On state regulation of tariffs in the field of water supply and sanitation.”
Building regulations
Residential building drainage and water supply systems are designed and built in accordance with regulatory rules regulated by certain documents. These rules are designed to guide external and internal communication systems.
The basic rules for supplying water to residential buildings include the following:
- All communication projects, the purpose of which is water supply to residential premises, must be coordinated taking into account all the nuances during the construction of a central sewer system.
- All water supply systems must be surrounded and protected by a water supply security zone.
- Water supplied to residential premises, the purpose of which is for household and food activities, must fully satisfy sanitary standards and comply with the state quality standard.
- All water supply and sanitation systems must be made in accordance with modern technologies, provide for complete automation of processes and mechanization of hard human work.
All construction work on water supply systems must include the following nuances:
- Features of the premises of those objects where supply is expected.
- Location and features of the source of drinking and industrial water.
- Required water flow, its maximum pressure and quality.
Rules and regulations for drainage systems:
- The sewer system must be located and equipped taking into account the premises for which it is intended.
- Drainage must be designed not only for the removal of domestic or industrial liquids, but also for melt and rain water.
- The locking system is the passage of sewer pipes in the ceiling, walls and floor of residential premises.
System connections
The main condition preceding the process of connecting to a water supply or drainage system is obtaining permission and technical conditions. This applies to both subscribers and subsubscribers of any departmental affiliation.
Permit mechanism
Permission to tap into the system is issued by the water and wastewater services organization, for which the applicant must provide:
- Application;
- Geodetic plan of the site with communications marked on it;
- Water Management Passport;
- Characteristics of the object as a whole, with a list of sub-subscribers.
The VX passport contains the following information
After the water and waste management organization receives an application with a package of documents and the corresponding payment, no more than 15 days later the subscriber is given technical conditions (indicating their validity period), in accordance with which connection to the system is carried out.
Circulation of papers in the water and utility system
The technical specifications contain the following data:
- Place of connection indicating the number or address of the chamber (well);
- The procedure by which the project will be approved;
- Ownership of structures and devices with the help of which the connection should be made and the diagram with the boundary of division of powers;
- Technical requirements for making the connection;
Installation of external water supply and sewerage systems: a builder’s handbook is unlikely to help you do it yourself
Additionally, for the water supply system, the technical specifications indicate:
- Design pressure at the insertion point;
- Requirements for piping a water meter unit;
- Number of inputs;
- Water consumption mode and vacation limit;
- Requirements for the design and equipment of wells.
The following data is also indicated for the sewer system:
- Mark the bottom of the tray at the attachment point;
- The mode of receiving wastewater, its quantity and concentration of pollution;
- Requirements for devices for measuring flow and sampling wastewater.
Note: If the capacity of the system serving the locality as a whole is insufficient, the water and wastewater utility company has the right to generally refuse to issue a permit to the permit applicant. It also has the right to issue it, subject to the customer investing in the development of sewer and water supply systems.
Design of structures and devices for connection
The project for which an autonomous network is inserted into a centralized water supply system contains the following documentation:
| № | Document's name | Note |
| 1. | General plan of the site with all existing and planned structures and communications. | Scale 1:500 |
| 2. | A copy from the general plan of the locality, which shows the location of the site. | Scale 1:2000 |
| 3. | Schemes and profiles with arrangement of reinforcement. | Accompanied by specifications for all equipment. |
| 4. | Floor plan with a water metering unit, on which the pipeline networks are marked. | Scale 1:100; 1:50 |
| 5. | Working drawings for inserting pipes and piping a water meter. | Scale 1:20: 1:10 |
| 6. | Explanatory note calculating water consumption for household or production needs. | Maximum hourly and daily consumption rates are indicated. |
As-built documentation for external water supply and sewerage is carried out on the basis of the working documentation with the introduction of agreed changes to it
- When designing a sewer line, data on the composition and degree of contamination of wastewater, the location of sewer outlets and information on the efficiency of local treatment facilities are added to the points indicated in the table.
