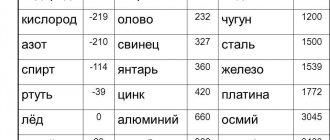
Where can I get lead at home for scrapping? Main Sources of Lead Scrap Metal |
Iron ore is difficult to mine, it is easier for enterprises to find secondary raw materials rather than use natural resources, so they think about where to get lead. You can help - this heavy non-ferrous metal is extracted at home. offers popular options. Choose a method that is effective in your opinion. We have established round-the-clock removal of lead scrap of various forms: seal, plate, cable protective sheath, production residues.
Lead prices in Moscow per kg
In order to know approximately the amount of possible benefits and plan expenses, we have provided a preliminary price list on the website. Ask the manager for the actual price for a battery, cable, or other lead-containing product.
Do you want to know the exact cost? It's easy! Just order
free estimate
and we will quickly determine the price
Lead in nature
Heavy non-ferrous metal is used for shipbuilding, hunting, fishing, and repair work. Contained in thorium and uranium ores. Assumes a minimal amount in nature in its pure form.
Properties of lead:
- excellent corrosion resistance;
- the surface is covered with oxides and becomes dull in air;
- immunity to radioactive radiation;
- soft metal that is easy to scratch;
- Fishing equipment is made from it.
To extract lead, ores containing galena are used. First, the concentrate is extracted, then melted and purified. Getting rid of bismuth in the composition, use calcium and magnesium.
The price of a kilogram of lead depends on the type of raw material. Cable and piece scrap is highly valued. The smallest reward is offered for slag. In each case, you receive financial compensation for raw materials that are not useful and are not used.
The main sources of lead in everyday life
This non-ferrous metal surrounds us in various places. Below we list where to find lead at home. Choose an affordable method of extracting valuable metal and increase your income.
Battery scrap
Spent power supplies contain a large supply of non-ferrous metals. To extract lead, carefully pour the electrolyte into a separate container. The plates are then melted down and used again. Disassembling the battery yourself is a dangerous activity. Don't take any risks - sell the entire battery. We buy a battery with a damaged case.
Cable scrap
Lead is usually contained in a protective sheath. We consider scrap cables to be valuable; the presence of blockage in the metal is no more than 1%.
Criteria for quality cable scrap:
- lead content in the shell 99%;
- no traces of oxidation;
- normal background radiation;
- no traces of PVC insulation;
- no contamination.
Properties
As noted earlier, there is a division of solders into two categories depending on the melting point. Soft or fusible are alloys that melt at less than 450 °C. It is worth noting that they are not necessarily made of tin. Gallium, bismuth, cadmium, and indium can be used here.
However, often not one, but a mixture of several elements is used. This is necessary to give the alloy the necessary characteristics and parameters. The most common are POS.
Solder chart for aluminum soldering.
General description of tin
It is important to note here that there are two types of these raw materials. The first type is called white tin, and is the β-modification of this substance. The second type is the α modification, which is better known as gray tin. When moving from one modification to another, namely from white to gray, a strong change in the volume of the substance occurs, as a process such as the dispersion of the metal into powder occurs. This property is commonly called tin plague. It is also important to note here that one of the most negative properties of tin is its tendency to freeze. In other words, at temperatures from -20 to +30 degrees Celsius, a spontaneous transition from one state to another can begin. In addition, the transition will continue even if the temperature is increased, but after the process has begun. Because of this, raw materials have to be stored in places with fairly high temperatures.
Technical Parameters of Tin
This chemical element has been known for more than 3,500 years and was originally intended for the manufacture of tableware. Modern consumption of tin is associated with the canning industry.
A patent for a method of storing food in tins belongs to a chef from France. Since 1810, humanity has been able to store food for a long time.
Tin is the main component of solders used for soldering and tinning of heat exchangers, radiators of automobile engines, and tinning of medical and food equipment.
The material is used for the production of tin bronze, which has excellent mechanical, casting, and anti-corrosion properties. Such alloys are used in parts intended for use in special conditions and under special loads.
An alloy with a low coefficient of friction is babbitt. It contains 83% tin, antimony and copper. It is used in the production of bearings. Thanks to the stable compound of antimony and copper, the alloy has high hardness.
The bearing operating mechanism and composition components eliminate the occurrence of mechanical damage on the surface of the part.
Tin has specific physical properties:
- Its deformation is accompanied by a sound generated as a result of shear under the influence of force.
- At temperatures of -39 °C and + 161 °C, tin turns into powder.
