Acceptance procedure
After receiving an application to Vodokanal to connect a new sewer system to municipal wastewater networks, an acceptance committee is formed whose responsibilities include:
- Reconciliation of executive and technical documentation with design documentation.
- Identifying deviations from the approved project, checking permitting documents for these changes.
- Inspection of communications on site.
- Identification of errors and shortcomings during construction (time is assigned for correction).
When the defects are eliminated, the commission members sign the act and the structure is put into operation.
During the on-site visit, the commission checks:
- Do the locations of fasteners and methods of fixing pipes correspond to those specified in the project?
- Is the pipeline securely fastened?
- Angles of pipeline connections (kinks, which provoke frequent clogging, are unacceptable).
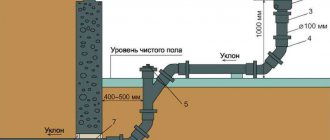
- The slope of the horizontal pipeline must correspond to the design data.
- The riser must be positioned vertically; a deviation of several degrees is permissible in accordance with the standards.
- The height of the exhaust part of the sewer system must correspond to the design.
- No blockages or construction debris in the pipes.
- Reliable fastening of plumbing fixtures.
- Quality of materials, reliability of installation, necessary equipment.
To check the tightness of the pipeline system, hydraulic tests are carried out. To do this, 75% of the plumbing fixtures connected to the site are opened. The system is considered to have passed the test if no leaks are detected at the joints, fittings and pipes. The result is certified by an act (appendix to appendix 4 of SNiP 3.05.01).
SP 40-102-2000: Testing and commissioning of pipelines
Introduction Scope of application General provisions Design of internal water supply networks Design of internal sewerage and watercourses Design of external water supply Design of external sewerage, gutters and drainages Installation of pipelines
8.1 According to SNiP 3.05.04, pressure and non-pressure water supply and sewerage pipelines are tested for strength and density (tightness) by hydraulic or pneumatic methods twice (preliminary and final).
8.2 Preliminary test (excessive) hydraulic pressure during strength testing, performed before backfilling the trench and installing fittings (hydrants, safety valves, plungers), must be equal to the design operating pressure multiplied by a factor of 1.5.
8.3 The final test hydraulic pressure for density tests performed after backfilling the trench and completion of all work on this section of the pipeline, but before installing hydrants, safety valves and plungers, in place of which plugs are installed during the test, must be equal to the design working pressure multiplied by coefficient 1.3.
8.4 Before testing pressure pipelines with socket connections with O-rings, temporary or permanent stops must be installed at the ends of the pipeline and at the bends.
8.5 Preliminary hydraulic testing of pressure pipelines should be carried out in the following order:
— fill the pipeline with water and keep it without pressure for 2 hours;
— create test pressure in the pipeline and maintain it for 0.5 hours;
— reduce the test pressure to the design pressure and inspect the pipeline.
The pipeline is kept under operating pressure for at least 0.5 hours. Due to deformation of the pipeline shell, it is necessary to maintain test or operating pressure in the pipeline by pumping water until complete stabilization.
The pipeline is considered to have passed the preliminary hydraulic test if no ruptures of pipes or joints and connecting parts are detected under test pressure, and no visible water leaks are detected under operating pressure.
8.6 The final hydraulic test for density is carried out in the following order:
— a pressure should be created in the pipeline equal to the design operating pressure and maintained for 2 hours; when the pressure drops by 0.02 MPa, water is pumped;
— the pressure is raised to the test level for a period of no more than 10 minutes and maintained for 2 hours.
The pipeline is considered to have passed the final hydraulic test if the actual leakage of water from the pipeline at the test pressure does not exceed the values specified in Table 5.
8.7 Hydraulic testing of gravity sewer networks is carried out after completion of waterproofing work in wells in two stages: without wells (preliminary) and together with wells (final).
8.8 The final test of the sewerage pipeline together with the wells is carried out in accordance with SNiP 3.05.04.
8.9 Hydraulic tests of systems made of polymeric materials of internal pipelines are carried out at positive ambient temperatures no earlier than 24 hours after the last welded and adhesive joint is made.
8.10 Hydraulic testing of internal drainage systems is carried out by filling them with water to the full height of the risers. Tests are carried out after external inspection of pipelines and elimination of visible defects. Hydraulic testing of glued pipelines begins no earlier than 24 hours after the last connection. The drainage system is considered to have passed the test if, 20 minutes after its filling, an external inspection of the pipelines reveals no leaks or other defects and the water level in the risers has not decreased.
8.11 Pneumatic tests of pipelines made of polymer materials are carried out during ground and above-ground installation in the following cases: ambient air temperature below 0 °C; the use of water is unacceptable for technical reasons; There is no water in the quantity required for testing.
The procedure for pneumatic testing of pipelines made of polymeric materials and safety requirements during testing are established by the project.
8.12 Preliminary and final tests of gravity sewer networks made of large-diameter pipes may be carried out pneumatically. Preliminary tests are carried out before the final filling of the trench (welded joints are not covered with soil). A test pressure of compressed air equal to 0.05 MPa is maintained in the pipeline for 15 minutes. At the same time, welded, glued and other joints are inspected and leaks are detected by the sound of leaking air, by bubbles formed in places of air leakage through butt joints coated with soap emulsion.
