Composition and properties
This steel is an analogue of Russian-made steel grade 08Х8Н1. Therefore, in their composition they are very close. The main element in it is iron from 66 to 74 percent. The rest is made up of so-called alloying additives. These include: chromium - about 20%, manganese - 2%, nickel - 8%, carbon - less than 8%. Based on this steel, depending on the amount of carbon contained in it, two additional grades of metal were developed: with a lower carbon content - this is AISI 304L, with a higher content - AISI 304 H. The Russian analogue of the first grade is steel 03Х18н11.
Collar flange made of steel 03Х18н11
The presence of just such a percentage of additives and appropriate processing give this metal much-needed and useful properties.
Beneficial properties include:
- Long-term resistance to high or low temperatures. The experimentally obtained range of permissible temperatures ranges from minus 200 °C to plus 650 °C.
- High resistance to long-term exposure to aggressive environments (salt water, acidic and alkaline solutions). That is, good anti-corrosion resistance.
- Weak magnetization. This can be achieved by creating a special structure and processing methods.
- Excellent environmental friendliness. It is positioned on the international market as an Inox material. It received this category due to the fact that it does not absorb any substances, including toxic ones.
- Well processed.
- High strength with low specific gravity.
- Great resistance to oxidation effect.
- Almost perfect prevention of contamination of products stored in containers made of this steel.
- Excellent aesthetics and ease of cleaning after use.
- Wide range of applications.
Additional advantages include a long service life of products made from this metal and low operating costs.
This steel has no serious disadvantages. There are some problems when processing and operating at high temperatures. For all austenitic stainless steels, when processed in the temperature range from 425 °C to 820 °C, the effect of precipitation of chromium carbides occurs. Such steels become susceptible to intercrystalline corrosion when products are placed in highly aggressive environments. Therefore, this effect, the so-called “sensitization,” can manifest itself in places of heating, for example during welding, in places of seams.
In Russia, steel grade 08Х18Н10 is an analogue of AISI 304, in the European Union it is 1.4301. It should be noted that many countries have their own classification system.
Description of steel
The brand described in the article has found its distribution in the manufacture of welded and prefabricated metal structures, household equipment and components of pipeline fittings. If we mention the shape of the sheet, then steel can be classified into hot-rolled and cold-rolled material, which is determined by the production technology. Flat metal products are sold in the form of rolls and sheets. The surface of the canvas can be processed in a certain way during the production process, as a result it is possible to obtain the following types of surface:
- mirror;
- polished;
- matte.
On sale there is a stainless steel pipe, which is produced by electric welding. The material does not corrode in places where mechanical damage or scratches have occurred. Containers made of this steel can be used for transporting and storing products from the chemical industry and food industry. In the first case we are talking about weak chemical reagents.
In the form of a pipe, steel can have a rectangular, round or square cross-section. Depending on the production method, products can be seamless or electric welded. The surfaces in these cases can be polished, matte or mirrored. AISI 304 (GOST 08Х18Н10) is used for the manufacture of barrels for fur, kvass and beer, as well as for the production of equipment, cooling coils, bunkers, dairy equipment, cryogenic vessels, evaporators, pans.
Characteristics of steel
AISI 304 steel has its own individual characteristics. They can be divided into three categories:
- physical;
- chemical;
- mechanical.
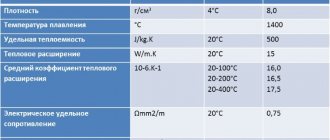
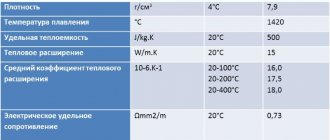
Physical characteristics are determined by the following parameters:
- the density of AISI 304 stainless steel is 7.78-7.93 g/cm3;
- melting point – 1450 °C;
- specific heat capacity – 500 J/kg×K;
- thermal expansion – 15 W/m×K;
- electrical resistivity – 0.8 Ohm×m2/m.
Physical properties of AISI 304
These characteristics determine many of the properties of this metal.
Chemical characteristics consist of the following indicators:
- percentage of various elements in the composition of the material;
- steel resistance to chemical reactions when exposed to aggressive environments;
- rate of natural oxidation (corrosion);
- ability to absorb and subsequently release harmful substances.
Chemical composition of AISI 304
Mechanical characteristics include:
- compressive strength (210 MPa);
- tensile strength (varies from 520 to 720 MPa);
- permissible yield strength (about 210 MPa);
- tensile strain (approximately 45%);
- Rockwell hardness (reaches 70 units).
Heat resistance of AISI 304 in comparison with other brands
Corrosion resistance AISI 304 compared to other brands
Food grade stainless steel: AISI 304, 430, 18/8, 18/10..
What is the difference between the different grades of stainless steel (304, 430, 220, etc.)? What do the different marking numbers mean (18/8, 18/10, 18/0, etc.)? We are often asked about this, so we decided to write a short article dedicated to food-grade stainless steel.
The “grade” of stainless steel determines its quality, durability, and heat resistance. Marking 18/8, 18/10, etc. denotes the composition of stainless steel, namely the ratio of chromium and nickel in it.
