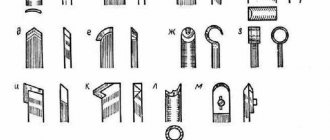
Types of cutters
There are several types of cutting tools. These include: cylindrical, end, disk, end and groove.
By type of purpose:
- angular;
- shaped;
- keyed;
- to provide T-type grooves.
On the surface:
- plastic;
- tree;
- metal;
- glass;
- others.
Sharpening is difficult, since the length of the cutting base is large. Therefore, specialized tools are used. And in some cases, grinding is carried out manually, but the worker performing this work must have experience. An employee who does not have the skills may allow defects and defects to appear on the teeth: cracks, burrs or cavities, due to which the tool will need to be ground again, and this will lead to a reduction in size.
Types of equipment used for fixing tools
The equipment used to fasten the tool is divided into 2 types:
The end equipment is attached using a collet and a chuck, and the attachment equipment is used by installing it on a spindle using a special mandrel. To fasten the tool, 2 types of mandrels are produced:
Center mandrels are produced with a conical shank, which has dimensions corresponding to the hole in the spindle, and are produced in 2 types 7:24 and Morse taper. When using this type of mandrel, it is allowed to install several cutting tools secured with special rings. When using a cylindrical end mill, a chuck with a collet is required. Typically, the equipment includes 7-11 collets, allowing you to select the required size for reliable fixation.
Collet chuck with collets
Milling cutter material
The following materials are used for the manufacture of technological equipment:
- hard alloys;
- high-speed steel;
- metal alloys of increased hardness;
- metal ceramics;
- diamonds.
For direct cutting of metal, the edges of the cutting tool are made of:
- cardan wire;
- diamonds;
- hard alloy compounds;
- ceramic coating.
The difference in technological equipment is determined by its appearance.
Cutter tooth geometry
Productivity depends on proper sharpening of the teeth. Work surface configurations are used to solve even the most complex problems.
The design of a spiral cutter is carried out with a large and small inclination of the teeth at a given angle. The purpose of this type of tool is to carry out roughing and finishing operations, including variable steps.
The rake angle is the angle formed between the flat end and the flute edge of a standard cutter.
Angle value:
- small no more than 35;
- large 35 and above.
An excellent option for initial and finishing machining is the tooth angle of 38. Rectangular tools have the maximum value.
A tool with a variable pitch is in demand; the pitch of the spiral is measured along the length.
Using Accessories
To fix cylindrical parts, a three-jaw chuck and special centers are used, which, with the help of clamps and steady rests, carry out fixation, as well as the use of dividing heads. These devices are used to process parts at a given angle during rotation. The dividing head consists of the following elements:
A three-jaw chuck is attached to the spindle, designed to fix the workpiece; the other end rests against the headstock. The block can rotate and lock at the required angle. When processing a long workpiece, steady rests are used for fixation.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Cleaning agent for cutters, drills, etc. - https://rubankov.ru/shop/UID_6849.html
Diamond sharpening stones DMT - https://rubankov.ru/shop/UID_6139.html
admin
Application area
There are various types of tools to perform technological operations. Which cutter to use in this or that case, for this you need to take into account what material needs to be processed.
Metal cutters
Common types include:
- Disk. Elements for cutting material are located on one or both sides at the same time. Used for cutting grooves, sampling, trimming and chamfering.
- End Designed for turning stepped and flat bases.
- Cylindrical. Available with helical and straight teeth.
- Angular. Used for cutting chip flutes in technological equipment.
- End. They are used for making ledges, contour recesses and grooves.
- Shaped. Designed for processing shaped surfaces.
- Worm-shaped. Processing is carried out using the rolling method - touching the workpiece with a tool at one point.
Wood cutters
The following tools are used for processing wooden structures:
- End. Outwardly they resemble a drill, but the conical part is missing.
- Edges. Used for cutting edges and various recess configurations. Tools for manual milling are structurally equipped with a bearing to regulate the depth of processing.
