Metal cutting – this is the separation of parts (blanks) from long-form, sheet or cast metal. Distinguish mechanical (using scissors, saws, cutters), impact (cutting) and thermal cutting. Thermal cutting – processing of metal by heating.
According to the shape and nature of the cut, there can be separation (dividing the metal into several parts) and surface cutting (for example, cutting holes in a part), according to the roughness of the cut - blank and finishing , when no further processing by milling is required.
In this article, we focused on 6 popular types of metal cutting: guillotine, band saw, oxy-fuel, plasma, laser and waterjet cutting. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages, is limited in the thickness and type of metal being cut, and is capable of providing a certain level of surface quality. In this regard, as a result, a summary table is presented, which reflects the assessments of a particular type of cutting according to the main indicators. The maximum score is 10 points, the minimum is 1 point. It is worth noting that these figures are quite subjective, but they reflect the main advantages and disadvantages of a particular method.
Guillotine: from an executioner's weapon to a tool for cutting metal
In 1789 in France, Dr. Guillotin showed the Legislative Assembly his invention - the guillotine. It was originally intended to be used as a tool for the most humane execution. It consisted of a pair of pillars 5 m high with a large blade suspended between them. To this day, its design has not changed dramatically, but today it is used not for decapitation, but for cutting off parts of sheet metal. Agree, this is indeed a more humane use.
The method is based on the use of mechanical means - special scissors and metal knives. First, the master places the metal sheet on the machine's work table and fixes it with a clamping beam. Then he installs the knife and makes the cut. The guillotine allows you to get a perfectly smooth edge, without nicks, burrs or extra edges. In this case, the curvature of the cut is zero, because cutting is carried out by the blade along the entire width of the sheet at the same time.
Today there are 4 types of guillotines for cutting metal: manual , hydraulic , pneumatic and electromechanical . The principle of their operation is the same, but in the last three types, electronics are used for accuracy and safety, and some machines are capable of cutting metal both crosswise and lengthwise. Metal cutting with a guillotine is used mainly for procurement work.
Disadvantages of the method:
- Limited by the type of metal and the thickness of the sheet being cut (for hydraulic machines, a maximum of 6 mm).
- Low accuracy of the resulting strips, which largely depends on the qualifications of the operator.
- Shape cutting cannot be performed.
Band saw cutting
Rarely does a metalworking exhibition go by without showing a new band saw machine. This popularity is due to the low cost of the equipment, ease of maintenance and acceptable performance. A band saw stretched on pulleys is used as a cutting tool.
The average cutting speed of the band saw machine (LSS) exceeds 100 mm/min. Modern models are equipped with electronics and a wide range of additional equipment, which makes it easy to adapt the machine to the production line.
When cutting on LPS, exact compliance with the specified parameters is ensured, and the cut site practically does not require additional processing (except for the production of high-precision products or products with a smooth surface). The machine is unpretentious to the type of material being processed - it cuts absolutely everything, and the cutting width is only 1.5 mm.
If, when determining the cutting speed and feed rate, it is not possible to use the manufacturer’s recommendations, then you can find out the optimal values by looking at the chips: thick chips with a blue tint are an indicator of the feed rate being too high, dusty chips – too low. At optimal conditions, the chips are slightly curly.
One of the most important conditions when working on automatic band saws is the precise selection of the pitch of the teeth of the cutting blade. Special tables will help you select the blade pitch that corresponds to the cross-section of the profile being cut. Feed rate and cutting speed are equally important.
One of the main advantages of LPS is the ability to cut at an angle. However, as in the previous case, it is impossible to obtain a figured cut using a LPS, and the dimensions of the workpieces are limited by the capabilities of the machine.
What can you do with machine cutting?
Cutting machines are used to automate and speed up the process. The equipment is capable of cutting workpieces along straight or wavy lines for further welding, chamfering edges, or cutting finished metal products (benchmen’s keys, flanges, metal decorations for fences, fragments of stairs, etc.). Depending on the type of torch installed, the machines cut carbon steel, stainless steel and aluminum. Batch cutting of thin 1.0 mm sheets is possible, reducing thermal deformation and the formation of smelted iron in the slag, as if each sheet was cut separately.