Note! This project is submitted to the water and waste management organization for approval. And the first thing its representative does is check the project’s compliance with the previously issued technical specifications. The conclusion is issued within two weeks, but if it is necessary to carry out measurements and examinations at the site, then this period can be extended to 30 days.
- Responsibility for identified inconsistencies lies with the design organization. But it happens that during the design process it is necessary to make changes that deviate from the requirements of the specifications. In this case, they must also be agreed upon with the water utility company.
- The project is drawn up in two copies, one of which goes to the subscriber, and the second is used for technical supervision during the construction and commissioning of the facility. Naturally, payment of all costs associated with obtaining specifications and approvals, as well as the execution of work, falls on the subscriber. Construction supervision is carried out by the water and wastewater treatment company, with which a separate agreement is concluded in this regard.
Between construction and commissioning of the facility
Not counting the fact that the construction of water supply and disposal facilities is supervised during the process, upon completion, the finished networks are presented by the subscriber for inspection by the same water and wastewater services organization. It must issue a certificate stating that the actual execution complies with the technical conditions, the project, and existing standards.
The installation is complete, all that remains is to test the water supply and sewerage systems and put them into operation
Note: standards for the preparation of working and as-built documentation, as well as requirements for the design and installation of systems, are presented in the following documents:
- GOST 21.601 (SPDS water supply and sewerage);
- JV internal water supply and sewerage 13330*2012;
- SP external water supply 13330*2012.
On the part of the contractor, which in this case is the subscriber, the following documentation must be provided:
| № | Title of the document | Note |
| 1. | Acts of hidden work on: |
|
| 2. | Certificates of conformity or passports for all equipment and factory designs | Other documents that replace them may be submitted. |
| 3. | Statement of test results | In the case of using ready-mixed concrete. |
| 4. | Pipeline sanitation certificates | Provided by builders. |
| 5. | Welder's ribbon | The name and certificate number of the specialist who worked on welding pipeline pipes is indicated. |
| 6. | Hydraulic test report | All structures and pipelines are tested for tightness and strength, and fire hydrants are checked for water loss. |
| 7. | Inspection report for plungers and outlets | Test the effectiveness of these nodes. |
| 8. | As-built drawings | Must be agreed upon with all interested persons and organizations. |
| 9. | Certificate of completion | Protection of tubes from corrosion. |
| 10 | Change Sheet | Coordinated with the design and supervising organizations. |
| 11. | Warranty passport for the object | Establishes the liability of builders for hidden defects. |
| 12. | PR magazine | A journal in which the entire process of work was recorded during construction. |
| 13. | Certificate of value of networks (balance sheet) that will be transferred to the management of the water and wastewater utility company | Issued by the subscriber's accounting department. |
| 14. | Certificate of improvement | This refers to the area adjacent to the pipelines. |
| 15. | Certificate of acceptance of devices for controlling water consumption | This applies to both drinking water and waste water. |
After presenting all the above documents and inspecting the object, both parties sign the corresponding act.
Please note: At the next stage, all network structures are subject to disinfection washing, which is carried out by the construction organization and at its expense. An act on this is also drawn up, also endorsed by a representative of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision Service of the Russian Federation. This act is a document authorizing the insertion - accordingly, after this the network can be put into operation.
Standards for water supply and sanitation in a residential building
Water supply standards
The water supply system for supplying water to each residential premises is designed in accordance with SNiP 2.04.02-84. It states that at each point of a residential building (apartment or private house) the water pressure from the tap is different. So, on the upper floors the indicator depends on that on the first.
For your information
The rate of water pressure in the tap depends on the number of floors of a residential building. For a one-story building, the pressure norm will be 10 m in. Art. For each upper floor, 4 m in. will be added. Art.
