Purpose and principle of operation
What is a compressor? The official definition is as follows: a device designed to compress gases and pump them to consumers is called an air compressor. How does he work? The principle of operation of the device is quite simple: atmospheric air enters a mechanism that compresses it. For this, different methods can be used; they will be discussed below. The mechanism that compresses air determines the design and principles of operation of the compressor. For the equipment to operate effectively, it must be connected to an electrical network and an air network through which compressed air will be transmitted. The connection diagram for the electric motor is usually indicated in the operating instructions.
What are compressors used for?
There are two types of such machines: high and low pressure. The first ones are designed for pumping compressed air into special cylinders. The latter are called blowers. They are something between fans and high-pressure compressors.
Both of them belong to industrial equipment and are used to carry out the following work:
- Construction;
- Repair;
- Mine;
- When extracting oil and gas;
- When laying fiber optic lines.
Types of compressors
There are many offers on the industrial equipment market for the supply of these devices. It can be divided into those that are used in industry and those that are used in everyday life, for example, for inflating car tires. All these devices can operate from different types of drive. An electric air compressor 220 V, as the name implies, operates from an electric power unit with a voltage of 220 V. But, there are also devices that operate on a voltage of 380 V.
The diesel compressor is powered by an internal combustion engine running on diesel fuel. The use of such equipment is quite popular among builders; it is used when there is no possibility of connecting electrically driven installations. Installations running on diesel fuel ensure operation at remote construction sites.
Atmospheric air is supplied to the cylinder head in which the pistons are installed. The power plant, in turn, transmits torque to the shaft, which ensures the movement of the pistons in the cylinder. It is there that the air is compressed to the required parameters. After compression, it is sent to the plant's air system. Piston compressors are divided into oil and oil-free. The oil version differs in that for its effective operation, a special oil is poured into it, which reduces the friction force between the rubbing parts and components of the device. This increases its service life.
There are many ways to transfer torque from the engine to the actuator. In the manufacture of compressors, couplings or belt drives are most often used. The device on which the latter type is installed is called a belt compressor.
The listed types of equipment are used in almost all industries; they differ from each other in performance, size and a number of other parameters. But, of course, the main characteristic is the amount of pressure that the compressor can create.
Air compressors are distinguished by their operating principle; more on this below.
Piston units
Piston compressors are one of the most common types of this equipment. As noted above, air compression occurs under the action of pistons moving inside the liners. To meet the needs of industry, high-pressure piston compressors are used. They can be powered by either an internal combustion engine or an electric motor. An industrial high pressure compressor produces between 40 and 500 bar. Compressors of this type are characterized by high efficiency and a service life of up to 2000 hours. Piston compressors are produced in both stationary and mobile versions. To move them, a wheeled or tracked chassis is used.
This is a rather complex device; its design includes oil scraper rings, filters for purifying oil and air, control automation, and this means that to maintain this device in working condition, qualified personnel and special tools and devices are required.
Diaphragm compressor
The gas is compressed in such a device under the action of a membrane, which performs a reciprocating motion. The membrane is driven by a rod, which is fixed to the crankshaft.
The membrane plate is fixed to the working chamber and thus there is no need to use additional parts, for example, piston rings, sealing devices, etc.
A membrane type air compressor has the following parameters:
- tightness;
- resistance to corrosion;
- high level of compression;
- reliable design;
- safety in operation and ease of maintenance.
A membrane-type belt-driven compressor is distinguished by the fact that the working medium comes into contact only with the membrane and the internal cavities of the chamber. At the same time, it does not come into contact with the atmosphere. This device is used for pumping harmful and toxic substances.
Another advantage of the membrane product is that it does not need to be lubricated, which reduces the risk of contamination of the transported working environment.
Positive displacement compressors
A device in which the process of producing compressed air occurs by reducing its volume is called a positive displacement compressor. These include the following types of equipment:
- oil-free screw compressors;
- diesel piston compressors;
- household air compressors.
Screw compressors
The history of this equipment began in 1934. Screw compressors are distinguished by high reliability, small dimensions, and low metal consumption, which have led to high consumer demand for equipment of this class. The use of this equipment allows you to reduce electrical energy costs by up to 30%. Installations of this type are installed in mobile compressor stations, ships and other refrigeration units.
