The nominal diameter of the pipe is an important indicator
To understand the importance of this criterion, you need to understand why it is needed and what it is.
To begin with, the most common problem faced by pipeline installers is the difference in the diameter of each pipe, as well as the fittings that are used in conjunction with it. The thing is that pipes for gas or water can be divided into three groups depending on their strength.
- The first category is light.
- The second category is ordinary.
- The third category is reinforced pipes.
The nominal diameter of the pipe is the standard diameter of the pipeline
People who deal with pipelines know that the nominal diameter of a pipe is a parameter that is used to mark water and gas pipelines. In addition, steel pipes and fittings are subject to the same marking. The main feature of the parameter is that it is almost never equal to the external or internal indicator.
The nominal diameter of the pipe is an important indicator
To understand the importance of this criterion, you need to understand why it is needed and what it is.
To begin with, the most common problem faced by pipeline installers is the difference in the diameter of each pipe, as well as the fittings that are used in conjunction with it. The thing is that pipes for gas or water can be divided into three groups depending on their strength.
- The first category is light.
- The second category is ordinary.
- The third category is reinforced pipes.
Difference in performance
It is also worth noting that the nominal diameter of the pipe is the internal diameter of the product, which is rounded up or down depending on which standard value is closer.
Some people have a logical question: why not use the external diameter indicator for pipes. Here you need to know that all pipelines, except gas and water, are marked in this way. But these two systems have their own specifics, which are related to throughput, which is based specifically on the internal diameter. The need for a conditional passage is justified as follows.
For example, there is a DN 25 pipe, the outer diameter of which is 33.5 mm. The thickness of the wall of such a product can be 2.8, 3.2 or 4 mm. This means that the internal value will also be different and be 27.9, 27.1 and 25.5 mm respectively. However, it is immediately important to note that all three types of design will be fully compatible with pipe threads with a diameter of 25 mm.
In other words, the nominal diameter of the pipe is an average value that facilitates the selection of suitable structural elements.
Why is the conditional passage indicator necessary?
The nominal diameter is also the nominal diameter. This value exists to describe the system. Here it is used as a characterizing feature during installation, as well as when connecting various parts of the pipeline to each other.
It is worth noting that on domestic shut-off valves, for example, those installed on pipes, the nominal bore is designated as DN (nominal diameter). However, at present, most manufacturers are switching to the designation system adopted abroad. Instead of DN, the designation is DN (nominal diameter - DN - diameter nominel). If such marking is indicated, then you need to know that the digital value can be in mm or inches. One inch is equal to 2.54 cm.
Bandwidth
An important requirement for throughput is that during a transition in the system it must increase by an amount that corresponds to a value from 60 to 100%. In order to achieve this indicator, it is necessary to calculate the appropriate calibration of the nominal diameter for a gas pipe or water pipe.
The maximum throughput will depend on the correct calculation. In other words, we mean the average design parameter for transmission. The result must be rounded to the nearest standard value. When installing a piping system, the true level rarely corresponds to the size of the structure.
The easiest way to show this is with an example.
The outer diameter of the system is 159 mm. The pipe wall thickness is 8 mm. The true exact value of the internal diameter will be 143 mm. If, for example, you change the wall thickness to 5 mm, the value will become 149 mm. However, despite the difference in numerical values in these cases, the piping system will be marked at 150.
Determination of internal dimensions
It’s worth mentioning an important rule right away: the actual internal diameter of the pipe will directly depend on the actual wall thickness of the product. This is important, since all remaining dimensions for gas and water supply systems will be determined in accordance with it. Other systems use the outside diameter as the primary measurement.
It is also important to understand that steel materials are used here, which means their size will always be constant.
The reason that the actual indicator will almost always differ from the nominal diameter is that these systems will be operated in an environment with increased pressure, which means that the thickness of their walls increases to minimize the risk of breakthrough.
An example of such a discrepancy can be given. The outer diameter of the reinforcement is 273 mm. The actual wall thickness is 9 mm, but with such indicators the actual internal diameter is 255 mm. What is the nominal diameter of the pipe in this case? It is equal to 250 mm - this is the closest standard value.