Water disposal standards
The rate of water disposal in a residential building is determined by the average daily amount of wastewater from one user. This indicator is determined in accordance with water supply standards depending on the climatic, sanitary, hygienic and environmental characteristics of the area.
Water disposal standards are made up of wastewater entering the sewer system from each apartment in an apartment building and from each private house. In areas without sewerage, the average daily norm is taken at the rate of 25 l/day per resident.
Housing and communal services in Russia
Unfortunately, some owners continue to violate the rules for the use of residential premises. As a result of unlawful actions of residents, personal hygiene items, newspapers, personal belongings, and food waste end up in the sewer riser, which causes clogging of the central riser and flooding of the technical basement of the house with sewage.
In this regard, it reminds you of the rules for using sewerage (clause 5.8.7 of the rules and regulations for the operation of the housing stock, approved by the Decree of the State Committee of the Russian Federation for Construction and Housing and Communal Sector No. 170 of September 27, 2003):
Rules for using sewerage
- Keep toilets, sinks and washbasins clean;
- Avoid damage to sanitary fixtures and fittings installed in the apartment.”
- It is prohibited to pour flammable liquids and acids into toilets, sinks and washbasins;
- It is prohibited to throw sand, construction waste, dry and diluted construction mixtures and their residues, rags, personal hygiene items, except toilet paper, bones, glass, metal and wooden objects into toilet bowls;
- It is prohibited to discharge food waste into the sewerage system;
- Avoid non-productive consumption of tap water, constant flow during water use, and leaks through water fittings;
- It is prohibited to use sinks, washbasins, toilets, dishwashers and washing machines if there is a blockage in the sewer network, i.e. It is prohibited to drain any water into the sewer until the blockage is removed;
- Immediately notify operating personnel of any malfunctions in the water supply and sewerage system;
- Protect sanitary fixtures and openly laid pipelines from impacts and mechanical loads;
- Protect plastic pipes (polyethylene sewer risers and cold water connections) from high temperatures, mechanical stress, shock, scratches, do not paint polyethylene pipes and do not tie ropes to them;
- To clean the outer surface of the plastic pipe, use a soft, damp cloth; It is strictly forbidden to use metal brushes;
- If polyethylene sewer pipes are clogged, it is prohibited to use steel wire; plastic pipelines should be cleaned with a piece of polyethylene pipe with a diameter of up to 25 mm or a rigid rubber hose.
We ask you to tell your children what items should not be flushed down the toilet.
Sewerage is designed to remove waste and liquid waste from residential buildings!
Features of water supply systems of an apartment building
Providing water supply and sewerage to an apartment building is regulated by RF Regulation No. 354 “On the provision of utility services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings” dated May 6, 2011.
To supply water resources to apartment buildings, a centralized communication system is used. It is characterized by the complexity of its design, since it involves the provision of water from a common source to each room of an apartment building.
Water flow diagram for central water supply:
- Water intake;
- Water treatment station;
- Water tanks;
- Pumping station;
- Water supply network;
- Consumer.
Water disposal
The sewer system of an apartment building requires regular cleaning, since waste and waste passing through the drainage pipes reduce their volume, which leads to clogging. Properly designed systems have the property of self-cleaning, which is possible due to the flow of wastewater under a certain pressure and slope.
Attention
Periodic cleaning and repair work are still necessary. These actions can also be carried out by the residents themselves, since cleaning is carried out in the connecting elements of the pipes between the toilet or sink and the waste pipe.
The drainage system of apartment buildings is equipped with a water seal. It is designed to eliminate gases accumulating in pipes and preventing their penetration into apartments. The water seal is a curved tube connecting sinks/toilets/baths with waste pipes.
The procedure for stopping or limiting the supply and intake of water
Shutting off the water supply and even sewerage is possible without prior notification in the following cases:
- emergency;
- power outages;
- the need for a large volume of water for fire extinguishing.