Screw rotors with cavities are used as a working body. They are installed in a housing that can be disassembled along several planes. It has holes and recesses for installation and bearings. In addition, air suction and discharge chambers are formed in the housing. Pumps of this type are distinguished by their performance.
These products can develop pressure from 8 to 13 atm, while the air flow can be from 220 to 12,400 liters per minute.
Quite often, one unit of such equipment can replace several units of compressors installed in production shops.
When installing and putting into commercial operation such compressors, it is advisable to install a device at the inlet to clean the air from excess moisture. Some manufacturers complete their products with such filters.
Vane rotary compressors
Compressors of this class operate on the same principle as piston ones, that is, on displacement. Energy transfer occurs during compression. During suction, the working medium enters the working chamber, and its volume decreases as the rotor moves. This compression leads to an increase in pressure and the escape of compressed air through the pipe.
Compressors of this type can produce pressures up to 0.3 MPa and are called blowers, and those that deliver higher pressures are called compressors.
Devices of this type have the following advantages:
A more stable, balanced stroke ensures the absence of reciprocating motion. The design of this equipment provides the possibility of direct connection to an electric power unit. The weight of a rotary compressor will be lower than a piston compressor with similar characteristics. The design does not provide for the use of valves. That is, the number of parts rubbing against each other decreases.
Dynamic compressors
Compressors in this group are divided into two types - centrifugal and axial. In the first, the air under the influence of centrifugal force is thrown to the outer part of the impeller. This creates a rarefied space on the suction side. Gas constantly enters the working chamber, after passing the wheel, the air is directed to the diffuser (flow rate damping device), where, in fact, its pressure increases.
In axial-type equipment, air moves along the rotor, and compression occurs as a result of changing the speed of its movement between the rotor blades and the guide device.
These compressors can be classified according to the following properties:
- Outlet pressure, those that provide pressure within 0.015 MPa are called fans or blowers.
- By the number of compression stages.
- In the direction of air movement. If it moves along the rotor axis, then it is centrifugal, if across, then it is axial. There are devices where air moves diagonally.
- By type of drive - it can be electric, steam or gas turbine.
Rotary compressors are used in aircraft engines. It is used to pump air into the combustion chamber.
Types of Air Compressors
- 12 volt air compressors are machines that require 12 volts of power to reduce the volume of air in a tank to increase pressure.
- Axial compressors have flow in the axial direction due to the tangential acceleration of air with blades attached to the rotors. This increases the kinetic energy of the air and dissipates it through the static blades, increasing its pressure.
- Centrifugal compressors force air with blades onto a rotating impeller. The rotating movement of the air causes an outgoing velocity from centrifugal force, and then the diffuser converts this outgoing velocity into pressure.
- Compressors are machines used to compress air to levels above atmospheric.
- Diaphragm compressors provide compression using a flexing diaphragm that moves back and forth within a closed chamber; the design is a reworking of the piston piston concept. The movement of the connecting rod under the diaphragm causes bending and only a short stroke is required to produce pressure effects similar to those of a reciprocating piston compressor.
- Double-acting compressors use both sides of the piston to compress air in both forward and reverse strokes.
- Ejector compressors use a high pressure jet. The flow drive is transmitted to low air pressure.
- Electric air compressors are machines that use electrical energy to compress air before releasing it in a high-energy form.
- Free piston compressors have an adjustable compression piston that moves along the length of a steel cylinder string. The guide piston and the compression piston collide during the return stroke because the compressed air pushes the compression piston away in the final stage.
- Gas-air compressors are gas-powered machines that reduce the volume of air to use the compressed air for energy.
- Industrial air compressors are mechanical devices used for industrial purposes that supply air at a pressure higher than atmospheric pressure.
- Labyrinth compressors are oil-free and operate without piston rings. A series of labyrinths creates a seal between the cylinder wall and the piston.
- Fluid ring compressors have only one moving part, the impeller shaft. The working fluid rotating in the housing forms a liquid ring seal, and air enters through the suction channel, moves between the impeller blades and is compressed before being released.
- Cam compressors use two mating cams on separate shafts that rotate in opposite directions to capture incoming air and force it against the housing. Vane compressors provide very high flows in pressure ranges between positive displacement compressors and other types of positive displacement units.
