A thrifty owner dreams of cheap energy resources, efficient waste disposal and obtaining fertilizers. A DIY home biogas plant is an inexpensive way to make your dream come true.
Self-assembly of such equipment will cost a reasonable amount of money, and the gas produced will be a good help in the household: it can be used for cooking, heating the house and other needs.
Let's try to understand the specifics of this equipment, its advantages and disadvantages. And also whether it is possible to build a biogas plant yourself and whether it will be effective.
Specifics of biogas production
Biogas is formed as a result of fermentation of a biological substrate. It is decomposed by hydrolytic, acid- and methane-forming bacteria. The mixture of gases produced by bacteria is flammable, because contains a large percentage of methane.
Its properties are practically no different from natural gas, which is used for industrial and domestic needs.
If desired, every home owner can purchase an industrial-made biogas plant, but it is expensive, and the investment pays off within 7-10 years. Therefore, it makes sense to make an effort and make a bioreactor with your own hands
Biogas is an environmentally friendly fuel, and the technology for its production does not have much impact on the environment. Moreover, waste products that need to be disposed of are used as raw materials for biogas.
They are placed in a bioreactor, where processing occurs:
- the biomass is exposed to bacteria for some time. The fermentation period depends on the volume of raw materials;
- As a result of the activity of anaerobic bacteria, a flammable mixture of gases is released, which includes methane (60%), carbon dioxide (35%) and some other gases (5%). Fermentation also releases potentially dangerous hydrogen sulfide in small quantities. It is poisonous, so it is highly undesirable for people to be exposed to it;
- the mixture of gases from the bioreactor is purified and supplied to a gas tank, where it is stored until it is used for its intended purpose;
- gas from a gas tank can be used in the same way as natural gas. It goes to household appliances - gas stoves, heating boilers, etc.;
- Decomposed biomass must be regularly removed from the fermenter. This is additional labor, but the effort pays off. After fermentation, the raw material turns into high-quality fertilizer, which is used in fields and vegetable gardens.
A biogas plant is beneficial for the owner of a private house only if he has constant access to waste from livestock farms. On average, from 1 cubic meter. You can get 70-80 cubic meters of substrate. biogas, but gas production is uneven and depends on many factors, including biomass temperatures. This complicates calculations.
Biogas plants are ideal for farms. Animal waste can provide enough gas to fully heat residential premises and outbuildings
In order for the gas production process to be stable and continuous, it is best to build several biogas plants, and add the substrate to the fermenters with a time difference. Such installations operate in parallel, and raw materials are loaded into them sequentially.
This guarantees a constant production of gas, so that it can be continuously supplied to household appliances.
Ideally, the bioreactor should be heated. Every 10 degrees of heat increases gas production by half. Although heating installation requires investment, it pays off in greater design efficiency
Homemade biogas equipment, assembled from scrap materials, is much cheaper than industrial production plants. Its efficiency is lower, but it is well worth the investment. If you have access to manure and the desire to put in your own effort to assemble and maintain the structure, this is very profitable.
General principles
Biogas is a product that is obtained from the decomposition of organic substances. During the process of rotting/fermentation, gases are released, collecting which you can meet the needs of your own household. The equipment in which this process occurs is called a “biogas plant.”
In some cases, the gas output is excessive, then it is stored in gas tanks for use during periods of insufficient quantity. If the process is properly organized, there may be too much gas, then the excess can be sold. Fermented leftovers are another source of income. This is a highly effective and safe fertilizer - during the fermentation process, most microorganisms die, plant seeds lose their viability, and parasite eggs become unviable. Exporting such fertilizers to the fields has a positive effect on crop yields.
Conditions for gas production
The process of biogas formation occurs due to the vital activity of various kinds of bacteria that are contained in the waste itself. But in order for them to actively “work”, they need to create certain conditions: humidity and temperature. To create them, a biogas plant is being built. This is a complex of devices, the basis of which is a bioreactor, in which waste decomposition occurs, which is accompanied by gas formation.