- Grooved. Used for cutting grooves.
- Copying. Arrangement of the milling head in the form of an arc.
Cutters for plastic
When processing plastic products, the following tools are used:
- End For processing large bases.
- Shaped. Used for cutting complex profiles.
- End. Used to produce pockets or grooves.
- For engraving. With its help, you can apply patterns or logos to the base.
Glass cutters
Diamond cutters are used to prepare glass products. Designed for creating edges and contours using manual or automatic equipment.
Types of Tools Used
Various types of tools are used in industrial enterprises:
- Cylindrical - for processing workpieces using machines equipped with a horizontal spindle.
- Face - for milling workpieces on machines with a vertical spindle.
- End - for driving ledges, recesses, contours (curvilinear). Used on installations for vertical milling.
- Disc - for driving grooves and grooves on horizontal machines.
- Keyed – for making grooves on machines with a vertical spindle.
- Angular – for milling planes (inclined), grooves, bevels.
- Shaped – when processing shaped surfaces.
Rice. 2 Set of hobs.
To process workpieces, equipment is used that is designed for the following work:
Milling cutters with appropriate equipment are usually produced as sets with mounting dimensions for fasteners of different diameters. In order for a cutter to be used for a long period, it must always be sharpened, and when carrying out a working operation, a temperature regime is required that does not allow overheating, which reduces their strength characteristics.
Methods for sharpening cutters
Sharpening cutters is difficult, since it is necessary to process curved and long surfaces. It is also necessary to ensure that the abrasive moves with precision along the edge.
Using the machine
The sharpening technology is carried out in stages:
- Fastening the cutter in a given position.
- Bring the surface to be treated to the abrasive wheel until there is no sparking.
- Removing a metal layer with a thickness of 25 to 50 microns.
- Sharpen each tooth separately. The work begins by positioning it in the groove formed by the tooth, and the needle should touch the surface of the instrument.
- Turn on the sharpening machine and, sequentially retracting the cutter, perform the operation.
To perform the work efficiently, each edge of the cutting base should be sharpened equally, that is, the movements should be uniform.
Using sharpening wheels
The choice of wheels depends on the material from which the tools are made. What kind of circles are there:
- Normal electrocorundum and white electrocorundum. Provides optimal sharpening of tools for metal or wood.
- Elborovye. Using wheels of this material you can sharpen high-speed steel products.
- Green and diamond silicon carbide are used for sharpening carbide products
Features of sharpening various types of cutters
For metalworking, cutters made of tool or high-speed steel are used. The teeth can be made of carbide materials and secured by soldering. Processing such materials is complex, so sharpening of cutters for metal, especially those with complex cutter shapes, is carried out using specialized equipment. To operate effectively, the machine must rotate and translate the item being sharpened relative to the abrasive wheel and allow the angle of their contact to be changed.
Sharpening of wood cutters (relevant for end cutters) can be done manually with a block or on a regular sharpener at low speeds. The main task is to ensure uniform surface treatment and maintain the original angle. It may not work out at first, but with experience you can achieve good results.
Sharpening spiral cutters is one of the most complex operations and is performed with a cup grinding wheel on a sharpening machine. It is carried out along the back surface of the teeth; a stop is used to ensure a stable angle, otherwise the geometry of the cuts will change and there will be strong runout. The circle is set at a slight angle, the depth of the layer for removal is about 20-40 microns, for cleanliness the pass is carried out 2 times. Sharpening end mills for metal is carried out in a similar way, but an operation with end teeth is added, each of which is set strictly horizontally, the circle moves along at a given angle, while it is important to maintain uniformity of operations for all cutters. Sharpening of hob cutters for metal is carried out depending on the shape of the teeth: for those sharpened along the back, for backed ones at the front.
