Historical information
Before studying the characteristics of the most refractory metals in the world, you should familiarize yourself with their discovery history. Metalworking has been known to man for several thousand years. However, active production of refractory metals began only in the second half of the 19th century.
Initially they were used only in electrical engineering. With the advent of new technologies in the construction of airplanes, cars, trains and rockets, parts with a high melting rate began to be used more actively. The peak popularity of blanks that can withstand temperatures of more than 1000 degrees occurred in the mid-20th century.
What brands are there?
Tungsten can be pure, with additives, or as part of an alloy that includes other metals.
The HF marking is used to designate pure tungsten. To mark the alloy of tungsten and rhenium, the designation VR is used.
The presence of different types of additives is indicated by the following combinations of letters:
• VA – silica-alkaline and aluminum;
• VM – silica-alkaline and thorium;
• VT – thorium oxide;
• VL – lanthanum oxides.
The indicated grades of tungsten are used most often in industry.
Kinds
Types of metals and alloys that are resistant to elevated temperatures:
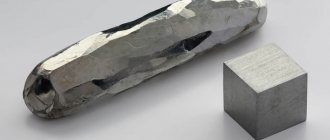
- Tungsten. They first learned about it in 1781. To melt it, it needed to be heated to 3380 degrees. Tungsten is considered the most refractory. It is made from powder, which is processed chemically. First, the mixture is heated and then subjected to pressure. The output is compressed blanks.
- Niobium. Melts at 2500 degrees. It has high thermal conductivity and is not as difficult to process as tungsten. It is made from powder that is baked and processed using high pressure. Niobium is used to make wire, pipes and tape.
- Molybdenum. Visually, it can be confused with tungsten. It is made from powder by baking and applying pressure. Like tungsten, it has paramagnetic properties. Used in radio electronics, manufacturing of industrial equipment, furnaces and electrodes.
- Tantalum. Melts at 3000 degrees. To make tantalum wire or harden the material, it does not need to be heated to critical temperatures. Used for the manufacture of elements in radio electronics (capacitors, film resistors). Popular in the nuclear industry.
- Rhenium. Material that scientists discovered later than others. You can find it in copper and platinum ore. Used in industrial production as an alloying additive.
Chromium is also a material with high melting points. Due to its unique characteristics, it is used in various industries. It has increased resistance to critical temperatures and corrosive processes. However, it is worth considering its fragility.
Tantalum
Refractoriness of metals
All engineers and designers working in mechanical engineering pay attention to this characteristic. Depending on the value of this characteristic, a person can calculate and determine in which design certain refractory materials can be used.
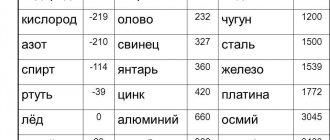
Materials whose melting point is higher than the melting point of iron, equal to 1539 ° C, are called refractory. The most refractory materials:
- tantalum;
- niobium;
- molybdenum;
- rhenium;
- tungsten.
Tantalum
Molybdenum
The full list contains more chemical elements, but not all of them are widely used in production and some have lower melting points or are radioactive.
Tungsten is the most refractory metal. It looks light gray in color and is quite hard and heavy. However, it becomes brittle at low temperatures and is easy to break (cold brittleness). If you heat tungsten above 400 °C, it will become ductile. Tungsten does not combine well with other substances. It is extracted from complex and rare ore minerals, such as:
- scheelitis;
- ferberite;
- wolframite;
- hübnerite.
Ore processing is a very complex and expensive process. The extracted material is formed into bars or finished parts.
Huebnerite
Tungsten was discovered in the 18th century, but for a long time there were no furnaces capable of heating to the melting point of this refractory metal. Scientists have conducted many studies and confirmed that tungsten is the most refractory metal. It is worth noting that according to one of the theories, seaborgium has a high melting point, but it is not possible to conduct a sufficient number of studies, because it is radioactive and unstable.
Adding tungsten to steel increases its hardness, so it began to be used in the manufacture of cutting tools, which increased cutting speed and thereby led to an increase in production.
The high cost and difficulty of processing this refractory metal affect its areas of application. It is used in cases where it is not possible to use another. Its advantages:
- resistant to high temperatures;
- increased hardness;
- durable or resilient at certain temperatures;
Metal ore processing
All these characteristics help tungsten find wide application in various fields, such as:
- metallurgy, for alloy steels;
- electrical engineering, for filaments, electrodes, etc.;
- mechanical engineering, in the manufacture of gear units and shafts, gearboxes and much more;
- aviation production, in the manufacture of engines;
- space industry, used in rocket nozzles and jet engines;
- military-industrial complex, for armor-piercing shells and cartridges, armor of military equipment, in the design of torpedoes and grenades;
- chemical industry, tungsten has good corrosion resistance to acids, which is why filter meshes are made from it. In addition, compounds with tungsten are used as fabric dyes, in the production of clothing for firefighters, and much more.