Organization of a cycle for processing manure and plant waste into biogas
There are three modes for processing manure into biogas:
- Psychophilic mode. The temperature in the biogas plant is from +5°C to +20°C. Under such conditions, the decomposition process is slow, much gas is formed, and its quality is low.
- Mesophilic. The unit enters this mode at temperatures from +30°C to +40°C. In this case, mesophilic bacteria actively reproduce. In this case, more gas is formed, the processing process takes less time - from 10 to 20 days.
- Thermophilic. These bacteria multiply at temperatures from +50°C. The process goes the fastest (3-5 days), the gas output is the largest (under ideal conditions, with 1 kg of delivery you can get up to 4.5 liters of gas). Most reference tables for gas yield from processing are given specifically for this mode, so when using other modes it is worth making a smaller adjustment.
The most difficult thing to implement in biogas plants is the thermophilic mode. This requires high-quality thermal insulation of the biogas plant, heating and a temperature control system. But at the output we get the maximum amount of biogas. Another feature of thermophilic processing is the impossibility of additional loading. The remaining two modes - psychophilic and mesophilic - allow you to add a fresh portion of prepared raw materials daily. But, in the thermophilic mode, the short processing time makes it possible to divide the bioreactor into zones in which their share of raw materials will be processed with different loading times.
Advantages and disadvantages of the system
Biogas plants have many advantages, but there are also a lot of disadvantages, so before starting design and construction you should weigh everything:
- Recycling. Thanks to a biogas plant, you can get the maximum benefit from waste that would otherwise have to be disposed of. This disposal is less hazardous to the environment than landfilling.
- Renewability of raw materials. Biomass is not coal or natural gas, the extraction of which depletes resources. When farming, raw materials appear constantly.
- Relatively small amount of CO2. When gas is produced, the environment is not polluted, but when it is used, a small amount of carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere. It is not dangerous and is not capable of critically changing the environment, because... it is absorbed by plants during growth.
- Moderate sulfur release. When biogas is burned, a small amount of sulfur is released into the atmosphere. This is a negative phenomenon, but its scale can be seen in comparison: when burning natural gas, environmental pollution with sulfur oxides is much greater.
- Stable work. Biogas production is more stable than solar panels or wind turbines. While solar and wind energy cannot be controlled, biogas plants depend on human activity.
- Multiple settings can be used. Gas always carries risks. To reduce potential damage in the event of an accident, several biogas plants can be dispersed throughout the site. If a system of several fermenters is properly designed and assembled, it will operate more stable than a single large bioreactor.
- Benefits for agriculture. Some types of plants are planted to obtain biomass. You can choose ones that improve the condition of the soil. For example, sorghum reduces soil erosion and improves its quality.
Biogas also has disadvantages. Although it is a relatively clean fuel, it still pollutes the atmosphere. There may also be problems with the supply of plant biomass.
Irresponsible plant owners often harvest it in such a way that they deplete the land and upset the ecological balance.
Biofuel efficiency
Biogas from litter and manure is colorless and odorless. It provides the same amount of heat as natural gas. One cubic meter of biogas provides the same amount of energy as 1.5 kg of coal.
Most often, farms do not dispose of waste from livestock, but store it in one area. As a result, methane is released into the atmosphere, and manure loses its properties as a fertilizer. Timely processed waste will bring much more benefits to the farm.
It is easy to calculate the efficiency of manure disposal in this way. The average cow produces 30-40 kg of manure per day. This mass produces 1.5 cubic meters of gas. From this amount, 3 kW/h of electricity is generated.
Calculation of installation profitability
Cow dung is usually used as a raw material for biogas production. One adult cow can produce enough to provide 1.5 cubic meters. fuel; pig – 0.2 cubic meters; chicken or rabbit (depending on body weight) – 0.01-0.02 cubic meters. To understand whether this is a lot or a little, you can compare it with more familiar types of resources.
