History of the discovery of duralumin
The unique properties of the compound were discovered in 1903 by a German engineer working in the German city of Duren. The term “duralumin” comes from the name of the city. The resulting metal alloy was distinguished by increased strength and low weight, as well as other useful properties.
In 1911, at an exhibition in St. Petersburg, duralumin received a silver medal as one of the best materials for creating aircraft.
This metal became most in demand during the Great Patriotic War. It was used to make parts for weapons, aircraft and tanks.
Over time, the composition of duralumin improved, and new types of alloy appeared.
A little history
Duralumin was developed by the German scientist Wilm in 1903. The metallurgist simply mixed aluminum, copper, and silicon. From this moment until the start of mass production, only 6 years passed. In 1911, duralumin began to be used in the construction of aircraft, in particular, airships and heavy bombers. The low weight of structures with comparable strength to steel made it possible to reduce the weight of aircraft by 2-3 times. This led to a dramatic development in the aviation industry.
Basic properties of these alloys
The basic composition of the alloy includes the following substances:
- copper - up to 0.5%;
- manganese up to 0.5%;
- magnesium up to 1.2%;
- silicon and many others.
By changing the proportions of the substances used, you can change the properties of duralumin.
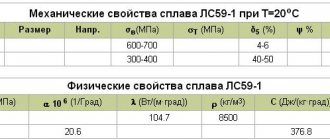
The strength of duralumin reaches up to 500 MPa under temporary loads and 250 - 300 under standard loads (the strength of pure aluminum is 70-80 MPa). This parameter has made duralumin a material used in many areas of industry, including high-tech ones. An alloy of aluminum with certain elements, in certain proportions, changes the resulting alloy.
Thanks to the components used in the production of duralumin, it acquires the following properties:
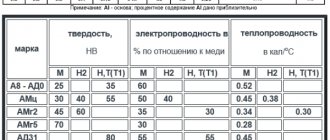
- strength that is comparable to certain grades of steel;
- high resistance to temperature influences. the material begins to melt at a temperature of 650 ºC.
- increased electrical conductivity. this is due to the presence of copper.
- duralumin tolerates rolling well using both hot and cold technologies.
The high technological properties of duralumin have led to high demand for it. About 60,000 thousand tons are produced in the world, almost half of which (over 30,000 thousand tons) are produced in China. Russia ranks second in terms of production volumes, metallurgical plants receive 3,580 thousand tons.
Production Features
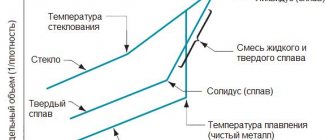
The production of duralumin, like most alloys, is associated with a number of difficulties. Receiving duralumin occurs sequentially. At the first stage, technical aluminum is obtained and only then additives are added to it that shape its properties. At the second stage, the production of primary duralumin passes through thermal annealing, carried out at 500 ºC. This processing mode ensures the flexibility and softness of the metal. To increase strength, duralumin goes through an aging operation.
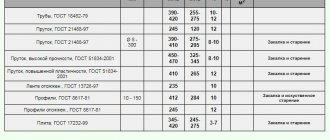
Domestic and foreign industry has mastered the production of the following types of rolled products:
- sheets and strips of different sizes GOST 21631-76;
- round and multifaceted rods according to GOST 21488-97;
- pipes of different diameters and different wall thicknesses GOST 18475-82 and GOST 18482-79;
- profiles of various section shapes.
Production technology
To obtain duralumin, a charge is first mixed - granules of various metals that will be fused into a single composition. Then the mixture is heated to a temperature of +500°C and sharply cooled with water or saltpeter to room temperature - hardened.
The industrial production of duralumin is based on the use of enormous power electricity.
After this, in most cases, the so-called “artificial aging” of the resulting alloy. This operation consists of additional exposure of the metal at elevated temperature for a long time, for example, at +150...+200°C for 2 hours (all conditions depend on the brand of the compound and the required qualities). The aging process is carried out to ensure that duralumin acquires special strength. Without it, the alloy is characterized by softness and pliability.
After manufacturing, the composition can be covered with a protective film that protects against corrosion.
Main types of duralumin alloys and their properties
Classification of duralumin alloys, list of typical areas of application of wrought Al-Cu 2000 series alloys according to GOST and ISO:
- AK8/2014: Heavy duty forgings, plates and extrusions for aircraft fittings, wheels and major structural components, tank and space booster structures, truck frames and suspension components. Applications requiring high strength and hardness, including service at elevated temperatures.
