Home / Welding technique
Back
Reading time: 2 min
0
649
Today, silumin is used to produce all kinds of complex elements. Welders connect silumin parts using this welding method.
This method cannot be called complicated, but when it comes to practice, many beginning craftsmen encounter a lot of difficulties when working with the alloy.
Parts made of this metal are more difficult to connect, since during welding the alloy oxidizes and heats up. Given these features, argon is used for this welding method. This element prevents the oxidation process during welding.
Note. Silumin is a silicon-containing alloy based on aluminum. Various products of intricate shapes are produced from it.
The physical properties of this alloy include wear resistance, high strength, corrosion resistance and low weight.
- Silumin welding using argon
- How to weld silumin correctly
- Welding silumin using the argon arc method: all the pros and cons
Preparation of welded surfaces
Cleaning aluminum before welding is the key to successfully joining parts. To remove aluminum oxides, you can use stainless steel brushes or solvents and etching reagents.
Rules for cleaning metal:
- Do not use a brush that has been used on any steel, such as stainless steel or carbon steel.
- You should not press hard on the brush - with strong pressure, oxides penetrate into the workpiece.
- Cleaning with a stainless steel wire brush is carried out in one direction only;
- When using etching fluids, care should be taken to remove them from the surface of the workpiece before welding using acetone or solvent.
Special properties of aluminum
The widespread use of aluminum is explained by its low specific gravity, fairly stable strength and corrosion resistance. But its behavior during heat treatment creates difficulties when connecting aluminum structures and parts by welding. This is explained by the specific physical and chemical properties of aluminum:
- it does not change its color when heated strongly, so it is difficult to understand from the color the degree of heating of the metal;
- has a wide melting temperature range, unlike steel alloys, and begins to melt at a low temperature threshold, losing its strength;
- does not show a tendency to magnetization;
- has high thermal conductivity (on average 5 times more than steel alloys), therefore, when the joint zone is heated, heat intensively spreads throughout the entire part being welded. In order not to lose it, before carrying out welding work, especially large aluminum products, they are pre-heated;
Due to the active interaction of aluminum with oxygen in the air, an oxide film is formed on its surface. Once a certain thickness is reached, it then begins to protect the aluminum from further oxidation. At the same time, the oxide film creates difficulties during welding, because it melts at a temperature of 2050-2200 o C, in contrast to the metal itself, which has a melting point in the region of 660 o C.
Equipment selection and configuration
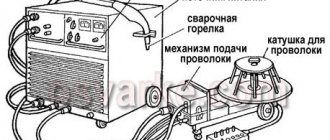
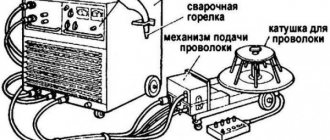
Semiautomatic welding machine for aluminum
Welding of aluminum with standard MIG machines is conditional, i.e. You can cook with it, but you shouldn’t expect good results.
The optimal solution in choosing is a semi-automatic aluminum welding machine with a pulse mode. The pulses penetrate the oxide film, reduce overheating of aluminum and reduce the likelihood of burnout.
Read also: Blade for jigsaw on laminate
Synergetic pulse-arc devices, equipped with a special program, make the task even easier. The welder needs to decide on the choice of alloys to be welded and select the appropriate program. Next, set the current value using the push-button regulator. The selection of other parameters is carried out automatically by the microcontroller.
I would like to note that these semi-automatic devices are not a cheap pleasure and are justified in professional use. At home, it is quite possible to get by with the equipment without fancy programs, however, the quality of the welding seam will not be comparable.
When purchasing a universal semi-automatic welding machine in a price range of up to 40 TR, designed for welding non-ferrous metals, incl. aluminum, you can take a closer look at the following models:
- Svarog REAL MIG 200 (N24002)
- Svarog PRO MIG 160 SYNERGY (N227)
- Svarog PRO MIG 200 SYNERGY (N229)
- Grovers MULTIMIG 200 SYN
- Aurora PRO OVERMAN 180
Wire for semi-automatic machine
When welding aluminum with a semi-automatic machine, certain requirements are imposed when choosing a welding wire. Important points to pay attention to:
- The melting temperature of the wire must be comparable to the temperature of the metal being welded. Less scatter – the welding process is easier;
- optimal wire diameter 1.2-1.6 mm;
- larger diameter means easier feeding into the welding zone.
