About the specialty
The profession of “gas-electric welder” is a qualified specialist who is engaged in connecting (welding) various structures and parts made of metals using electricity or gas. What’s interesting is that it combines three types of employment:
- Electric welder (manual welding).
- Gas welder.
- Welding equipment operator.
Main tasks and additional functions of a specialist
There are two main tasks of a gas-electric welder:
- Connection of metal parts.
- Cutting metal structures using special welding machines.
Additional functions of the specialist are as follows:
- Regulation and installation of the mode required for operation on the welding machine.
- Control of the connection mode (welding in this case).
- Elimination of defects on metal structures and parts.
- Cleaning the seams after finishing your actual work (welding).
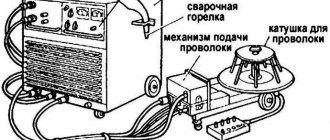
Working as a gas-electric welder requires possession of a set of tools:
- Gas welding torch.
- Forceps.
- Electrodes.
- Hoses.
- Semi-automatic and automatic welding devices.
Electric and gas welder
Type and class
The profession of an electric and gas welder belongs to the “Man-Technology” type, because this profession is associated with the maintenance and operation of equipment for welding work. To successfully perform such work, a high level of development of visual-figurative and spatial thinking, good motor skills, physical endurance, and an aptitude for technical manual work are required. Additional type of profession: “Sign Man”, since it can be associated with working with diagrams and drawings. The profession of an electric and gas welder belongs to the performing class; it involves performing actions according to certain algorithms in compliance with existing rules, regulations, and standards.
Description
An electric gas welder is a specialist who welds various metal products (metal structure components, pipelines, machine parts and mechanisms, etc.).
Contents of the activity
An electric gas welder connects (welds) elements of metal structures, pipelines, machine parts and mechanisms using a welding machine. He assembles workpieces (assemblies) of structures, transports them within the workplace, sets up welding equipment, sets the required welding mode, and prepares the parts to be joined for welding. He carries out visual inspection of welds and cleans seams after welding, welds horizontal, vertical and ceiling seams, welds cavities and cracks on parts, and performs metal cutting on semi-automatic and automatic machines. Prevents the occurrence of stress and deformation in the product. The main tool for manual welding is the electrode. During work, the electric welder performs translational and oscillatory movements of the electrode, regulates temperature, arc length and seam formation. For welding thin metal, non-ferrous metals, their alloys and cast iron, a gas torch is used, in which a combustible gas is displaced with oxygen and a flame is formed. A gas welder, in addition to welding, performs work on cutting parts of various lengths and along various contours, carries out surfacing, soldering and heating of metal. At first, he completes his work independently and bears responsibility for it. The profession of an electric gas welder includes the following specializations: gas welder, manual arc welder (electric welder), gas metal cutter.
Must know
safety regulations; properties of metals; methods of connecting them; design and operating principles of welding machines; properties of electrodes and methods of their selection for various grades of metals; rules for preparing parts and assemblies for welding; technical requirements for the quality of welded joints; measures to prevent defects and ways to eliminate them; reasons for the occurrence of internal stresses and deformations in welded products.
Should be able to
understand the drawings from the technical data sheet of the equipment; read drawings of complex products; connect (weld) elements of metal structures, pipelines, machine parts and mechanisms using a welding machine; assemble blanks (assemblies) of structures; set up welding equipment; set the required welding mode and perform welding in various ways; carry out visual inspection of seams; perform soldering and heating of metal; carry out surfacing of defects of medium complexity and complex parts of machines, mechanisms, structures and castings for machining and test pressure; perform work on cutting parts; take measures to prevent the occurrence of stresses and deformations in the product
Professionally important qualities
neuropsychic stability; ability to concentrate and distribute attention; visual-figurative, technical thinking; developed hand-eye coordination; sharp vision and good color perception; mobility of arms, legs and whole body; good sense of balance; physical endurance; accuracy, responsibility.
