Copper ore: properties and characteristics
Copper is a plastic element with a golden-pink hue.
In the open air, the metal is immediately covered with an oxygen film, which gives it a specific red-yellow color. Characteristic properties: corrosion resistance, high thermal and electrical conductivity.
At the same time, the element has high antibacterial properties and destroys influenza viruses and staphylococci.
In the industrial complex, copper is most often used in alloys with other components: nickel, zinc, tin, gold, etc.
Nurkazgan. Kazakhstan
The entire periodic table has been collected in the depths of the Kazakh steppes. And one of the largest copper mines in Kazakhstan is located in the north of the country, and is part of the unified system of the Nurkazgan Mining and Processing Corporation.
Exploration work has been carried out since the late 90s, and the mine was put into operation in 2006. A little more than 700 workers are employed in mining.
Employees of Kazakhmys, which owns the rights to develop and mine gold and copper, estimate Nurkazgan’s copper reserves at 1.8 million tons.
Groups of copper ores
All copper ores are usually divided into nine industrial-geological types, which in turn are divided into six groups according to origin:
Pyrite group
This includes native copper, vein and copper-pyrite compounds. The native metal is most often found in the oxidation zones of copper sulfide mines, along with other oxidized minerals.
Copper pyrite metals differ in shapes and sizes. The main mineral in the ore is pyrite; chalcopyrites and sphalerites are also present.
Vein ores are characterized by a vein structure with inclusions. Such ores, as a rule, occur in contact with porphyries.
Porphyry copper (hydrothermal)
These deposits, together with copper and molybdenum, contain gold, silver, selenium and other useful elements, the presence of which is significantly higher than normal.
Copper-nickel
The deposits are presented in sheet, lens-shaped, irregular and vein forms. The metal has a massive texture interspersed with cobalt, platinum group metals, gold, etc.
Skarn Ore
Skarn ores are local deposits in limestones and calcareous-terrigenous rocks. They are characterized by small sizes and complex morphology. The copper concentration is high, but uneven - up to 3%.
Carbonate
This group includes iron-copper and carbonatite ore. So far, the only deposit of this type of copper has been discovered in South Africa. This complex mine belongs to the alkaline rock massif.
Interesting! Copper is very rarely found in nature in the form of nuggets. To date, the largest such find is considered to be a nugget discovered in North America in the United States weighing 420 tons.
There are almost 250 types of copper, but only 20 types are used in industry. The most common of them:
Chalcozine
A compound of minerals containing sulfur (20%) and copper (80%). It is called "copper luster" because of its characteristic metallic luster. The ore has a dense or granular structure of black or gray hue.
Bornite
A common mineral of the sulfide class in nature, one of the main elements of copper ores. It has a characteristic bluish-purple tint. Contains copper (63.33%), iron (11.12%), sulfur (25.55%) and silver impurities. It occurs in the form of dense, fine-grained masses.
Depending on the depth of the mine, open and closed methods of metal extraction are used.
In closed (underground) mining, mines are built several kilometers long. The mines are equipped with elevators to move workers and equipment, as well as to transport minerals to the surface.
Closed (underground) method of copper ore mining
Underground, the rock must be crushed using special drilling equipment with spikes. Then, with the help of buckets, the ore is collected and loaded.
The open method is relevant when the deposits are located at a depth of 400-500 meters. First, the top layer of waste rock is removed, after which the copper ore is removed. To make it easier to get hard rocks, it is first destroyed with explosive devices.
Open pit method of copper ore mining
There are two main methods for producing copper:
- pyrometallurgical;
- hydrometallurgical.
The first method involves fire refining of metal and allows you to process any raw material with the extraction of all useful elements. Using this technology, it is possible to obtain copper even from poor rock, in which the metal content is below 0.5%. The second method is used, as a rule, only for processing oxidized or native ore with a low copper content.
Copper mines are not concentrated in specific geographical areas, but are found in different countries. In America, chalcocite deposits are being developed in the states of Nevada and Arizona. Deposits of copper oxide, cuprite, are common in Cuba. Copper chloride is mined in Peru.
