- Video author: DoHow
- Author's channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCVan_d0CRKJZ3j2qwPA8c4Q
- Video:
Our advice on laying sewer pipes in a country house is addressed to those who decide to do this work themselves. We need to take certain measures to ensure that this sewer system works properly and does not silt up.
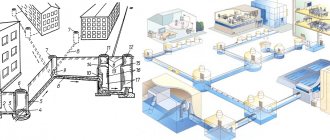
The external sewer route from the house to the septic tank can have a different appearance.
Preparing the trench
Let's start by preparing the trench for the pipes. When using a standard sewer pipe with a diameter of 110 mm, the width of the trench can be one shovel bayonet.
However, in places where the pipe approaches the sewer septic tank and where the pipe exits the house, the trench must be expanded for ease of operation. The depth of the trench for laying sewer pipes is selected based on experience in operating sewer systems in your region. For the middle zone, you can focus on the average trench depth: 80 - 120 cm. To be sure, you can increase the depth of laying the pipes, but remember that in this case, several upper rings of the septic tank will not be used. When preparing the trench, it is necessary to add 10-15 cm of depth to the sand that will be laid at the bottom. Sand allows you to level the bottom of the trench and creates a cushion on which the sewer pipe is laid. The sand leveled at the bottom of the trench must be compacted to prevent further shrinkage.
How to lay sewer pipes in the ground
Installation of external sewerage into the ground occurs in three stages:
- Preparation of trenches.
- Pipeline installation.
- Backfilling.
Digging a trench
Before digging trenches for laying sewers, calculate the network configuration and determine:
- The optimal geometric shape of the pipeline: the most efficient and easiest to maintain will be a pipeline with a minimum number of corners and branches; if possible, the pipeline is led in a straight line from the house to the place of wastewater discharge. To avoid obstacles, it is permissible to turn the pipeline at an angle of 30-45 degrees. Right angles in the sewer network are unacceptable due to the increased pressure of wastewater on the walls of the pipeline and the increased likelihood of blockages.
- The depth of the trenches, which allows maintaining the operability of the channels in winter: below the depth of soil freezing per pipe diameter plus 15-20 cm for the sand cushion. The minimum permissible trench depth is 0.5 m, the optimal depth varies from 2 m in the southern regions of Russia to 3.5 m in the northern regions.
- Angle of inclination ensuring free flow of wastewater: usually, a slope of 1-2 cm per meter of pipeline is sufficient;
- Trench width: 40 cm is added to the pipe diameter; for large depths and pipe diameters greater than 20 cm, the trench width is increased for ease of installation.
We recommend that you read: Types and applications of double-wall corrugated pipes
After the calculations are completed, excavation work begins. Small trenches are dug by hand; an excavator is used to dig deep and long channels.
Prepare a trench for laying sewer pipes in two or three steps:
- They dig a trench.
- Level and compact the bottom, remove clods of earth and stones.
- In a trench dug in loose soil, additional formwork is installed to prevent the soil from crumbling during work.
At this stage, you can check for obstacles to the free flow of water. To do this, pour water into the trench and monitor how freely it flows through the channel. If the slope is insufficient, puddles accumulate; if the channel turns too sharply, water washes away its walls.
Identified problems are resolved before laying pipes by increasing the slope of the trench and the turning radius in problem areas.
Laying rules
Pipe connection method:
- welded - a welding machine is required for the connection, the connection is unreliable, the unit may depressurize as a result of corrosion or mechanical stress;
- fitting - connected using shaped elements, depending on the type of fitting, it can be dismountable or non-separable;
- socket - the end of one pipe is inserted into the socket of another, the tightness is ensured by a rubber seal fixed in the socket.
To lay external sewerage, pipes with a cross-sectional diameter of 11 cm or more are used.
To install a sewer system, in addition to pipes, you will need tees, the side hole of which will serve as an inspection. Tees are installed in the pipeline at intervals of 3-4 m for ease of sewerage maintenance.
To distribute the pressure that the earth covering it exerts on the pipeline and to prevent deformation and breakage of the pipes, a shock-absorbing layer of sand is required.
- Fill in a shock-absorbing “cushion” of sand and compact it.
- Lay out the pipes in the trench. With the fitting method of connection, the presence of the necessary shaped elements is checked; with the socket method, the pipes are laid out with sockets against the direction of the drain.
- The sections of the pipeline are hermetically connected, starting with the connection to the sewer outlet from the house. Every 3-4 meters, tees are installed with a side branch upward, inspection pipes are brought above the ground level and closed with plugs. The pipeline is brought to the place of wastewater discharge.
- Check the tightness of the connections. You can lubricate the joints with a soap solution and blow out the pipeline with a compressor or run water through the pipes. In the first case, soap bubbles will appear in places where the seal is broken, in the second, water will leak.
- Sand is poured in layers on the sides of the pipes, each layer is compacted.
- The top layer of shock absorption is filled in and the final backfill is carried out with the earth remaining after digging the trenches. Backfilling is done with a reserve - gradually the earth will settle under its own weight.
Note! The bottom and side sand cushions are compacted to prevent pipeline distortions. The top layer of shock absorption and soil are not compacted so as not to deform the pipes.
Horizontal puncture method
It is possible to lay external sewerage without digging trenches - using the horizontal puncture method. This method is relevant for areas where there are outbuildings, road surfaces or landscape design, and excavation work is undesirable. A suitable method for removing sewage from a site into a general sewer system if there are serious obstacles in the way, for example, a road.
We recommend that you read: The height of ventilation ducts above the roof: 5 factors influencing the calculation
Using an HDD drilling rig - horizontal directional drilling - a well is laid, it is widened and a metal or plastic pipe is pulled through. The work is carried out in stages, for each action there is a separate set of attachments attached to the drill rod of the installation.
- A drill head with a beveled edge is attached to the rod. The head facilitates the advancement of the drill rod when drilling a horizontally directional pilot hole.
- The drill head is replaced with a reverse-action expander - a rimmer. This conical nozzle, when passing through the pilot hole, expands it. The finished well has a cross-section approximately 1.5 times larger than that of the pipe being laid.
- A loop is attached to the expander, which is brought out from the end of the well opposite from the drilling rig. The end of the pipeline is grabbed with a loop and the pipeline is pulled through the well.
Using a locator, the drilling rig operator controls the direction and intensity of movement of the drill head and rimmer.
Checking the standard slope
One of the main tasks when laying external sewer pipes is checking the standard slope. For external sewerage, red pipes of two diameters are used: for an average country house with two bathrooms and toilets, a pipe with a diameter of 110 mm is used, and if there are three or more toilets, it is recommended to use a pipe with a diameter of 160 mm.
For each of these pipes, the standard slope with which the pipe must be laid in the trench is calculated. For a pipe with a diameter of 110 mm, the slope is 0.02. This means increasing one of the sides by 2 cm per 1 meter of length. For a pipe with a diameter of 160 mm, the slope is 0.008, which means an increase in one of the sides by 8 mm per 1 meter of pipe length.
Compliance with these slopes allows you to maintain the transport capacity in the pipes, which in turn reduces the gradual silting of the pipes to zero. The best device for
Installing a level ruler at the control point of the trench allows you to adjust the depth of the trench with high accuracy. Remember a simple rule: the closer the trench slope is to the standard, the better the external sewage system will work.
Checking the slope on long sections without a level
There is a simple way to check the slope, which involves the presence of a cable, two pins and a building level.
Pins are installed in the dug trench - at the very beginning and at the very end, then at a height convenient for control, a cable is tied to the pins. Using a building level at one of the pins, the cable is adjusted horizontally, then measurements are made at two points. At the very beginning, the height of the trench is checked along the cable, and then the height of the trench is checked at the very end, and also up to the cable.
Next, a simple geometric problem of finding the slope is solved. So, if the height at the first point at the exit from the house is 0.5 meters, the total length of the segment is 30 meters, then at the final point of measurement the height to the cable should be 1.1 meters.
We get a difference between the two measuring points of 60 cm, which for 30 meters of length corresponds to a slope of 2 cm for each meter. In this example, the calculation was made for a pipe with a diameter of 110 mm. Now let’s try to figure it out: what will happen if for some reason you don’t comply with the established slope? With a standard slope, the liquid passes through the pipes at a certain speed, carrying feces along with it. If the slope changes upward, the speed of the liquid will increase, while its transporting capacity will sharply decrease, and some of the solid contaminants will remain on the pipe.
A variant of uneven slope is possible, when individual segments have different slopes. In this case, part of the pipe will also become silted. And here's another incorrect option:
But what about owners of plots that have a natural slope that exceeds the standard? In this case, if you simply lay the pipe along a natural slope to the septic tank, this will lead to constant silting. There are two ways to solve this problem. The first option is to create a system with several transitions, where there are strictly vertical sections and inclined sections with a standard slope.
The second option will require more excavation work.
It has only one vertical section at the very beginning. The inclined part is located at a greater depth, but has a standard slope.
Insulation of pipes and work in winter
Another question that should be considered is whether it is worth insulating the pipes? Energyflex material is often used to insulate sewer pipes. It is available in different diameters and easily fits onto the appropriate pipe.
Let's see how the sewer pipe works in winter, especially in the part leaving the house. As the liquid drains, the pipe is partially filled. The drains always have a positive temperature, so water vapor forms in the pipe.
In winter, the section of the sewer pipe located close to the surface partially cools, causing first condensation to appear, and then frost, which will tend to the center of the pipe. Under certain circumstances, it is frost that can cause a blockage in the pipe, so the use of insulation prevents frost from appearing inside the pipe.
Which pipe to use for underground sewerage
Cleaning sewer pipes
According to statistics, about 90% of pipelines in the private sector are made of low-density polyethylene. Experts recommend using HDPE pipes for external sewerage for the following reasons:
- long service life (minimum 40 years);
- corrosion resistance;
- chemical resistance;
- low thermal conductivity;
- resistance to water pressure and water hammer.
When laying HDPE sewer pipes in the ground, you do not have to worry about freezing of the drains. The material expands by 7% and then returns to its original state.
Light weight makes installation of the system easier. Compared to steel products, welding to connect HDPE pipes underground is much easier to perform, and the seams are more durable.
Polyethylene pipes, having excellent performance characteristics, are relatively cheap.
Laying and joining of pipes
All pipes have rubber seals, which may not be so easy to insert into another pipe.
To facilitate this process, use silicone plumbing grease or regular dishwashing detergent. The lubricant is applied around the perimeter of the pipe and ensures easier joining. Do not try to push the pipes by force, as you may tear the rubber out of the seat and break the seal of the pipe. When laying long sections of sewer, all pipes are joined in advance. Before laying the assembled pipe, a pipe having a given angle is usually put on the pipe exiting the house.
When laying long sections of external sewers, it is better to use assistants to prevent the pipe from breaking. A properly laid pipe should lie evenly on the sand bed. The other end of the pipe is inserted into the opening of the septic tank.
If the septic tank was recently dug, do not rush to seal the hole with cement mortar. This will prevent the edge of the pipe from breaking when the septic tank settles. When filling a pipe, sand comes first, hiding the top of the pipe. The sand can be spilled with water to make it shrink, and then add more. Only after this is the soil backfilled from the trench.
Inspection device
According to the rules, after each turn of the external sewer pipe, an inspection or cleaning must be installed.
In addition, it is recommended to install revisions for every 15 meters of straight sections. What is the simplest revision?
It is collected from the same sewer pipe, but exits vertically to the surface. The inspection consists of a tee, a straight piece of pipe and a plug covering the pipe.
All these parts fit into the main sewer system in the right places. The inspection pipe will be used to clean the relevant sections of the sewer system. It is also recommended to insulate it.
Whether to make revisions or not is up to everyone to decide for themselves, but, in our opinion, this is a practical and inexpensive solution that allows you to keep the external sewage system in good condition.
Pipe materials
Traditionally, sewer pipes were made of cast iron. But with the development of the chemical industry, new materials appeared. Now the construction market has a large selection of more modern products in this category. Which pipes are best suited for external sewerage, and what requirements must they meet?
Features of operation highlight such characteristics as:
- durability;
- strength;
- resistance to aggressive substances;
- throughput;
- ability to withstand low temperatures.
The weight of the product and ease of installation are also of great importance.
Guided by these criteria, we will consider sewer pipes made from different materials.
Cast iron
Its durability is confirmed by extensive experience in both civil and industrial construction. But it is difficult to call cast iron pipes the optimal choice for sewerage - they are heavy, and this causes problems with installation. The need to ensure the tightness of joints also causes a lot of trouble. The characteristic rough surface of the material leads to the accumulation of deposits over time.
Cast iron pipes
Black steel
Durable and inexpensive, but not corrosion-resistant products. They are rarely used for domestic needs.
Ceramics
Pipes are made by firing clay and covered with glaze on top. They have good resistance to corrosion and aggressive chemical influences, but are heavy, expensive, fragile and do not withstand shock loads well. If the glaze breaks off, the product loses all its protective properties.
Reinforced concrete
The material is very reliable, chemical and biological resistance. However, their heavy weight and installation problems make reinforced concrete pipes not the most attractive choice for installing a sewer system in a private home.
Asbestos cement
Pros: strength, chemical resistance, lack of corrosion, excellent heat-shielding characteristics, low weight and low price. The disadvantages include fragility.
Polymers
This category includes products made from PVC, polypropylene, low-density polyethylene, etc. They have undeniable advantages over pipes made from the above materials: cheap, lightweight, reliable, very easy to install, with a smooth inner surface.
The use of polyethylene for the production of pipes made it possible to develop a trenchless installation method. Double-layer corrugated pipes have such ring rigidity that they are suitable for use even at a depth of 20 meters. Polypropylene pipes have a long service life and are very easy to assemble.
Corrugated HDPE pipe with a smooth inner surface