Such a list of industries where this refractory metal is used suggests that its importance for humanity is very great. Every year, tens of thousands of tons of pure tungsten are produced around the world, and every year the demand for it grows.
Properties
To understand where it is best to use a material, you need to know the properties of refractory metals. They are used to make parts for industrial equipment, machinery and electronics. The characteristics of heavy refractory metals will be described below.
Physical properties
Characteristics:
- Density - up to 10000 kg/m3. For tungsten this figure reaches 19,000 kg/m3.
- The average melting point is 2500 degrees Celsius. Tungsten has the highest metal melting point - 3390 degrees.
- Specific heat capacity - 400 J.
Refractory objects cannot withstand impacts and falls.
Chemical properties
Chemical properties:
- These are solid substances with high chemical activity.
- Strong interatomic structure.
- Resistance to long-term exposure to acids and alkalis.
- High paramagnetic index.
These materials have some disadvantages. The main one is the difficult process of processing and manufacturing products from it.
Receipt
The industrial production of metal from ore is preceded by enrichment. These are crushing, grinding, flotation. WO3 is then separated from the concentrate, which is then reduced to the metal with hydrogen at a temperature of about 700°C.
Compact tungsten is obtained:
- Using powder metallurgy method. The advantage of the method is the possibility of uniform introduction of additives.
- Electron beam melting, or melting in electric arc furnaces. The advantage of the method is the ability to obtain large (up to 3 tons) metal blanks.
Tungsten powder
Application
Initially, refractory metals were used in the manufacture of capacitors and transistors for radio electronics. The number of their areas of application increased only by the middle of the 20th century. The industrial complex expanded to produce parts for machine tools, cars, airplanes and missiles.
Alloys that can withstand exposure to critical temperatures began to be used to make tableware. Refractory metals are used in the production of building and connecting materials. They are used to make parts for household appliances and electronics.
Tungsten is considered the most refractory.
Its melting point of 3390 degrees exceeds other materials. However, we must not forget that if a tungsten part falls from a height, it will crack or break into separate parts. Other materials with a high melting index are little different from tungsten. They are used in mechanical engineering, shipbuilding, nuclear energy, and the manufacture of industrial equipment. Their development and research continues to this day.
What alloy is considered the strongest in the world?
Metals together with alloying additives form the strongest alloy. First of all, this concerns hardness.
In addition, they differ in a number of indicators, including heat and electrical conductivity. Strong alloys are in demand in industry.
This is especially true for aircraft construction, where lightness is required along with strength. Such alloys are needed in the automotive and shipbuilding industries.
About metals in nature
Metals are divided into ferrous and non-ferrous. The classic representative of the first type is iron. People of color form a more expensive group.
How metals are produced
Metals do not occur in nature in their pure form. They are contained in ores.
Their production proceeds in the following stages:
- identification of deposits;
- ore mining:
- metal extraction.
The strongest of metals
Strength is the ability of a metal to withstand external loads. The resistance of an element is provided by its internal structure, which is capable of creating internal tension that resists external pressure.
The strongest metals include:
- titanium;
- rhenium;
- beryllium;
- chromium;
- tantalum;
- iridium.
The most durable alloy
The hardest alloys in the world are tungsten. The basis is powders consisting of several metal carbides and cobalt. Mixing is carried out in a certain proportion. The technology developed by scientists makes it possible to obtain alloys with a high degree of hardness.
Such compounds are marked with the letter designation: VK3, where B is the tungsten group. K is the cobalt content in percent.
Physical and chemical properties
Basic physical properties of tungsten alloys:
- A characteristic feature is red fastness. It is 800 degrees. The term means that the cutting edge is able to withstand that temperature. This is ensured by high thermal conductivity. Due to this, heat is dissipated.
- High hardness, which is 90 Rockwell units.
- The melting point reaches 2780 degrees.
Chemical resistance to the external environment increases with increasing percentage of cobalt.
Chemical properties of titanium
Features of manufacturing and scope of application
The technology for producing hard alloys from tungsten consists of the following stages:
- First, coarse tungsten powder is formed, which is then crushed and sifted.
- Tungsten carbide and cobalt powders are obtained in the same way.
- They are mixed with the addition of glue. This is performed by rubber dissolved in gasoline.
- The mixture is dried and pressed.
- The technological process ends with two sinterings.
Solid material is used in the manufacture of the following products:
- cutters for lathes;
- stamp;
- rolling rolls;
- balls and races for bearings.
- soldering for tools of mining equipment;
Any production requires processing of products. To ensure this process, a material of higher hardness is needed. This function is performed by hard alloys.