- Mini air compressors are machines that reduce the volume of air to create pressure in it and convert mechanical energy into pneumatic energy. The compressed air can then be used for various purposes; However, due to the limited size of mini air compressors, the power output is low at 250 pounds per square inch (PSI).
- Indirect displacement compressors rely on motion to transfer energy from the compressor rotor to the air. The initial acceleration of the air creates a negative (suction) pressure at the inlet, which draws in air.
- Oil-free air compressors provide air and energy to a variety of tools, equipment and manufacturing processes in industries that require clean air.
- Portable air compressors are portable systems that do not require an electrical outlet.
- Positive displacement compressors work by successively holding a volume of air and reducing it, thereby increasing the pressure. The amount of heat generated increases in proportion to the increase in pressure, which leads to a significant increase in the temperature of the air and the compressor itself.
- Reciprocating compressors move a piston to the top of a cylinder to create compression. They require water or air cooling.
- Rotary compressors reduce the volume of air by compressing it between interacting, counter-rotating components that force air into a reservoir.
- Screw compressors use two counter-rotating rotors that rotate synchronously. As air enters the sealed chamber, the rotors rotate, reducing the volume of trapped air and sending it compressed through the outlet at a preset pressure level.
- Swashplate compressors move pistons parallel to the crankshaft by means of a cam or plate mounted axially on the shaft and inclined towards it.
- Vane compressors have an eccentrically mounted rotor, which is the only moving part and rotates inside the stator. As the rotor rotates, centrifugal force pushes the vanes out of their slots to form compression cells, and this pumping action of the vanes sliding in and out moves air from the intake side of the compressor to the exhaust side.
Compressor performance
This term refers to the volume of gas that is injected in a certain unit of time. The unit of measurement for productivity is m3 per minute. This parameter can be specified either at the input or at the output, of course, these will be different numbers. The thing is that when pressure changes, volume changes. This characteristic indicates performance at a working environment temperature of 20 degrees Celsius.
Depending on the value of this characteristic, the following groups are distinguished: high productivity (over 100 cubic meters of air per minute), medium (up to 100 cubic meters of air per minute) and low productivity (10 cubic meters).
Dynamic devices have some advantages over piston devices. They are simple in design and operation. They have small overall and weight parameters. Smooth air supply and they do not require additional lubrication. Their installation does not require the manufacture of massive foundations. But, at the same time, their efficiency is somewhat lower than that of piston engines.
These compressors have found their application in many industries. For example, the chemical and oil and gas industries, metallurgy, mining and many other industries. One of the types of dynamic compressors, turbocompressors, is installed in gas pumping pipelines.
Over many years of operation of such equipment, many devices with different characteristics have been designed and put into operation, in particular, modern machines are capable of providing productivity up to 200 m3 per minute, with a wheel rotation speed of 250 revolutions per second. And all this with small overall and weight parameters.
Classification of compressors according to other parameters
In addition to classifying compressors according to the compression principle, it is customary to divide these units according to the following parameters:
- Type of drive. Compressors can work with both electric motors and internal combustion engines (ICE). Accordingly, the devices come with direct transmission (coaxial) and belt drive. As a rule, a direct drive compressor is a unit for domestic use. The coaxial compressor attracts consumers with an affordable price and is widely used in dachas, garages, etc., since the air pressure produced by the device does not exceed 0.8 MPa. If we compare a gasoline and diesel compressor, the latter is more reliable in operation. Also, diesel has a simpler design and is easy to maintain.
- Cooling system. The devices come with liquid and air cooling or without it at all.
- Terms of Use. The devices can be stationary, operating only indoors from the power supply, and mobile (portable), which can be operated outdoors and at low temperatures. For example, mobile compressors with an internal combustion engine are widely used in places where there is no centralized power supply.
- Final pressure. According to this parameter, devices are divided into four groups. Low pressure units (0.15-1.2 MPa) are used as part of installations for compressing gases (air). Medium pressure devices (1.2-10 MPa) are used for separation, transportation and liquefaction of gases in the oil refining, gas and chemical industries. High pressure (10-100 MPa) and ultra-high pressure (over 100 MPa) devices are used in gas synthesis plants.