Working conditions
An electric gas welder works both indoors and outdoors. It is possible to perform work at heights and in very uncomfortable and dangerous positions. Heavy load on the musculoskeletal and visual systems. To protect against heat and light radiation, the electric gas welder must use special clothing and a mask (shield) with protective light filters. The pace of work is free. An electric gas welder can work either alone or in teams, interacting with specialists of other profiles. In this case, he needs the ability to work in a team, a developed sense of responsibility for the work of the team as a whole, as well as for the high-quality performance of all work performed by different specialists.
Areas of use
Electric and gas welders work:
in factories; at manufacturing enterprises; in organizations involved in construction and repair; in HOAs, housing cooperatives, management companies, etc.; in repair shops.
Basic education and career paths
Basic knowledge of the profession of electric and gas welder can be obtained in institutions of primary and secondary vocational education.
Career prospects
Possible development paths for an electric and gas welder: for an electric and gas welder, horizontal (according to qualification categories) and vertical (according to positions) growth is possible. A specialist in this profile may eventually become a foreman and engineer. An electric and gas welder can engage in entrepreneurial activity independently or as part of a construction organization.
Where do they teach
- High altitude worker
- Institute of Vocational Education
- Perspective, training center
Where required
- ARIANT
- Ashinsky Metallurgical Plant
- Bakal Mining Administration
- Vostokmetallurgmontazh-1
- Gazprom-gazoraspredelenie-Chelyabinsk
- Greenflight
- ZhBI-2
- Investment development
- CONAR
- Kyshtym Machine-Building Association
- Forest Lake, sanatorium
- Miassvodokanal
- Niagara
- Porphyrite
- PRiS
- Constellation, management company
- Stroysistema, industrial group
- Uralspetsmash
- Uraltrubmash
- Chelyabinskgorgaz
- Chelyabinsk metal structures plant
- Chelyabinsk Compressor Plant
- Chelyabinsk Experimental Mechanical Plant
- ChTZ-Uraltrak
- ESCON, plant
- Yuzhuralzoloto, group of companies
- Yuzhuralmost
- Total vacancies: 27
Advantages of the profession
Why are courses for gas-electric welders so popular? The point is the undeniable advantages of this work activity:
- High wages (depending on the qualifications of the specialist).
- Kudos. Despite the fact that a gas-electric welder is a working profession, it remains honorable and respected.
- Opportunities for additional income. In addition to his main activity (say, at an enterprise), a specialist can take on additional private orders in his free time.
- Career opportunities. A professional in his field relatively quickly “grows up” to a foreman or engineer.
general information
Electric and gas welders are in great demand on the labor market. Even despite the fact that hundreds of students throughout Russia receive this specialty every year. Electric and gas welders are needed in many areas: from construction to the oil refining industry. There are many welders in the country, but among them there are not enough truly qualified craftsmen.
Professionals in their field receive decent pay. Most of the interviewed craftsmen claim that the size of the salary directly depends on the qualifications and desires of the worker himself.
But remember that welding is one of the most dangerous fields of activity for humans. You must be physically fit and healthy to handle this type of work. Sometimes electric and gas welders have to work in less than comfortable conditions and in awkward positions.
Responsibilities
There are many responsibilities of an electric and gas welder. A specialist in this profession must prepare equipment for work, perform plasma, arc, and gas welding of any level of complexity. It should be able to cook any type of metal, from steel to copper.
His responsibilities include working with various metal structures, including construction and engineering. Welded structures must withstand heavy loads and serve well for many years.
Disadvantages of the profession
However, performing the labor functions of a gas-electric welder also has significant disadvantages:
- Eye strain. High brightness of the electric arc, strong infrared and ultraviolet radiation adversely affect vision.
- Work in any weather, in dangerous conditions (for example, in construction - at high altitude).
- High risk of injury. First of all, these are burns during welding work.
Notes
- Top list of the 50 most promising and in-demand professions in secondary education in the Russian Federation according to the Ministry of Labor.
- Monument to a welder near JSC Krivorozhstalkonstruktsiya.
