Elbor - chemical formula, properties
Its chemical formula is BN. Another name is borazon , which is closer in sound to the formula of the material. Externally, these are transparent yellow crystals, the shape of which is octahedral. In terms of hardness, elbor is only slightly inferior to diamond. So, if the microhardness of diamond is 1000×10^2 MPa, then for CBN this figure is (800-900)×10^2 MPa, and compared to other traditional abrasives, it is three to four times higher:
- for silicon carbide, the microhardness is (300-320)×10^2 MPa;
- for electrocorundum it is (180-220)×10^2 MPa.
Thus, there is a significant advantage over them, since the wear of CBN grains will obviously take several times longer.
Another thing that makes a CBN wheel better than a diamond wheel is its thermal and chemical resistance .
CBN oxidation begins to occur at temperatures of 1000-1200 °C, when similar processes in diamond begin at 600-700 °C.
The chemical resistance of the material is expressed in the fact that it does not react with alkalis and acids, and is also inert to many chemical elements that make up alloys and steels. It is especially important that CBN is inert to iron, something that diamond cannot “boast” of, since it dissolves very well in it. Because of this feature, diamond wheels wear out quickly when grinding steel.
Based on the characteristics, it is recommended to use CBN grinding wheels for final processing of parts, or for semi-finishing. Materials – alloys of heat-resistant, difficult-to-cut, high-speed, high-alloy steels. Also among the requirements for the processed parts is that they must consist of alloys that are hardened to at least HPC 50.
We will produce a profile grinding wheel to order
Upon request, we can make any other profile of the Borazon sharpening disc with other geometric dimensions. Lead time: 3-10 days. The service life of WESTRON discs is on average 10-15 km or a year of operation of the 1st sawmill.
The worst thing for a disk is machine play. If they are, then the disk begins to hit unpredictably, first on the front edge, then on the back, respectively, breaking the profiles of the saw teeth. Then the sharp tips of the teeth begin to cut the disk, significantly reducing its service life, making sharpening on such machines economically ineffective. Therefore, we recommend using our blades on WESTRON equipment, which will significantly increase the service life of the blade as well as the saw.
Grinding wheels: is the difference in angles important?
As practice shows, all conversations about summer and winter angles, about the need to change the angle when sawing various types of wood, are carried out when sharpening the saw on conventional sharpening machines, when a narrow sharpening stone sequentially passes each saw tooth. For various reasons, mainly due to improper preparation of the sharpening stone and machine play, the actual value of the rake angle when measured with a protractor instead of the stated 10° can have values from 8° to 12°, and sometimes from 0° to 15°. But the most important thing is that the spread of angle values from the average on different teeth is usually additionally ±1°-2°. With such variations in the actual values of the rake angle, talking about winter 9°, summer 12° or certain angle values for different types of wood is simply meaningless. Like any tool, a saw cuts well only when the rake and back angles, as well as the shape of the cavity on all saw teeth, are the same, and 10° rake angle and 30° back angle are optimal for working in winter and summer when cutting any wood.
We draw your attention to the fact that the rake angle (compare the decoding of the disk profiles and Fig. 2) is the same for all saw manufacturers. All of them differ slightly only in the size of the rear angle, as well as the shape and depth of the cavity, which is not of fundamental importance for sawing. Many incorrectly say that profiles differ in tooth height, but they always measure tooth height not near the leading edge of the tooth, the height of which is approximately the same for all manufacturers, but at the deepest point of the cavity, that is, they actually measure the depth of the cavity, and not the height of the tooth. Also, for technological reasons, no manufacturer ever repeats exactly the tooth profile from batch to batch. Therefore, when a saw is installed for sharpening in a machine with a profile sharpening wheel for the first time, its teeth must first be additionally profiled, that is, the saw is sharpened 2-4 circles. Thus, you can get the required profile on almost any saw. All subsequent sharpening will be done in one circle.
Main characteristics of CBN elements
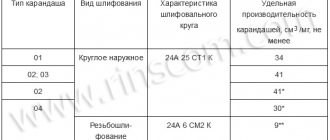
- The first can be called the type of circle according to the above-mentioned GOST 17123.