Image gallery
Photo from
Construction of a bioreactor made from an insulated plastic container
Convenient transport for transporting substrate
Compact plant for industrial production
Biogas plant on a dairy farm
1 cubic meter biogas provides the same amount of thermal energy as:
- firewood – 3.5 kg;
- coal – 1-2 kg;
- electricity – 9-10 kW/h.
If you know the approximate weight of agricultural waste that will be available over the coming years and the amount of energy required, you can calculate the profitability of a biogas plant.
One of the main disadvantages of biogas production is the smell. The ability to use small compost heaps is a big plus, but you will have to endure the inconvenience and carefully control the process so as not to provoke the spread of pathogens
To put it into the bioreactor, a substrate is prepared, which includes several components in the following proportions:
- manure (best cow or pork) – 1.5 t;
- organic waste (this can be rotten leaves or other components of plant origin) – 3.5 t;
- water heated to 35 degrees (the amount of warm water is calculated so that its mass is 65-75% of the total amount of organic matter).
The calculation of the substrate was made for one laying for six months, based on moderate gas consumption. After about 10-15 days, the fermentation process will give the first results: gas will appear in small quantities and begin to fill the storage. After 30 days, you can expect full fuel production.
Equipment for the production of biogas is not yet particularly widespread in our country. This is largely due to poor awareness of people about the advantages and features of biogas systems. In China and India, many small farms are equipped with makeshift plants to produce additional clean fuel
If the installation is working correctly, the volume of biogas will gradually increase until the substrate rots. The performance of the structure directly depends on the rate of biomass fermentation, which in turn is related to the temperature and humidity of the substrate.
What can be recycled
A biogas plant is essentially omnivorous - any organic matter can be processed. Any manure and urine, plant residues are suitable. Detergents, antibiotics, and chemicals negatively affect the process. It is advisable to minimize their intake, as they kill the flora that processes them.
How much biogas can be obtained from various wastes?
Cattle manure is considered ideal, since it contains large quantities of microorganisms. If there are no cows on the farm, when loading the bioreactor, it is advisable to add some of the manure to populate the substrate with the required microflora. Plant residues are pre-crushed and diluted with water. Plant materials and excrement are mixed in a bioreactor. This “filling” takes longer to process, but at the end, under the correct mode, we have the highest product yield.
Instructions for self-construction
If you have no experience in assembling complex systems, it makes sense to select online or develop the simplest drawing of a biogas plant for a private home.
The simpler the design, the more reliable and durable it is. Later, when you develop skills in building and handling the system, you can redo the equipment or install an additional installation.
Expensive industrial designs include systems for biomass mixing, automatic heating, gas purification, etc. Household equipment is not that complicated. It is better to assemble a simple installation, and then add elements that are needed
When calculating the volume of the fermenter, you should focus on 5 cubic meters. This installation allows you to obtain the amount of gas necessary to heat a private house with an area of 50 square meters, if a gas boiler or stove is used as a heat source.
This is an average figure, because The caloric content of biogas is usually not higher than 6000 kcal/m3.
In order for the fermentation process to proceed more or less stably, it is necessary to achieve the correct temperature conditions. To do this, the bioreactor is installed in an earthen pit or reliable thermal insulation is thought out in advance. Constant heating of the substrate can be ensured by placing a water heating pipe under the base of the fermenter
The construction of a biogas plant can be divided into several stages.
Stage 1 – preparing the pit for the bioreactor
Almost the entire biogas plant is underground, so a lot depends on how the pit was dug and finished. There are several options for strengthening the walls and sealing the pit - plastic, concrete, polymer rings.
The optimal solution is to purchase ready-made polymer rings with a solid bottom. They will cost more than available materials, but no additional sealing will be required. Polymers are sensitive to mechanical loads, but are not afraid of moisture and chemically aggressive substances. They cannot be repaired, but if necessary they can be easily replaced.