- ↑ 123456
Unified tariff and qualification directory of works and professions of workers. - GOST 23949-80 Non-consumable tungsten welding electrodes. Specifications (unspecified)
. Access date: July 20, 2010. Archived March 12, 2012. - GOST 2246-70 Steel welding wire. Specifications (unspecified)
. Access date: July 20, 2010. Archived March 12, 2012. - Electrodes for arc welding (undefined)
. Website www.techno-sv.ru. Access date: July 20, 2009. - arc welding in shielding gases (Russian) // Wikipedia. — 2016-10-01.
- [1] Occupational safety during welding work
Rank
It will be important to present the categories of gas-electric welders:
- First. Vocational school student, aspiring master. Performs simple cutting and cooking operations.
- Second. A specialist who has completed gas-electric welding courses, a technical school, and a vocational school. Can weld in downward and vertical positions.
- Third. A graduate of a specialized educational institution with no practical experience. Able to weld vertical, bottom, corner seams, sealed pipe structures. Understands welding equipment, is familiar with the rules of its operation and safety precautions. Able to read blueprints and weld parts based on them.
- Fourth. Works with structures of medium complexity. Able to cook in all positions except ceiling. Creates sealed seams. Can read blueprints.
- Fifth. Performs welding in any position. Can cut parts of various configurations from sheet metal. Allowed for welding of any types of pipelines. Welds various workpieces - any type of metal, thickness, configuration.
- Sixth. Performs all of the above operations. In addition, only this specialist is trusted to join workpieces from experimental alloys and carry out work that no one has done before. Can independently choose the welding mode and consumables for work.
Applicant qualification requirements
The job description of a gas-electric welder assumes that a specialist must know:
- Types of titanium alloys, their mechanical and welding properties.
- Kinematic diagrams of automatic and semi-automatic devices, content of electronic control circuits.
- Rules for working with welding robotic systems.
- Types of metal corrosion, as well as the factors that cause it.
- Methods for conducting special tests of welded structures, the purpose of each of them (methods).
- Passing the fire minimum for a gas-electric welder.
- Basic methods of processing welded connecting seams.
- Basics of metallography of these welds.
Functional responsibilities of a specialist
We continue to analyze the job description of a gas-electric welder. An important point here will be the listing of the specialist’s responsibilities. The employee's job functions are as follows:
- Manual plasma, arc, gas welding of parts, devices, structures, assemblies, pipelines made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous alloys and metals that are designed to work under vibration and dynamic loads, under increased pressure.
- Manual gas-electric and arc welding of technological and construction parts, structures that operate under vibration and dynamic loads, and connections of complex configurations.
- Automatic welding of various structures from special alloy steels, titanium and other alloys on machines of various designs, multi-electrode and multi-arc devices equipped with photoelectronic, television and other special devices, on automanipulators (robots).
- Mechanized welding of components, apparatus, pipeline structures, technological and construction facilities operating under vibration and dynamic loads. Performing welds in a vertical and overhead position.
- Welding of a number of experimental structures made of metals and alloys with limited weldability, as well as titanium and its alloys.
- Welding of complex parts in a block structure in all positions in the weld space.
Welding specializations
Welder on resistance (press) welding machines
Professional Features
The professional functions of a welder on 4th category resistance (press) welding machines include:
- Welding on contact and spot machines of products, assemblies, structures, pipelines and containers made of various steels, non-ferrous metals, alloys and non-metallic materials. Friction welding of a composite cutting tool.[3]
Professional tools and equipment
| This section is not completed. You will help the project by correcting and expanding it. |
Welding electrodes brand ESAB OK 48.00
- Welding electrodes are a metal or non-metallic rod made of electrically conductive material designed to supply current to the product being welded. Welding electrodes are divided into consumable and non-consumable. Non-consumable electrodes are made from refractory materials, such as tungsten according to GOST 23949-80 [4] “Tungsten welding non-consumable electrodes”, synthetic graphite or electrical coal. Consumable electrodes are made from welding wire, which, according to GOST 2246-70[5], is divided into carbon, alloyed and high-alloyed[6]. A layer of protective coating is applied over the metal rod using pressure crimping. The role of the coating is to metallurgically treat the weld pool, protect it from atmospheric influences and ensure more stable arc combustion.