Setting parameters according to documents
As has already become clear, the nominal diameter (clearance, DN) is the value of the internal diameter of the pipe, taking into account the thickness of its walls. GOST 28338-89 describes all technical requirements, markings and other important parameters, including the nominal diameter of the pipe, in full. Knowing this value is necessary in order to successfully create a water supply, gas pipeline, sewerage, etc. system in such a way as to have an integral structure that will not have the risk of depressurization.
This fact alone is enough to make it clear: remote control is the most important indicator that is necessary for setting up a reliable and working system.
Difference in performance
It is also worth noting that the nominal diameter of the pipe is the internal diameter of the product, which is rounded up or down depending on which standard value is closer.
Some people have a logical question: why not use the external diameter indicator for pipes. Here you need to know that all pipelines, except gas and water, are marked in this way. But these two systems have their own specifics, which are related to throughput, which is based specifically on the internal diameter. The need for a conditional passage is justified as follows. For example, there is a DN 25 pipe, the outer diameter of which is 33.5 mm. The thickness of the wall of such a product can be 2.8, 3.2 or 4 mm. This means that the internal value will also be different and be 27.9, 27.1 and 25.5 mm respectively. However, it is immediately important to note that all three types of design will be fully compatible with pipe threads with a diameter of 25 mm. In other words, the nominal diameter of the pipe is an average value that facilitates the selection of suitable structural elements.
The nominal diameter of the pipe is: the standard diameter of the pipeline
GOST 28338-89 clearly regulates the parameters and marking of all tubular products, regardless of the material of their manufacture. And one of the important ones here is the conditional passage of the tube. The nominal diameter (clearance, passage, DU) is the internal diameter of the product, which differs from the outer diameter due to the thickness of the walls of the product.
Understanding and knowing the size of the internal clearance (CL) of the tube, you can select all the connecting elements in such a way that the water supply system (sewerage, etc.) has a single and complete appearance without the risk of depressurization.
Based on this, it becomes clear that the nominal diameter of all products for installing a sewer or water main is the most important parameter that contributes to the assembly of a straight and high-quality operating system.
Important: initially the nominal diameter of the pipe was marked with the letters DU. Today this value is determined by the letters DN.
Note that most often the dimensional parameters of prefabricated elements made of cast iron or steel are marked by the internal diameter (nominal clearance/DN), while rolled products made of polymers, copper and sometimes steel are marked by the outer diameter.
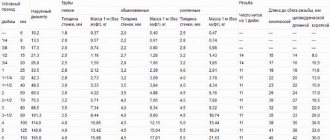
Dimensional chart of rolled pipes
All tubes produced in modern and foreign production are manufactured in accordance with the size range, which has 49 options
All tubes produced in modern and foreign production are made in accordance with the size range, which has 49 options. In this case, the diameter (DN) of products varies from 2.5 mm to 4000 mm.
It is worth noting that only three types of tubes from the entire size grid can be used for the installation of hydraulic and pneumatic lines. These are elements with a diameter of 16, 63 and 160 mm. There are also five types of round sections that are not used as general purpose pipe fittings. These are hoses with diameters of 0.175 m, 2.6 m, 3.2 m, 3.6 and 3.8 m.
Such exceptions indicate that GOST 28338-89 has clear regulations for 40 standard and 8 specialized pipe dimensions.
Definition of marking
According to established norms and standards, today the nominal diameter is indicated by the letters DN (formerly DU), and the clearance value is marked in mm
According to established norms and standards, today the nominal diameter is designated by the letters DN (formerly DU), and the clearance value is marked in mm.
Thus, if we have a tube marked DN150 in front of us, this does not mean at all that its internal lumen is equal to this value. This marking can mark elements with outer and inner diameters of 156/149 or elements with outer and inner sections of 156/144 mm.
According to the table of permissible conditional values in GOST 28338-89, both the indicator 144 and the indicator 149 mm are rounded to a conventional section of 150 mm.
And to accurately calculate the nominal diameter of a pipeline, you can use the formula:
D(in) - 2S =DN (formerly DU)
- In the formula, the value D(ext) means the outer diameter of the circular element. S is the thickness of its wall.
For example, we have a section with a cross-section of DN110 mm and a wall thickness of 6 mm. You need to subtract 110 (6x2). We get an exact pipe clearance of 98 mm.
Nominal diameters for steel pipes
Rolled steel has conditional clearances, which are formed depending on the method of production of the elements
Rolled steel has conditional clearances, which are formed depending on the method of production of the elements. Therefore, there is a table of conditional values, which are reduced to the following values:
- For tubes made using hot rolling technology - 20-500 mm (in accordance with GOST 8732-78);
- If the products were produced using cold rolling technology, the values are narrowed to 5-250 mm (according to GOST 8734-75);
- Welded tubes with a longitudinal seam - 10-1400 mm (in accordance with GOST 10704-91);
- For welded pipe elements with a seam in the form of a spiral - 160-2400 mm (GOST 8696-74).
Important: all rolled steel has a 38-digit dimensional grid with conventional numerical values for each diameter. In addition, the range of steel products includes tubes with four special clearances, which are used for pneumatic and hydraulic lines.
Conventional diameter values for polymer pipes
The parameters of polymer elements for a main (pipeline) of circular cross-section are regulated by GOST 18599-2001
The parameters of polymer elements for a main (pipeline) of circular cross-section are regulated by GOST 18599-2001, which clearly states that the range of products can be manufactured in 32 standard sizes. Their size range is 10-1600 mm.
Moreover, all 32 types of size range of plastic products are additionally divided into four groups according to the wall thickness of the product. That, in turn, varies in the range of 2-70 mm. The pressure resistance inside the tube for rolled polymer products can be in the range of 0.16-2 MPa.
Thus, by understanding the internal nominal diameter of each element, it is possible to design the main line (pipeline) as accurately as possible, determining its internal pressure and network capacity.
Source: https://vodakanazer.ru/truboprovod/diametr-uslovnyj.html
Why is the conditional passage indicator necessary?
The nominal diameter is also the nominal diameter. This value exists to describe the system. Here it is used as a characterizing feature during installation, as well as when connecting various parts of the pipeline to each other.
It is worth noting that on domestic shut-off valves, for example, those installed on pipes, the nominal bore is designated as DN (nominal diameter). However, at present, most manufacturers are switching to the designation system adopted abroad. Instead of DN, the designation is DN (nominal diameter - DN - diameter nominel). If such marking is indicated, then you need to know that the digital value can be in mm or inches. One inch is equal to 2.54 cm.
Bandwidth
An important requirement for throughput is that during a transition in the system it must increase by an amount that corresponds to a value from 60 to 100%. In order to achieve this indicator, it is necessary to calculate the appropriate calibration of the nominal diameter for a gas pipe or water pipe. The maximum throughput will depend on the correct calculation. In other words, we mean the average design parameter for transmission. The result must be rounded to the nearest standard value. When installing a piping system, the true level rarely corresponds to the size of the structure. The easiest way to show this is with an example.
The outer diameter of the system is 159 mm. The pipe wall thickness is 8 mm. The true exact value of the internal diameter will be 143 mm. If, for example, you change the wall thickness to 5 mm, the value will become 149 mm. However, despite the difference in numerical values in these cases, the piping system will be marked at 150.
Features of pipe passage
The most important characteristic of any design is the diameter. It can be conditional, nominal, external and internal. In order to accurately make a design calculation taking into account all the necessary characteristics, you need to know a lot about the products used. For this purpose, the existing classification by size and wall thickness is used. Designers' work is greatly facilitated by standards regulating this value.
To calculate the parameters of the future design, it is necessary to take into account such an important indicator as the passage of pipes.
What is the nominal diameter of a pipe?
This is an indicator of a nominal parameter that exists to describe the system as a characterizing feature when installing and connecting various parts to each other (the parts themselves, fittings, other equipment for the pipeline).
The diameter of the pipeline lumen has the approximate value of the nominal diameter. It is labeled as, for example, DN 100.
Diagram of the nominal diameter of the pipe.
The throughput capacity of the pipeline during the transition must increase by an amount corresponding to a value from 60 to 100%; it is for this that the corresponding calibration of the nominal diameter is calculated. The throughput capacity of the pipeline will depend on the correctness of the calculation.
In other words, this concept is understood as the average parameter of the product (for light). The value is rounded up or down to the standard notation.
The passage designation is as follows: Du. Numbers corresponding to the size in millimeters are added to the letter value.
The true level usually does not exactly correspond (there are rare exceptions) to the size of the structure.
- Let's give an example. The system, which has an outer diameter of 159 mm and a wall thickness of 8 mm, has a true accurate internal dimension of 143 mm. If the wall thickness is 5 mm, then 149 mm. But, despite the difference, in both cases the passage will be designated as equal to 150 mm.
GOST 28338-89 standards set the basic parameters for the passage of fittings, fittings and connecting parts of technological and plumbing devices to be connected to fittings.
Pipe Internal Size
The actual internal diameter of the pipes directly depends on the actual thickness of the walls.
Table comparing the conditional passage of water mass through the pipe body.
Dimensions for a water or gas pipeline are determined by this parameter, and other types - in accordance with the external one.
Steel products are characterized (according to technological production conditions) by constant values. And due to the fact that for structures intended for use in high-pressure conditions, the thickness of the walls is increased, this size will differ from the passage. An example of such a difference is the following calculation.
- The external reinforcement parameter is 273 mm with a wall thickness of 9 mm, while the actual internal parameter (excluding tolerances) is 255 mm. But the value of the nominal diameter will be indicated by the closest standard value, that is, 250 mm.
Variety of diameter types
Classified as follows:
- conventional (DN) - the nominal value of the internal size in millimeters or a rounded digital value in inches;
- nominal (Dn);
- outer;
- interior.
Since a combined system is often used, for an easier and more correct choice, a special table has been developed for matching the diameters of, for example, steel products to polymer reinforcement.
The material of the pipes is of great importance when calculating their required diameter.
Let's say if you need to lay a system using only steel structures, then there will be no difficulties. The diameter of steel products is indicated in inches.
If you need to connect steel and plastic structures, then in order not to make a mistake in the dimensions, you need to use a special table.
This regulatory document is intended to determine the exact correspondence of the inch length of steel parts to plastic parts. Since the diameter of most plastic structures is indicated in millimeters.
The inch is a unit of distance used in several non-metric measurement systems. Typically, an inch value of one will correspond to 1/12 or 1/10 of a foot, depending on the country. Nowadays, an inch value is understood as a value in English inches equal to 2.54 centimeters.
Why is the exact size of the systems used determined?
The exact diameter value will allow you to calculate the planned volume of the substance to be transported through the pipeline. Knowledge of the characteristics of the parameters of various systems is important both on an industrial scale and at home.
The installation of a heating system or its repair in your home is carried out with preliminary calculations so that winter does not take you by surprise and all living rooms are heated efficiently and evenly. The recommendations and features described above will allow you to learn more about the parameters of the pipeline. If you have any doubts or difficulties, it is better to consult a specialist.
Share a useful article:
:
Source: https://experttrub.ru/osnovnye-operacii/uslovnyj-proxod.html
Determination of internal dimensions
It’s worth mentioning an important rule right away: the actual internal diameter of the pipe will directly depend on the actual wall thickness of the product. This is important, since all remaining dimensions for gas and water supply systems will be determined in accordance with it. Other systems use the outside diameter as the primary measurement. It is also important to understand that steel materials are used here, which means their size will always be constant. The reason that the actual indicator will almost always differ from the nominal diameter is that these systems will be operated in an environment with increased pressure, which means that the thickness of their walls increases to minimize the risk of breakthrough.
An example of such a discrepancy can be given. The outer diameter of the reinforcement is 273 mm. The actual wall thickness is 9 mm, but with such indicators the actual internal diameter is 255 mm. What is the nominal diameter of the pipe in this case? It is equal to 250 mm - this is the closest standard value.
Indication of the nominal diameter depending on the type of pipe
When indicating the nominal diameter for pipeline fittings, everything is extremely simple. The rounded internal diameter is indicated, for example, like this: DN20, but sometimes an outdated designation can be found: DN20, or Dy20, according to the previously valid CMEA 254-76.