- D16/2024: Aircraft structures, rivets, hardware, truck wheels, propeller products and other various structural applications. The first hardened alloy ever discovered.
- 1201/2219: Welded space oxidizer boosters and fuel tanks, supersonic aircraft skin and structural components. Welding duralumin is easy and the alloy is useful for applications in the temperature range of -270 to 300 C (-450 to 600 F). It has high fracture toughness and the T8 hardening is highly resistant to stress corrosion cracking.
- AK4 1/2618: stamping and hand forging. Pistons and rotating parts of aircraft engines for operation at elevated temperatures. Press molds for tires. The high static strength of the alloy, which determines its resistance to single loads, is why it is used in the production of critical components. Tests have proven that it is quite difficult to destroy such products.
Dural AK8/2014
Duralumin: composition
The main part of the alloy is aluminum. The share of this component can reach up to 94% of the total mass. The next component that is present most often is copper. The weight of other additives - manganese, magnesium, iron and others - is small.
This is interesting: Metal cutting
An example of the composition of commonly used duralumin grade D16:
- aluminum - 93-94%;
- copper - 3.8-4.9%;
- alloying alloys - 1.5-2%.
Chemical composition of duralumin.
Properties of duralumin
The excellent properties of duralumin make it suitable for use in many areas of production, parts manufacturing, and insulation.
Physical and mechanical
A special feature of duralumin is its lightness with increased strength and heat resistance. Thus, the specific gravity of this metal is 2.8 g/m³, while for steel this figure is 8 g/m³. The melting point of duralumin is +500°C.
The disadvantage of the alloy is the increased susceptibility to corrosion as a result of exposure to elevated temperature or load.
Technological
A distinctive property of duralumin is the ease of its production. This alloy can be made even in domestic conditions: for example, in the garage. It does not need to be heated to extreme temperatures. Thanks to its simple manufacturing technology, this metal is relatively cheap.
The duralumin casting procedure can be done at home.
Technological properties
The technological features of duralumin include the ease of its production, which is due to the low temperature of the working environment. If there is an urgent need, it is not difficult to produce an alloy at home due to the low melting point of the main components.
If pure aluminum begins to melt at a temperature of 660 degrees, then reducing its share in the alloy to 99% entails a decrease in the melting threshold to 643 degrees.
The temperature threshold that allows you to start forging grades D16, D16P is 450 degrees. Pressed products made from an alloy of these grades that have undergone hardening or natural aging are prone to intergranular corrosion when heated to 100 degrees.
It is not recommended to solder duralumin material at high temperatures due to the risk of burnout.
The advantages of the material include:
- long service life;
- resistance to chemical, mechanical, thermal effects;
- high level of static strength;
- weldability;
- wide scope of application.
Types of alloys
Depending on the application and the need to acquire the desired characteristics, various substances are added to the alloy.
To avoid corrosion, the metal is anodized, i.e. covered with a special film.
All types of duralumin can be divided into:
- hardened, having the letter “T” in the designation;
- those that have gone through the stage of artificial aging - the designation is “T1”;
- anodized - with the letter “A” in the brand name.
Depending on the formula and heat treatment, the properties of the compounds change. Alloys widely used:
- Aluminum+copper+magnesium with manganese additives. Examples include alloys of grades D1, D16. These compounds are called "duralumin". They are not protected from corrosion and require additional coating.
- Aluminum + magnesium or manganese. In addition to corrosion resistance, this composition allows welding. The alloy is called "magnalium".
- Aluminum+magnesium+silicon. The material is protected from corrosion. It is used at high humidity, in conditions of passage of electric current. It's called "avial".
Duralumin alloy. Properties, production, application and price of duralumin
Plastic like aluminum, but several times harder. This is duralumin , an alloy created by German metallurgist Alfred Wilm. He worked at a factory in the city of Düren.
The name of the alloy is derived from his name. Alfred's name is known only in a narrow circle of scientists and industrialists. Let's expand the scope by talking about the discovery of the German metallurgist and what this discovery gave to the world.
Chemical and physical properties of duralumin
Duralumin was obtained by Wilm in 1903. The master mixed some copper, manganese and magnesium into pure metal No. 13. The entire ligature accounted for only 7% of the duralumin composition .
But this turned out to be enough to strengthen the alloy. True, it did not become hard immediately, but only after hardening. Metallurgists call it artificial aging of the material.
The process involves heating and gradually cooling the metal. Rearrangements of atoms take place inside it, which under natural conditions last for decades. As a result, the result is an alloy that seems to have lived its life, tempered in the “hardships of life.”