- Performance. Indicated in units of volume for a certain period of time (m3/min). The performance of the unit directly depends on parameters such as shaft rotation speed, cylinder diameter, and piston stroke length. Based on productivity, it is customary to divide devices into 3 categories: low – up to 10 m3/min; medium – from 10 to 100 m3/min; large – over 100 m3/min.
In addition, compressors are divided depending on the area of application into general purpose units, petrochemical, chemical, energy, etc.
Features of oil-free appliances
These devices have found their application where it is necessary to ensure high requirements for air purity. They are installed in medical institutions, pharmaceutical and chemical industries. To be fair, it must be said that these devices are considered to be the most affordable devices in terms of their cost. These compressors are easy to operate and maintain. This suggests that there is no need for trained personnel, and no special requirements are imposed when installing them at the workplace.
But oil-free compressors have some disadvantages, such as excessive noise that occurs during operation. But, manufacturers were able to solve this problem by installing soundproof casings on these products.
When choosing an oil-free compressor, you need to pay attention to the power of the device, their performance and operating pressure parameters, which are indicated by the devices installed on the compressor. We must not forget about the volume of the receiver. As a rule, containers with a volume of 50 liters are installed in the compressor device.
Advantages of oil units
The most common method of reducing friction that occurs during the operation of various parts and assemblies is their lubrication. This allows you to reduce the load on the product as a whole, in particular on its key part - the engine.
To solve this problem, special compressor oils are used, which can be used in various operating conditions.
Compressors of this type are cheaper to manufacture. Therefore, the cost of such equipment is significantly cheaper than oil-free analogues. But they are more expensive to operate. This is due to the fact that during operation, along with the removal of air from the working area, oil is released. By the way, it must be replaced every 2,000–3,000 hours of operation.
Since microparticles of oil are present in compressed air, oil-collecting elements, such as filters, have to be installed in the system. After a certain amount of time, they also need to be replaced, and this complicates maintenance and requires additional costs for purchasing replacement filters.
However, despite the measures taken, it is not possible to completely clean the air passing through the oil compressor. For example, after air treatment on a screw device, its pollution is 3 mg per cubic meter. The purity of air after it has been processed by a piston compressor directly depends on the level of wear of its parts and components.
This has led to the fact that the use of oil compressors is prohibited in certain technological processes.
How to choose a compressor
Obviously, the choice of compressor depends on the intended purpose. No one will use a car compressor, for example, in a refrigerator or vice versa.
The main consumers of atmospheric injection machines are car enthusiasts, master builders, mechanics, and furniture makers. As practice has shown, screw and piston compressors are most suitable for their needs. Moreover, oil-free ones are used for small volumes of work - inflating tires, painting small body parts, etc., while more powerful ones are used for pneumatic tools - oil-based piston and screw compressors.
Piston injection machines appeared earlier than others and are still the most common.
The operating pressure of such units reaches 25–30 atmospheres, which other compressors cannot boast of. The main advantages are low cost, simplicity of design and ease of repair. In addition, the devices are insensitive to the composition of the air environment - dust, moisture and temperature changes have virtually no effect on the quality of work. The service life with proper operation and timely maintenance is very long. The disadvantages of piston compressors include the need to regularly replace parts that wear out quickly - piston compression rings, seals and valves, as well as a high level of noise pressure, which reaches 95 dB (this is comparable to the roar of a locomotive running on a railway). In industries that intensively use such compressors, special rooms are allocated to accommodate “noisy” equipment. Based on the listed features, piston machines are used in the following cases:
- high compressed air pressure is required;
- technological processes do not require high productivity;
- operation occurs in difficult conditions of increased dust or humidity.
Piston compressors are used to generate compressed air for construction tools, clean rooms from dust and remove small abrasive particles from structural elements
Screw compressors differ favorably from piston compressors in that there are no wear parts in the design. The screw block, which is the main working mechanism, is designed for a service life of 15–20 years without major repairs. The absence of reciprocating parts and valves makes screw compressors very reliable and durable. The dynamics of compressed air supply are less dependent on the speed of rotation of the drive shaft, while in a piston compressor the slowdown of the piston leads to pressure dips. Due to the fact that there are no pistons and connecting rods in the design, vibration and noise are reduced. Therefore, such units do not require a separate room for installation. In addition, the compressor emits a large amount of heat, which is generated during the compression of gases. It can be used to heat the workspace during the cold season. The cost of screw compressors is an order of magnitude higher than that of piston devices. This is due to more complex production. But such equipment pays for itself faster, since it is more productive and economical. The use of “screw guns” is justified in cases where large quantities of compressed air are needed in uninterrupted mode.
The main parameters that you should pay attention to when choosing a working tool:
- The pressure created by the compressor. One of the most important parameters by which one can judge the performance characteristics of a product. Pressure is measured in atmospheres (atm.) or bars. In order not to get confused in units of measurement, you need to know that one atmosphere is approximately equal to one bar. Knowing the maximum pressure value of the compressor, you can determine which tool it is suitable for. In practice, they always purchase a compressor with a reserve. If, for example, a pneumatic impact wrench is driven by an air pressure of 6–7 bar, it is recommended to choose a compressor that compresses air to 10 bar.
The impact wrench is driven by compressed air supplied from the compressor - Performance level. Expressed in the number of liters of air pumped per minute. You should pay attention to the fact that in piston machines there is the phenomenon of “air failure” - a decrease in productivity during operation associated with changes in the external air environment. Therefore, such a compressor is chosen with a performance margin of up to 20% of the nominal one.
- Power. A value indicating the operating potential of the equipment. In simple terms, power represents the speed at which a machine can handle a job. It is measured in watts and is displayed in the technical data sheet of the device. As in the first two cases, the calculated power value must include an error for the difference between the nominal and real value. Over time, due to wear of parts and engine wear, power decreases, which can lead to incompatibility with the working tool. Based on this, it is recommended to purchase compressors with a power exceeding the specified one by 20–25%.
- Receiver volume. Immediately after compression, the air enters a storage metal tank, which serves to stabilize the air supply. In technical terminology, it is called a receiver. The larger the volume of the receiver, the less pressure drops there will be during operation. But you should also take into account that the compressor will need more time to pump the required amount of air into the sealed container.
Depending on power and performance, compressors can be equipped with receivers with a volume of 25 to 250 liters - Rated operating voltage and current. In domestic conditions - where there is no three-phase current connection - single-phase equipment is used, designed for a voltage of 220 V and a current of 6 A. In domestic networks, the current frequency is 50 Hz. When purchasing an imported compressor, you need to make sure that it is compatible with these parameters. Otherwise, overheating and premature failure of the tool is possible.
- Weight. As a rule, it is directly related to the power and performance of the compressor. Household models, designed for home and garage use, weigh up to 5 kg. This compressor is more mobile, easy to move and transport. Professional models installed permanently weigh 20 kg or more.
- Dimensions. This indicator is directly related to the weight of the compressor. Ease of use depends on the size of the device. If you need to move frequently, it is advisable to choose a small compressor with a carrying handle. Powerful and heavy devices with large-volume receivers are installed on mobile platforms that roll on wheels.
- Noise pressure indicator. It is believed that a comfortable and healthy noise level is up to 70 dB. Many manufacturers, solving this problem, use additional noise-reducing and anti-vibration structures. Information about the noise level is reflected in the technical data sheet of the product.
Video: how to choose a compressor for your home and garage
Table: pneumatic tool parameters
| Pneumatic tool | Pressure (Bar) | Air flow (l/min) |
| Spray gun | 3–6 | 150–400 |
| Grinder | 6–7 | 180–450 |
| Bit | 6,5 | 220–390 |
| Impact wrench | 6–7 | 400–450 |
| Angle wrench | 6–7 | 85–250 |
| nail gun | 6–7 | 100–350 |
| Rivet gun | 6–7 | 100–350 |
| Drill | 6 | 110–280 |
| Scissors | 6,2 | 200 |
| Blow gun | 4 | 150–250 |
| Sandblasting gun | 8 | 250 |
| Tire inflation gun | 3 | 50 |
| Needle scale cleaner | 6–8 | 150–200 |
| Vacuum cleaner | 6 | 100–150 |
When purchasing a compressor, you should give preference to those manufacturers who enjoy well-deserved authority. Among them there may be both foreign and domestic companies. When making a decision, you should familiarize yourself with consumer ratings that are published online and read user reviews. Based on last year's sales results, the top five brands include Fubag, Remeza, Kronvuz, Fiac, and Kachok.
Video: how to choose a compressor for inflating car tires
Features of operation
The normal operation of the compressor primarily depends on the operation of all its components and parts. In particular, intake and exhaust valves. Inside the compressor, where air distribution occurs, a certain number of spools, distributors and valves are installed. The following types of valves are installed in compressors: poppet, plate, spindle, etc.
To ensure that the equipment does not reduce power indicators and does not consume excess power, the valves that are installed in the compressor must be ground in and must not allow air to pass through. When the valves wear out, they must be urgently replaced. Increased air flow can sooner or later lead to a reduction in the life of the equipment.
Delayed valve response leads to knocking noises; knocking indicates that the seat is wearing out. In addition, a knocking sound may indicate that the upper part of it is pinched in the housing.
The quiet operation of the compressor is a kind of indicator of the quality of the settings and, accordingly, the operation of the device as a whole.
Vane rotary compressors
The design of the vane-rotor unit consists of one rotor, stator and at least eight plates, the mass of which, and therefore the thickness, is limited. The following forces act on the plate during operation: centrifugal and friction/elasticity of the oil film.
Since the oil film normalizes and becomes uniform and sufficient only after several minutes of compressor operation, during starts and stops there is friction of the plates on the stator and, accordingly, increased wear and tear.
The greater the pressure such a block must pump, the greater the pressure difference in adjacent compression chambers, and the greater the centrifugal force must be to prevent the flow of compressed air from a chamber with a higher pressure to a chamber with a lower one. In turn, the greater the centrifugal force, the greater the friction force at the moments of starting and stopping and the thinner the oil film during operation - this is the main reason why this technology has become widespread in the vacuum field (that is, pressure up to 1 bar) and in the area of pressure injection up to 0.3-0.4 MPa.
Since the oil film between the plates and the stator is only a few microns thick, any dust, especially larger solid particles, act as an abrasive that scratches the stator and causes wear on the plates. This leads to bypasses of compressed air from one compression chamber to another and productivity drops noticeably.
Unlike small vacuum pumps, where vane-rotor technology is widely used, in compressors of high capacity and pressure above 0.5 MPa, over time it will be necessary to change the entire unit assembly, since replacing individual plates is effective only if the stator geometry is restored, and Such large stators cannot be restored (polished).
Manufacturers usually do not provide any data on the service life of the vane-rotor unit, since it very much depends on the air quality and the operating mode of the compressor. For gas compressors that pump gas practically non-stop all year round, the service life can actually reach more than 100 thousand hours because the oil film is uniform and sufficient all the time of operation without stopping.
And in industrial use, where the air intake is extremely uneven and the compressor is started and stopped dozens of times a day, most of the time there is no normal oil film inside the unit, which causes aggressive wear of the plates. In this case, the block resource is no more than 25 thousand hours.
Safety regulations
Compressor units of various operating principles and purposes are widely used on construction sites and in production. Compressors can be permanently installed on concrete foundations or mobile, that is, mounted on a chassis.
Regular use of compressor equipment is permissible subject to a number of conditions:
- The compressor must be equipped with automatic devices that prevent the permissible operating limit from being exceeded.
- There is a relief valve designed to quickly relieve excess pressure.
- This equipment must have filtration devices installed at the inlet and outlet, which ensure the purity of the air sent for processing to the compressor and create an obstacle to its entry into the room.
- The presence of installed pressure gauges provides control over the pressure parameters created by the compressor.
- An oil separating filter must be installed between the compressor unit and the receiver.
- In addition, air that contains toxic or harmful substances must not be supplied to the compressor stop.
Installed equipment must be subject to appropriate supervision and maintenance. It must be remembered that maintenance and routine maintenance must be carried out by trained personnel. The equipment that is under the supplier's warranty must be serviced by specialists from the appropriate service centers.
In particular, when washing compressor components and parts, only those liquids and compositions recommended by the manufacturer of this equipment should be used. Containers for storing compressed air must be equipped with safety valves, a drain valve, and a pressure gauge. In accordance with the requirements of the operational documentation, these tanks (receivers) must undergo routine maintenance and testing. Their results should be recorded in the maintenance log.
When organizing the operation of compressor and related equipment, it is necessary to use guidelines and other regulatory documents published by control bodies, for example, Rostechnadzor.
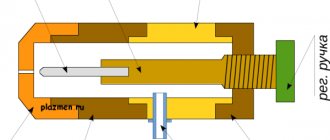
Compressors: design and principle of operation
An air compressor is a unit whose operation is based on compressing air and supplying it under a certain pressure to pneumatic equipment. When choosing compressor equipment to perform various types of work, it is necessary to take into account the design of the compressor, its design features, as well as the technical and operational characteristics of the installation.
The design features, operating principle and structure of the air compressor depend on the type of installation. Modern compressors have several classifications, the main of which is the difference between compressors according to the principle of operation. Today, manufacturers of compressor and pneumatic equipment offer a large number of these installations of various types, the most common of which are screw and piston installations .
Piston compressors
Screw compressors
All types of compressors have both common elements and differences in design. In addition, depending on the type of equipment, different materials can be used in the manufacture of certain components of compressors.
Design of screw compressors
In industrial sectors, the most common use is of screw air compressors, which are characterized by high technical characteristics. The design of a screw air compressor differs from similar installations in the presence of a screw unit, which includes two rotors with a leading and driven type. The screw block is the main working element of this equipment.
When this compressor operates, the air that passes through the filtration system and valve enters a block with screws, where air and oil are mixed. The use of oil is necessary to eliminate air bubbles and seal the space.
Next, the air-oil mixture is pumped by a screw block into the pneumatic system. At the next stage, the mixture enters the separator, where the air is separated from the oils and, through the radiator system, supplied to the receiver or to pneumatic equipment.
Since the block in which the screws are located is the main working element of the compressor, the principle of its operation must be considered separately. The teeth of the rotors - driving and driven - are in a meshed state. The body of the screw block and the open cavities of the rotors create a volume into which air enters when the screws rotate. The rotors rotate in opposite directions. In this case, the open cavities close, which leads to a decrease in the volume between them and an increase in discharge pressure.
Such a design of a screw compressor and its operating principle ensures high efficiency of the entire installation, uninterrupted supply of compressed air to pneumatic equipment and the possibility of intensive operation of this system for a long time.
The design of a piston compressor and its principle of operation
Another type of compressor systems widely used in everyday life and in small businesses is piston-type equipment. The main difference between this installation and screw and other types of equipment is the fairly simple design of the piston compressor and the principle of its operation.
The main elements of this installation can be divided into groups depending on the functions performed:
- cylinder group;
- piston group;
- movement mechanisms;
- control systems, which are elements that regulate the performance of equipment - pipelines, auxiliary valves;
- lubrication systems;
- cooling elements;
- parts for installing equipment.
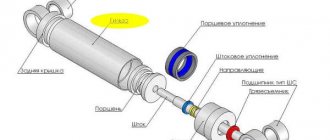
Structurally, a piston compressor is a housing made of cast iron, aluminum or other material and equipped with a cylinder, the location of which can be either vertical or horizontal. The main moving and working part of the compressor is the piston itself and two valves that perform suction and discharge functions.
The basis of the operation of this equipment is the movement of the piston - translational movements lead to the suction of air into the cylinder, and during the return action the air is compressed. This process leads to an increase in pressure force. At this moment, the suction valve closes, and the discharge valve supplies compressed air to the line. This cycle is repeated throughout the entire period of operation of the equipment, providing pneumatic tools with air under pressure at the required level. The design of a piston air compressor is distinguished by its comparative simplicity combined with high performance and performance characteristics.
Taking into account the design of piston and screw compressors, their design, technical and operational features, you can easily select the most suitable type of equipment in accordance with the requirements for them and for use with various pneumatic tools when carrying out both industrial and domestic work.
Criteria for choosing compressor equipment
What should a consumer consider when choosing an air compressor? Most importantly, he must understand for what purposes the purchased equipment will be used. It should be noted right away that there are separate industries, and technological operations can only be used with compressors operating without oil.
The key parameters of compressor equipment are:
- Air flow (performance).
- Operating pressure.
- Requirements for air purity.
As a rule, these parameters must be determined by process engineers who develop technological processes involving compressor equipment.