History knows cases of such transformations. Buttons made from pure material lost their shape in the cold, and the “tin plague” destroyed metal ingots.
Classification
Particularly common are alloys of tin and lead, called babbitts. They can be divided into several groups:
- Tin - designated as B83, B89. Contains antimony and lead. Tin acts as a base. Used in the manufacture of bearings for industrial equipment. However, the base metal is considered expensive, so cheaper analogues are often used.
- Lead - designated as B16. Lead-based alloys are considered more advantageous analogues of tin compounds. Their high wear resistance allows them to be used to make parts for machine tools and moving mechanisms.
- Calcium - solid particles that make up this alloy are a compound of calcium and lead. Tin acts as an additional component.
Purpose
Depending on the content of a particular material, alloys have different areas of application.
Table of types of solders.
POS-90 is used in the repair of food utensils and medical supplies. It contains a small amount of plumbum, a material toxic to humans.
POS-40 is most often used when working with electrical devices and parts made of galvanized iron. Also serves as a basis for repairing brass and copper pipelines. This connection can replace POS 18 solder, used for the same purposes.
Alloys with 30% stanum content are excellent for the cable industry, tinning and zinc soldering.
Alloy systems
Here it is important to start with the fact that an alloy of tin and lead is an even more fusible material than separately. Such mixtures are most widely used as solders, for the manufacture of typographic fonts, casting fuses, etc. A system such as “tin-lead” belongs to the eutectic type group. An important property of all materials belonging to this category is that their melting temperature ranges from 120 to 190 degrees Celsius. In addition, there are groups of ternary eutectics. An example is the alloy system of tin, lead, zinc. The melting temperature of such materials drops even lower, and its limit is 92-96 degrees Celsius. If you add a fourth component to the alloy, the melting temperature will drop to 70 degrees. If we talk about using an alloy of tin and lead as solder, then most often up to 2% of a substance such as antimony is introduced into their composition. This is done in order to improve the spreadability of the solder. It is worth noting here that the melting temperature can be adjusted by the tin/lead ratio. The most fusible raw material melts at 190 degrees.
Silver and silver plating: how to distinguish
There are several signs that can be used to identify a fake with a high degree of accuracy. True, the basis is simple logic. Criteria to distinguish Ag from silver-plated jewelry:
- the presence of a stamp: on a fake coated with precious metal there will be no test, since too little Ag is used, but even if the stamp is still applied, its quality and shape are assessed, for example, sloppy embossing, incorrect contour geometry - these are signs handicraft production;
- quality of the coating: if the product has already been in use, damage remains on it (scratches, cracks, chips, etc.), a fake can be immediately distinguished - another metal will be visible under the coating, silver has a characteristic color - gray-white;
- rusting: Ag in combination with a ligature (as part of an alloy) is not subject to corrosion, while steel or other base metal may become covered with red spots, this indicates that a fake is being considered.
Characteristics of Tin and Lead
It’s worth starting with the fact that recrystallization of cold-worked tin-lead and alloys occurs at a temperature that is considered below room temperature. For this reason, their processing process is of the hot type.
The general indicator was resistance to corrosion under atmospheric conditions. However, a slight difference lies in the resistance to corrosion under the influence of minor substances. For example, lead shows itself best when interacting with concentrated compounds of certain acids - sulfuric, phosphoric, etc. Tin, in turn, best resists solutions of food acids. The scope of application of these substances individually also differs. Tin is widely used for tinning tin, while lead has found its application for lining equipment for sulfuric acid production.
Tin, lead and their alloys
Tin is a soft and ductile shiny metal of silvery-white color. It is characterized by good corrosion resistance in atmospheric conditions, soluble in dilute strong acids and concentrated alkalis. Tin is used for coating (tin-plating), producing alloys and solders for soldering, and also as alloying additives.
Tin alloys are systems tin - antimony - copper and tin antimony - lead, which contain from 3 to 90% tin. They are used as antifriction alloys - babbitts for filling bearings and as solders. The use of lead reduces the cost of solder, and the introduction of antimony increases the strength of the seam.
Lead
Lead is a soft malleable ductile metal of light gray color with a bluish tint. Significantly softer than tin, it can be cut with a knife and scratched with a fingernail, and is easily rolled into thin sheets. Lead is resistant to corrosion and the effects of a number of chemicals, especially sulfuric acid. Lead smelting was one of the first metallurgical processes. It is widely used in the chemical industry to protect equipment from corrosion. Lead is used to make sheaths to protect electrical cables, shot, paints and lead batteries.