Duralumin is an alloy launched into mass production in 1909. Only 6 years have passed since the discovery of Alfred Wilmom. This indicates the importance of development, its necessity.
The properties of duralumin and its low cost immediately won over, for example, aircraft manufacturers. Already in 1910, the production of airships began from the new material. Dural made them light, because aluminum is light too. At the same time, the new alloy could withstand high temperatures. The material melts only at 650 degrees Celsius.
The density of duralumin is 2.5 grams per cubic centimeter. It is this indicator that determines the lightness of the alloy. Some of its brands have a density of up to 2.8, which is also below average. Steel, for example, has 8 grams of weight per cubic centimeter.
The combination of static strength and fatigue strength is also valuable in duralumin. The first refers to the ability to withstand a single load. Fatigue strength is the critical load at which a material fails.
So, it’s not easy to destroy duralumin. This is more likely to be done by corrosion than by force or pressure. Therefore, the destruction of the aluminum-copper mixture in the presence of oxygen is blocked by applying a protective coating to the alloy. It can be pure aluminum. Covering duralumin parts with it is called cladding.
Application of duralumin
The refractoriness of duralumin has made it the main material not only for aircraft construction, but also for the manufacture of high-speed trains. They can become very hot when moving. An alloy of aluminum and copper is used both for the casing and for internal components, as well as fasteners. So, bolts, rods, and rivets are made from duralumin.
Welding duralumin is simple, carried out using argon, and is possible even at home. This simplicity of handling the material is another reason for its prevalence. So, pipelines are made from duralumin. We are talking about conductors of gas and other energy resources for housing and communal services.
The plasticity of the hero of the article allows him to be rolled into thin sheets. As a result, melting duralumin “gives birth” to foil no more than 0.2 millimeters thick. Construction products are wrapped in it.
Duralumin foil is also used as heat shields. They are used to insulate baths and saunas. In the food industry, candies are wrapped in sheet duralumin .
In other words, the alloy is used for candy wrappers. Gardeners wrap trees in foil to protect them from rodents and frost. Tourists construct something like dishes from rolled duralumin.
Circles made from an aluminum-copper alloy are purchased for the drilling industry. It is important not only the layout, but also the weight of the passage columns. The lightness of duralumin combined with strength and resistance to high temperatures makes the choice of industrialists a clear choice. Drills made of aluminum alloy perfectly dampen vibrations, are non-magnetic and have a reduced longitudinal shear value.
Duralumin is also useful in production workshops. Here, floors and other surfaces are lined with alloy sheets. The coating is made corrugated to provide anti-slip properties.
But the properties of a current conductor in duralumin are, so to speak, in the basic configuration. Therefore, wires made of an aluminum-copper alloy are no less common than just copper wires. More precisely, aluminum wires are more popular, because they weigh less and cost less.
The availability of the material has made duralumin sheets one of the materials for cladding houses. As a rule, these are country houses. Their duralumin coating requires an additional façade and protection against corrosion.
But the alloy is resistant to chemical reagents, therefore, it is often used in ventilation systems and becomes a material for the manufacture of hoods.
Duralumin production
The production of the alloy takes place in several stages. First, a charge is formed from granules of pure aluminum and alloying metals. Fusion is carried out in stages. As a result, primary duralumin is obtained.
Now, hardening is needed. It begins by heating the material to 500 degrees Celsius. Annealing at this temperature provides sufficient softness and flexibility of the alloy. Next, it needs to be cooled. This takes several days. The temperature is maintained at 20 degrees. They wait until the duralumin reaches it. Alloy aging is complete.
In order to speed up the hardening, industrialists often carry out it in a few hours under conditions of slight heating of the material. At the same time, the quality of duralumin decreases. On the other hand, production costs are falling and production is accelerating.
Meanwhile, the main thing is to maintain a balance between the strength and ductility of duralumin. If you make it a little harder than necessary, you will lose not only the ability to take the desired shape, but also its resistance to corrosion.
Therefore, before buying duralumin , industrialists, as a rule, visit its production, making sure that the standards are followed. Samples are taken for examination. Only then does the deal happen. Let's find out the prices.
Duralumin price
The plasticity of duralumin allows you to make blanks of any shape from it. So, a kilo of hexagons according to GOST 21488-97 costs around 100-160 rubles. Round bars cost between 90 and 230,000 rubles.
The price tag depends on the brand of duralumin and the cross-section of the parts. The same goes for sheets. For samples half a millimeter thick, for example, they ask for about 300,000 rubles per ton.