Which alloy is considered the most durable in the world Link to main publication
Vanadium
Gray metal with a silvery sheen. It has a fairly high fusibility index (1920 °C). It is used mainly as a catalyst in many processes due to its inertness. It is used in the energy sector as a chemical current source, in the production of inorganic acids. It is not the pure metal that is of primary importance, but rather some of its compounds.
Niobium and its alloys
Nb, or niobium, is a silvery-white shiny metal under normal conditions. It is also refractory, since the temperature of transition to the liquid state for it is 2477 °C. It is this quality, as well as the combination of low chemical activity and superconductivity, that allows niobium to become increasingly popular in human practice every year. Today this metal is used in industries such as:
- rocket science;
- aviation and space industry;
- nuclear power;
- chemical apparatus engineering;
- radio engineering.
This metal retains its physical properties even at very low temperatures. Products based on it are characterized by corrosion resistance, heat resistance, strength, and excellent conductivity.
This metal is added to aluminum materials to improve chemical resistance. Cathodes and anodes are made from it, and non-ferrous alloys are alloyed with it. Even coins in some countries are made with niobium content.
Refractory Tungsten Production Process
This material is classified as a rare metal. It is characterized by relatively small volumes of consumption and production, as well as low prevalence in the earth’s crust. None of the rare metals are obtained by recovery from raw materials. Initially, it is processed into a chemical compound. And any rare metal ore undergoes additional enrichment before processing.
There are three main stages for obtaining rare metal:
- Ore decomposition. The recovered metal is separated from the bulk of the processed raw materials. It concentrates in a precipitate or solution.
- Obtaining a pure chemical compound. Its isolation and purification.
- The metal is isolated from the resulting compound. This is how pure materials without impurities are obtained.
also several stages . The starting materials are scheelite and wolframite. Typically they contain from 0.2 to 2% tungsten.
- Ore beneficiation is carried out using electrostatic or magnetic separation, flotation, and gravity. As a result, a tungsten concentrate is obtained, which contains approximately 55–65% tungsten anhydride. The presence of impurities in them is also controlled: bismuth, antimony, copper, tin, arsenic, sulfur, phosphorus.
- Preparation of tungsten anhydride. It is the raw material for the production of metal tungsten or its carbide. To achieve this, a number of procedures are carried out, such as: leaching of cake and alloy, decomposition of concentrates, production of technical tungsten acid and others. As a result of these actions, a product should be obtained that will contain 99.9% tungsten trioxide.
- Obtaining powder. In powder form, pure metal can be obtained from anhydride. This is achieved by reduction with carbon or hydrogen. Carbon reduction is carried out less frequently because the anhydride is saturated with carbides and this leads to brittleness of the metal and poor processing. When obtaining powder, special methods are used that make it possible to control the shape and size of grains, granulometric and chemical compositions.
- Production of compact tungsten. Basically, it is in the form of ingots or bars and is a blank for the manufacture of semi-finished products: tape, rods, wire and others.
Rhenium and alloys based on it
Which metal is the most refractory after tungsten? This is rhenium. Its fusibility index is 3186 °C. It is superior in strength to both tungsten and molybdenum. Its plasticity is not too high. The demand for rhenium is very high, but production is difficult. As a result, it is the most expensive metal existing today.
Used for making:
- jet engines;
- thermocouples;
- filaments for spectrometers and other devices;
- as a catalyst in oil refining.
All areas of application are expensive, so it is used only in cases of extreme necessity, when there is no possibility of replacing it with anything else.
How it happens
Melting of all metals occurs approximately the same way - using external or internal heating. The first is carried out in a thermal furnace; for the second, resistive heating is used by passing an electric current or induction heating in a high-frequency electromagnetic field. Both options affect the metal approximately equally.
As the temperature increases, the amplitude of thermal vibrations of molecules also increases, and structural defects in the lattice appear, expressed in the growth of dislocations, atomic jumping and other disturbances. This is accompanied by the rupture of interatomic bonds and requires a certain amount of energy. At the same time, a quasi-liquid layer forms on the surface of the body. The period of lattice destruction and defect accumulation is called melting.
Tungsten carbides
Let's look at hard alloys in more detail. Refractory metal can form different carbides: semi-carbide and monocarbide. They are distinguished by their ability to dissolve refractory metals and interaction with various acids.
Tungsten is a metal having different carbides
Monocarbide is also inferior to polycarbide in stability and hardness. And the advantages of monocarbide include the ability to form crystals in molten tungsten, which makes it possible to use it in mineral ceramic products. Semi-carbide has greater resistance to temperatures, ease of incorporation into solid solutions of monocarbide with other metals (ferrum, cobalt), and increased wear resistance.