There are almost no sources of enriched ores left in the world; copper has been mined for several hundred years, so all the rich mines have long been developed. In industry it is necessary to use low-grade minerals (up to 0.5% copper).
Interesting! In terms of global production, copper is in third place after iron and aluminum.
The list of countries rich in copper ores includes: Chile, America, China, Kazakhstan, Poland, Indonesia, Zambia. The Russian Federation's share in world ore production is 9% (this is third place after Chile and the USA). Chile is the leader in mineral reserves, containing 33% of the world's copper.
The largest mines are:
- Chuquicamata mine (Chile). Development has been carried out for more than 100 years, during this period 26 million tons of metal were developed;
Chuquicamata Quarry (Chile)
- Escondida mine (Chile). Mining has been carried out since 1990;
Escondida Quarry (Chile)
- Grasberg mine (Indonesia).
Grasberg Quarry (Indonesia)
Chalcopyrite
The metal is of hydrothermal origin and is found in skarns and greisens. Most often it is part of polymetallic ore along with galena and sphalerite.
Processing the resulting ore
As of today, there are 3 ways to process the resulting copper ore. Pyrometallurgical, hydrometallurgical and electrolysis.
The pyrometallurgical method is the most popular. The most common chalcopyrite is taken as the “working material”.
At the very beginning, enrichment is performed. For this purpose, the oxidative firing method is used. This method is very suitable for chalcopyrite, since it is primarily designed for ores with high sulfur concentrations. With this technology, the ore is heated to high temperatures (sometimes up to 8 thousand degrees Celsius), during which sulfur and oxygen interact, after which almost half of the sulfur evaporates. Next, the ore is heated even more in shaft or reverberatory furnaces. We are already talking about 1.4-1.5 thousand degrees.
Sometimes fake jewelry is made from copper, as a similar-colored material. To avoid counterfeits, be aware that copper darkens over time, and a metallic smell remains in the water.
The output, after exposure to such temperatures, is an alloy of copper and iron sulfides - matte. The alloy is blown through convectors, due to which both iron and sulfur are oxidized once again, evaporating in some places and settling as slag in others. The product becomes 91% blister copper.
In order to achieve almost standard copper content in the alloy, fire refining technology is used. An acidified solution of CuSO4 is also used with it. After these manipulations, which, by the way, are called electrolytic refining of copper, we get “pure” copper, with a concentration of 99.9%.
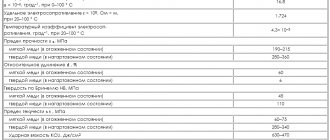
Basic properties of copper
Physical properties
In air, copper acquires a bright yellowish-red hue due to the formation of an oxide film. Thin plates have a greenish-blue color when examined through them. In its pure form, copper is quite soft, malleable and easily rolled and drawn. Impurities can increase its hardness.
The high electrical conductivity of copper can be called the main property that determines its predominant use. Copper also has very high thermal conductivity. Impurities such as iron, phosphorus, tin, antimony and arsenic affect the basic properties and reduce electrical and thermal conductivity. According to these indicators, copper is second only to silver.
Copper has high densities, melting points and boiling points. An important property is also good resistance to corrosion. For example, at high humidity, iron oxidizes much faster.
Copper lends itself well to processing: it is rolled into copper sheets and copper rods, and drawn into copper wire with a thickness brought to thousandths of a millimeter. This metal is diamagnetic, that is, it is magnetized against the direction of the external magnetic field.
Chemical properties
Copper is a relatively low-active metal. Under normal conditions in dry air, its oxidation does not occur. It reacts easily with halogens, selenium and sulfur. Acids without oxidizing properties have no effect on copper. There are no chemical reactions with hydrogen, carbon and nitrogen. In humid air, oxidation occurs to form copper (II) carbonate, the top layer of platinum.
Copper is amphoteric, meaning it forms cations and anions in the earth's crust. Depending on the conditions, copper compounds exhibit acidic or basic properties.