Duralumin corners, used in construction as guides, are valued at 300 rubles per kilogram. 1,000 grams in a slab is estimated to be approximately 100 rudders. The thickness of the slabs is usually 1.5 centimeters.
Duralumin pipes cost around 130 rubles per kilogram of weight. Parts differ from rods in the presence of internal cavities. They are also found in circles made of aluminum and copper alloy. The diameter of the cavities in circles is smaller than in pipes. The parts used in drilling rigs cost 140-200 rubles per 1,000 grams.
All that remains is to find out the prices for foil. For its technical version they ask for only about 200 rubles per ton. If food foil is purchased, the price tag reaches 350 rubles per kilo. The material is usually sold in rolls weighing no more than 200 grams. This is several meters of foil.
Areas of application
Sheets, rods, plates, and wire are made from duralumin. These materials are used to make various parts.
This is interesting: Cutting metal
Main Applications:
- Aircraft. An important area is the use of duralumin in aircraft construction and the construction of other aircraft - space rockets, airships. This composition is used to make the casing, steering rod parts, power elements, etc.
- Construction. Sheets, pipes, angles, etc. are widely used in this industry.
- Automotive industry. Bodies, radiators and other parts are made from the alloy.
- Drilling industry. Circles, drills, etc. are made from duralumin.
Duralumin is often used in everyday life, for example, in the form of baking foil or candy wrapping.
Use of duralumin
This family of alloys is, in fact, the base material used in the construction of aviation and space technology. Its use began at the beginning of the twentieth century with the construction of the first airships.
Today, more than ten grades of this alloy are used in practice. When constructing aircraft, a material called D16t is most often used. It consists of nine substances - nickel, titanium, copper, silicon, etc. are used as alloying components. But with everything. The share of aluminum remains unchanged - 93%.
When choosing a material for parts and assemblies, the technologist must remember that not all duralumin can be welded or soldered well. In this case, rivets are used to assemble parts from it. Such operations are widespread in the assembly of fuselages and planes during the construction of aircraft and water transport of all types. Thus, a small boat used for its own purposes can serve its owner for 20 years more.
On the other hand, some grades of duralumin are welded well when using argon welding machines.
By the way, back in the 20th century, experimental work was carried out on the use of duralumin in the automotive industry. The bodies of buses and some brands of passenger cars and sports cars are made from it. Of course, duralumin is also used in power units.
Some grades of this alloy are used to produce pipes that are installed on ships, aircraft, and cars.
The properties of duralumin have made it possible to use it in the food industry, for example, candy wrappers for candies and chocolate are made from duralumin foil.
We must not forget that many housewives use kitchen utensils made from this material.
The low weight of duralumin allows its use in drilling operations. The thing is that duralumin is 3-4 times lighter than steel. In addition, duralumin pipes more easily withstand vibration, which invariably occurs during drilling operations.
The use of duralumin in the construction industry requires a separate discussion. It is used for the production of facing materials, various enclosing structures, etc.
The difference between duralumin and aluminum
Dural has a characteristic gray color. But its main differences from aluminum are the lack of ductility, hardness and fragility. The alloy cannot be bent or made a dent. Duralumin shavings are brittle and brittle. It is easy to scratch; when examining the damage, the fine-crystalline structure of the material is visible.
The type of metal can be determined more accurately by dropping caustic sodium on it. If after 10 minutes the stain darkens, it is duralumin.
Aluminum and duralumin differ from each other in their chemical composition.
A bit of economics
Products made from duralumin alloy are not difficult to purchase. Its production is deployed at almost all non-ferrous metallurgy enterprises. The price of products is determined depending on the composition, assortment, size of shipment and, of course, the distance of the manufacturer to the place of sale.
A few words in conclusion
As for duralumin, we can safely say that its appearance provided technological breakthroughs in aircraft construction and the space industry, and without its timely appearance we would have been flying airplanes made of wood.
Rate this article:
Rating: 0/5 — 0 votes
Advantages and disadvantages
A significant advantage of duralumin is its lighter weight than steel, despite the strength of this material. This allows it to be used in the manufacture of cars, airplanes, and rockets to facilitate construction.
An important property of duralumin is its high heat resistance, which facilitates its use in the production of radiators.
Duralumin is more resistant to vibrations than steel. Due to this, it is widely used in the manufacture of drilling equipment.
This is interesting: Metal straightening
Disadvantages include high sensitivity to corrosion. Not all types of duralumin are suitable for welding.