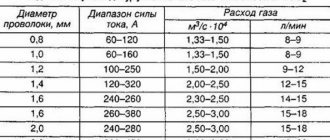
Common types of aluminum welding wire are ER4043 and ER5356. Designed for welding and repairing products made of aluminum and its alloys with a silicon content of no more than 5%.
Welding modes for ER4043 and ER5356 wires
| Wire diameter, mm | Voltage, V | Current, A | Gas consumption, l/min |
| 0,8 | 13-24 | 60-170 | 15 |
| 0,9 | 13-24 | 60-170 | 15 |
| 1,0 | 15-26 | 90-210 | 16 |
| 1,2 | 20-29 | 140-260 | 19 |
| 1,6 | 25-30 | 190-350 | 25 |
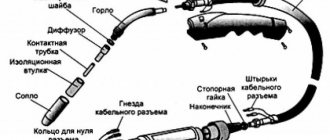
Welding torch
The welding torch adopts Teflon guide to reduce wire friction. It is advisable that the hose for welding aluminum is intended only for welding aluminum and is not too long - 3 m is just right.
The straighter the wire in the channel, the more freely it feeds, so try to keep the sleeve without kinks or loops.
The contact tip must be designed for welding aluminum (in addition to the wire diameter, the AL marking is stamped on them); simple ones used for welding ferrous metals and stainless steel are not suitable. This is due to the strong expansion of aluminum during heating. The diameter of the hole should be approximately 0.4 mm larger than the diameter of the wire, and at the same time not too large, in order to ensure good electrical contact.
It is difficult to use aluminum wire with a diameter of 0.8 mm due to the plasticity of the metal and the difficulty of drawing. The solution to this problem can be the use of a Push Pull welding torch. A special built-in mechanism will improve wire feeding and increase the length of the torch.
If welding is carried out at currents above 200 A, it is worth taking care to reduce heat generation and reduce problems with wire feeding by using a water-cooled torch.
Wire feeder
Due to the increased ductility and softness of aluminum wire compared to steel, the feeding mechanism must have a number of features, such as:
- four-roller feeder. Necessary for uniform pressure on each pair of rollers;
- Feed rollers with U-shaped grooves, designed specifically for working with aluminum wire.
Shielding gas
Argon is most often used as a shielding gas, which has a good cleaning effect and good penetration into the weld pool. When welding aluminum alloys with a high magnesium content, mixtures of argon and helium (up to 75% helium in the mixture) are used as a shielding gas. Such mixtures prevent the formation of magnesium oxides.
Here the question may arise: how to cook aluminum in a carbon dioxide environment or without gas at all, since argon is quite expensive?
Cheaper carbon dioxide, used for welding low-carbon steels, is not suitable in this case. CO2 is an active gas, it will protect the weld pool from air, but at the same time it will react with aluminum, preventing the formation of a strong connection. Therefore, in this case, it is inert gas that is used.
Read also: Timer 555 datasheet in Russian
Semi-automatic welding without gas is possible using a special flux-cored wire that protects the weld pool.
Advantages and disadvantages of silumin argon welding
Among the advantages are:
- the narrowly directed effect of the arc prevents deformation of the elements being welded;
- argon is much heavier than air, so it displaces oxygen from the welding zone, increasing quality;
- high speed of the process;
- the presence of a variety of developed techniques for welding various compositions.
Disadvantages of the method:
- work can only be done indoors, otherwise gusts of wind will blow away the argon from under the burner;
- high welding currents require additional heat removal;
- expensive equipment;
- long selection of modes.
The process of welding silumin is a rather complicated task. For high-quality execution, extensive practical experience is required.
Correct welding modes
Equipment setup
Welding aluminum semi-automatically in garage conditions, on machines that are not equipped with additional functions: hot start, smooth rise and fall of the welding current, etc., the selection of optimal modes can only be done experimentally, through trial and error.
The optimal values of voltage and welding current may vary depending on the metal thickness and grade. For example, for the semi-automatic welding machine OVERMAN 180 AuroraPRO for welding aluminum 2 mm thick, the settings are as follows:
- voltage around 15 V;
- current within 130-150 A at slow feed;
- inductance is set to position 3.
The “inductance” setting allows you not to increase the temperature of the weld pool
In more advanced models, aluminum welding is carried out in a 4-stroke mode. When you press the torch button, the welding process starts; then you can lower it and control the application of the welding seam. Upon completion, the button is pressed again, the argon welding process stops. By pressing and lowering the button, various functions can be activated to make aluminum welding easier. The use of the 4-stroke method is most justified on long seams during long-term welding.
The tension of the wire should ensure its uniform feeding. Over and under tension reduces arc stability and causes weld porosity.
Gas burner position
The burner position should be at an angle of 10–20° to the vertical. The optimal distance between the nozzle and the parts to be welded will be 10-15 mm; increasing it significantly increases gas consumption.
You need to weld aluminum with a semi-automatic machine from right to left, the so-called “push” welding. The movement of the torch away from the weld pool leads to better cleaning of the weld, reducing contamination and improving the protective effect of argon.
Seam speed
Welding should be done quickly, with an active hot arc. The high thermal conductivity of aluminum dictates the rules for high currents and voltages and higher translational speeds of the burner to avoid burn-throughs.
Convex seams
When welding aluminum, the most common type of defect is cracking, which occurs as a result of significant expansion of aluminum when heated and, accordingly, significant compression when the welded joint cools. The most significant risk of cracking occurs in craters, as the crater contracts when cooled, causing cracks to appear in the crater. Craters should be welded until a dome-shaped surface is formed. When the welded joint cools, the convex surface will interfere with the action of compression forces.
One of the common techniques for filling craters is to pass in the opposite direction without turning off the arc.
Summarize
Welding aluminum with a semi-automatic machine is a rather complex technological process that requires not only the presence of an argon-arc welding machine with a pulse welding function, but also a certain amount of experience; if the second criterion is missing, it is better to entrust the work to an experienced craftsman. As a rule, the price for aluminum welding is negotiable and ranges from 100-300 rubles per 1 cm.
If you nevertheless decide to carry out the work yourself, the cost of the seam will be proportional to the market price of a spool of wire (if you have a semi-automatic machine and special gas, without the use of argon, the quality of the seam is much worse).
Safety precautions
The use of protective equipment is a necessary condition for welding work. It is mandatory to use a respiratory respirator, a protective mask, special clothing and shoes to protect against the glow of the welding arc and splashes of molten metal. The acrid white smoke released when welding aluminum causes coughing and headaches.
Particular attention should be paid to protecting exposed areas of the body from the influence of UV radiation, because when welding aluminum it is much more intense than when welding other metals. When you try to weld in “shorts” and in a “T-shirt”, you will get the solarium effect after 30 minutes.
Semi-automatic welding of aluminum is not comparable in quality to using TIG, but it is more than compensated for by significant productivity. It is an excellent solution for surfacing or filling large gaps. In industrial production conditions, the use of semi-automatic machines is most appropriate due to the volume and high speed requirements. The use of industrial equipment and highly qualified welders allow us to achieve excellent results.
Setting up a semi-automatic machine
It’s not enough to choose a machine for welding aluminum; you also need to configure it correctly. As we wrote earlier, the outcome of your work largely depends on the correct settings. Most likely, you will not be able to find the right settings the first time, since this is a matter of experience. You can watch dozens of training videos and read articles, but that's not enough. You need your experience.
However, we will try to simplify the task of your first acquaintance with a semi-automatic welding machine and give you a few recommendations that always work. First of all, the semi-automatic welding machine for aluminum welding has its own functions. In a standard semi-automatic machine, you can adjust the current strength, voltage value, wire feed speed and polarity.
There are no specific universal settings that you can use to weld any parts. Here you need to build on the thickness. As an example, let's take a part made of aluminum 2 millimeters thick. We recommend welding such metal by setting the voltage to no more than 15 volts; the current can be set in the range from 100 to 150A.
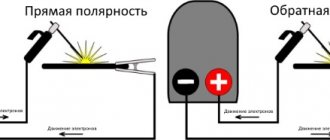
Set the wire feed speed based on the speed of your work. If you are a beginner, then set the minimum speed on your welder. Although welding aluminum must be done quickly. Set the polarity to straight (if you cook using gas). If you work without gas, then set the polarity in reverse.
If you have a professional or semi-professional semi-automatic machine with the ability to operate in four-stroke mode, then turn it on. This will significantly improve the quality of the seam.
Aluminum is perhaps the most capricious metal
Aluminum is not steel; if you know how to cook steel, you should immediately understand that aluminum is a light alloy metal. It requires warming up at the beginning of welding, stay for a few seconds at the beginning of welding in one place, create a bath, allow the metal to warm up. Continue to run the burner, aluminum heats up very quickly, if you stand in one place for a long time, the metal will most likely melt through. Everything needs to be done promptly. You will quickly understand this and select the desired speed.
Preparing material for welding
Before the process you need to do the following:
- sand the surface;
- remove plaque and oxide film : with brushes, special machines or fluxes;
- degrease the surface with acetone;
- embroider the edges (if the thickness of the workpiece is more than 5 mm);
- cut the edges of the parts at an angle of 30-45 degrees and treat them with flux;
- To prevent parts from deforming, they need to be preheated.
Welder tasks when working with aluminum
Taking into account the peculiarities of the behavior of aluminum alloys during welding, you must solve the main tasks during the work: get rid of the oxide film, ensure a stable arc during welding and timely supply of welding wire so that the aluminum welding process is continuous, otherwise it will have to start again.
The welder must:
- get rid of the oxide film at the seam: pierce it with an electrical impulse or mechanically clean the surface using a metal brush or by chemical etching. To pierce the film, a special pulse operating mode of the equipment is used;
- when choosing a welding mode, avoid burning through the metal due to the increased thermal conductivity and low melting threshold of aluminum, leading to a rapid loss of strength when heated. To do this, he must ensure the required process temperature and an arc of 12 to 15 mm in length, select the correct electrodes and filler wire size suitable for the thickness of the aluminum parts being connected and the torch nozzle;
- take into account the tendency of aluminum to significant linear shrinkage (almost twice as much as steel) upon rapid cooling after heating, since this leads to the creation of internal stress with the formation of deformation cracks or craters in the weld area. To prevent this, you need to start the welding process with a high welding current in order to break through the oxide film, and finish it by gradually reducing it towards the end of the process, this will soften the sudden change in temperature and prevent the formation of a crater.
Pros and cons of semi-automatic aluminum welding
Any semi-automatic welding machine has in its device a source for producing a welding arc, a torch with a protective sleeve for the wire, a cable with a clamp at the end for connecting to the part, a motor and a gearbox.
Pros of semi-automatic:
- This design of the device allows it to be used in a wide range with different settings that help you select the desired mode of the welding process.
- Arc control can be carried out at any torch position.
- You can weld parts of any size. If it is necessary to connect large structures, work can be carried out without the use of protective argon.
- The device provides high precision welding.
- Ensures economical consumption of consumables and electricity with great efficiency.
- Semi-automatic devices can be light in weight and small in size, as well as mobile, allowing them to be installed in the right place.
- They have high efficiency, reaching 95%.
- The main disadvantage of an inverter-type semiautomatic device is its high cost compared to transformer devices.
- Such devices are afraid of dust, which is sufficient in industrial conditions or on a construction site. Therefore, unlike other devices, they need regular cleaning and purging of the inverter.
- Electronic control circuits do not respond well to sub-zero temperatures, and temperature changes can cause condensation and damage the system.
Having become familiar with the process of welding aluminum using a semi-automatic machine and its intricacies, you can start working on your own. Compliance with all the recommendations of the article and the correct implementation of the technological process will allow you to achieve a high-quality reliable connection of an aluminum product.
What shielding gas is used?
When working with aluminum on a semi-automatic machine, it is recommended to use argon or a mixture of argon and helium. The latter mixture is used for workpieces with a large cross-section.
In some cases, semi-automatic welding of this metal can be carried out without gas, but then it is necessary to use a special flux-cored wire, the evaporation of which forms a protective environment, or to carry out the process under a layer of flux.
Argon creates a protective layer that weakens the effects of atmospheric air, therefore, there will be fewer various oxides on the seam.
The use of gas slows down the work process, but the result is a high quality seam.
Is it possible to weld aluminum semi-automatically without protective gas?
Sometimes aluminum is cooked without gas, but to create a protective environment around the metal, flux-cored wire is used. Its evaporation protects the metal from the formation of oxides.