- Reports
- Different
- Metal alloys
There are many metals in nature with different impurities. Metals with additives are called alloys. There are metals that are called basic because they are more abundant in the alloy.
Metal alloys have common properties: thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, metallic luster and others. To impart certain properties to the alloy, alloying additives are added to it.
The bulk of metals that are used in industry are alloys.
Main types of alloys
Aluminum - alloys, as the name suggests, based on aluminum. Such alloys are often used in the manufacture of parts and structures for mechanical engineering.
Amalgam - the glory of mercury with other metals. Most often, this alloy is used for “gold” coating of parts. Used in metallurgy and dentistry.
Tungsten - alloys with the addition of tungsten. Due to its high heat resistance and strength, it is often used in rocket science. Also used for the manufacture of devices with high temperatures.
Iron-carbon alloys. This type includes cast iron, ferroalloys and steel. Used in almost all industries.
Gold alloys. This alloy is also used to coat items that require a “golden” sheen, such as coins, jewelry, etc.
Low-melting alloys. This type of alloy has the ability to begin to melt at fairly low temperatures.
Magnesium alloys. Alloys with added magnesium are very resistant to corrosion.
Copper - alloys with the addition of copper. Small parts such as bearings, screws, and washers are made from this alloy.
Nickel - alloys that are highly resistant to corrosion.
Tin - alloys that are made on the basis of tin. Such alloys, like nickel alloys, are resistant to corrosion, but they are softer and have a low melting point.
Platinum alloys - begin to melt at high temperatures, are resistant to corrosion, hard and not brittle.
Lead - alloys that have the properties of lead. Resistant to some acids and corrosion.
Hard alloys are alloys made from hard metals. Such alloys are used to make materials and tools used to process metal.
Printing alloys have a low melting point.
Titanium alloys are also used in rocket science.
Zinc alloys are easy to process, have high hardness and also a high melting point.
Classification
Metallurgists classify metal alloys according to several criteria:
- manufacturing method:
- cast;
- powder;
- production technology:
- foundries;
- deformable;
- powder;
- homogeneity of structure:
- homogeneous;
- heterogeneous;
Types of alloys based on them
Metals and alloys based on them have different physical and chemical characteristics.
The metal having the largest mass fraction is called the base.
Metal classification
In nature, there are several types of metals that differ in their properties, characteristics and appearance. Each variety behaves differently when interacting with other materials or under the influence of environmental factors.
Types of metals
Black
This group includes iron and alloys based on it. Characteristic features of ferrous metals:
- high density;
- the melting point is much higher than that of representatives of other groups;
- color - dark gray.
Representatives of the group of ferrous metals include: tungsten, chromium, cobalt, molybdenum, iron, nickel, titanium, manganese, uranium, neptunium, plutonium and others. They are used in various industries and have different properties. Steel and cast iron are considered popular.
The composition of ferrous metals includes not only iron, but also various impurities, which include sulfur, phosphorus or silicon. They contain different amounts of carbon in their composition.
Colored
Representatives of this group are more in demand. This is due to the fact that non-ferrous metals are used in more industries. They can be used in mechanical engineering, advanced technologies, radio electronics, and metallurgy. Key features of non-ferrous metals:
- low melting point;
- large color spectrum;
- good ductility.
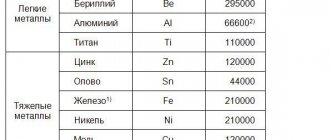
Due to the low strength of representatives of the color group, they are used in conjunction with different types of denser materials. Representatives of this group: magnesium, aluminum, nickel, lead, tin, zinc, silver, platinum, rhodium, gold and others.
Gold bars (Photo: pixabay.com)
Soft
It is possible to distinguish certain types of metals, which will belong to the group of hard and soft. The soft ones are:
- Aluminum - has corrosion resistance, light weight, good ductility. It is used in the electrical industry, in the construction of aircraft and in the manufacture of dishes.
- Magnesium is a lightweight material that is susceptible to corrosive processes. To get rid of this drawback, it is used in alloys with other materials.
These are key representatives of the group of soft metals.