The intensity of fermentation of the substrate and the release of gas depend on the preparation of the walls and bottom of the bioreactor, so the pit is carefully strengthened, insulated and sealed. This is the most difficult and time-consuming stage of work
Stage 2 – arrangement of gas drainage
Purchasing and installing special mixers for biogas plants is an expensive proposition. The system can be made cheaper by installing gas drainage. It consists of vertically installed polymer sewer pipes with many holes made in them.
When calculating the length of drainage pipes, you should focus on the planned filling depth of the bioreactor. The tops of the pipes must be above this level.
For gas drainage, you can choose metal or polymer pipes. The former are stronger, and the latter are more resistant to chemical influences. It is better to give preference to polymers, because metal will quickly rust and rot
You can immediately load the substrate into the finished bioreactor. It is covered with a film so that the gas released during the fermentation process is under slight pressure. When the dome is ready, this will ensure a normal supply of biomethane through the outlet pipe.
Stage 3 – installation of the dome and pipes
The final stage of assembling the simplest biogas plant is the installation of the dome top part. At the highest point of the dome, a gas exhaust pipe is installed and extended to a gas holder, which is indispensable.
The bioreactor container is closed with a tight lid. To prevent biomethane from mixing with air, a water seal is installed. It also serves for gas purification. A release valve must be provided that will operate if the pressure in the fermenter is too high.
Read more about how to make biogas from manure in this material.
The free space of the bioreactor to some extent serves as a gas storage facility, but this is not enough for the safe operation of the installation. Gas must be consumed constantly, otherwise an explosion from excess pressure under the dome is possible
Insulation layer
After manufacturing the bioreactor, it can be immediately filled with raw materials. The biomass must be covered with film. This is necessary to ensure low gas pressure during the fermentation process.
- Solar collectors for home heating: advantages, disadvantages, myths, truth and reviews from owners (130 photos + video)
- Wind power plants for home - pros, cons and review of the best modern models (105 photos)
- How to make a 220V wind generator with your own hands: a step-by-step description of making homemade wind turbines (diagrams, projects, photos and videos)
Once the dome is made, this ensures that biogas flows efficiently through the system.
Methods for heating a bioreactor
Microorganisms that process the substrate are constantly present in the biomass, but for their intensive reproduction they need a temperature of 38 degrees or higher.
For heating during cold periods, you can use a coil connected to the home heating system or electric heaters. The first method is more economical, so it is used more often.
The biogas plant does not have to be buried in the ground; there are other options for arrangement. An example of the operation of a system assembled from barrels is shown in the video below.
The easiest way to arrange heating from below is to lay a pipe from the heating system, but the efficiency of such a heat exchanger is relatively low. It is better to arrange external heating, ideally steam, so that the biomass does not overheat
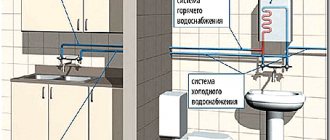
Gas removal problem
When designing bioreactors for producing biogas with your own hands, it is necessary to think about the issue of fuel removal. Taking into account the ability of the gas mixture to accumulate under the lid, the outlet is made in the upper part of the reactor, taking care to ensure its tightness after installing the pipeline. To maintain the concentration of fuel and prevent its mixing with air, the discharge is carried out through a hydraulic seal, displacing air masses from the system.
In case of intense gas formation, in order to prevent the container from rupturing, the design of the lid is made quite light. This allows it to function as a valve to release excess gas mixture. To ensure that the lid is tightly closed at a normal level of pressure, and valuable fuel does not leak through the cracks, it is reinforced with an ordinary weight. Before connecting the reactor to the heating pipeline system, the recommended amount of raw material should be loaded into it and its processing should be monitored, monitoring the pressure parameters and the volume of the released gas mixture.
For farming
If a farm or other small enterprise has an average amount of organic waste (sawmill, greenhouse, poultry farm, etc.), it becomes possible to install a larger installation that allows it to meet its own needs for thermal and electrical energy. In this case, the fuel production process is similar to the process when used privately, the only difference is in the power of the units and, accordingly, the volume of processed raw materials.
Structurally, it might look like this: