What properties do different types of polypropylene pipes have?
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic synthetic non-polar polymer. The polymerization method using a Ziegler-Natta catalyst was invented in 1957, and since then the production of products with an isotactic structure characterized by high strength
, heat resistance and a high degree of crystallinity.
Polypropylene is a material that is resistant to acid, alkaline and saline solutions, as well as other inorganic substances. It does not absorb liquid and retains its electrical insulating properties over a wide range of temperatures.
Based on polypropylene, various modified materials are produced, such as thermoplastic, high-strength plastic and other environmentally friendly products. Recycling and recycling are a technological process, due to which polypropylene is actively displacing products made from other types of plastics from the world market.
Polypropylene melts at a temperature of +164…+170 °C
, Brinell hardness ranges from 40 to 70 MPa, brittleness temperature - from
-10 to -15 ° C
, tensile failure stress (kgf/cm2) - from 250 to 400, flexural modulus of elasticity (kgf) - from 6700 to 11900 .
A huge number of products that are popular on the market today are made on the basis of sheet propylene. To produce this material, the extrusion method is used. Depending on the shade, smoothness and other factors, sheets are divided into two classes. They are used for the production of pipeline systems, connecting them together in different ways, one of which is welding.
Material for the manufacture of water supply and sewerage systems
These products can be used to organize water supply and heating. How to choose polypropylene pipes for water supply based on its purpose?
The following restrictions apply to the transported liquid:
- Operating temperature – no more than +70 degrees.
- The pressure at a temperature of +70 degrees should not be more than 10 bar, at a temperature from 0 to +25 degrees - 25 bar.
- Short-term increases in temperature up to +90 degrees are allowed.
Depending on the purpose of the system, the selection of appropriate products will be required:
- Gray polypropylene pipes are characterized by the ability to withstand operating loads more resistant than similar white products. For heating products they are a more preferable option.
- For hot water, thicker pipes are used.
- Products with aluminum or fiberglass reinforcement are sometimes used in systems equipped with geysers. However, this is a violation of their operating conditions, which leads to a reduction in service life.
Types of polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene (accepted international designation - PP) has been used for quite a long time for the manufacture of pipes as a base material. However, only the development of modern technologies has made it possible to obtain products that can be used for hot water supply and heating systems.
Polypropylene itself is characterized by its pronounced inertness to the chemical effects of a possible liquid coolant medium. However, in terms of heat resistance and strength, different types can differ significantly from each other.
So, pipes made of this material are divided into three main types, which have their own designations:
PP-N are intended for cold water only
- PP-N is the first type of polypropylene pipes, inert to chemical influences, but not resistant to elevated temperatures. Therefore, they are intended for cold water supply, sewerage, drainage systems, ventilation and other applications where elevated temperatures are not expected. Very often, this type of pipe is prevalent for industrial production lines, as it is highly resistant to increased internal pressure.
The range of possible applications of PP-V pipes is somewhat wider, but for heating they are still “weak”
- PP-B is the second type of polypropylene pipes, which has all the same advantages of PP-N, but, in addition, has the ability to withstand temperature loads of low amplitude. Therefore, they can be installed on separate main sections of “warm floor” systems. And also in hot water supply circuits, provided that the water or coolant does not heat above 50 degrees.
However, the main scope of application of PP-B is different. Most often, such pipes are used for sewer systems, since the material from which they are made has a sufficient degree of impact strength and heat resistance for this area.
Only PPR pipes are fully suitable for heating systems
- PPRC, PPR or PP-3 is the most advanced type of pipes that is used in hot water supply and heating systems, that is, where temperatures can exceed 50 degrees and there is a possibility of increased compression loads. Increased heat resistance and mechanical strength are achieved thanks to special production technologies, in which ethylene molecules are introduced into the molecular lattice of propylene during synthesis.
PPR are pipes that are most widely used in domestic conditions, as they have a pronounced resistance to internal pressure and temperature changes.
Polypropylene pipes (PPR), used in domestic conditions, in turn, are divided into several types, depending on resistance to baric loads: PN -25; PN -20; PN -16; PN -10. Their main characteristics are given in the table:
| Type of polypropylene pipes | Nominal working pressure | Scope of pipe use | |
| MPa | technical atmospheres (kgf/s²) | ||
| PN-10 | 1 | 10.21 | Connection to the “warm floor” circuit, the coolant in the system of which has a temperature of no higher than 45 ° C, or cold water supply. This type of pipe is designed for a system pressure of no more than 1 MPa. It is the most affordable due to its rather low performance characteristics. |
| PN-16 | 1.6 | 16.32 | Cold and hot water supply with a temperature of no more than 60˚C and a pressure of no more than 1.6 MPa. |
| PN-20 | 2 | 20.40 | Cold and hot water supply in an autonomous system with low pressure and no water hammer. The coolant temperature for this type of product should not exceed 80˚C, and the pressure should not exceed 2.0 MPa. |
| PN-25 | 2.5 | 25.49 | Hot water supply and heating with coolant up to 90÷95˚С, including in the central heating system. The pressure for which they are designed is 2.5 MPa. |
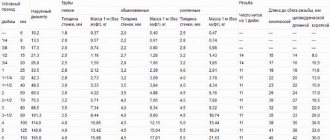
Each type of pipe is produced in a fairly wide range of diameters, internal and external: on which the wall thickness depends
| Outer diameter, mm | PN-10 | PN-16 | PN-20 | PN-25 | ||||
| Internal Ø, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Internal Ø, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Internal Ø, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Internal Ø, mm | Wall thickness, mm | |
| 16 | — | — | 11.6 | 2.2 | 10.6 | 2.7 | — | — |
| 20 | 16.2 | 1.9 | 14.4 | 2.8 | 13.2 | 3.4 | 13.2 | 3.4 |
| 25 | 20.4 | 2.3 | 18 | 3.5 | 16.6 | 4.2 | 16.6 | 4.2 |
| 32 | 26 | 3 | 23 | 4.4 | 21.2 | 5.4 | 21.2 | 3 |
| 40 | 32.6 | 3.7 | 28.8 | 5.5 | 26.6 | 6.7 | 26.6 | 3.7 |
| 50 | 40.8 | 4.6 | 36.2 | 6.9 | 33.2 | 8.4 | 33.2 | 4.6 |
| 63 | 51.4 | 5.8 | 45.6 | 8.4 | 42 | 10.5 | 42 | 5.8 |
| 75 | 61.2 | 6.9 | 54.2 | 10.3 | 50 | 12.5 | 50 | 6.9 |
| 90 | 73.6 | 8.2 | 65 | 12.3 | 60 | 15 | — | — |
| 110 | 90 | 10 | 79.6 | 15.1 | 73.2 | 18.4 | — | — |
Naturally, the values of diameters and wall thicknesses directly affect the resistance of pipes to temperature and pressure, which, in principle, determines the duration of their possible operation in certain conditions:
| Coolant temperature ˚С | Service life, years | Pipe type | |||
| PN-10 | PN-16 | PN-20 | PN-25 | ||
| Permissible excess pressure (kgf/cm²) | |||||
| 20 | 10 | 13.5 | 21.7 | 21.7 | 33.9 |
| 25 | 13.2 | 21.1 | 26.4 | 33 | |
| 50 | 12.9 | 20.7 | 25.9 | 32.3 | |
| 30 | 10 | 11.7 | 18.8 | 23.5 | 9.3 |
| 25 | 11.3 | 18.1 | 22.7 | 28.3 | |
| 50 | 11.1 | 17.7 | 22.1 | 27.7 | |
| 40 | 10 | 10.1 | 16.2 | 20.3 | 25.3 |
| 25 | 9.7 | 15.6 | 19.5 | 24.3 | |
| 50 | 9.2 | 14.7 | 18.4 | 23 | |
| 50 | 10 | 13.9 | 17.3 | 23.5 | 21.7 |
| 25 | 8 | 12.8 | 16 | 20 | |
| 50 | 7.3 | 11.7 | 14.7 | 18.3 | |
| 60 | 10 | 7.2 | 11.5 | 14.4 | 18 |
| 25 | 6.1 | 9.8 | 12.3 | 15.3 | |
| 50 | 5.5 | 8.7 | 10.9 | 13.7 | |
| 70 | 10 | 5.3 | 8.5 | 10.7 | 13.3 |
| 25 | 4.5 | 7.3 | 9.1 | 11.9 | |
| 30 | 4.4 | 7 | 8.8 | 11 | |
| 50 | 4.3 | 6.8 | 8.5 | 10.7 | |
| 80 | 5 | 4.3 | 6.9 | 8.7 | 10.8 |
| 10 | 3.9 | 6.3 | 7.9 | 9.8 | |
| 25 | 3.7 | 5.9 | 7.5 | 9.2 | |
| 95 | 1 | 3.9 | 6.7 | 7.6 | 8.5 |
| 5 | 2.8 | 4.4 | 5.4 | 6.1 | |
The data presented in the tables is the result of long-term testing of pipes under various conditions, which even theoretically may arise during their operation, so it is worth taking them into account in the process of selecting the required material.
Polypropylene pipes can have different colors, but when choosing them you should not pay special attention to it (perhaps only from an aesthetic point of view) since the external color does not in any way determine the characteristics of the products and does not affect their quality.
A red or blue stripe may be applied to the surface of some pipes - it serves as a specific indicator of the purpose of a particular type. Thus, blue color is applied to cold water supply pipes, and red indicates the ability of the products to withstand elevated temperatures in the hot water system or heating circuit.
When purchasing pipes, be sure to pay attention to their markings.
In addition to colored stripes, the pipes are marked with letters, which indicate their characteristics and intended purpose for installation in certain water supply or heating systems, and you also need to pay attention to it. The meaning of the marking indicators corresponds to the information given in the tables.
As can be seen from the presented characteristics, PN-20 products are optimally suited for the heating system, but the ideal option would still be PN-25 pipes, which have pronounced resistance to elevated temperatures and pressure, even with a good margin.
Selection of heating pipes
The choice of heating system components is influenced by the same properties of polypropylene pipes, which are important for the supply of hot water. First of all, the quality of the polymer itself.
Inexpensive single-layer block copolymer PP pipes can be used in low-temperature heating systems
P.P.S. made of a special polymer without reinforcement are used for heating, provided that the temperature in the system is less than 95 degrees C
However, reinforced products for heating purposes are more reliable and acceptable.
PPR-AL-PPR – with an outer layer of aluminum film. PP-RCT-AL-PPR – a new type of propylene is used, sandwiched with aluminum with an external polymer coating.
PPR-FB-PPR – propylene layered with fiberglass fiber.
PPR/PPR-GF/PPR – three-layer, inside and outside made of polypropylene, the middle layer is made of a composite in which glass fiber is distributed in a polypropylene matrix.
PP-RCT + BF is a pipe with basalt fiber, characterized by low weight and good throughput.
Reinforced pipes are more expensive, but also more reliable; they are initially produced for coolants with a wide temperature range.
Marking of polypropylene pipes
When choosing polypropylene pipes, in addition to the PP type and the presence of reinforcement in the marking, you must also look at the maximum operating pressure. According to GOST, this parameter is designated PN and a number from 10 to 25.
Marking of polypropylene pipes
Depending on this designation, PPR pipes are distinguished as follows:
- PN10 – thin-walled for cold water and “warm floors” with water up to +450C.
- PN16 – universal for cold water and hot water supply up to +600C.
- PN20 – thick-walled for water with temperatures up to +950C.
- PN25 – with reinforcement for hot water supply and heating (also up to +950C).
For a short period of time, one or another PPR pipe for water supply can withstand exceeding the specified temperatures. But with prolonged excessive heating, it will gradually begin to collapse. And as a result, its service life of half a century declared by manufacturers will be significantly reduced.
Welding and heating time of polypropylene pipes
Types of sewer pipes
Polypropylene pipes are often used to construct sewer systems of various types. When going to a plumbing store, it is important to know which polypropylene pipes are best to choose. Intra-house networks are equipped with products with a diameter of 110 mm.
Corrugated pipe is used to organize external communications. Polypropylene sewer pipes have a diameter of 150 mm and a length of 5 m; a diameter of 600 mm is up to 10 m. If it is necessary to drain aggressive industrial wastewater, a double-layer corrugated pipe is used.
Communications arranged in this way are able to withstand significant loads on the soil: this is favored by their high rigidity. Highways, airports and bridges can be built over such lines.
The PP product of SN8 stiffness class can be laid to a depth of 6-8 meters. To organize a sewer system from them, great efforts will not be required. Each of the pipes is inserted at one end into the socket, where rubber O-rings are used for tightness.
Main pipe diameters according to GOST
The diameter in the marking of PPR water pipes is indicated as the outer diameter. Moreover, the larger it is and the higher the PN, the thicker the pipe wall. Products of 16–20 mm are used for installing water pipes throughout the apartment and cottage. 25–32 mm is for the riser. Larger diameter options are intended for pipelines in multi-storey buildings, main networks and sewerage.
How to correctly calculate the diameter of a pipe based on its purpose
Popular manufacturers
On the domestic PPR market, water pipes are represented by products of Russian and foreign manufacturers. There is no particular difference between them; the plastic production technology is used in all cases. However, it is extremely important to look at the numbers written on the product label. Manufacturers often add various plasticizers to their plastic to enhance certain characteristics.
Popular manufacturers of polypropylene pipes
Among the popular manufacturers of the pipes in question are:
- Banninger and Rehau (Germany);
- Valtec (Italy);
- Ecoplastic FIBER (Netherlands);
- TEBO and Vesbo (Türkiye);
- BLUE OCEAN (China);
- ProAqua and Politek (Russia)
The quality of these manufacturers is almost the same. But for German pipes you will have to pay a little more due to the brand, and for Chinese ones, on the contrary, a little less. At the same time, Russian analogues also maintain their brand, having a very affordable cost per linear meter.
Aluminum reinforcement
There are solid and perforated reinforcement with aluminum foil.
Continuous reinforcement with aluminum foil is the most economical option for reinforced pipes.
In this case, a thin layer of aluminum is located between the layers of propylene, due to which the structure of the pipe is significantly strengthened. But these types of products, as well as others, are distinguished by a number of limitations in operation:
- the water temperature should not reach +60 °C, otherwise the pipe may become deformed and burst if overheated;
- all joints should be cleaned before soldering, which will significantly reduce the time spent on installing the system;
- the temperature at which aluminum-reinforced pipes freeze is only -5 °C. Therefore, when using this type of polypropylene pipe in a private house, it is strictly forbidden to turn off the heating;
- Experts do not recommend using these types of products to supply hot water, since due to constant temperature changes, the aluminum layer may collapse over time.
Aluminum perforation means a mesh with small holes. During the extrusion of polypropylene pipes, viscous material enters the perforations, thereby ensuring adhesion between the polymer and metal.
Thanks to aluminum reinforcement, the coefficient of thermal expansion is significantly reduced. However, some difficulties may arise during the installation of engineering systems. When socket welding, the aluminum shell and outer layer of polymer are first removed, and the pipe is cleaned to an amount that corresponds to the depth of its insertion into the fitting.
There are types of polypropylene pipes that do not require removal of the outer layer during installation. They, in turn, also have some disadvantages:
- Only the outer layer of the product, equal to half the wall thickness, is attached to the fitting;
- a nozzle for welding equipment is required;
- After you cut the pipe, it will need to be trimmed.
Glass fiber reinforcement
Types of pipes marked PPR-FB-PPR consist of two layers of polypropylene, between which fiberglass is located, which is why this product is called a “fiberglass” pipe.
A pipe reinforced with glass fiber compares favorably with a product with aluminum reinforcement:
- installation does not require calibration and cleaning;
- material and time costs are reduced due to the fact that the soldering procedure is similar to the connection of solid plastic pipes or other stripped polymer products;
- a pipe reinforced with fiberglass does not delaminate because it has a homogeneous structure;
- Glass fiber increases the rigidity of the pipes.
The disadvantage of a fiberglass pipe is that its thermal expansion is 6% higher than that of products with aluminum reinforcement.
Internal reinforcement with polypropylene
These types of products are essentially metal-plastic pipes, the outer layer of which is made of polypropylene. Such pipes are resistant to high temperatures.
The disadvantages of this type of polypropylene pipes are characterized by:
- multilayer - the presence of adhesive joints of two different materials;
- attaching only the outer layer of the product to the fitting;
- the possibility of contact of reinforcement with the transported medium.
Metal-polymer polypropylene pipes
Modern types of polypropylene pipes are distinguished by a classic five-layer metal-polymer construction, shown in the figure below:
This type of polypropylene pipes is used for water supply and heating systems.
Modern polypropylene products have a multilayer construction, just like metal-plastic products. The only difference is that for a classic metal-plastic pipe, PEX or PE-RT polyethylene is used as a polymer, and not polypropylene.
Below is a small table that will help you understand the technical characteristics of all types of polypropylene pipes and the features of their application:
| Types of reinforcement | Specifications | ||||
| Maximum temperature, °C | Minimum temperature, °C | Thermal expansion, deformation | Maximum pressure, atm | Scope of application | |
| Solid aluminum | 60 | 5 | Average | 1 | Cold water system |
| Perforated aluminum | 70 | 10 | Average | 1.5 | Open type heating |
| Fiberglass | 90 | 20 | Low | 2 | Hot water supply system, heating, heated floor |
| Composite | 95 | 20-30 | Absent | 2,5–3 | Any |
Polypropylene taps
When using plastic pipes, it will be more aesthetically pleasing to use taps coated with polypropylene. This is usually what inexperienced plumbers think about. In fact, it is better to use regular brass taps with a transition to polypropylene through a coupling.
At first glance, a faucet filled with a polypropylene shell seems to be the ideal solution. Does not spoil the overall appearance of the plastic pipeline, does not require additional parts for connection to a common unit.
The fact is that taps filled with plastic have lower reliability. The faucet consists of two fundamentally different materials (metal and plastic), with different densities and thermal expansions. Due to different properties, problems often arise in the form of leaks or breakdowns. Global manufacturers recognize the shortcomings of polypropylene cranes and are working on the mistakes, but it is too early to say with complete confidence about reliable cranes of this type.
A much more reliable solution would be a brass tap with two threaded couplings. The coupling also contains two materials, metal and plastic, but these parts are stationary, unlike a tap.
In addition to reliability, there is also an aesthetic side to using conventional taps: the tap can be rotated along its axis and given a more even position. The sealed plastic tap cannot be turned on the pipe; you need to do the soldering very clearly the first time; the soldering can only be corrected by soldering in a new tap.
In fact, brass faucets provide more options. They can be replaced without soldering, if the faucet comes with an American one; the connection is detachable in case of other repairs. American becomes relevant when installed in hard-to-reach places.
In addition, conventional cranes are, as a rule, smaller in size, and the range of products is much wider.
Just like brass, polypropylene taps come in two types: valve and ball. Please note that ball valves can only be used in two positions: open and closed, adjustment is not allowed.
All manufacturers say so. However, on this score, in the process of working as a plumber, a different opinion was formed...
The above is true for expensive, high-quality products, but in our realities, as a rule, we have to deal with budget faucets. So, if we compare two budget products, a valve and a ball valve, the ball wins in terms of reliability, even with constant adjustment. Although the valve is specifically designed for regulation, it fails very quickly. This opinion has been formed over many years of work. These considerations are valid both for brass shut-off and control valves, and for products filled with polypropylene.
And finally, I would like to say: you should not skimp on taps, as well as on all plumbing fixtures. Pipes and all components should be purchased from reliable stores; this should be done slowly and thoughtfully!
MANUFACTURERS OF POLYPROPYLENE PIPES
Domestic and foreign manufacturers offer a wide selection of high quality polypropylene pipes. Moreover, the products of Russian concerns (Valtec, Pro Aqua) are not inferior to foreign brands.
| Manufacturer | Polypropylene material | Operating temperature, ºC | Working pressure, bar | Outer diameter, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Service life, years |
| Valtec (Russia) | PPR | 70-95 | 9-25 | 20-110 | 2,8 — 8,3 | 50 |
| BANNINGER (Germany) | PP-RST, PP-RCT, PP-RCT, PP-R CT | -10 +95 | 0-10 | 20-110 | 2,3-15 | 50 |
| Ecoplastic FIBER (Netherlands) | PP-RCT | up to +70 | 6-35 | 20-125 | 2,5-4.0 | 50 |
| About Aqua (Russia) | PP-R | -10 +100 | 0-10 | 20-125 | 3,4-20,8 | 50 |
In our company you can order Valtec products. It is used for external and internal communications and has an optimal combination of price and quality. As the official distributor of this Russian-Italian manufacturer, we have the opportunity to offer you Valtec PP pipes and fittings at a better price than our competitors.