Limitation of drinking water supplies with prior notification to users is carried out if its quality has deteriorated, contamination has occurred, or planned repair work is being carried out, as well as the connection of new subscribers.
Communications will be disconnected if unauthorized connection to the systems or non-payment for services provided is detected.
Features of water supply and sanitation of a private house
Implementation of water supply to private houses is feasible in two ways:
- private;
- centralized.
Private water supply is much easier to implement, since it involves drilling a well or well on a separate residential plot, the extracted water from which is supplied only to one house. Private water supply is important for areas remote from cities.
Additional Information
A centralized water supply system for private houses is designed less frequently than an autonomous one, and is intended for cottage villages or town-house complexes.
Water disposal
Sewage systems must be designed together with water supply systems. Moreover, drainage of private houses should imply the removal of not only domestic wastewater, but also the consequences of rainfall and melted snow. Currently, each residential plot has an autonomous drainage system. Its location should be 10-15 meters from the house, and also fenced.
The wider and deeper the sewer drain is dug, the more wastewater can be discharged.
Structure of the water intake structure
A water intake structure is a set of objects or a unit of engineering equipment designed to collect water from a source, which can be surface or underground.
Such equipment includes:
- primary lift station (or submersible pump);
- flow meters (water metering devices);
- stations for bringing water quality to standard (water treatment);
- reservoirs (clean water and fire reserve);
- secondary lift stations - distribute volumes of water to consumers, maintain the necessary pressure (as an alternative, a water tower can be installed);
- backup stations (fire extinguishing);
In the photo - a stationary fire extinguishing station
- a drainage system that removes water in case of emergency flooding of structures;
- a set of automatically operating instruments (instruments and controls) that monitor the operating condition of the equipment and perform its round-the-clock maintenance.
Note: the full list of actions of the instrumentation and control unit depends on the purpose and scale of the water intake; it is set out by the customer for the construction of the facility in the technical specifications for the design. Large units can generally be fully equipped with their own infrastructure - up to an electrical substation, a boiler room, a laboratory, and a control room manned by a watch.
Operation tasks
A water intake can be a fairly large structure with a branched structure. In order for it to work like a clock, the operation of the facility must be carried out in accordance with the rules of MDK 3-02*2001.
Their main requirements are:
- The need to monitor the status of sources and equipment operation with registration in logs.
- Prevention and timely elimination of accidents, carrying out technical inspections and scheduled repairs.
- Keeping records and regularly assessing the quality indicators of the resource taken. The frequency of sampling is agreed with the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Inspectorate. He is the first person to be notified in case of deterioration in water quality.
Note: if it is not possible to restore water quality under normal operating conditions, the water supply and sewerage sector (WSS), in agreement with the SES and the municipality, carries out a number of measures that include reducing the volume of water intake and treatment.
Industrial water treatment
Documentation for water intakes
In addition to the mandatory construction documents, the list of which is given in clause 1.6.6 of the rules, operational technical documentation must also be stored at the water intake:
| For surface water intake | For underground water intake |
| General plan of the site with structures and communications. | Drilling log. |
| Technological switching diagrams. | Sectional drawings of a well. |
| Automation schemes. | The act of pumping the water intake after drilling. |
| Passports for all equipment in use. | Results of water analysis at the end of drilling. |
| Logbook (by quantity and quality of water taken). | Acts on project changes and deviations when drilling a well, indicating the reasons. |
| Audit log (it records the operation of the equipment). | Data on the operational flow rate of the well. |
| Drawing of the water intake part of the 1st lift station and the structure itself. | Data on the depth and method of mounting the submersible pump. |
| Instructions for operating the water intake (providing protection for fish, as well as from sediment and slush). | Drawings for the construction of the well head and piping. |
The storage of documentation is entrusted to the permanent staff or division of the water utility responsible for the operation of the water intake.
Responsibilities of surface water intake personnel
Surface water intakes are installed at reservoirs and in river beds, which are more exposed to pollution than underground sources.
Therefore, the responsibilities of service personnel include:
- Regular monitoring of the characteristics of the source - and not only in terms of water quality and level, but also in changes in the fairway, the sanitary condition of the banks (sediments) and the bottom (siltation). In winter, the process of freeze-up and ice drift, slush movement, and formation of bottom ice is monitored; in summer, the quantity and quality of aquatic flora is monitored.
- Monitoring of all water intake structures: bucket and water intake parts, protective devices, siphons and gravity lines, coastal wells, water pumping units. The rules for operating water supply networks provide for regular cleaning of structures from clogging with floating debris, ice, and algae.
Cleaning a water source from floating objects
- In order to detect pollution in time, water-measuring posts are organized at surface sources. The frequency of water level measurements may vary for regions, and is carried out in accordance with the results of previous many years of experience in operating a given water intake.
- Inspection of the water intake is carried out by probing with hooks from boats in the summer, from the ice cover in winter; if necessary, divers are involved in the inspection.
- The water depth is measured along the structure and compared with its level in the coastal well. A deviation of the drop from the calculated one towards an increase, at which sediment is carried into the well, means that either the filter cassettes in the water inlet openings are clogged, or the pipeline is clogged.
- If the cassettes are destroyed or the siphon pipeline ruptures, the difference, on the contrary, will become smaller. The tightness of the pipelines is controlled either by air injection or by flushing with the addition of a dye to the water.
Note: the condition of the coastal well is checked twice a year: 4 weeks before freeze-up, and immediately after the spring flood.
Features of underground water intake control
The operation of cold water supply networks, regulated by rules, concerns not autonomous wells and wells fed from a pool of groundwater, but deep artesian water intakes, through which water supply is most often organized for small settlements. Such a source also requires constant monitoring of the level and quality of water, not only at the very point of its rise to the surface, but also within the entire sanitary protection zone.
Boundary of the water intake sanitary protection zone
- Just as in the case of surface water, underground water requires preliminary water treatment. In the artesian depths it is oversaturated with iron, for which purpose a deferrization station is usually built near the water intake.
- There is also a technology for neutralizing iron directly in the aquifer. When using it, well operating personnel are required to constantly monitor the aeration system and the purified water supply mode, and monitor the concentration of iron content in it.
Iron removal from underground water intake
- The volume of water taken from the well is recorded using a flow meter installed on the pressure pipeline. For activities related to monitoring the resource level in the aquifer, observation wells are installed, in which measurements are taken. As for the dynamic water level, it is measured in the production well once a month. Water samples are also taken there for analysis.
- If, as a result of the inspection, a deterioration in the composition of the water or a decrease in its level is noted, the enterprise operating the well is obliged to conduct an inspection of the facility, preferably with the involvement of the organization that designed it. In any case, the main expert should be a company licensed to design (construct) drinking water supply systems.
- Among the measures taken due to the deterioration of water intake, the possibility of artificial replenishment of the underground pool can be considered. If the water quality cannot be compensated through treatment facilities, the well is pumped, or it can be completely turned off and mothballed or plugged.
Canned well
- Once a year, the organization responsible for the operation of a well or an entire network, if there are several water intakes, is obliged to carry out a general inspection of the structure to assess its technical condition. At the same time, not only the flow rate is specified and the water quality is checked, but also the mouth and casing pipes are examined, the nature of deposits on the walls of the shaft, and corroded areas are searched for.
- Naturally, all pumping and power equipment, shut-off and other valves and automation are also inspected. Based on the results of the study, the type of necessary repairs and other measures are prescribed to ensure further trouble-free operation of the water intake structure.
The daily responsibilities of the maintenance personnel include monitoring the readings of control instruments, the degree of heating of the engine and pump bearings, changes in the oil level (in some deep-well pumps), and the general sanitary condition of the well. The main task is to notice deviations in time and inform the dispatcher, who will send the necessary specialists to fix the problem.