READ ALSO: How to tie peonies - several ways 2019
But with the indication for different types of metal and plastic pipes, not everything is so simple, and confusion often occurs due to incorrect indication or uncertainty as to what diameter is indicated, external or internal (nominal diameter).
And the question arises, how is the pipe diameter correctly indicated? The following are examples of correct designations for some types of pipelines.
Designation of water and gas pipe (VGP pipe)
Water and gas pipes (WGP) include metal welded products made of steel in accordance with GOST 1050 and GOST 380, as well as other approved regulations. Applicable:
- In building heating systems;
- Various types of water pipelines;
- In the designs of gas pipeline systems and gas pipelines;
Example notation
Steel pipe manufactured in accordance with GOST 3262-75, with a nominal bore of 32 millimeters and a wall thickness of 3.2 millimeters.
The same thing only with the clutch.
Steel VGP with thread, zinc coating, cut to length. And so on.
Designation of electric-welded straight-seam pipes
Straight-seam electric welded steels are made from low-alloy or carbon steels. Used for the manufacture of pipelines for various applications.
Example notation
Steel pipe, produced in accordance with GOST 10704-91, with an outer diameter of 70.0 millimeters, a wall thickness of 4.0 millimeters, measured length (5000 mm), class II (manufacturing accuracy along the length), made of steel “StZsp”, produced in accordance with group “B” of GOST 10705- 80.
READ ALSO: At what temperature to solder polypropylene pipes, Aqua-Info
Specifying the diameter of seamless steel pipes
Seamless steel pipes are made from alloy or carbon steels. The absence of seams increases the resistance of the pipeline to various physical influences, such as operating temperature and nominal pressure.
Example notation
Steel pipe produced in accordance with GOST 32528-2013, with an outer diameter of 60.0 millimeters, a wall thickness of 4.0 millimeters, measured length (6000 mm), increased manufacturing accuracy, grade 40X steel, produced according to group “B”.
Unmeasured length, produced in accordance with GOST 32528-2013, with an outer diameter of 95.0 millimeters and an internal diameter of 76.0 millimeters, steel grade 10, produced according to group “B”.
Indication of plastic pipe diameters
Plastic pipes and various fittings are made from the following types of thermoplastics:
They are used for the manufacture of heating pipes, hot and cold water pipelines in accordance with GOST 32415-2013.
Example of designation of plastic pipes and fittings
Manufactured from uPVC, with a nominal outside diameter of 25.0 millimeters, a nominal wall thickness of 2.3 millimeters, and a pressure rating of PN25.
Symbol for plastic fittings:
Coupling made of PVC-U for connecting pipelines with DN 63.0 mm, complies with SDR 13.6, nominal design pressure PN16.
READ ALSO: How to cut a 110mm plastic pipe - photo - Mastergrad Forum
Setting parameters according to documents
As has already become clear, the nominal diameter (clearance, DN) is the value of the internal diameter of the pipe, taking into account the thickness of its walls. GOST 28338-89 describes all technical requirements, markings and other important parameters, including the nominal diameter of the pipe, in full. Knowing this value is necessary in order to successfully create a water supply, gas pipeline, sewerage, etc. system in such a way as to have an integral structure that will not have the risk of depressurization.
This fact alone is enough to make it clear: remote control is the most important indicator that is necessary for setting up a reliable and working system.
Why determine the exact parameter
Some may ask: why carry out calculations down to such details?
The answer is that knowing the exact size of the internal diameter of the pipe and the nominal diameter will allow you to accurately calculate the volume of the substance that this pipeline system can supply. Knowing and being able to calculate these details is an important skill both on an industrial scale and at home.
This skill can be useful if, for example, heating pipes leading to a private house are being installed or repaired, or replaced. In such a situation, it is necessary to thoroughly accurately measure all diameter indicators, since the quality and uniform distribution of heat throughout the entire area of the building depends on this.
When installing the same heating system, you will also have to figure out what heat flow is and how to increase it. There are two ways to do this - increasing the internal diameter, as well as increasing the coolant speed. If we talk about the first case, then it is unprofitable, since the cost of the pipe will increase greatly with increasing DP, which will lead to a significant increase in costs.