What is special about polypropylene pipes?
Polypropylene pipes have the following strengths:
- Light weight compared to a metal pipe. This greatly simplifies the installation and transport of pipes and fittings.
- Not afraid of rust, dirt, aggressive liquids.
- The organization of the pipeline occurs very quickly: no complex devices or special skills are required.
- Duration of operation – 50 years or more.
- Many types of polypropylene pipes have good sound insulation characteristics.
- Polypropylene for heating is completely environmentally friendly.
There are also some disadvantages:
- Significant coefficient of thermal expansion. Reinforced products have it at a level of 2-3.5 mm per 1 m, solid ones are 4-5 times more pliable.
- As for pipes with external reinforcement, it will need to be treated with special devices.
- The market is replete with counterfeits of polypropylene pipes: in this case, the outer layer is especially susceptible to defects.
- The high fluidity of polypropylene pipes means that even the product’s own weight can contribute to deformation. To avoid such phenomena, the polypropylene pipeline is equipped with special fasteners, which are installed every half meter.
- The significant rigidity of polypropylene implies the need for a large number of fittings when organizing rotary sections.
Characteristics of PPR pipes and scope
Each PPR product is marked with encrypted data on the diameter and wall thickness, operating pressure, service class, pipe material and much more.
There are several modifications of polypropylene, each of which has its own operating characteristics:
- PPH – products made from homopolymer, used exclusively in cold water supply.
- PPV pipes are made of block copolymer, the scope of application is cold water supply and installation of heated floors.
- PPR is the most common material - a random copolymer of polypropylene, used in the installation of heated floors, for hot water supply and water heating.
- PPs – polypropylene with improved heat-resistant properties, rarely used in domestic water supply systems.
For cold water supply and drinking water supply, it is enough to use PN10 pipes made of homopolymer, since the low temperature environment practically does not cause linear expansion, and the pressure in the household pipeline is below 1 MPa.
In heating systems and for supplying hot water, it is advisable to install reinforced pipes with fiberglass or aluminum foil (basalt fiber has only recently appeared on the pipe market and has not yet gained much popularity).
Reinforcement in a hot water pipeline is necessary as it restrains the linear expansion of polypropylene and prevents deformation of the pipes. Products with an aluminum layer can be used in any conditions, since the metal foil provides additional rigidity without practically increasing the outer diameter. Fiberglass is best used indoors.
Important! If the pipeline section will pass through open air, it must be protected from ultraviolet rays. The ideal solution would be to use a polyurethane foam shell.
Selection of pipes for water supply
Polypropylene piping components are a practical and relatively inexpensive option for installing water pipes in homes.
To supply cold water, a simple version of polypropylene pipes without special layers that strengthen the element is suitable. These are inexpensive single-layer pipes without reinforcement. Feel free to choose them.
RPH single-layer pipe made of solid homopropylene, durable, can withstand heating up to 60 degrees C, higher temperatures are not recommended
PPV single-layer pipe made of flexible block copolymer, resistant to defrosting.
PPR single-layer random copolymer pipe, more durable and resistant to temperature rise, recovers after defrosting.
They differ in diameter - from 20 to 40 mm, and shell thickness - from 1.9 to 6.7 mm. The shell thickness is indicated by the parameter PN10 or PN20. These parameters affect the hydrodynamic properties of the system and the throughput of the water supply system. Pipes ⌀ 32 mm are connected to the central water supply; for internal communications, ⌀ 16 - 25 mm are sufficient.
To supply hot water, it is possible to choose the connection of single-layer inexpensive polypropylene pipes:
- PPR, PPRC from a copolymer of propylene and ethylene - coolant temperature less than 70 degrees C
- PPS – made of special polypropylene – heating no more than 95°C
However, for greater reliability it is worth using reinforced pipes. Experts recommend pipes reinforced with fiberglass:
PPR-FB-PPR – propylene sandwiched with fiberglass fiber
PPR/PPR-GF/PPR – three-layer pipe, inside and outside made of polypropylene, the middle layer is made of a composite material in which glass fiber is distributed in a polypropylene matrix. A colored intermediate layer on a light background is a distinctive external feature of these pipes.