Terms of use and provision
Water resources intended for food and household use are supplied to residential apartments and houses from a supplier (organization) with which all owners have entered into an agreement, through a management company. Contractual relations are based on the rules of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
These rules describe the rules for drawing up a contract, the algorithm for accounting and payment for the resource used, the procedure for installing and taking readings from meters. Based on a mutual agreement, residents have the right to use water supply. Without official documentation, using water provided by the supplying organization is a violation of criminal and administrative codes. This procedure also applies to the use of drainage systems.
In what cases can the supply of water or the intake of domestic wastewater be suspended?
Wastewater treatment scheme.
- Lack of power supply.
- Force majeure circumstances: accidents, fires, natural disasters, sewage entering the water supply system, etc.
- Deterioration of the hygienic parameters of the supplied water (but this can only be done by order of the relevant services after taking the necessary samples).
- Unauthorized intake of water or increase in flows that can harm centralized systems.
- Lack of agreement and unauthorized connection to existing networks.
- Work to eliminate accidents and breakdowns carried out by service organizations, as well as connecting new network subscribers.
- Planned repairs.
The subscriber should remember that he may be disconnected from central networks:
- in case of late payment. Its terms and procedure are specified in the contract;
- in case of unsatisfactory condition of the subscriber's receiving equipment (faulty plumbing fixtures and pipes);
- in case of unauthorized tapping and discharge of wastewater in the absence of an agreement or its expiration.
Payment rules for water supply and sanitation
Owners of houses and apartments pay for water supply and sewerage monthly, according to the calculations presented in the receipt. Payment is made to the account of the management company.
According to the Russian Federation Regulation dated May 6, 2011 No. 354, the amount in the receipt for hot and cold water is formed based on the amount of its consumption (in cubic meters). Generally established rules determine that the number of cubic meters of waste water is equal to the number of cubic meters of water supply.
Attention
Payment for consumed water is based on meter readings, which are established by the management company. Meters must fully comply with the standards of the Russian Government, and must also be sealed. His testimony is entered monthly into the receipt, on the basis of which the payment amount is formed.
If cold and hot water meters are not installed in an apartment or house, then the payment amount is determined by standards calculated for each person registered in the apartment. Payments are made for the residents actually living in the premises.
Rules for calculating water supply and sanitation
Calculation of water disposal and water supply is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Readings are taken from the installed meter and entered in the column on the receipt. If there are no meters, then payment is made according to average consumption standards established by the local administration.
- The amount (in cubic meters) of cold/hot water consumed (indicators taken from meters) is multiplied by the sewerage tariff (indicated in the receipt).
- The final indicators of cold and hot water are added up and the amount of payment for sewage disposal from a residential premises is obtained.
The readings of the sewer systems of an apartment building and a residential building differ in that in the first case, payment is formed from the data of the general building meter, and not from each device in each apartment.
How is consumable and sewage water accounted for?
Both the volume of water supplied and the amount discharged must be taken into account through the use of water metering units. The only place where potable water is not counted is in fire stations when it is used to fill tanks.
Water metering unit
- When the device is faulty, the amount of water is determined by the average calculated based on consumption over the last three months - but only for one billing period.
- If the meter is not repaired during this time, this is no longer considered as a malfunction, but as an evasion from installing the device, and the calculation is made differently.
- In this case, the flow rate is calculated based on the throughput of the system at a flow speed of 1.5 m/s around the clock. In this case, the volume of water discharged is assumed to be equal to the volume consumed, and recalculation is not performed after installing the meter.
- So, rushing to repair or replace devices will cost much less. The same measures are taken if the subscriber has not provided the controller with access to the water metering unit, as well as if unauthorized tapping or construction of structures for connection to pumps, hydrants, etc. is detected.
Where water supply is carried out according to a temporary scheme without metering devices, the procedure for payment with the supplying organization is determined by the relevant agreement.