Optical properties
| Color in reflected light | pinkish white |
| Pleochroism | does not pleochroate |
| Luminescence in ultraviolet radiation | not fluorescent |
Crystallographic properties
| Point group | m3m (4/m 3 2/m) - hexoctahedral |
| Space group | Fm3m (F4/m 3 2/m) |
| singonia | cubic |
| Cell Options | a = 3.615Å |
| Morphology | cubes, dodecahedrons and tetrahexahedrons; rarely octahedra and complex combinations; thread-like, tree-like |
| Twinning | {111} twins according to the spinel law |
Natural compounds containing copper in their composition
Pure copper nuggets are found in our Earth in small quantities. It is mainly mined in combination with other elements, here are the most famous of them:
- Bornite is a mineral that was named after the Czech scientist Born. It is a sulfide ore. It also has alternative names, such as copper purple. It is mined in two types: low-temperature tetragonal-scalenohedral and high-temperature cubic-hexahedral. The different types of this material depend on where it originated. Exogenous bornite is a secondary early sulfide, is unstable and is subject to destruction when exposed to winds. Endogenous bornite has a variable chemical composition and may contain various elements, for example, chalcocite and galena. In theory, bornite can contain 11% iron and more than 63% copper, but, unfortunately, in practice this composition is not maintained.
- Chalcopyrite - this type of mineral was originally called copper pyrite; it originates hydrothermally. Chalcopyrite is classified as a polymetallic ore. In addition to copper, this mineral contains iron and sulfur. It is formed as a result of metamorphic processes, and is present in metasomatic types of copper ores.
- Chalcocine - this ore contains a large amount of copper, almost 80%, the remaining place is occupied by sulfur. This type is often called copper glitter, as its surface is similar to shiny metal, shimmering in several shades. In ores, chalcocite forms as a fine-grained or dense inclusion.
- Cuprite - this mineral belongs to the oxide group, and it originates in places where native copper or malachite is contained.
- Covellite is a mineral that is formed only metasomatically. It contains almost 67% copper. There are large deposits of copper ores in Serbia, Italy and the USA.
- Malachite, or, as it is also called, an ornamental stone, is very popular; it is a copper carbon dioxide green. If this mineral is found somewhere, it means that others containing copper can be found nearby.
Application
Copper bracelets
Due to its low resistivity, copper is widely used in electrical engineering for the manufacture of power cables, wires or other conductors, for example, in printed circuit wiring. Copper wires, in turn, are also used in the windings of energy-saving electric drives and power transformers.
Another useful quality of copper is its high thermal conductivity. This allows it to be used in various heat removal devices and heat exchangers, which include well-known radiators for cooling, air conditioning and heating.
Alloys using copper are widely used in various fields of technology, the most widespread of which are the above-mentioned bronze and brass. Both alloys are general names for a whole family of materials, which in addition to tin and zinc may include nickel, bismuth and other metals.
In jewelry, alloys of copper and gold are often used to increase the resistance of products to deformation and abrasion, since pure gold is a very soft metal and is not resistant to these mechanical influences.
The predicted new mass use of copper promises to be its use as bactericidal surfaces in medical institutions to reduce intra-hospital bacterial transfer: doors, handles, water stop valves, railings, bed rails, table tops - all surfaces touched by the human hand.
Copper - Cu
| Molecular weight | 63.55 g/mol |
| origin of name | From the Greek "Kyprium", that is, "Cypriot metal", after the name of the island of Cyprus |
| IMA status | valid, first described before 1959 (before IMA) |
Uyu Tolgoi. Mongolia
The Mongolian mine specializes in the extraction of gold and native copper. Experts consider the mine one of the most promising in terms of the use of new technologies that will increase production volumes.
Copper mining was suspended in 2013 due to disagreements between Mongolian authorities and the Austro-Belgian exploration and mining company.
But Rio Tinto PLC, which owns the majority of the shares, presented a new promising project in which it invested more than $5 billion.
Raw materials for copper production
To obtain copper, copper ores are used, as well as waste of copper and its alloys. The ores contain 1-6% copper. Copper, like many other non-ferrous metals, is becoming increasingly scarce. If in the 19th century. Copper was mined from ores containing 6-9% of this element, but now 5% copper ores are considered very rich, and the industry of many countries processes ores containing only 0.5% copper.