Solid
Popular materials in this group are:
- Tungsten is considered the most refractory metal. In addition to this, it is one of the most durable. Resistant to chemical influences.
- Titanium - the fewer inclusions of other materials in this metal, the stronger it becomes. It is used in the construction of cars, rockets, airplanes, ships, as well as in the chemical industry. It is well processed under pressure and is not susceptible to corrosive processes.
- Uranium is another metal considered one of the strongest in the world. It is radioactive and is used in various industries.
Representatives of the “hard group” are less amenable to processing and are used in fewer areas of human activity than soft ones.
Aluminum alloys
If the first half of the 20th century was the century of steel, then the second was rightly called the century of aluminum.
It is difficult to name a branch of human life in which products or parts made of this light metal would not be found.
Aluminum alloys are divided into:
- Foundry (with silicon). Used to produce conventional castings.
- For injection molding (with manganese).
- Increased strength, with the ability to self-harden (with copper).
Main advantages of aluminum compounds:
- Availability.
- Low specific gravity.
- Durability.
- Cold resistance.
- Good machinability.
- Electrical conductivity.
The main disadvantage of alloy materials is low heat resistance. When reaching 175°C, a sharp deterioration in mechanical properties occurs.
Another area of application is the production of weapons. Aluminum-based substances do not spark under strong friction and collisions. They are used to produce lightweight armor for wheeled and flying military equipment.
Aluminum alloy materials are widely used in electrical engineering and electronics. High conductivity and very low magnetizability make them ideal for the production of housings for various radio and communications devices, computers and smartphones.
Aluminum alloy ingots
The presence of even a small proportion of iron significantly increases the strength of the material, but also reduces its corrosion resistance and ductility. A compromise on iron content is found depending on the requirements for the material. The negative effect of iron is compensated by adding metals such as cobalt, manganese or chromium to the alloy composition.
Magnesium-based materials compete with aluminum alloys, but due to their higher price they are used only in the most critical products.
Report: Alloys
Alloys of chromium and nickel - nichrome - successfully serve as heating elements. The addition of cobalt and molybdenum to chromium-nickel alloys gives the metal the ability to withstand heavy loads. For example, gas turbine blades are made from these alloys. An alloy of cobalt, molybdenum and chromium (“comochrome”) is harmless to the human body and is therefore used in reconstructive surgery. New materials have recently been created, based on compounds of manganese, chromium and antimony, which will find application in various automatic devices and can replace more expensive thermoelements. The bulk of chromium ore mined in the world today goes to ferroalloy plants, where various grades of ferrochrome and chromium metal are smelted.
Manganese alloys
Modern technology uses a large number of manganins - alloys of manganese, honey and nickel, which have high electrical resistance, practically independent of temperature. Manganins have another valuable property - the ability to absorb vibration energy. In forging and stamping metalworking shops, using these alloys can significantly reduce harmful production noise. Manganese bronze, an alloy of manganese and copper, can be magnetized, although neither component individually exhibits magnetic properties.
We became acquainted with one of the manganese compounds—potassium permanganate, or, simply put, “potassium permanganate”—in childhood.
Beryllium alloys
Alloys of copper and beryllium - beryllium bronzes - are widely used in aviation. They are used to make many products that require greater strength, good resistance to fatigue and corrosion, retention of elasticity over a wide temperature range, and high electrical and thermal conductivity. Due to its elastic properties, beryllium bronze serves as an excellent spring material. Springs made of such bronze practically do not experience fatigue; they can withstand up to 20 million load cycles!
A great future apparently belongs to beryllium-lithium alloys. The union of these two lightest metals will perhaps lead to the creation of alloys that do not sink in water.
Magnesium alloys
Magnesium is a very light, silvery-white metal. Its lightness could make this metal an excellent structural material. But, alas, pure magnesium is soft and fragile. Therefore, designers are forced to use magnesium alloys with other metals. Alloys of magnesium with aluminum, zinc and manganese are especially widely used. Each of the components of this community contributes its own “share” to the overall properties: aluminum and zinc increase the strength of the alloy, manganese increases its anti-corrosion properties. Well, what about magnesium? Magnesium gives the alloy lightness - parts made of magnesium alloy are 20-30% lighter than aluminum and 50-75% lighter than cast iron and steel. Alloys of this element are increasingly being “invited to work” in the automotive industry, textile industry, and printing.
Magnesium alloys have many friends who, while increasing their heat resistance and ductility, reduce their oxidation. These are, for example, lithium, beryllium, calcium, cerium, cadmium, titanium. But, unfortunately, there are also enemies - iron, silicon, nickel; they worsen the mechanical properties of alloys and reduce their resistance to corrosion. Magnesium alloys are widely used in aircraft construction.
Copper alloys
The number of copper alloys used in various industries is constantly increasing. If some 38-40 years ago only alloys of copper and tin were called bronze, today aluminum, lead, silicon, manganese, beryllium, cadmium, chrome, and zirconium bronzes are already known.
113 aluminum bronze (an alloy of copper with about 5% aluminum) makes copper coins in particular.
A large group of copper-based alloys consists of brasses. Recently, in some areas of technology, copper and its alloys have been replaced by other metals, primarily aluminum.
Tin alloys
Tin is part of various bronzes, printing alloys, and babbitts (bearing alloys that have the ability to resist abrasion well).
Chemical compounds of tin are also widely used in technology.
Tantalum alloys
A very important area of application of tantalum is the production of heat-resistant alloys, in which everything. rocket and space technology needs more and more. Tantalum carbide is characterized by very high hardness (close to the hardness of diamond), due to which it is widely used in the production of hard alloys. During high-speed cutting, the metal heats up so much that the chips are welded to the cutting tool - its edge chips and breaks. Cutters made from hard alloys based on tantalum carbide are not at risk of chipping, and they last a very long time.
Aluminum alloys
The first alloy of aluminum with copper, magnesium, manganese was created in 1911, which was called duralumin. In 1919, the first aircraft made of duralumin appeared. Since then, aluminum has forever linked its fate with aviation. It has rightfully earned the reputation of “winged metal.”
In our country, the production of aluminum alloys was then carried out only by the Kolchuginsky non-ferrous metals processing plant, which produced small quantities of chain mail-aluminum - an alloy similar in composition and properties to duralumin. Now in our country many enterprises are already producing “winged metal”, but the need for it continues to grow. The shell of the first Soviet artificial Earth satellite was made from aluminum alloys.
They are used to make various parts of space equipment - brackets, fastenings, chassis, cases and housings for many instruments and instruments.
Titanium alloys.
Not so long ago, scientists created an amazing alloy of nickel and titanium - “nitinol”, which has the mysterious property of “remembering” its past, or more precisely, of accepting it after deformation and accordingly! processing its previous form. Today metallurgy is one of the main consumers of titanium. You can count hundreds of grades of steel and alloys that contain this element in varying quantities. It is introduced into stainless steels to prevent intergranular corrosion. In heat-resistant high-chromium alloys, it reduces the grain size, making the metal structure homogeneous and finely crystalline. In other heat-resistant alloys, titanium serves as a strengthening element.
Cobalt alloys
Cobalt alloys are widely used in the metalworking industry. One of the best stellites, as the new alloys were named, contained more than 50% cobalt. The production of hard alloys is steadily growing and cobalt plays an important role in them.
Soviet scientists and engineers have developed a superhard alloy that is superior in quality to similar foreign alloys. The composition, along with tungsten carbide, includes cobalt.
In some cases, cobalt acts in alliance with platinum. It is used to make miniature magnetic parts for electric watches, hearing aids, and sensors for various purposes.
Cobalt-chrome alloy has proven to be an excellent material for denture frames: it is twice as strong as the gold commonly used for this purpose and significantly cheaper.
Nickel alloys
An important “occupation” of nickel is the creation of various alloys with other metals. Scientists have managed to obtain copper-nickel alloys that are very similar to silver.
After some time, cupronickel, alfenade and other silver substitutes appeared, which certainly included nickel. Nickel alloys quickly gained popularity and came into use.
Monel metal, for example, works successfully in chemical engineering and shipbuilding. Nichrome spirals are used in heating devices and resistance electric furnaces.
The elastic alloy Elinvar is an excellent material for springs, in particular watch springs.