- Welding machines, semi-automatic welding machines, rectifiers.
Welder on diffusion welding installations
Professional Features
The professional functions of a welder on diffusion welding installations of the 6th category include:
- Welding on multi-chamber diffusion welding installations of experimental, expensive, unique units and parts made of metals and alloys in various combinations, subjected to special tests. Welding in special furnaces of structures such as honeycomb panels with filler with an area of over 1.7 square meters. m. Carrying out work on saturating metal materials with nitrogen in special equipment.[3]
Welder on electron beam welding installations
Professional Features
The professional functions of a welder on electron beam welding installations of the 6th category include:
- Electron beam welding in vacuum of expensive components and parts made of special alloys. Welding of complex components and parts, welding of products with a limited degree of heating. Welding of small-sized and miniature products. Welding of products designed to operate under shock and vibration loads. Maintenance of high-vacuum systems with automatic control or continuous production cycle. Welding of metals and alloys in various combinations with metal thickness up to 0.8 mm. Continuous monitoring of the pumping process based on instrument readings and control of the welding process. Obtaining optimal parameters of the electron beam and changing them in order to obtain the optimal cross-section of the welds.[3]
Thermite welder
Professional Features
The professional functions of a 2nd category thermite welder include:
- Thermite welding of parts of varying complexity. Installation and alignment of the press, straightening of welded surfaces, installation and coating of molds. Stuffing molds, removing models and drying molds. Preparation of mixture for crucibles, their manufacture and firing. Heating of the surfaces to be welded using a gas apparatus and a brazier. Sifting by hand or with a seeder and crushing thermite components with a crushing machine, mixing them, packing and laying them in portions. Cutting off metal after welding. Regulation of the operation of the ventilation unit. Mechanism lubrication.[3]
Gas welder
Professional Features
The professional functions of a 6th category gas welder include:
- Gas welding of complex parts, mechanism components, structures and pipelines made of high-carbon, alloy, special and corrosion-resistant steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys designed to operate under dynamic and vibration loads and under high pressure. Cutting metal with a gas cutter. Hard alloy surfacing of complex parts, assemblies, structures and mechanisms.[3]
Electric and gas welder
Professional Features
The professional functions of a 6th category electric gas welder include:
- Manual arc, plasma, gas-shielded arc welding[7] and gas welding of particularly complex apparatus, parts, assemblies, structures and pipelines made of various steels, cast iron, non-ferrous metals and alloys, designed to operate under dynamic and vibration loads and under high pressure . Manual arc and gas-electric welding of building and technological structures operating under dynamic and vibration loads, and structures of complex configuration. Automatic welding of various structures from alloyed special steels, titanium and other alloys on specially designed machines, multi-arc, multi-electrode machines and machines equipped with television, photoelectronic and other special devices, on automatic manipulators (robots). Mechanized welding of devices, components, pipeline structures, building and technological structures operating under dynamic and vibration loads, when performing welds in the ceiling position and on a vertical plane. Welding of experimental structures made of metals and alloys with limited weldability, as well as titanium and titanium alloys. Welding of complex structures in block design in all spatial positions of the weld.[3]
Gas cutter
Cutting the drive shaft of an excavator with a gas cutter to sell it as scrap metal.
Professional Features
Manual oxygen cutting and cutting of lightweight steel scrap with petrol and kerosene cutting devices. Preparing castings for cutting, removing burnt marks, profits and sprues and placing them for cutting. Charging and discharging a gas generator installation. Oxygen-flux cutting of parts made of high-chromium and chromium-nickel steels and cast iron. Gas cutting of ship objects afloat. Cutting profits and sprues for castings that have multiple connectors and open core marks.
The welder must know the structure of stationary and portable oxygen and plasma-arc machines, gas cutters and generators of various systems; arrangement of special devices; properties of metals and alloys subjected to cutting; requirements for copiers for machine figured cutting, and rules for working with them; accuracy tolerances for gas cutting and planing; the most favorable relationships between metal thickness, mouthpiece number and oxygen pressure; cutting mode and gas consumption for oxygen and gas-electric cutting.