Food grade stainless steel marking
18/8 and 18/10 are the two most common grades of stainless steel used for:
- stainless steel furniture
- kitchen utensils
- cutlery
These grades are also known as 304 ( AISI 304) and are part of the 300 series. The first number, 18, indicates the proportion of chromium and the second - nickel. For example, 18/8 stainless steel contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel.
304 stainless steel also contains no more than 0.8% carbon and no less than 50% iron. Chromium binds oxygen on the surface of the product, forming a film that protects the iron from oxidation (rust). Nickel also improves the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. Therefore, the higher the nickel content, the more resistant stainless steel is to corrosion.
AISI 304 steel is an austenitic steel (steel alloyed with chromium, nickel and manganese, which, when cooled to room temperature or below, retains the structure of a solid molten solution - austenite) with a low carbon content. This grade of steel is the most widely used of all steel grades, and its characteristics make it versatile in use.
This steel and its analogue - steel grade 08Х18Н10 is used for the manufacture of equipment for chemical and food enterprises and public catering establishments, equipment for the production, storage and transportation of milk, beer, wine and other drinks, as well as chemical reagents, kitchen and tableware.
18/0 steel contains a small amount of nickel (0.75%) and therefore has reduced corrosion resistance - it is more susceptible to it compared to grades 18/8 or 18/10. However, this is high quality steel. 18/0 food grade steel is also known as 430 steel and is part of the 400 series of stainless steels which, unlike the 300 series, is magnetic.
Food grade 200 series stainless steels are often used for cookware, kitchen utensils, cutlery, and containers. These steels, as a rule, are significantly cheaper than 304 steel - in the 200 series, expensive nickel is partially replaced by manganese. Although 200 steel products are just as safe, they are not as corrosion resistant as 304 steel.
You can order any neutral stainless steel furniture from us.
Using food grade stainless steel for cutlery
It is sometimes believed that 18/10 steel is heavier and therefore less suitable for cutlery. In fact, there is no difference between the weight of cutlery made from 18/8 steel and 18/10 steel. Nickel in cutlery made from 18/10 steel provides additional strength - for example, forks made from this steel do not bend well. Cutlery made from 18/10 steel also has a shinier surface.
Using food grade stainless steel for cookware
Stainless steel is an excellent alternative to Teflon-coated aluminum cookware. However, a stainless steel stovetop, frying or cooking surface alone does not provide optimal heat conduction, which is why pots and other cookware are typically made of a three-ply material. For example, in a stainless steel frying pan, a layer of aluminum is sandwiched between two layers of 18/10 steel, allowing the heat to be distributed evenly throughout the pan. In these pans, aluminum does not come into contact with food.
How safe is stainless steel?
Stainless steel is one of the most common materials used in kitchens today. It is used for cutlery, dishes, work surfaces of a wide variety of heating equipment. This is a durable material that is easy to sanitize and disinfect, resistant to corrosion and the action of various aggressive acids contained in meat, milk, fruits and vegetables. Equally important, stainless steel contains no chemicals that can migrate into foods and drinks.
We believe that stainless steel, glass, cast iron, wood, and ceramic with lead-free enamel are the safest materials to use in the kitchen. Our company offers a wide range of stainless steel products.
Processing methods
AISI 304 steel is quite easily susceptible to almost all types of mechanical processing: stamping, forming, rolling. In addition, it drills, cuts, mills and sands well. Steel is well suited to deep drawing on a press, as well as cold bending and forming. For this metal, the permissible bending radius depends on the thickness of the sheet. It is calculated using the formula r=2×s. Where s is the thickness of the sheet.
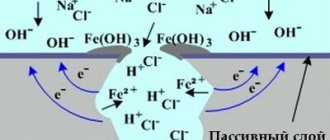
During heat treatment it is allowed: firing, tempering. To carry out firing, the temperature of the workpiece must be 1050 °C. The permissible interval is 25 °C in both directions. After firing, rapid cooling is carried out. This allows you to give the metal good anti-corrosion properties. After the firing process, two more types of processing are necessarily carried out: etching and passivation.
The process of etching, that is, cleaning the surface, is carried out using a mixture of two acids: nitric and hydrofluoric. This process is carried out by heating to 60 ° C, and passivation using a 20% solution of nitric acid using special pastes, especially for the area where welding was carried out.
Tempering is carried out at a lower temperature (450 - 600 °C) for 60 minutes. To preserve the heat treatment technology, it is necessary to remember that for stainless steel the homogeneous heating time is twice as high as for carbon steel.
Parts or structural elements made of AISI 304 steel can be welded quite easily. This is due to good fusibility. To do this, you can use autogenous welding without adding filler materials.
Heat resistance
AISI 304 has good oxidation resistance at temperatures up to 870 °C, and during long-term use up to 925 °C.
However, prolonged exposure to temperatures between 425 and 860 °C is not recommended if corrosion resistance in an aquatic environment is required. In this case, AISI 304L steel due to its resistance to carbide precipitation.
In cases where high strength is required at temperatures from 500 °C to 800 °C, it is better to use AISI 304H steel . This material will remain corrosion resistant in water longer.