Final pneumatic tests are carried out when the groundwater level above the pipe in the middle of the pipeline under test is less than 2.5 m. Final pneumatic tests are carried out on sections 20-100 m long, and the difference between the highest and lowest points of the pipeline should not exceed 2.5 m. Pneumatic tests are carried out 48 hours after backfilling the pipeline. The test excess pressure of compressed air is indicated in Table 6.
| Outer diameter of pipes, mm | Permissible leakage, l/min, for pipes | |
| with permanent (welded, glued) connections | with socket connections on sealing rings | |
| 63-75 | 0,2-0,24 | 0,3-0,5 |
| 90-110 | 0,26-0,28 | 0,6-0,7 |
| 125-140 | 0,35-0,38 | 0,9-0,95 |
| 160-180 | 0,42-0,6 | 1,05-1,2 |
| 200 | 0,56 | 1,4 |
| 250 | 0,7 | 1,55 |
| 280 | 0,8 | 1,6 |
| 315 | 0,85 | 1,7 |
| 355 | 0,9 | 1,8 |
| 400-450 | 1,1-0,5 | 1,95-2,1 |
| 500-560 | 1,1-1,15 | 2,2-2,3 |
| 630 | 1,2 | 2,4 |
| 710 | 1,3 | 2,55 |
| 800 | 1,35 | 2,70 |
| 900 | 1,45 | 2,90 |
| 1000 | 1,5 | 3,0 |
| 1200 | 1,6 | 3,0 |
| Groundwater level h | Test pressure, MPa | Pressure drop, | |
| from the pipeline axis, m | redundant initial p | final p1 | p — p1, MPa |
| h = 0 | 0,01 | 0,007 | 0,003 |
| 0 | 0,0155 | 0,0124 | 0,0031 |
| 0,5 | 0,021 | 0,0177 | 0,0033 |
| 1 | 0,0265 | 0,0231 | 0,0034 |
| 1,5 | 0,032 | 0,0284 | 0,0036 |
| 2 | 0,0375 | 0,0338 | 0,0037 |
8.13 Acceptance of pipelines for operation must be carried out in accordance with the basic provisions of SNiP 3.01.04, as well as SNiP 3.05.04. When testing water supply and pressure sewerage pipelines and putting them into operation, the following must be drawn up:
— acts for hidden work (on the base, supports and building structures on pipelines, etc.);
— acts of external inspection of pipelines and elements (units, wells, etc.);
— test reports for the strength and density of pipelines;
— certificates for washing and disinfecting water pipelines;
— establishing compliance of the work performed with the project;
— acts of incoming quality control of pipes and connecting parts.
8.14 In addition to the acceptance of hidden work and verification of pipeline testing reports for density and external inspection, the acceptance of non-pressure pipelines must be accompanied by a straightness check, as well as an instrumental check of trays in wells.
When accepting internal water pipelines, passports or certificates for polymer pipes, connecting parts and fittings are additionally checked.
Safety precautions when installing pipes made of polymer materials Transportation and storage of pipes made of polymer materials Appendix A Appendix B Appendix C Appendix D Appendix E Appendix E
Video diagnostics
Communications owners resort to video diagnostics at the stage of handing over the object to the contractor in order to assess the quality of work and, if necessary, have photo and video materials that can be used in court.
Depending on the length of the pipeline and the diameter of the pipe, different devices for teleinspection are used:
- Pushable module (chamber on a cable) - used for pipes with a diameter of 70 to 400 mm or in places where the robot can get stuck.
- Floating module (boat with a camera) – used for large-diameter flow-through sewerage.
- Robot (self-propelled system with a camera) – for diagnosing long-distance pipelines with a diameter of 150 to 1200 mm.
Photos and video materials transmitted by the camera can be viewed in real time on the remote control monitor or saved on digital media. Depending on the equipment model, you can get a color image of 420-480 TV lines. Illumination is provided by LEDs.
What is the design of external and internal networks
Internal networks are a complex of pipelines, equipment and metering devices inside a building, i.e. within its outer walls. Accordingly, external networks are designed and connected outside the facility; they can be connected to public communications or to autonomous sources. Design of external and internal networks involves the following activities:
- study of the features of the site, parameters of the future building, communications in the underground and above-ground parts of the territory;
- obtaining technical conditions from resource supply organizations, which determine the possibility of connection, tie-in points, power and load limits;
- selection of solutions for laying pipelines and equipment in the building and premises, on the site;
- registration of design and working documentation, its approval by authorized departments.
For a new building, network design is a mandatory requirement. In relation to an existing building, it is possible to design a reconstruction with changes in parameters, and develop new engineering systems. For major repairs and reconstruction, you can prepare a project for the replacement and restoration of pipelines, installation of new equipment.
Dear Clients!
The information in this article contains general information, but each case is unique. You can get a free consultation from our engineers using one of our telephone numbers - call:
8 Moscow (our address)
8 St. Petersburg (our address)
All consultations are free.
Regulatory acts
The content of the design documentation must comply with the Urban Planning Code of the Russian Federation, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 87, SP, GOST, and other regulations. For example, Resolution No. 87 provides for the registration of subsections as a mandatory part of the project for the construction of a new facility, reconstruction or major overhaul.
There are special regulations for the design of each type of external and internal networks:
- SP 30.13330.2016 for internal water supply and sewerage of buildings ();
- SP 31-110-2003 for the design and installation of electrical installations in residential and public buildings ();
- SP 402.1325800.2018 for the design of gas supply systems in residential buildings ();
- SP 60.13330.2012 for heating, ventilation and air conditioning ().
For each set of rules there are many GOST and SNiP standards. There are also special guidance documents for the design of fire water supply systems.
In simple terms
For the construction and operation of apartment buildings, the regulations contain clear instructions on the types of public services, the procedure for their connection and provision. Accordingly, when designing an apartment building, it is necessary to provide for all mandatory types of engineering systems and communications (electricity, water supply and sewerage, heating, etc.).
For non-residential buildings there are no such strict requirements, i.e. The final decision on the types of utilities and equipment is made by the owner or tenant. However, no building can operate without electrical, water supply and drainage systems. Therefore, the project for a non-residential property will also include sections into external and internal networks. The designer's task is:
Documentation required
To obtain permission to connect the sewer system to the city network, the owner must send an application to Vodokanal and attach the following documents:
- A list of characteristics of the sewer system (length, depth, year of commissioning, number and description of fire hydrants, wells and shut-off valves, thickness and material from which the pipes are made).
- General plan of the site where underground communications are described.
- As-built drawings of sewer and water supply networks, which indicate the length and diameter of the pipeline, diagrams of wells and the material from which the pipes are made.
- Schemes indicating the division of balance zones of water-bearing and sewerage systems (schemes are agreed upon with the balance holder and persons acting as managers of sewerage and water supply workshops).
- Financial documentation for the sewer network (estimates, accounting).
Source of the article: https://vistaros.ru/
Hidden works
Hidden activities are all actions with pipes or other elements of the sewer system carried out below the 0.00 mark. They can equally refer to the internal or external part. Upon completion of the work, a hidden sewer work report is drawn up, which may include:
- preparation of trenches;
- laying and insulation of pipelines;
- construction of chambers, wells, collectors;
- backfilling of trenches;
- sealing areas where communications pass through walls or foundations;
- removing blockages.
All acts of hidden sewerage work, the list of which is quite wide, are drawn up based on the results of tests and examination by a special commission. This also includes acts of hidden work on storm drainage, since all work is carried out in conjunction with domestic or industrial systems. The storm network in industrial conditions must have its own, separate design. This is required by current rules and regulations, since rainwater runoff may be saturated with harmful or toxic substances. Compliance with the condition is confirmed by the technical acceptance certificate of the rainwater drainage system, which is drawn up upon commissioning. Sometimes the storm drain becomes clogged and needs flushing. Cleaning is carried out in accordance with current regulations. The pressure (hydrodynamic) method of cleaning pipes is used, after which a storm sewer flushing report is drawn up. Problems with blockages are common to all parts of the system, so cleaning is carried out periodically in problem areas. The result reflects the act of flushing the sewerage system, certifying the restoration of functionality.
Sample form
Features of the work
Installation of external utility networks may be accompanied by the following difficulties:
- the most accurate calculation will be required to ensure the appropriate level of quality and optimize costs;
- high quality installation of all communications for future long-term trouble-free operation of already created networks and reducing the risk of equipment failure before the end of the design life;
- an individual approach to installation and taking into account all possible risks.
By contacting, you insure yourself against all the above risks and receive timely and high-quality installation of external utility networks.
Coordination after design of external and internal networks
Standard approval schemes are also used when designing external and internal networks. For a construction and reconstruction project, you need to undergo an examination and obtain a building permit. After completion of work on the facility, you must obtain a statement of compliance and permission to put it into operation.
Special requirements are provided for network connectivity. For example, on the territory of Moscow the following are involved in these approvals:
- MosSvet - for building lighting and power supply systems, street networks;
- Vodokanal – on the water supply and sewerage network;
- heat supply organizations - for heating systems;
- gas distribution organizations - for commissioning of gas supply systems.
These organizations issue technical specifications and sign acts on the commissioning of engineering systems. ]Smart Way[/anchor] specialists will provide assistance in completing all approvals.
Reconstruction of NVC networks
When carrying out major repairs or restoration of a building, it is necessary to pay attention to the existing service life and assess the general condition of the NVC networks. If their design life has long expired, then it is necessary to order a complete reconstruction of the NVC networks. During the reconstruction process, the following components are subject to complete replacement:
- storage tank together with a pumping group;
- local treatment facilities, which are designed to filter and timely drain stormwater with the performance required for a specific area and conditions;
- filter cartridges to ensure the necessary environmental safety requirements.
For all questions regarding the design, installation and reconstruction of external utility networks, please contact.