What types of machines are used to cut metal largely determine the production tasks. The more powerful the current source, the greater the thickness the torch will cut through. The more functional the device, the more complex shapes it can cut. The accuracy of the finished part depends on the flame source, and the dimensions of the work table determine the maximum size of the workpieces processed.
The speed of gas-flame machine cutting is much higher than that of manual cutting. Preparatory straight cutting on a sheet 5 mm thick is carried out at a speed of 660 mm per minute. On a workpiece with a cross-section of 300 mm, this figure is 110 mm/min. Cutting of shaped elements is possible up to 590 mm at a thickness of 5 mm in 60 seconds.
The use of machine cutting allows you to narrow the working area, concentrating the implementation of numerous preparatory processes in one place. This also helps to save on the number of personnel, where one or two people will be required to install parts, depending on the dimensions of the product. Cutting material using a machine provides high accuracy and protects against human error and defects due to the high error of manual cutting. Automatic machines can cut narrowly and leave less waste, which reduces material costs. With such equipment, production volumes increase.
I guarantee that in the future we will have tons of useful materials and insights from the world of industrial equipment - don’t forget to subscribe to the newsletter so you don’t miss out!
Dmitry Yagolnik
Welding Equipment Expert
Oxygen gas cutting of metal
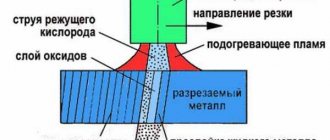
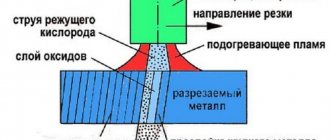
Today, oxy-fuel cutting is perhaps the most popular type of metal cutting due to its high productivity. It is ensured thanks to a completely different principle of operation, which consists in the combustion of metal. Before this, it is necessary to preheat the cutting site to the ignition temperature, which is carried out by the preheating flame of the cutter without the supply of cutting oxygen. Depending on the thickness of the metal and the condition of its surface, the initial heating time ranges from 5 to 40 seconds. Once sufficient heating is achieved, oxygen is supplied, and when its jet cuts through the entire thickness of the metal, the cutter begins to move evenly along the cutting line. Oxygen cuts the heated metal and at the same time removes the formed oxides, and due to the released heat of combustion, the adjacent layers of the metal are heated. In this case, the nozzle cut must always be at the same distance from the surface of the part, which is selected experimentally. The maximum thickness of oxy-fuel metal cutting is 200 mm.
However, not all metals are amenable to oxy-fuel cutting. For example, you will never be able to cut aluminum. Firstly, its combustion temperature is 900°C, and its melting temperature is 660°C, therefore, it will only burn in a liquid state, and it is simply impossible to obtain a stable cut shape. When burned, aluminum forms oxides with a melting point of 2,050°C. Such oxide will be hard when cutting and difficult to remove. And finally, aluminum conducts heat very well, so a high concentration of power and high gas flow will be required. Similarly, high-alloy, high-carbon and chromium-nickel steels are not subject to oxy-fuel cutting.
When working with oxy-fuel cutting devices, it is important to correctly select the nozzle speed and air and gas flow rates. For example, too high a cutting speed, in addition to a significant lag of the cutting jet, produces an uneven grooved cutting surface; Too low a cutting speed causes melting of the edges on the entry side and increases the width of the cut, which entails significant metal loss. The easiest way to determine the cutting speed is by the nature of the emission of sparks and slag: they should be ejected from the back side of the workpiece at a slight angle from the vertical axis.
The disadvantages of this type of cutting include the large width of the cut (along which, in addition, there are beads, burrs and oxides), its poor quality, the impossibility of passing along curved contours of small radii, and a significant thermal effect on the metal.
Uneven heating creates stress in the metal and deforms it, distorting its geometric shape. Stress can be completely relieved only through heat treatment, and this is a large additional cost. In addition, this method is not suitable for every type of metal.
Disadvantages and advantages of mechanical metal cutting.
The main disadvantage of mechanical metal cutting is that all its methods allow cutting only in a straight line. In the event that it is necessary to cut metal along a complex curved path, this type of cutting cannot be used. In addition, the disadvantages of mechanical cutting include not very high labor productivity, as well as an insufficiently large cutting depth.
But mechanical cutting of metals also has its advantages - high quality of the cut and its high accuracy, the ability to cut metal at an angle and small losses of metal during its processing (when using band saw equipment).
Plasma cutting of metal
Almost all of the disadvantages of oxy-fuel cutting can be eliminated when using plasma. The first machines for plasma cutting of metal appeared somewhere in the 50-60s of the last century. This equipment was so bulky and expensive that it was purchased mainly only by engineering giants. At the end of the last century, plasma cutting of metal became more accessible and is now widespread.
Plasma cutting of metal is carried out due to the intensive melting of the metal along the cut line by the heat of a compressed electric arc and the subsequent removal of liquid metal by a high-speed plasma flow. At its core, plasma is a fully or partially ionized gas with a temperature of 15,000 - 20,000°C. Accordingly, it is not difficult to guess that the productivity of plasma cutting will be many times higher than gas-oxygen cutting, the temperature of which reaches only 1,800°C.
Today, plasma cutting is the most effective method of cutting metal, which has a number of features that make it a leader in the field of metalworking. Thus, the process of cutting metal with plasma does not require refilling gas cylinders and their delivery, additives for cutting valuable metals or special compliance with fire safety measures. Plasma cutting requires only electricity and air, and nozzles and electrodes as consumables, so this type is one of the most economical methods.
Plasma cutting is economically feasible for processing:
- aluminum and alloys based on it up to 120 mm thick;
- copper up to 80 mm thick;
- alloy and carbon steels up to 50 mm thick;
- cast iron up to 90 mm thick.
With a metal thickness of 120 to 200 mm, plasma processing is possible, but in this case it is more profitable to use oxygen gas cutting.
In the process of cutting metal, characteristics such as thickness and thermal conductivity are extremely important. Accordingly, when selecting equipment, it is necessary to take into account a simple fact: the higher the thermal conductivity of the metal being cut, the greater the heat removal and the smaller the possible thickness of the processed sheet. For example, the thickness of a copper sheet should be less than a stainless steel sheet.
The advantage of plasma cutting is the increase in cutting speed. This fact allows this method to prevail over an oxygen burner, since the speed increases by 6-10 times, which is important when processing workpieces 40-60 mm thick.
Thermal cutting methods
Gas cutting
A heat treatment method in which a material is heated to its ignition temperature, after which a stream of oxygen is supplied under high pressure. It cuts the metal over its entire thickness, smoothly moving along the cutting direction.
Used for correcting defects, cutting workpieces and cutting holes.
PROS:
- high cutting speed;
- no restrictions on shape and size;
- Can be used for cutting rusty and painted metal;
- the thickness of the sheet being processed is up to 200 mm.
MINUSES:
- low processing quality (increased cutting width, oxides and sagging);
- not suitable for the production of small workpieces.
Plasma cutting
It is carried out by a high-temperature plasma jet produced using an electric arc discharge. Exposure to plasma causes melting, burning and blowing of material from the sheet. Metal processing occurs at temperatures from 15,000 to 30,000 degrees °C, which makes this processing method applicable to any type of metals and alloys.
Used for cutting flexible sheets up to 200 mm thick. At the same time, extremely high temperatures in the cutting zone do not have a thermal effect on the material next to it, so the sheet does not deform and the characteristics of the material do not deteriorate.
PROS:
- suitable for processing all types of steels, including alloys with a high expansion coefficient;
- high cutting speed and accuracy;
- ease of operation with a plasma cutter;
- possibility of figure cutting;
- process safety (due to the absence of gas cylinders).
MINUSES:
- relatively small maximum cut thickness (up to 50 mm depending on the power of the plasma cutter);
- the need to strictly adhere to the perpendicular cutting angle.