In ores, copper is usually found in the form of sulfur compounds (copper pyrite or chalcopyrite CuFeS2, chalcocite Cu2S, coveline CuS), oxides (cuprite Cu2O, tenorite (CuO) or hydrocarbonates (malachite CuCO3 × Cu(OH2), azurite 2CuCO3 × Cu(OH) 2).
The gangue rock consists of pyrite FeS, quartz SiO2, magnesium and calcium carbonates (MgCO3 and CaCO3), and various silicates containing Al2O3, CaO, MgO and iron oxides. Copper ores sometimes contain significant amounts of other metals: zinc, tin, nickel, gold, silver, silicon, etc. Copper ores are divided into sulfide, oxidized and mixed ores. Sulfide ores are usually of primary origin, and oxidized ores are formed as a result of the oxidation of metals in sulfide ores. So-called native ores, in which copper is found in free form, are found in small quantities.
A little history
In what area copper began to be mined and used by humans for the first time in ancient times, archaeologists, unfortunately, were unable to find out. However, it is known for certain that it was this metal that people were the very first to process and use in everyday life.
Copper became known to man back in the Stone Age. Some nuggets of this metal found by archaeologists bear traces of processing with stone axes. Initially, people used copper mainly only as jewelry. At the same time, for the manufacture of such products, people in ancient times used exclusively nuggets of this metal that they found. Later, people learned to process copper-containing ore.
Many peoples of antiquity had an idea of how Cu is mined and how it is processed. Archaeologists have found plenty of evidence of this. After man learned to make alloys of copper and zinc, the Bronze Age began. Actually, the name “copper” itself was once coined by the ancient Romans. Such metal was brought to this country mainly from the island of Cyprus. That's why the Romans called it aes cyprium.
Reserves in nature
Where can you mine copper in the wild today? Currently, deposits of this popular metal have been discovered on all continents of the Earth. At the same time, Cu reserves are considered to be practically unlimited. Geologists nowadays are finding more and more new deposits of pure copper, as well as ores containing it. For example, in 1950, world reserves of this metal amounted to 90 million tons. By 1970, this figure had already increased to 250 million tons, and by 1998 - to 340 million tons. Currently, it is believed that copper reserves on the planet amount to more than 2.3 billion tons.
Chuquicamata. Chile
One of the world's oldest and largest copper deposits, copper mining began in 1915, and the quarry is located at an altitude of 2,840 m in the Central Andes.
In terms of the volume of ore mined, it lost the palm to Escondida, but in terms of size it remains one of the largest. The quarry is 4.3 km long and 3 km wide. Moreover, work is already underway at a depth of over 850 m.
At the turn of the 60-70s of the last century, the Chilean industry began to develop ore. It should be noted that the company’s employees conduct not only production, but also active exploration to find new deposits.
How copper ore deposits are developed
Various types of rocks containing Cu, as well as nuggets, can be mined on the planet using two main technologies:
- closed;
- open.
In the first case, mines are built at the deposit, the length of which can reach several kilometers. To move workers and equipment, such underground tunnels are equipped with elevators and railway tracks. Rock crushing in mines is carried out using special drilling equipment with spikes. Copper ore is collected and loaded to be sent upstairs using buckets.
If the deposits are located no further than 400-500 m from the surface of the earth, they are mined using the open-pit method. In this case, the top rock layer in the field is first removed using explosive devices. Next, the copper ore itself is gradually removed.
This is interesting: Marquis canopy
Deposits and methods of mining pure copper
As already mentioned, initially people used native copper in everyday life. Of course, such pure copper is still mined today. Nuggets of this metal are formed in the earth's crust as a result of exogenous and endogenous processes. The largest known deposit of native copper on the planet is currently located in the USA, in the Lake Superior region. In Russia, native copper occurs in the Udokan deposit, as well as in some other places in Transbaikalia. In addition, the answer to the question of where copper can be mined in Russia in the form of nuggets is the Ural region.
In nature, pure metal of this variety is formed in the oxidation zone of copper sulfate deposits. Typically, nuggets contain about 90-99% copper itself. The rest comes from other metals. In any case, the answer to the question of how native copper is mined is provided by two main technologies. Such deposits, like ore deposits, are developed using closed mine or open pit methods. In the first case, technological processes such as drilling and mining are used.
Copper nuggets can weigh a lot. The largest of them were once found on Lake Superior in the United States. The weight of these nuggets was about 500 tons.
We found out where copper is mined in Russia. These are mainly Transbaikalia and the Urals. In our country, of course, very large nuggets of this metal were also found at different times. For example, copper pieces weighing up to several tons were often found in the Middle Urals. One of these nuggets weighing 860 kg is now stored in St. Petersburg, in the Museum of the Mining Institute.
Sibay. Russia
The quarry located in Bashkiria was opened in 1913, and copper mining began in the 30s of the twentieth century. The first exploration work was carried out in 1915, and already at that time a small copper smelter began operating nearby.
The largest site, Novo-Sibaisky, consists of 3 large lenses connected to each other by a common ore column. The depth of the quarry is just over 500 m, and its dimensions are 1.4 km by 1.3 km.
The deposit is considered the standard of pyrite ore deposits of the Ural group. In addition to copper, zinc is also mined at the mines, and according to experts, the reserves will last for many more decades.
By the way, on our website thebiggest.ru there is an informative article about the highest mountains of Bashkortostan.
Mining of copper ores in the world
Copper mines are not concentrated in specific geographical areas, but are found in different countries. In America, chalcocite deposits are being developed in the states of Nevada and Arizona. Deposits of copper oxide – cuprite – are common in Cuba. Copper chloride is mined in Peru.
There are almost no sources of enriched ores left in the world; copper has been mined for several hundred years, so all the rich mines have long been developed. In industry it is necessary to use low-grade minerals (up to 0.5% copper).
Interesting! In terms of global production, copper is in third place after iron and aluminum.
Leading countries in copper ore reserves and production
The list of countries rich in copper ores includes: Chile, America, China, Kazakhstan, Poland, Indonesia, Zambia. The Russian Federation's share in world ore production is 9% (this is third place after Chile and the USA). Chile is the leader in mineral reserves, containing 33% of the world's copper.
The largest mines are:
- Chuquicamata mine (Chile). Development has been carried out for more than 100 years, during this period 26 million tons of metal were developed;
Recently, large mines were discovered in Peru (Antamina), Brazil (Salobu), and Kazakhstan (Nurkazgan).
Experts say that the volume of economically viable copper is more than 400 million tons. Worldwide.
Bingham Canyon. USA
A giant deposit, where open-pit copper mining has been carried out since 1863. This is the deepest copper quarry, with a depth of 1,200 m.
The size of the anthropogenic formation is truly amazing. It covers an area of 7.7 km2 and its width is 4 km. According to geologists, ores containing copper will last for many decades, because reserves are estimated at 640 million tons.
Every day, 450 thousand tons of rock are extracted to the surface, and 1,400 workers work on the extraction. In 2013, a landslide occurred in the quarry, stopping work for several months.
Copper ore mining in Russia
The structure of the copper raw material base in Russia differs significantly from the world market. The main share in it falls on sulfide copper-nickel (40%) and pyrite (19%) mines. While in other countries porphyry copper deposits and cuprous sandstones predominate.
Sources
- https://promdevelop.ru/industry/mednaya-ruda-svojstva-primenenie-dobycha/
- https://nzmetallspb.ru/stanki/mednaya-ruda-mestorozhdeniya-dobycha-vidy-pererabotka.html
- https://cu-prum.ru/med.html
- https://mineralpro.ru/minerals/copper/
- https://intehstroy-spb.ru/spravochnik/mednaya-ruda-svoystva-primenenie-dobycha.html
- https://poliasmet.ru/svojstva-medi/proizvodstvo-medi.html
- https://FB.ru/article/464216/kak-dobyivayut-med-sposobyi-istoriya-i-mestorojdeniya
- https://mining-prom.ru/cvetmet/med/poluchenie-medi/