For example, air flow can be calculated according to the following scheme:
- Calculation of air quantity during continuous operation.
- Making adjustments to the obtained value taking into account the operating time of the equipment per shift or day.
When selecting equipment, it is necessary to take into account the growing number of compressed air consumers.
Compressor equipment control systems
To ensure that the air is under constant pressure in compressor systems, control equipment is installed. The simplest system consists of a pressure sensor and a simple adjustment system. It allows you to maintain constant pressure in the receiver. If the specified parameters are exceeded, the compressor is switched off, and after the pressure has dropped to a certain minimum, the automation is activated and turns on the compressor. Such, or almost such systems, are installed in almost all compressor installations. Their presence ensures safe operation of the equipment.
All about compressors
Compressors are in great demand in industry and construction. They are used in medicine and dentistry. In every household refrigerator and air conditioner, the compressor plays the role of the main driving mechanism. The production of compressor equipment is considered a separate industry that is rapidly developing, absorbing advances in electronics and new technologies. Knowledge about the device, operating rules and technical service will help you make the right choice when purchasing a compressor, as well as solve problems related to repairing a failed unit.
Household devices
To perform certain jobs that are performed at home or in the garage, household compressors are used. As a rule, these are small-sized electrically driven piston compressors. The power of this product is 2.2 kW. Such compressors are able to pump air up to 8 atm.
For the most part, they can easily provide a pressure of 10 atm. Receivers with a capacity of up to 100 liters are used to store compressed air.
As a rule, they are used when performing painting work, internal and external.
What is a compressor and how does it work
The name "compressor" comes from the Latin word compressio, which means compression. This is a device for creating increased gas pressure and supplying it in the desired direction. Depending on how the task is achieved, compressors are divided into groups. A distinctive feature of each type of these devices is the design solution of the process of compression and air supply. In general, all units are divided into two large categories - volumetric and dynamic. Each group, in turn, has its own ramifications.
The variety of compressor machines is due to their wide range of applications
Dynamic compressors are based on the principle of compressing gases through mechanical energy. A distinction is made between axial and centrifugal machines depending on the direction of air movement, as well as on the type of rotating wheel. One of the brightest representatives of this group is the turbocharger. Its design is based on the interaction of moving air with a stationary grille and rotating drive blades.
In dynamic compressors, gas is compressed due to mechanical energy supplied from a rotating shaft
Positive displacement compressors use the property of gases to compress when the size of the enclosed space in which it is placed changes. Reducing the dimensions of the working chamber leads to an increase in pressure. This group includes most household and industrial units; there are more than 10 different types:
- Piston. The most common type of injection machines, which are used to supply gas or steam under pressure. There are a great many design solutions, but the main feature of a piston pump is considered to be compression of the working medium due to a decrease in the volume inside the cylinder, produced by the reciprocating movement of the piston. Such compressors have found application in heavy engineering, chemical, textile and refrigeration industries. According to their design characteristics, piston devices are classified into vertical, horizontal, and angular. There are multi-stage piston compressor stations - when gas is compressed to high pressure, there is a danger of explosion or ignition of oil deposits that accumulate in the pipeline and the surface of the exhaust valves, so this procedure is carried out in several stages.
A piston compressor increases gas pressure by reducing its volume during the working stroke of the piston
A screw compressor pumps air under pressure due to the synchronous rotation of two shafts with screw blades
Rotary gear compressors can be designed with water or air cooling
A diaphragm compressor compresses air due to a flexible membrane that vibrates due to the mechanical action of the rod making reciprocating movements.
Industrial compression units use the principle of compressing air with water.
In a Roots blower, the work of moving and compressing air is done by a pair of rotors with helical blades.
In a scroll compressor, operating clearances are measured in fractions of a millimeter, so such devices require careful running-in
In a rolling-rotor compressor, the working cylinder is fixed and the piston rotates around it.
The creation of the scroll compressor dates back to 1905. The idea belongs to an engineer from France, Leon Croix. But introduction into industry turned out to be possible only in the middle of the 20th century, when the level of technology made a serious step in the field of materials processing. The design gained widespread use at the end of the century, when scroll compressors began to be used in climate control and refrigeration equipment. It turned out that the efficiency and level of pressure created by this type of units are superior to all other devices known at that time.