- The second characteristic is the outer diameter. Depending on the type, it can be up to 10 mm, from 100 to 200 mm, from 30 to 135 mm, etc. The maximum value of the outer diameter of the CBN circle is 500 mm.
- The third parameter is grain size.
- The fourth parameter is the degree of hardness.
The remaining parameters relate to the minimum time periods of durability (in minutes) and operating time (in square meters). The maximum value of the roughness parameter (in micrometers) is also important. It must comply with GOST 2789 standards.
CBN wheels can work with both dry and coolant. These data are also indicated in GOST 24106-80 for each type. The coolant can be:
- industrial oil (pure or with the addition of sulforesol);
- special emulsion;
- aqueous solutions of sodium nitrite or other solutions.
Application of CBN wheels
The main area of use of the tool is grinding and sharpening; it is used both as an independent tool and as an element of grinding machines. Wheels are effective when processing small holes, profiles, gears, screw and threaded guides, and other products for which compliance with the specified geometric accuracy is important.
Using CBN wheels, finishing and sharpening of cutting tools made of high-speed steels (including band saws), superfinishing of hardened steels, precision gear grinding and thread grinding are performed.
CBN grinding wheels serve better than other abrasive materials when processing parts made of cemented, complex alloyed, bearing, nitrided, and die steels with a high content of cobalt, vanadium, tungsten, and molybdenum.
Highly porous wheels are effective when working with less hard alloys based on nickel and wear-resistant coatings: detonation, plasma, hardened cast iron and chromium.
The use of borazone wheels improves the quality and accuracy of processing, increases productivity and brings significant savings.
GOST requirements
CBN grinding wheels are manufactured in accordance with GOST 24106-80, which specifies the requirements for the CBN-containing layer and body, and specifies the relative concentration, grain size and grade of CBN. The sizes and types of circles are determined by GOST 17123, and the speeds at which the tool is used are determined by its mechanical strength and can correspond to 60, 50, 45 or 35 meters per second.
Main technical characteristics
The main characteristics are four:
- wheel type according to GOST 17123;
- outer diameter (up to 10mm, 100-200mm, 30-135mm, etc. with a maximum value of 500mm);
- grain;
- degree of hardness.
Other data includes the ability to work dry or with coolant, the maximum roughness parameter measured in micrometers, tool hours in square meters and tool life in minutes.
Circle body
The body material used is ceramic or metal, which meets safety requirements in terms of strength and rigidity. The maximum operating speed of the machine depends on the body material:
- ceramic body - up to 60 m/s;
- ceramics with a steel body glued in – 80 m/s;
- metal body - 125 m/s.
Using circles with different connections
| Bunch | Designation | Note |
| Organic | ABOUT | Sharpening cutting tools made of high-speed steels. Grinding the guide frames. Surface grinding of difficult-to-cut steels |
| Ceramic | TO | Cylindrical internal and flat grinding of cutting tools and other parts made of difficult-to-cut steels. Thread grinding and gear grinding. Grinding of bores and raceways of small precision bearings |
| Metal | M | Grinding of threads with small pitch. Finish honing of steels |
CBN wheels with a ceramic binder are highly porous, which reduces their contamination, reduces the frequency of dressings and improves the supply of coolant during wet working. As a result, the operating temperature range can increase without causing burns. These wheels are effective for performing profile and depth grinding, processing steels with low hardness, heat-resistant and tough alloys. The usual grain concentration for wheels with a ceramic bond is 100%; if this figure is higher, the service life of the wheel increases, as well as its cutting ability.
Organic bonds are intended for wheels used in the following work:
- fine grinding and sharpening of tools made from high-speed steels (tungsten - R9, R19, R18, tungsten-molybdenum - P6M5), alloyed with cobalt and vanadium with increased productivity (R12F4K10M2, R12F5K5, P9F5);
- final and finishing grinding of precision parts made of high-hard steels (HRS55 and more), structural high-alloy, stainless and heat-resistant steels, the high-precision processing of which is impossible with conventional abrasive tools;
- final and finishing grinding of lead screws of guide mills and other precision large-sized parts, during the processing of which the temperature increases significantly, leading to deformation;
- final and finishing grinding on machines operating in semi-automatic and automatic cycles.