Advantages and disadvantages of plasma cutting:
- plasma cutting is highly accurate and eliminates the formation of sagging;
- it is possible to carry out figure cutting;
- overheating of the product is eliminated due to local heating of the cut area;
- the ability to process various metals, including titanium, cast iron, chalk, steel and others, without changing equipment;
- the design does not have explosive gas cylinders;
- quite low cost.
- A significant increase in processing speed during plasma cutting is ensured by modern machines that have automatic CNC program control. This fact also allows for high-quality work to be performed regardless of the operator’s qualifications.
- When processing metal using a plasma jet, there is no need to carry out additional preparation of the part, that is, cleaning it, since the quality indicators remain unchanged, even in the presence of rust, paint and dirt residues.
However, this method also has a number of disadvantages . First of all, the plasma cutting method is thermal, which inevitably affects the quality of metal edges: partial loss of material occurs, the edge becomes more hard, and subsequent processing requires additional costs. However, the quality of the edges formed during plasma cutting is much better than with oxy-fuel cutting: there is no scale, and the width of the zone with tarnished colors is five times smaller.
Metal cutting: method and performer
The correct choice of cutting type is determined by a number of factors:
- type of metal to be processed. For example, plasma cutting is better suited for aluminum or alloy steel;
- rolled thickness, which can range from 20 to 300 mm;
- requirements for the shape, accuracy and condition of the cut upon completion of the operation.
The quality of metalworking determines the functionality of the metal structure as a whole, therefore, despite all its apparent simplicity, metal cutting in Moscow
requires the attention of an experienced specialist.
The site Obrabotka.net can help you choose one, taking into account the employer’s requirements for the ratio of cost to quality of work. It contains a significant base of private companies at a professional level engaged in metal cutting in Moscow
. As a rule, their production facilities are equipped with all the necessary equipment: microprocessor-controlled CNC machines for laser cutting, plasma cutting inverters and even band saws if the need arises.
Laser cutting of metal
This is one of the advanced methods that involves intense exposure of the metal to a laser beam.
We will not dwell on the technical aspects of obtaining a laser, we will only say that this method has many advantages: the smallest cutting width, which can reach only 0.1 mm, high productivity, excellent surface quality, the absence of dynamic or static stresses affecting the metal, thanks to a clearly directed laser light stream into the cutting zone. The resulting edges of the metal products are smooth, without burrs, but a mark from exposure to high temperatures may be visible on the cut. If a “critical” part is being manufactured, then additional machining cannot be done.
The largest company producing special road equipment is Vermeer Manufacturing Co. uses only two laser cutting installations in its production, which cut 20-25 tons of metal per day and supply 9 assembly lines of road equipment with blanks.
The laser beam allows cutting metals up to 15-20 mm thick, although the greatest effect is achieved with a thickness of 6 mm. A significant disadvantage of laser cutting is the low efficiency of the laser itself (only 15%), which does not allow processing sheets thicker than 12 mm. In addition, not all metals can be cut with a laser: aluminum, titanium and high-alloy steels have strong reflective properties, and the laser power simply may not be enough to cover the entire thickness of the metal.
Advantages of metal laser cutting:
The highest quality processing of steel, as well as brittle materials, is ensured by the use of a laser beam instead of a drill or cutter. This cutting technique avoids deformation of the steel, which is its main advantage.
- laser cutting works using the “flying optics” method, which eliminates the mobility of the metal sheet when cutting, since in this case only the cutting head moves;
- the line thickness when using laser cutting is minimal - no more than 0.5 mm;
- complete absence of damage when cutting gloss and mirror surfaces;
- laser cutting of products with complex geometry;
- complete elimination of the possibility of burr formation due to the use of high-quality cutting;
- The use of CNC makes it possible to process parts with micron precision.
- the qualifications of the operator working with the machine have virtually no effect on the quality of the workpiece, since all control is completely entrusted to the computer, which operates cutting in automatic mode.
- the presence of a minimum amount of waste and the complete absence of chips, which makes the process economical.
Waterjet cutting of metal
Waterjet cutting is the most innovative and advanced metal cutting technology. The power of the water jet coming out of the nozzle under enormous pressure is truly amazing: it is capable of cutting up to 300 mm (!) of steel.