Specialist rights
The job description of a gas-electric welder presupposes the following specialist rights:
- Give subordinate employees tasks and instructions within the scope of their job competence.
- Monitor compliance of subordinate employees with production tasks and timely execution of distributed assignments.
- Request and receive documents and information necessary for work activities.
- Interact with other employees and services of the employing company on production issues.
- Familiarize yourself with projects and decisions of the management of the enterprise, the employing company, directly related to the work of its department.
- Offer for consideration by the company's top management your solutions to improve your own labor functions, the workplace, and the activities of the organization as a whole.
- Submit for consideration by the management of the enterprise proposals for the promotion of certain employees subordinate to it. And also propose imposing penalties on those who violate labor discipline at work.
- Report to management about identified shortcomings and shortcomings in the work of the unit.
Subscribe to news
A letter to confirm your subscription has been sent to the e-mail you specified.
13 April 2015 13:43
In the practice of applying legislation on early pension provision, many difficulties arise due to the existing inconsistencies in the lists, the variety of names of professions and positions, as well as the large number of industries contained in them. Difficulties are also caused by the fact that the work on organizing preferential pension provision in some enterprises and organizations is not at a high enough level.
Unfortunately, managers and personnel workers of many enterprises still treat the maintenance of work records with annoying frivolity. With their illiteracy in filling out work books, they deprive workers of the right to early retirement and lay the foundation for a conflict to arise.
It is not uncommon for enterprises to include arbitrary names and positions in their staffing schedules that do not correspond to the nature of the work performed and the Lists of preferential professions, in accordance with which the right of the insured person to receive an early retirement pension is determined.
According to the Instructions on the procedure for maintaining work books , approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003. No. 225 “On work books”, the names of professions must be entered in them in accordance with the UTKS (Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory), and the names of positions - with the Unified Nomenclature of Employee Positions . Lists of preferential positions and professions are also compiled in strict accordance with these documents. Therefore, the basis for providing a pension benefit is work in a specific profession (position) directly provided for by Lists No. 1, 2 of industries, works, professions and positions giving the right to preferential pension provision.
Section XXXIII “General Professions” of the List dated January 26, 1991. No. 1 names electric and gas welders engaged in cutting and manual welding, on semi-automatic machines, as well as on automatic machines using fluxes containing harmful substances of at least hazard class 3.
In addition, a prerequisite for the appointment of an early retirement pension is periods of work performed continuously during a full working day.
In connection with this, when determining the right to assign an early retirement pension to insured persons who have periods of work as an electric and gas welder (gas and electric welder), I include confirmation of full employment and clarification of the type of welding performed.
When deciding on the issue of granting an early retirement pension to this category of workers, difficulties often arise in confirming the type of welding, which is associated with indicating in the work books the name of the profession - electric and gas welder without specifying the type of work performed. To assign an early pension, a clarifying certificate from the enterprise of the established form is required, confirming permanent employment as an electric and gas welder in cutting and manual welding, on semi-automatic or automatic machines. At the same time, electric and gas welders working on automatic machines are assigned a pension according to List No. 2, provided that they are constantly engaged in work using fluxes containing harmful substances of at least hazard class 3.
Employee Responsibility
The job description introduces certain responsibilities of a gas-electric welder:
- For improper and untimely performance of their functional duties within the limits provided for by Russian labor legislation.
- Violation of the regulations and rules governing the activities of the employing company.
- Offenses that were committed during the performance of labor functions. Within the limits provided for by the administrative, civil and criminal legislation of the Russian Federation.
- Causing material damage to the employing company and its employees.
- Compliance with current instructions, orders, management orders, local regulations of the organization, as well as requirements for maintaining trade secrets and other proprietary confidential information.
- Following the rules of labor internal regulations, labor protection, fire safety.
Gas-electric welder is a working specialty that remains prestigious and relevant in our age of information technology. In the article, we got acquainted with the profession, the job description of a specialist, as well as the six categories of gas-electric welders that exist today.