The service life of cutting tools and the quality of processed surfaces directly depend on the timeliness of sharpening. When working with a dull tool, there is not only an increase in the time required to perform operations, but also a violation of the temperature regime, which in turn leads to deformation of the material being processed and the cutter itself. The process is growing and there may come a time when restoration becomes impossible, and the purchase of new ones will lead to financial costs and possible downtime. The costs of additional sharpening equipment with the active use of a large number of cutters will quickly pay off.
Specifications
When choosing machine equipment, you should pay attention to the technical indicators:
- Voltage is 220 V, if the power is high, then the power is supplied from 380 V.
- Consumer power 200 -5000 W.
- Spindle rotation without load – 900 -3000 rpm.
- Accuracy is determined depending on the design of the device.
- At what speed is the abrasive supplied?
- From the type of drive: electric and mechanical.
- Sharpening angle.
- Availability of water baths for cooling.
- Equipped with a ventilation device.
- Characteristics of noise level.
- Protective cover against rotating elements.
Machine tools can be floor-mounted or table-top.
Manual sharpening of end mortises designed for processing tough materials
To sharpen an end mill designed for processing tough materials (such as wood), you will need the following tools, equipment and materials.
- Table or workbench.
- Diamond beam.
- Soap solution.
- Solvent.
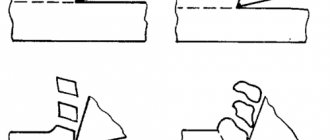
The end mill is sharpened according to the following scheme.
- Soak the diamond bar in soapy water and secure it to the edge of the table.
- Remove the guide bearing (if equipped) from the cutter.
- Clean the cutter with solvent.
- Sharpen all cutters.
Image No. 3: cutter sharpening diagram
Please note the following features.
- Before sharpening, be sure to make sure that the diamond stone has the correct shape.
- To achieve uniform sharpening of the cutters, make the same number of movements with approximately the same pressure.
- If you don't have a diamond wheel, you can use sandpaper to sharpen it. Glue it to a solid piece of wood or strip of steel.
Advantages and disadvantages of application
Advantages of using the equipment:
- High torque, which speeds up the processing process.
- Achieving the specified accuracy of processed corners.
- Quality improves.
- It is not necessary to be highly qualified, since the process is automated.
List of disadvantages:
- Consumes a lot of energy.
- High price.
- Carrying out all types of maintenance.
- Selecting a workstation for installation.
The process of sharpening cutters on a machine
Sharpening a cutting tool requires special precision so that the geometric dimensions and properties are restored. A professionally performed operation helps to increase the durability of the metal and reduce tooth wear.
The machine equipment set includes two clamping chucks, one for a three-flute tool, and the second for four and two. No installation error.
Sharpening on a ribbon
Select one of the cup sockets and a collet that matches the size.
Execution process:
- Insert a collet into the chuck and tighten it with a nut, but there is no need to tighten the latter too much.
- Set the length of the ribbon to be processed. The distance is adjusted by unscrewing screws. By moving the bottom of the socket, you should set the desired length, after which fix it with screw connections.
- Install the tool into the chuck through the top, specifying the angle and diameter. Secure the cartridge in the glass with the tool line aligned in relation to the sharpening element. Fastening is done to the pin using grooves.
- Turn on the equipment and ensure the supply of the processed element to the sharpening wheel. By means of regulators, you can reduce or increase the removal of the metal surface.
Sharpening the end cutter
You need to use another socket on the machine tool.
Work process:
- Set the settings on the socket; they depend on the hardness of the material. If the metal is hard, then the socket is larger.
- Turn on the machine, insert the chuck and process the element until the noise stops.
- In another socket, ensure sharpening of the tool from the end.
- Treat the back wall of the tool by inserting the chuck into the socket of the machine equipment.
Features of operation
The service life of a tool largely depends on the quality of cooling. For working with parts made of structural and alloy steels, it is recommended to use emulsols of type ET 1, with a concentration of 5 to 10%. For more durable materials, heat-resistant and stainless steels, oil-based lubricating fluids or emulsol ET 2 with a concentration of 10 to 15 are recommended %.