The heart of the waterjet cutting system is the ultra-high pressure pump. There are now experimental models of machines with water pressure of 6,000 bar. Passing through a ruby, sapphire or diamond nozzle just 0.1mm wide, water is accelerated to three times the speed of sound to produce a fine, focused jet that can process virtually all types of materials.
The speed of waterjet cutting is very high: for example, when cutting a stainless steel sheet with a thickness of 100 mm, it reaches 22 mm/min, and with a thickness of 1 mm – 2,700 mm/min. When cutting glass, the speed can be up to 11,000 mm/min.
When cutting soft materials, a clean stream of water is used, and by mixing garnet sand as an abrasive, materials of any hardness can be cut.
Experiments have been conducted abroad to compare the effectiveness of the waterjet cutting method with traditional technologies. Laser was chosen as the “strongest competitor”. Both installations cut packages from metal plates with a thickness of 0.3 mm each. As a result of the tests, it was found that when the thickness of the destructible package of plates is less than 6 mm, the laser cutting method turned out to be more efficient in terms of energy intensity and speed, and when the package thickness is over 6 mm, the waterjet cutting method is absolutely in the lead.
The most important advantage of water jet cutting technology over other types of processing is the absence of heating of the cut workpieces, i.e. no thermal effect on the material, which eliminates stress and deformation of the processed material. The result is amazingly high-quality cuts that do not require expensive post-processing.
Some materials cannot be cut by a laser due to reflection, and in the case of plasma cutting, when the material is not conductive. In this regard, waterjet cutting is a universal method, however, it involves getting the part wet, which can be critical for metals susceptible to corrosion.
Water cutting technology has another undeniable advantage - a hair-thin jet creates significantly less material loss compared to traditional processes.
A huge disadvantage of the waterjet metal cutting method is the extremely high cost of cutting: one hour of work on such a machine will cost you about 1,500 rubles. In addition, working parts wear out very quickly due to high pressure and require constant monitoring and repair. In general, if you decide to purchase a waterjet cutting machine, be prepared for ongoing high costs.
Machine cutting of metal: principle of operation and types
Machine cutting helps speed up monotonous metal cutting processes and improve the quality of the result. They use the same operating principles as manual equipment: a mixture of flammable gas and oxygen to form a flame, as well as supplying a jet of cutting oxygen, or air plasma cutting with a jet of air from a compressor and an electric arc. In the latter type, the air is heated by the arc and turns into a plasma state, which is used for cutting. The difference between automatic installation and manual installation is that the machines have CNC, which fully controls the movements of the burner. The cutting head with nozzle moves on brackets and rollers, ensuring uniform passage and precision. The operator can only place the part on the table and run the program.
Types of metal cutting machines are divided into:
- cutting method (which affects the metal);
- dimensions (for garage or production);
- structural design;
- cut thickness (from 1.5 to 300 mm).
Another difference is the cleanliness of the cut, where after some you can immediately weld the parts, while after others you will need to lightly clean the angle grinder.
Large and powerful thermal cutting machines are used in factories and other metalworking plants. In the private sector, compact machines are used at a relatively affordable price, located on a workbench or a separate stand, which can easily fit in a garage or small workshop. The main advantage of thermal cutting machines is the complete automation of the process.
Advantages of waterjet cutting:
Cold processing at 55-90 °C is a key advantage of the waterjet cutting method, which allows high-quality work with certain types of metals whose physicochemical properties change when heated
- the possibility of using harmless abrasive additives;
- carrying out work with various types of materials, except tempered glass and diamonds;
- cutting metal up to 30 cm thick;
- eliminating the presence of gas and vapor formation;
- cutting materials at an angle by tilting the head.
- can be used in gas hazardous areas, since it is absolutely safe from a fire safety point of view.
- ensures a reduction in the degree of roughness and the formation of a high-quality edge, and the metal surface does not melt in this case.