The grain size of the CBN-containing layer depends on the type of binder. So, for a ceramic bond, its indicators should be equal to 250/200 -14/10. And for an organic binder - 250/200 -3/2.
Regardless of the type of bond, CBN wheels can work both with water cooling and using the dry method. A special emulsion, industrial oil (with or without the addition of sulforesol), an aqueous solution of sodium nitrate, etc. are used as a coolant.
CBN grain size
Elbor for wheels can be in the form of grinding powder, micropowder or grain. The use of the wheel depends on the grain size; this distribution can be seen in the table:
| Grain | Grain size of the main fraction, microns | Application |
| LM1 | 0-2 | Finishing |
| LM3 LM5 LM7 LM10 PM14 LM20 | 1-3 3-5 5-7 7-10 10-14 14-20 | Polishing |
| LM28 LM40 L4 L5 | 20-28 28-40 40-50 50-63 | Fine sanding, super finishing |
| L6 L8 L10 | 63-80 80-100 100-125 | Fine grinding |
| L12 L16 L20 L25 | 125-160 160-200 200-250 250-315 | Grinding |
CBN concentration
In addition to the grain size, the concentration of CBN also matters. The maximum concentration is 150%, the minimum is 25%, in addition, circles are produced with concentrations of 125, 100, 75 and 50%. In circles with a concentration of 100% (the most common), the abrasive layer contains 0.878 mg of CBN per 1 mm3.
The choice of this characteristic depends on the conditions of use and other data:
- high concentration of material in wheels with a grain size of 150/125 or more, with a diameter of less than 50 mm, a cup profile and a working layer width of less than 5 mm, intended for profile grinding;
- medium is used in wheels with grain size 125/106 - 63/53, with a cup profile and a wide working layer (7-20mm), for most operations;
- low concentration is used in fine-grained wheels (40/28 and less).
Hardness
Hardness characterizes the strength with which grains are held together. This indicator determines the performance of the tool. Marked according to ISO standards or Russian standards:
| Hardness groups | Soft | Average | Solid | |||||||
| Russian standard | M3 | SM1 | SM2 | C1 | C2 | ST1 | ST2 | ST3 | T1 | T2 |
| ISO standard | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S |
CBN brands
For the CBN-containing layer of circles, various grades of material are used, each of which is intended for a specific type of work:
| Brand ELBOR | Material characteristics | Bunch | Application |
| LO | medium strength material | ceramic | fine grinding |
| LP | high strength material | ceramic | fine grinding |
| LKV | high strength material | ceramic, metal | honing, high-performance grinding |
| LKV30 | high strength material | ceramic | fine grinding of hardened alloy steels, bearing steels |
| LKV40 | high strength material | ceramic, metal | high-performance grinding of hardened alloy steels, bearing steels, honing |
| LKV50 | very high strength material | ceramic, metal | high-performance and creep-feed grinding of hardened alloy steels, bearing steels, special alloys. |
| VOC, LPS | ceramic coated material | organic | cutting tool sharpening |
| LKV40M, LKV50M | metal (nickel) coated material | organic | sharpening of cutting tools, sharpening on CNC machines, grinding of chip flutes |
| LM | micropowders | ceramic, organic | superfinishing, polishing, lapping |
Types of CBN wheels
To perform various jobs, many CBN wheels are produced with different profiles and types, each of which is designated by its own abbreviation:
| Type designation | Description |
| 1A1 | Flat straight profile |
| A8 | Flat straight profile without housing |
| 1E1, 1E6Q, 1D1 | Flat with double-sided conical profile |
| 1V1, 1R1 | Flat with one-sided conical profile |
| 1A2 | Flat straight profile |
| 1F1X | Flat with semicircular-convex profile |
| 4V9 | Profile |
| 6A2 | Flat with double-sided groove |
| 9A3 | 1A1 |
| 12A2-45, 11A2, 12V5-45, 12B2, 12C2 | Cup conical |
| 12R9, 12V9, 12A2-20, 12R4, 12V5-20 | Disc-shaped |
| 14A1 | Flat straight profile |
| 14EE1 | Flat with double-sided conical profile |