All processing parameters such as speed, width and depth must correspond to the tool material, its hardness and diameter. To do this, you must use technical literature and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Thus, to process parts made of steel with a hardness of HRC 47, the cutting speed should be in the range of 25 - 35 m/min. for tools with a diameter of 3 to 6 mm. When using the same tool for processing heat-resistant steels, the speed must be reduced to 10 - 15 m/min.
Sharpening end mills
Completing of the work:
- Sharpening of this type of cutter is done using a diamond stone, which is installed on the edge of the tabletop. If the tool has a large recess, it can be installed along the tabletop.
- When sharpening, the edge will become sharp and the diameter will decrease.
If the tool is equipped with a bearing, it must be dismantled. Clean the surface with a special solvent.
Sharpening cylindrical point cutters
Sharpening is done using a cup wheel with a specified clearance angle. At the centers of the sharpening machine, the cutter is placed on a mandrel. When the axes of the circle are located and the tool is located in the same plane - horizontally, then a back angle at the tooth will not form, for this purpose the location is determined - below the axis. When sharpening, the position of the tooth must be fixed with a stop.
Equipment for fixing the workpiece
To carry out the milling process, it is necessary to fix the workpiece, for which the following are used:
Read also: How to measure a battery with a multimeter
Round rotary tables are used for milling operations on workpieces with a curved surface. This type of table has a wide range of offsets:
- rotation;
- changing the angle of the table plane;
- Possibility of processing products in a vertical position.
Clamps or clamps allow you to fix products using special elements, which in turn are attached to the table using bolts and nuts. To fix small-sized workpieces, a simple vice with a rotating mechanism is used.
Finishing of cutters made of carbide material
The material is sharpened with a grinding wheel, and then microcracks may form on the base. As work is carried out, the formations increase in size, which leads to chipping of the teeth. The purpose of finishing is to remove the damaged layer. This is the primary task, the second is to improve the surface cleanliness of the working edge, the third is to give the appropriate geometric parameters.
How the finishing is carried out:
- Cast iron discs installed on machine tools. The optimal result will be when sharpening at a speed of 1 to 1.5 m/sec.
- Manually, providing light pressure on the cast iron whetstone.
Boron carbide paste is used with a grain size ranging from 170 to 230.
When carrying out finishing work manually, it is necessary to control the correct location of the touchstone in relation to the working edge, and ensure the following technological operations:
- Finish the surface: back and front.
- To form chamfers: at an angle of 450, the plane of the touchstone is brought to the leading edge, and then, using gentle pressure from the touchstone, a series of passes are made along the working edge.
- Each individual knife takes 2-3 seconds.
The strongest abrasive agent is boron carbide, with its help it is easy to remove holes on worn teeth without removing the tool from the machine.
Tool sharpening
Sharpening is carried out to restore cutting ability, with operations performed contour-wise and separately.
Cutters received for sharpening are usually pre-ground on a cylindrical surface using a cylindrical grinding machine to eliminate damage, followed by further sharpening of the back or front of the teeth.
End mills with pointed teeth are sharpened along the back surface with a special disk- or cup-shaped wheel. To do this, the circle is installed with respect to the axis at an angle of 89°, which makes it possible to achieve the required contact between the contacting surfaces. When sharpening the back surfaces of end mills, 2 main methods are used:
When using the multi-element method, the cutting edges are sharpened separately. First, the main surfaces of all teeth are sharpened, then the auxiliary and transitional ones. With the contour method, sharpening is performed sequentially on each tooth in one operation. A single-turn sharpening method is also used, when the cutting edges are processed in one operation. All teeth are sharpened in one revolution and the allowance is removed using a grinding operation.
Work quality control
When carrying out quality control after work, the following are checked:
- geometry of cutting edges;
- beating;
- cleanliness class.
For this, specialized devices are used:
- a protractor made with a number of angles equal to the number of teeth;
- sector for moving the arc and fixed with a screw in the desired position;
- sector equipped with a degree scale;
- indicator for monitoring tooth runout directly in the center being processed.