They are produced, for example, by the Italian-Chinese company Valtec and the Russian company Kontur. They are superior to aluminum-coated options in a number of characteristics; they are easier to install, do not need to be cleaned during assembly, and do not swell during operation or collapse from the inside.
Meanwhile, aluminum pipes are impermeable or almost impermeable to oxygen. This is an important property, since oxygen, saturating the coolant water with bubbles, creates so-called cavitation processes in all metal components of the water supply system. They destroy the walls of pumps, valves and other parts.
The main reasons for choosing polypropylene pipes for the heating circuit
The reasons, which, in fact, are the advantages of polypropylene pipes are as follows:
- Polypropylene has a distinctly low weight, which greatly simplifies its delivery to the work site and installation itself - no special devices or equipment are required.
- If you have the necessary tools, polypropylene pipes are easy to install, and welding techniques can be learned very quickly.
- The manufacturing material is absolutely harmless for residential premises, since it does not change its chemical composition even with strong heating and does not emit toxic fumes into the air.
- Thanks to the stabilizers included in polypropylene, pipes can withstand water hammer and thermal loads, and even freezing of water inside without rupture.
- The smooth inner walls of the pipes promote uniform, turbulence-free and noise-free circulation of the coolant.
- Both the pipes themselves and their components are inexpensive. A wide selection of components allows for installation of a circuit of any complexity.
A little training and any owner can carry out independent installation
- A circuit made of high-quality pipes, if installed correctly, will last at least 20–30 years.
- The aesthetic appearance of the pipes makes it possible not to spoil the interior, and the contour itself usually does not require either painting or additional decoration.
So, polypropylene pipes with a reinforcing aluminum layer are excellent for heating circuits of autonomous and central systems. In addition, the installation of this material is quite simple and feasible even for people who have no experience in such work. After several training sessions on the installation of individual components, the assembly process of the entire circuit can be carried out on your own.
Basic properties of polypropylene pipes and their GOST
Modern polypropylene pipes, the technical characteristics and properties of which can be seen in the table, are reliable, durable and quite affordable. The main and indisputable advantage is the fact that they are not subject to corrosive processes, are resistant to temperature conditions, are easy to install, and are made of environmentally friendly materials. The main properties according to GOST are presented below.
| GOST | Parameter | Index |
| DIN52612 | Thermal conductivity, at +200С | 0.24 W/cm |
| 15139 | Density | 0.9 g/cm3 |
| 23630 | Heat capacity at +200С (specific) | 2 kJ/kgf |
| 21553 | Melting | +1490С |
| 11262 | Tensile strength (at break) | 34 ÷ 35 N/mm2 |
| 18599 | Yield Strength Elongation | 50% |
| 11262 | Yield strength (tensile) | 24 ÷ 25 N/mm2 |
| 15173 | Expansion coefficient | 0.15 mm |
Which PPR pipes are more convenient to install?
The easiest and fastest way to install, of course, is single-layer polypropylene pipes. For installation it is enough:
- cut the product with a hacksaw or pipe cutter,
- rub away burrs on the edges,
- connect structural elements using a fitting or special glue (liquid welding).
We recommend that you read: Replacing old pipes with polypropylene on your own
The principle of installing multilayer PPR pipes is the same, however, in this case cold welding is not suitable, since it will only glue the outer layers and will not provide a reliable connection.
Therefore, multilayer pipes are best connected by hot welding or using special multilayer threaded fittings.
Attention! Do not attempt to thread a pipe or fitting yourself. There is a high probability that the resulting threads will not match, which means the connection will not be airtight. It is better to buy fittings with ready-made standard threads.
Pipes with aluminum reinforcement require special preparation before installation. If layers of fiberglass pipes are literally soldered into each other, then aluminum foil is connected to polypropylene using glue, which means there is a possibility of delamination.
To avoid this negative consequence, before welding PPR pipes with aluminum reinforcement, it is necessary to remove a small section of foil and solder the inner and outer layers of polypropylene together. Thanks to this action, water will not be able to penetrate between the layers, which means there will be no threat of deformation and destruction of the pipeline.
PPRC pipes
These are pipes made of high-temperature polypropylene. Available with a cross-sectional diameter of 20÷160 mm. Reinforced with fiberglass or aluminum. Their main difference is their low temperature expansion and low pressure loss. The production technology fully complies with GOST and the requirements of foreign standards. What are polypropylene pprc pipes? Technical characteristics, properties and advantages of a plastic product:
- low thermal conductivity;
- high level of sound insulation;
- resistance to corrosion processes;
- resistance to the effects of aggressive substances;
- high strength;
- resistance to bending more than once;
- environmentally friendly material;
- ease of installation;
- affordable price;
- long service life.
Installation of systems made of PP pipes and fittings
Installation of a polypropylene pipeline has its own characteristics.
First of all, this is the order of work and the order of installation of individual elements. The installation method plays an important role - external with the help of clips and internal, when the pipes are installed in the wall.
Wiring in the bathroom and toilet: recommendations
The beginning of work on installing a water supply system in the bathroom and toilet is the marking of the pipe route and the installation locations of taps and mixers. When using filter batteries, taps for connecting a washing machine and a boiler, it is recommended to measure all distances in advance and take into account the dimensions of both household appliances and plumbing fixtures.
It is recommended to install pipes at a distance of 10-15 cm from the floor level. For installation, it is better to start soldering from permanently fixed objects - boiler, toilet, mixer. It should be taken into account that all objects must be securely attached to the walls.
First, connecting elements with metal threads are mounted to the connection point of the boiler or toilet, and then the extension is done in separate sections.
It is possible to assemble small structures separately, and after that install them on clips or clamps to the wall.
Fastening to the wall with clips or other elements
For fixation use:
- plastic clips;
- metal clamps;
- plastic clips;
- plastic staples;
- dowel hooks.
Metal clamps are used to secure vertical main pipelines and horizontal sections of large diameter. For pipelines with a diameter of 20-25 mm, single, paired or stacked clip models are used. It is recommended to prepare holes for installing clips before starting installation.
As the water supply system is built up, it is recommended to fix sections of the finished system. When installing internally, metal products must be galvanized to prevent corrosion under the plaster layer.
Fastening distance between clamps during installation (fastening pitch)
When installing pipes of small diameters 20-25 mm, the fastening step on horizontal sections with plastic clips should be 0.5-0.8 meters; for vertical sections, a step of 1 meter is allowed.
GOST for plastic pipes: decoding
To standardize polyethylene pipes, the interstate standard GOST 32415-2013 is used; it applies to all types of polymer materials used for the manufacture of pressure pipes and other connecting elements. It is important to remember that this standard determines the scope of application of materials and products - water supply and heating systems.
Gosstandart uses the international designation of polypropylene materials in Latin, and the national abbreviation in Russian
Marking for different types of materials is as follows:
- polypropylene homopolymer is designated - PP-N (PP-G);
- polypropylene block copolymer is marked -PP-B (PP-B);
- polypropylene random copolymer is marked PP-R (PP-R);
- polypropylene random copolymer of increased heat resistance with modified crystallinity is designated PP-RCT (PP type 4);
For marking, the following order is used with the symbol applied to the outer surface of the pipes:
- names of the material type in Latin or Cyrillic characters;
- designations of the size ratio standard;
- outer diameter of the pipe and wall thickness;
- purpose of the product and maximum operating pressure in the system;
- indicator of the nominal value of internal pressure in the system:
- number of the state standard applicable to the product.
Types of propylene pipes
For communications equipment inside the house, products of the same type and design are most often used. In this case, you can choose polymer pipes that have not only unique design and technical quality properties, but also color.
Various colors
Polypropylene for the manufacture of water fittings is initially white. But for convenience, products are also available in other colors:
- gray;
- green;
- orange;
- red;
- black.
For internal installation, the material most often used is gray, green and white.
Constructions of various types
For low-pressure water supply, both conventional and foil-reinforced materials are used.
For hot water supply, multilayer structures with aluminum foil are used. For heating, multilayer pipes with reinforcement in the form of foil or fiberglass are used.
Varieties of layering
Multilayer ones consist of an inner layer of polypropylene reinforcing and an outer layer. The aluminum layer can be either seamless or in the form of a strip welded along the seam. Fiberglass fibers are used both in the form of a continuous braid of the inner layer and in the form of a perforated one.