Prospects for the development of the metal cutting industry
The listed methods are used in practice and are known to everyone. But scientists are developing new methods: for example, in Germany they have created an installation for cutting metal using an electromagnetic pulse, which works quickly, silently and leaves no traces. Ultrasonic cutting experiments are also being conducted. It is possible that in the foreseeable future they will become widespread.
Cutting width and maximum workpiece thickness (points):
| Type of cutting | Thickness | Width |
| Guillotine | 1 | 10 |
| LPS | 9 | 9 |
| Oxygen gas | 8 | 5 |
| Plasma | 6 | 6 |
| Laser | 3 | 10 |
| Waterjet | 9 | 8 |
When cutting metal 50 mm thick, the cutting width when using a water jet machine is 2 mm, and with an oxygen gas machine it is 20 mm. This saves 15 kg of metal per 1 meter of cut.
Cut quality and productivity (points):
| Type of cutting | Cut quality | Performance |
| Guillotine | 9 | 9 |
| LPS | 8 | 4 |
| Oxygen gas | 5 | 6 |
| Plasma | 7 | 9 |
| Laser | 9 | 7 |
| Waterjet | 10 | 5 |
Sheet metal cutting (cutting). Press scissors. Guillotine shears. Vibrating scissors.
Purpose and types of metal cutting
Before individual parts of certain sizes are manufactured, sheet and profile materials are cut.
In boiler production, three cutting methods are used: mechanical, autogenous and electrical. These cutting methods have a fundamental difference in the impact they have on the properties of the metal, in their implementation and in their efficiency.
With the mechanical method, metal separation occurs due to the action of an external force. With the autogenous method - due to the combustion of the metal in a stream of oxygen. In electric cutting, metal is melted in the flame of an electric arc. Both methods can be manual or mechanized. In addition to the above, the mechanical method can be divided into two types:
— cutting carried out by clean cutting (removal of chips with a cutter).
Depending on the profile of the material being cut, special tools, devices and machines are used during cutting.
Rice. 1. Scissors:
a – manual; b – chair.
Cutting thin sheet metal with scissors. Chip cutting.
Cleaving cutting is carried out using hand and chair shears (Fig. 1, a and b), lever (Fig. 2), vibration, guillotine, disk (Fig. 3) shears, press shears, and special cutting dies.
Rice. 2. Lever scissors.
Looking at the cut part of the sheet, we see three stripes: two of them, which are at the edges, will be narrow and shiny, these are traces of the cutting of knives (a and c), and the surface in the middle will be matte (b) from chipping (Fig. 4). Small cracks and burrs can be observed along the cut line. In addition, a strip of metal with a thickness of 2 - 3 mm, when squeezed with knives along the entire cut line, will be hardened.
Depending on the structure being manufactured, work hardening and cracks must be planed.
Rice. 3. Disc shears.
Cleaving cutting occurs as follows: the material to be cut 2 is placed between two knives 1 and 3 (Fig. 5), of which the lower 3 is usually stationary, and the upper 1 is movable. The upper knife 1, lowering, presses on the metal, pressing it against the lower knife. Both knives are somewhat pressed into the metal. As the knives are pressed into the metal, its cross-section decreases, first small and then large cracks appear, and it breaks off.
Rice. 4. Diagram of the action of knives on metal.
Under the action of the knives on the metal being cut, the part of it lying on the table rises and rotates around the edge of the lower knife. To prevent this, the metal is pressed to the table with a special clamp. However, when cutting metal between the knife and the clamp, it tends to bend perpendicular to the cutting plane. Based on this, the distance between the clamp and the cutting edge of the knife is chosen such that the bending of the sheet is minimal.
Rice. 5. Scheme of operation of knives:
α – knife opening angle; ẞ – knife sharpening angle; ɣ – bevel angle; δ – cutting edge angle.
Shear angle.
To cut a long sheet of metal in one stroke of the knife, considerable effort is required, which will be spent on cutting the knives into the metal and chipping it. To reduce power consumption for all these operations, the knives are installed at an angle to each other (Fig. 5). The greater the angle α, the less force required for cutting. So, for example, if you cut sheets of the same thickness with and without tilting the knives (tilt angle 5°), the difference in effort will be significant: